Palatines, Maxilla, Zygomatics, Vomer, Mandible, Nasal, Lacrimal, Inferior nasal conchae flashcards set (SBA4)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
posterior nasal spine
pointed bony projection at the posterior end of the hard palate
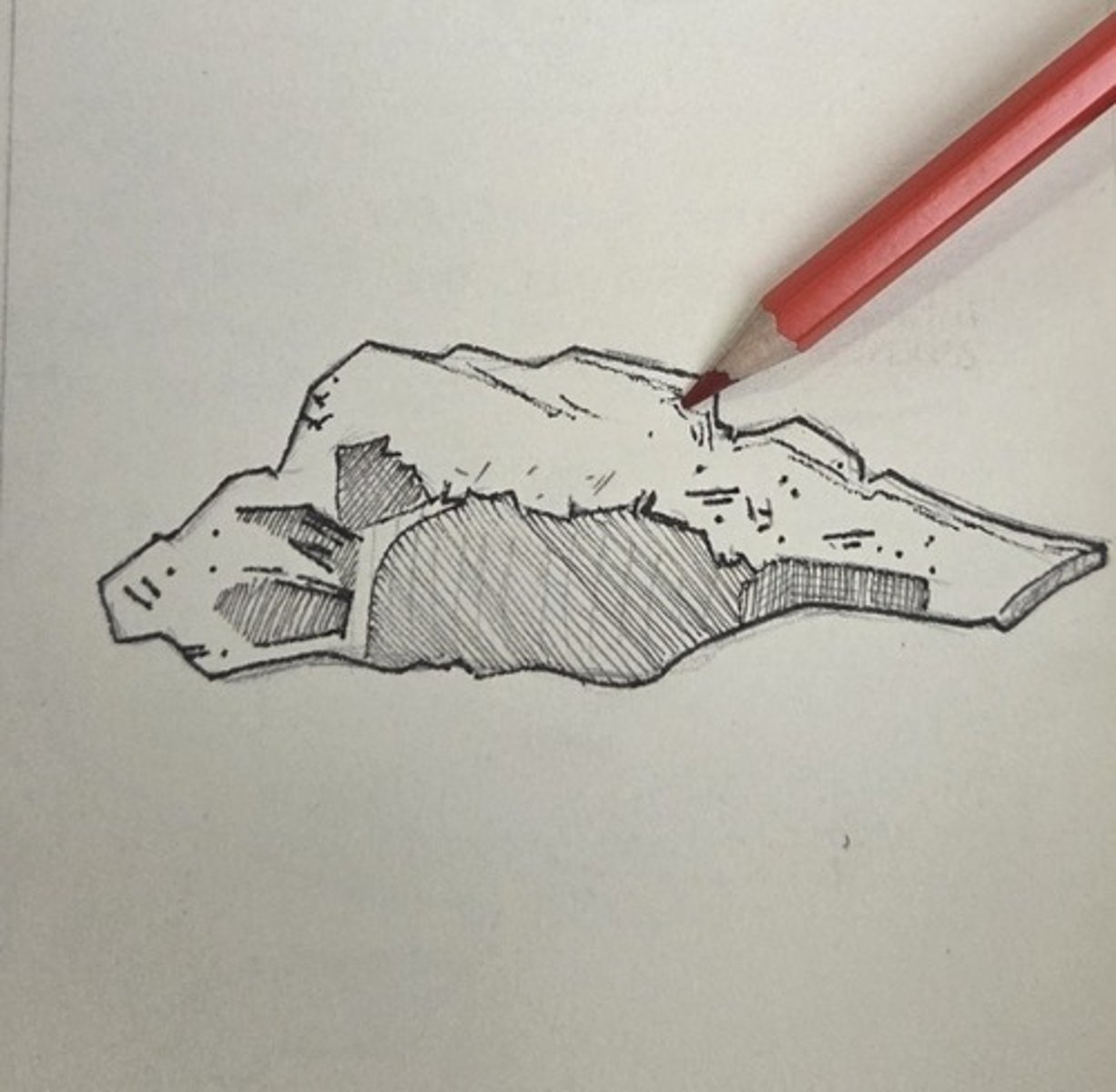
pyramidal process
The posterior border of the perpendicular plate is the thickest border.
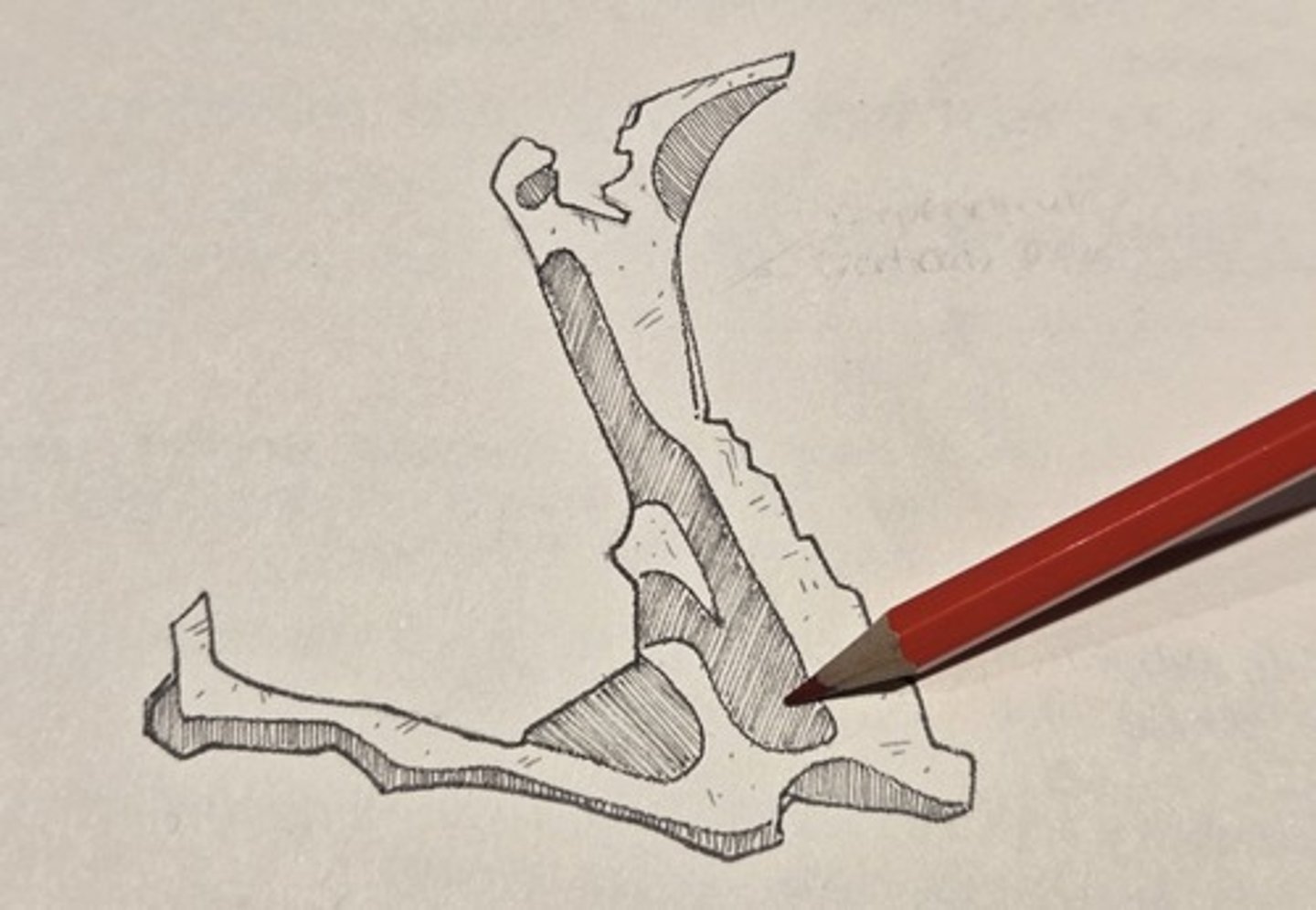
horizontal plate
forms the posterior portion of the hard palate
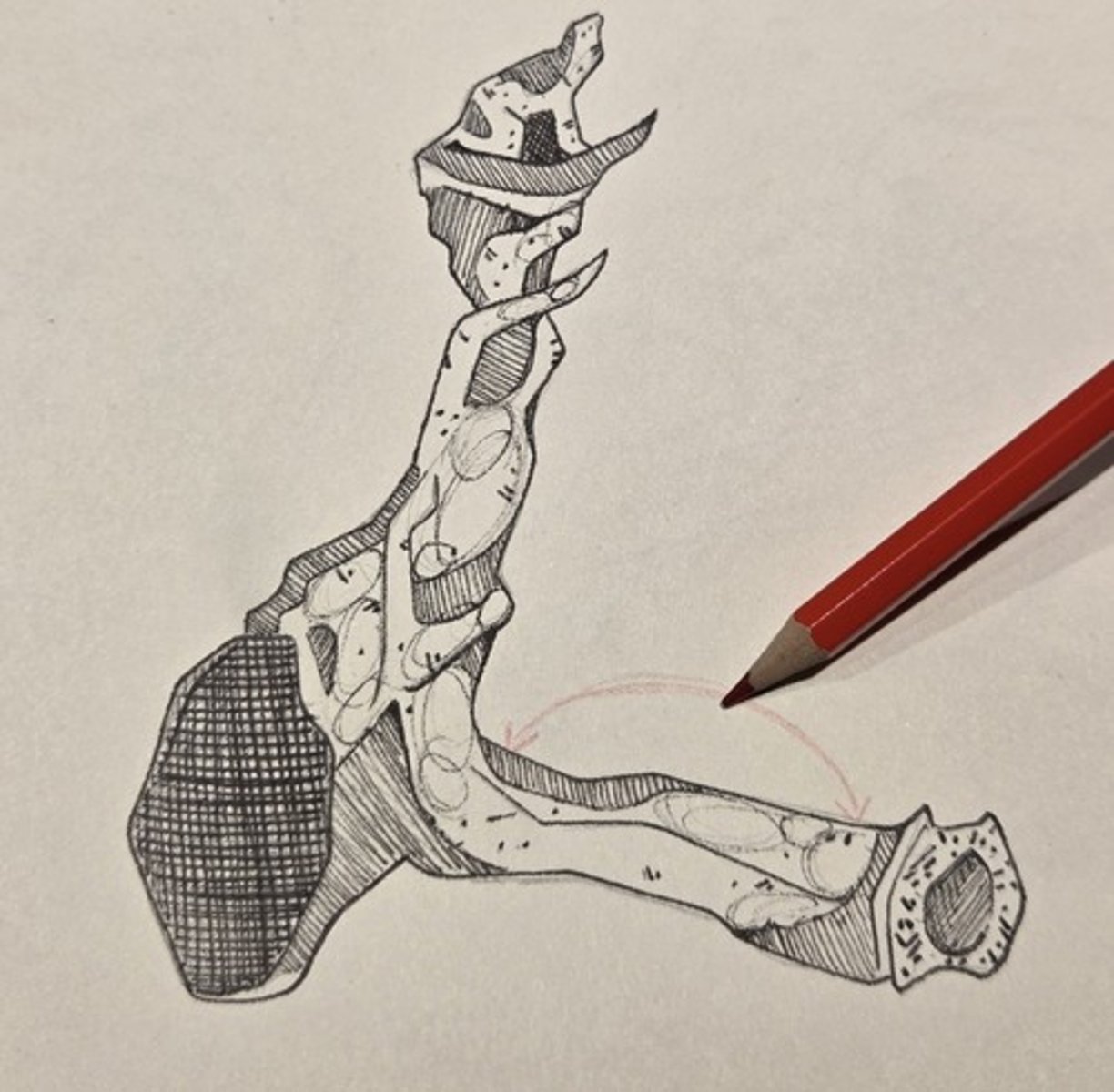
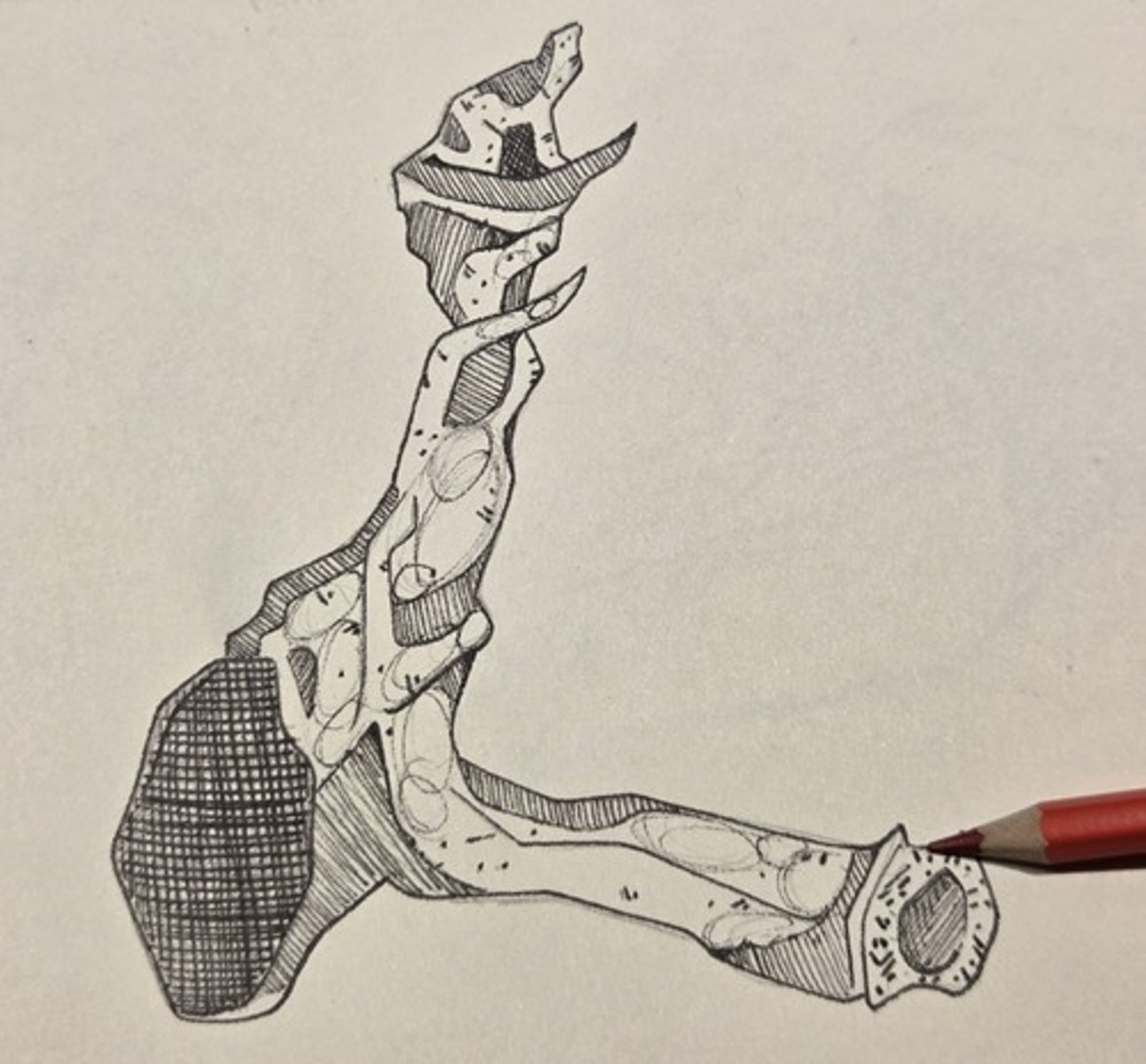
perpendicular plate
appressed tightly to the posteromedial wall of the maxilla opposite the maxillary sinus, between the pterygoid plates of the sphenoid and the posterior margin of the alveolar process of the maxilla.
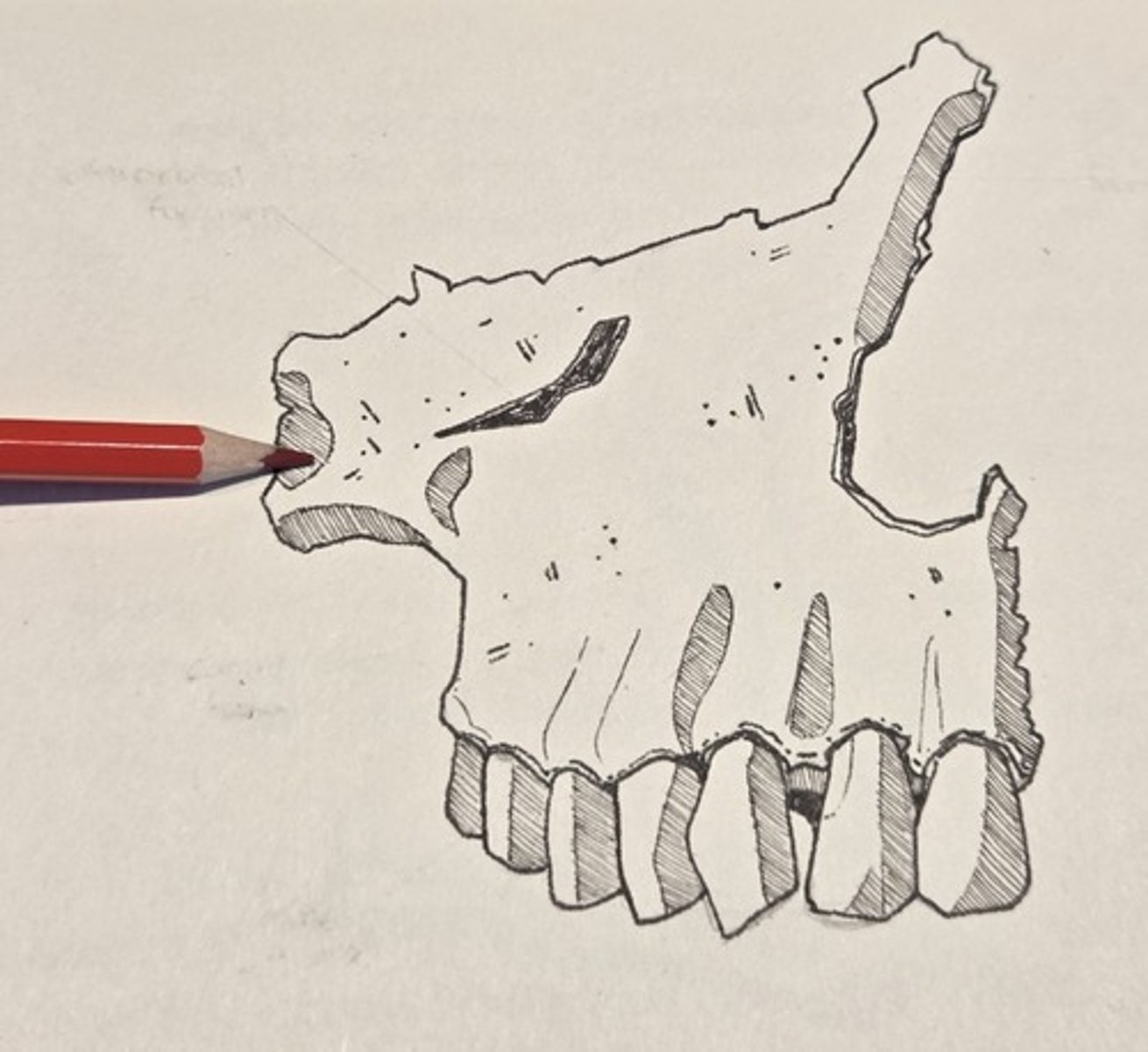
medial border
thick and serrated, articulates with the opposite bone to form the nasal crest
alveolar process
Portion of the maxillary bones that holds the tooth roots
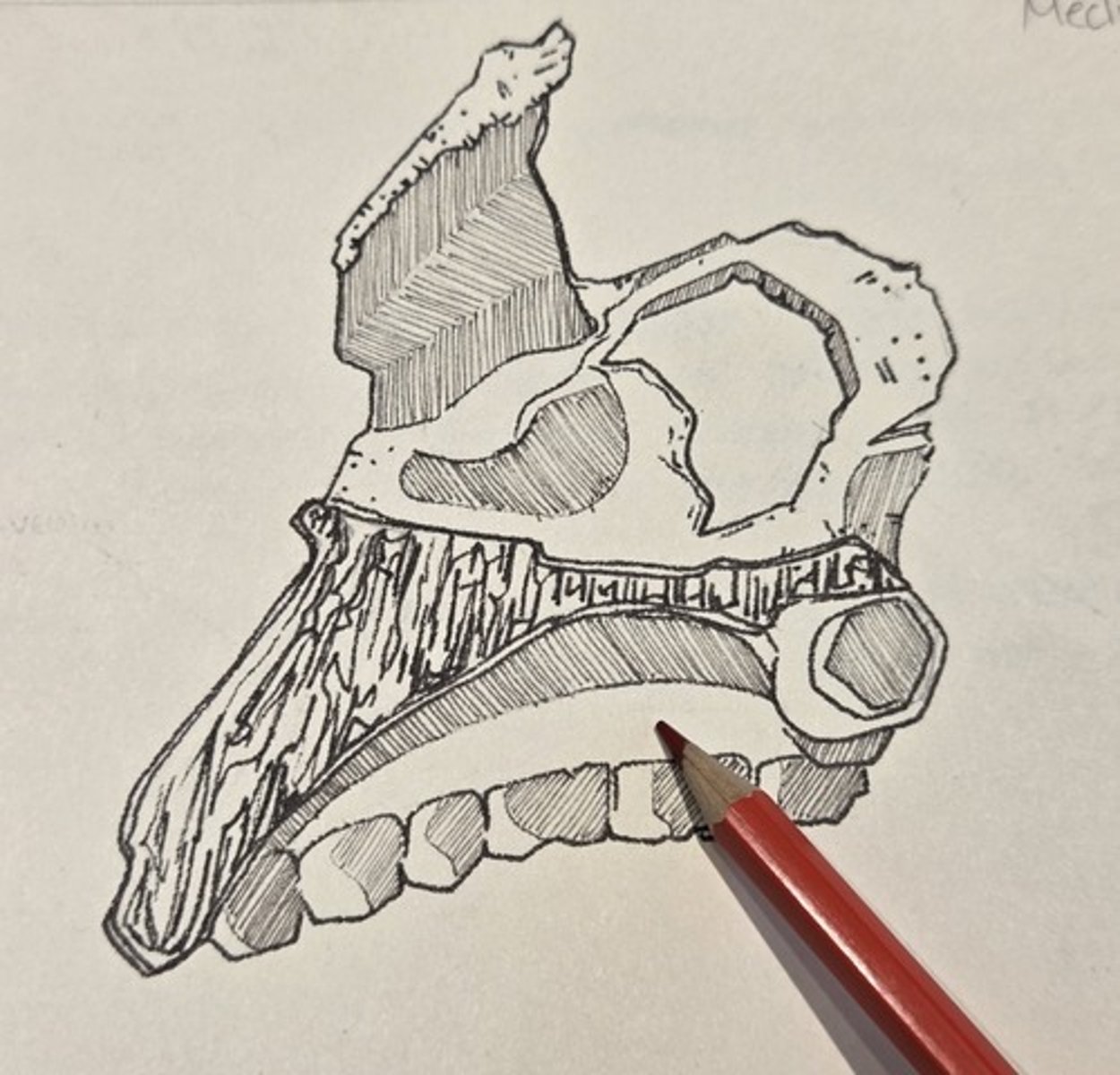
canine jugum
bony eminence over the maxillary canine root on the facial surface of the maxilla
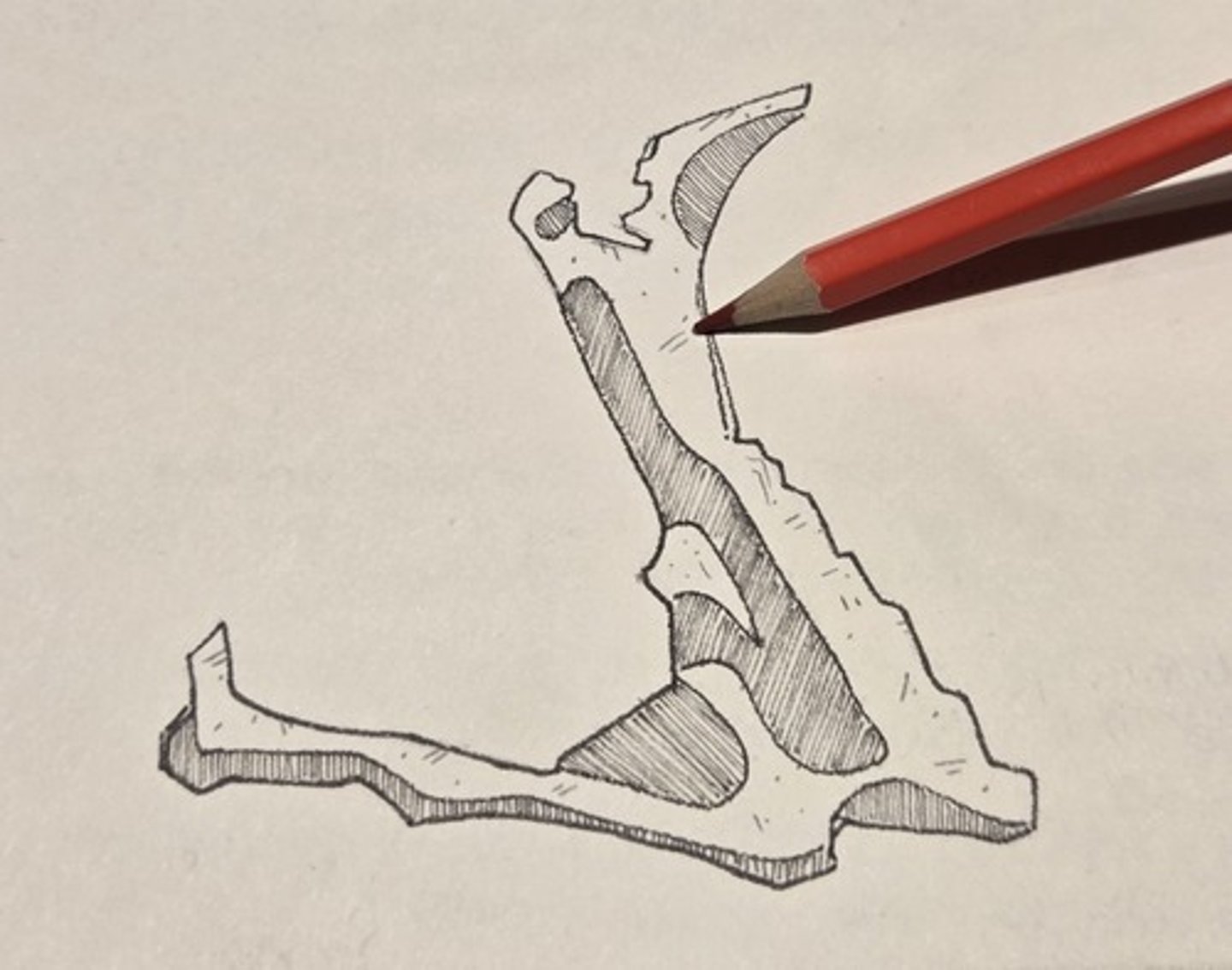
zygomatic process
forms the cheekbone
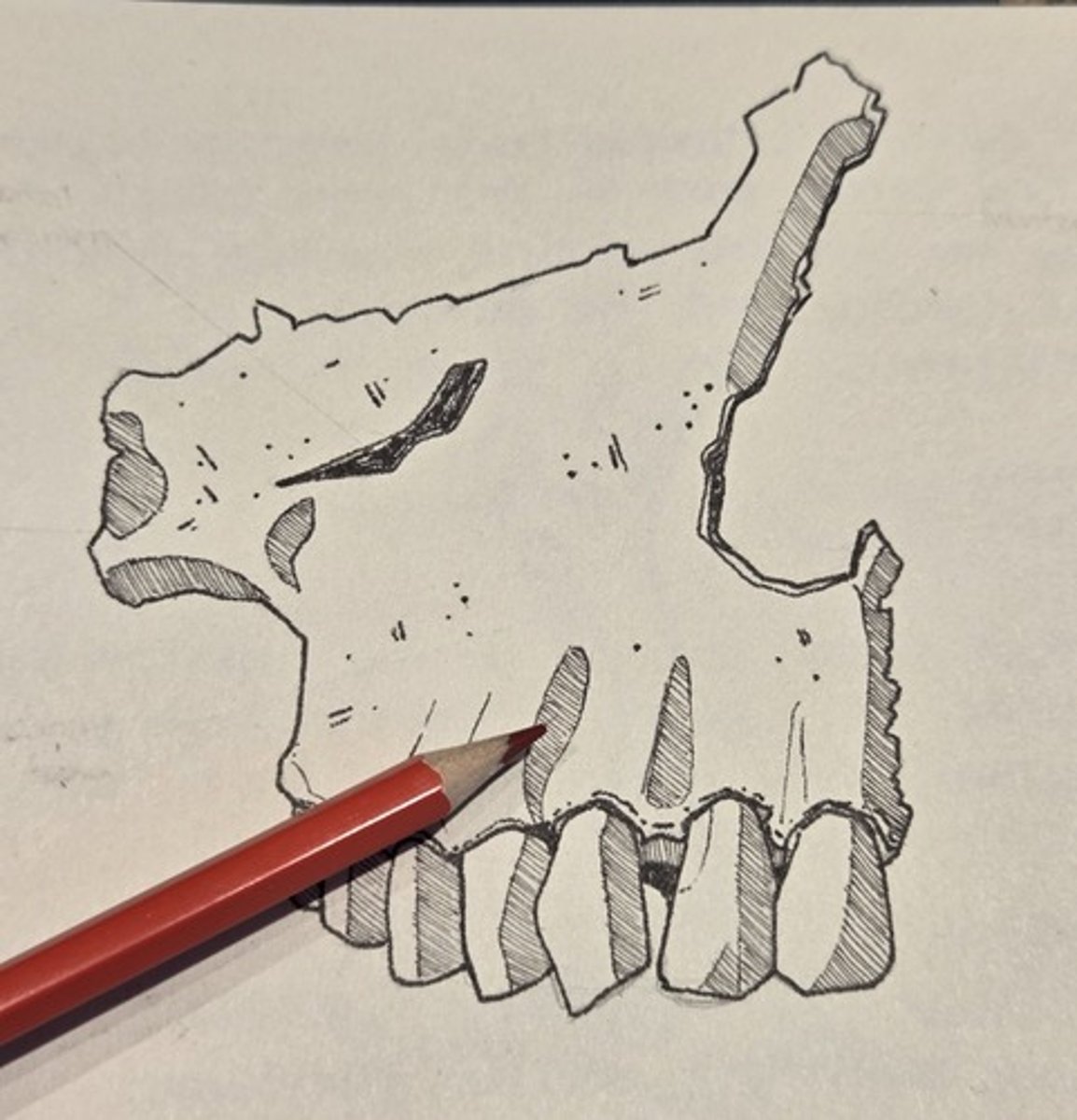
infraorbital foramen
opening under the orbit carrying the infraorbital nerves and blood vessels the nasal region
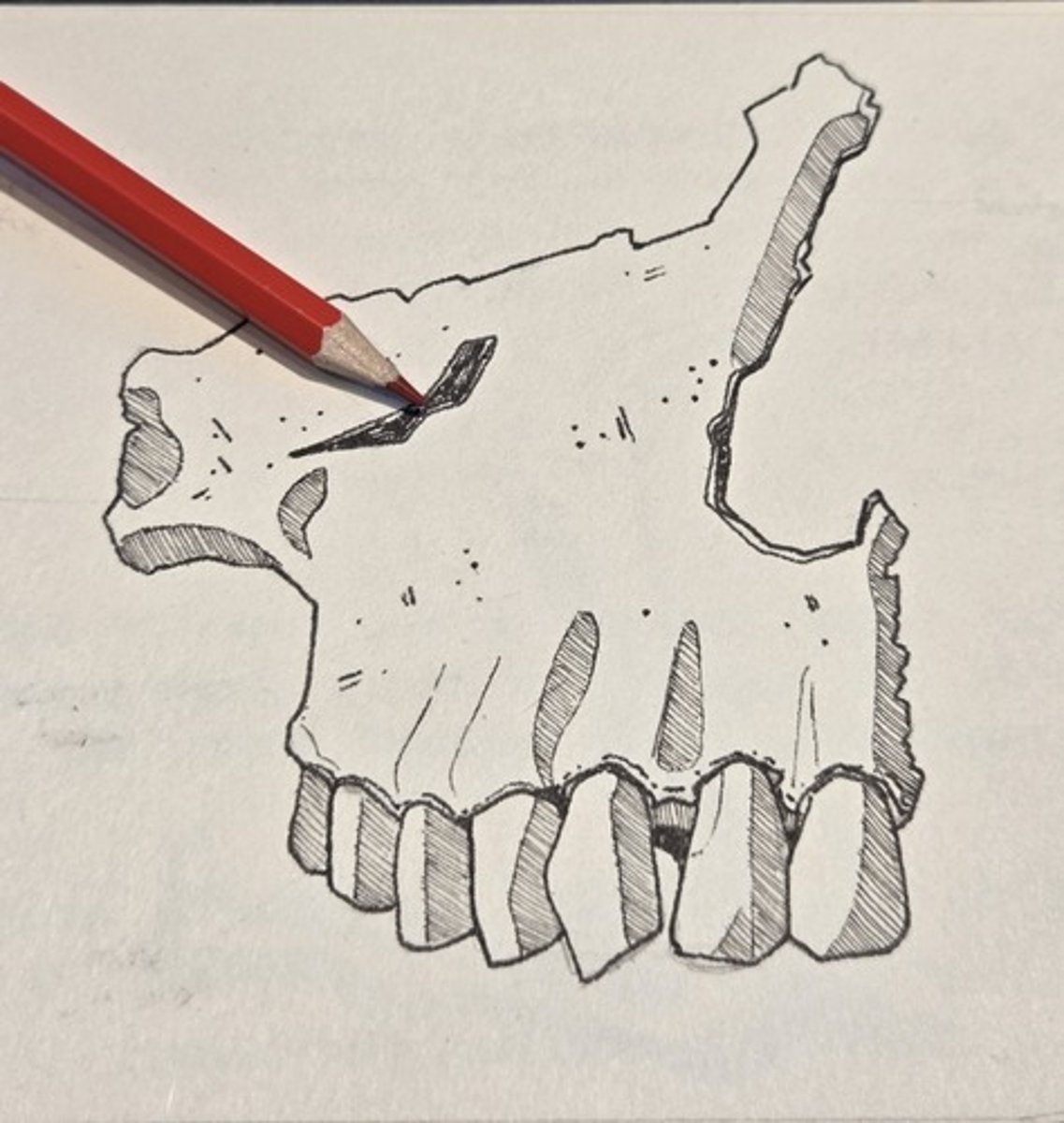
nasoalveolar clivus
The sloping surface between the nasal aperature and upper teeth
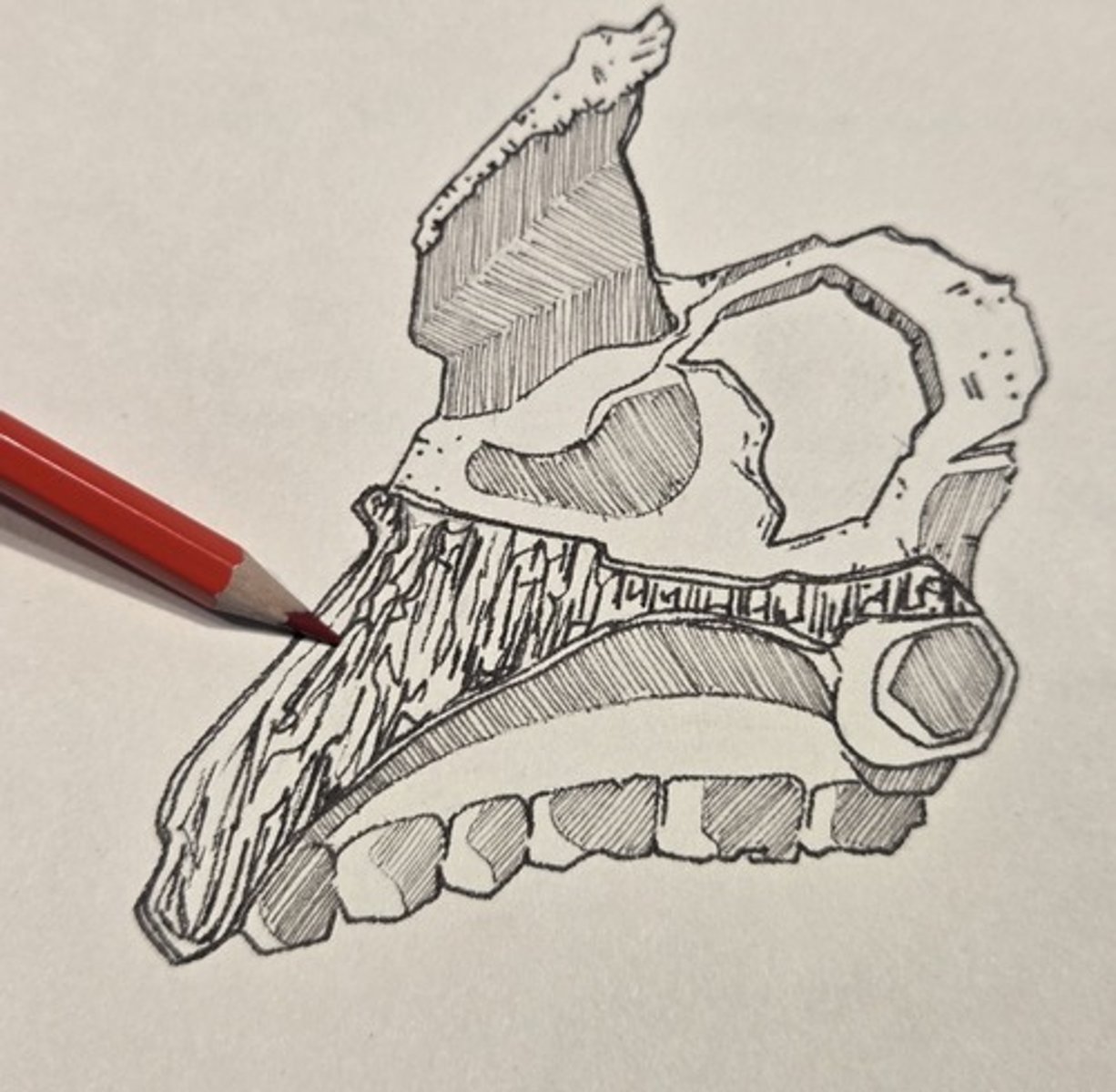
frontal process
rises to articulate with the frontal, nasals, lacrimal, and ethmoid
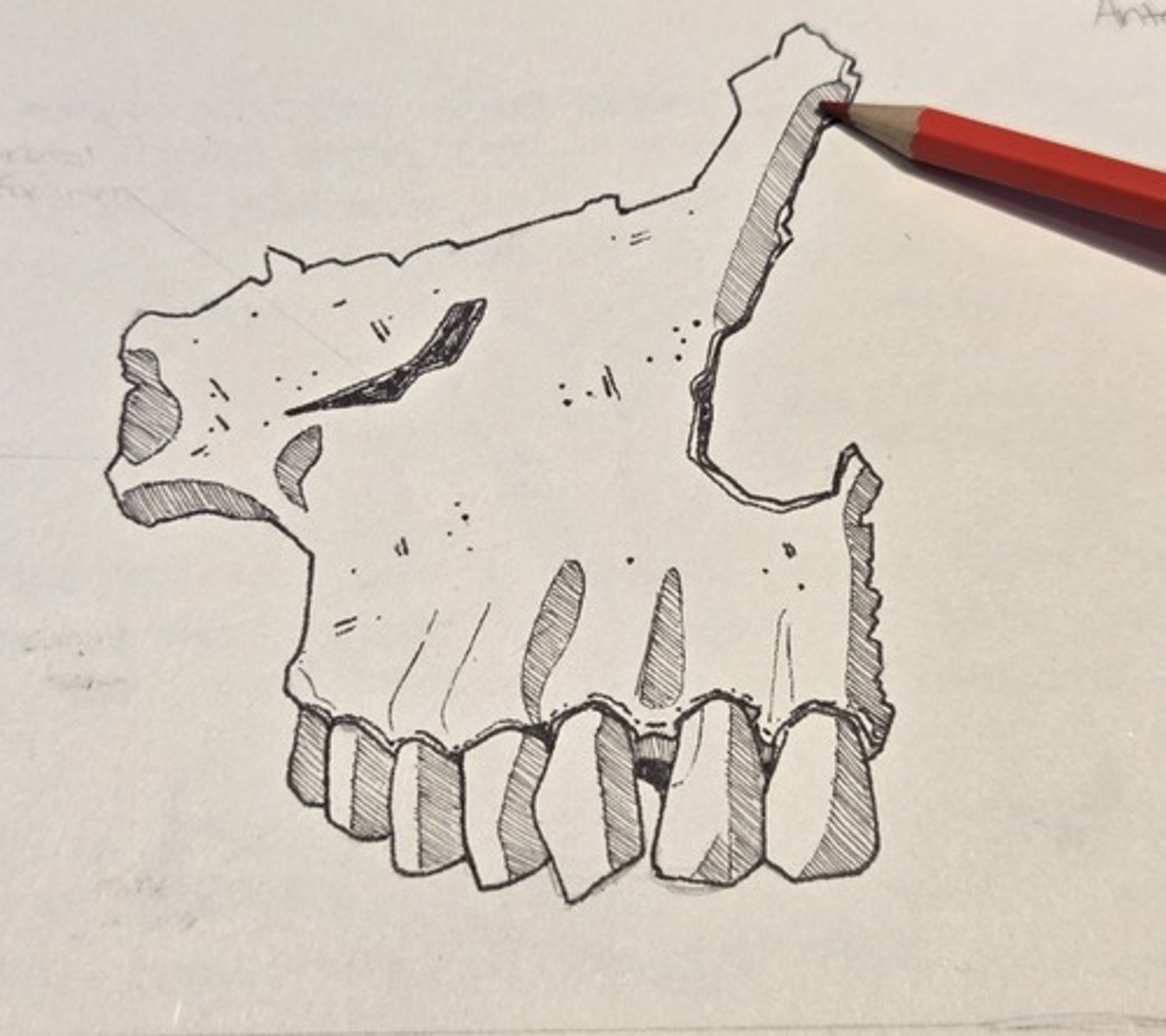
anterior nasal spine
thin projection of bone on the midline at the inferior margin of the nasal aperture
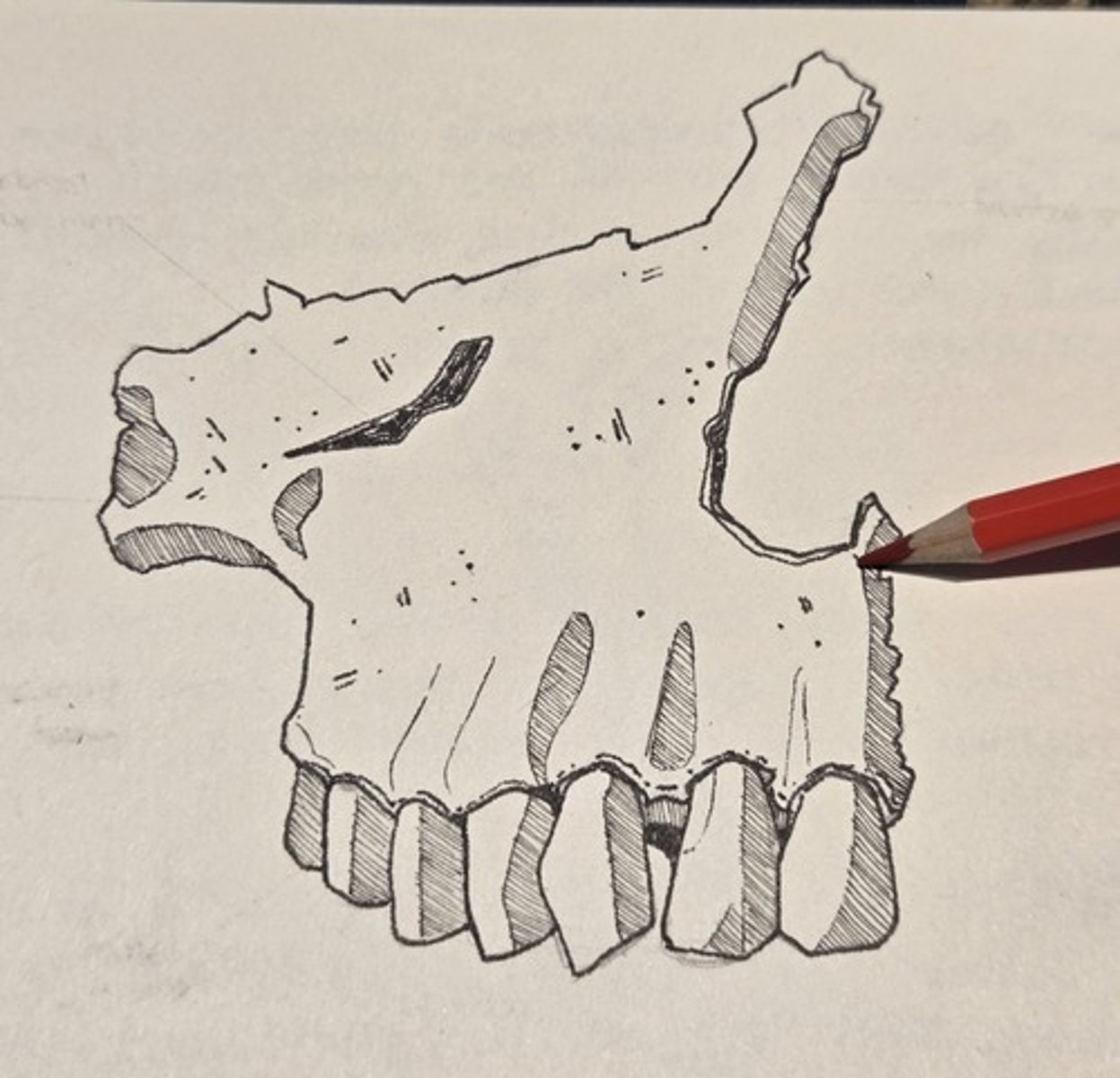
palatine process
forms the anterior part of the palatine and floor of the nasal cavity
frontal process
rises vertically and separates the orbits from the temporal fossa
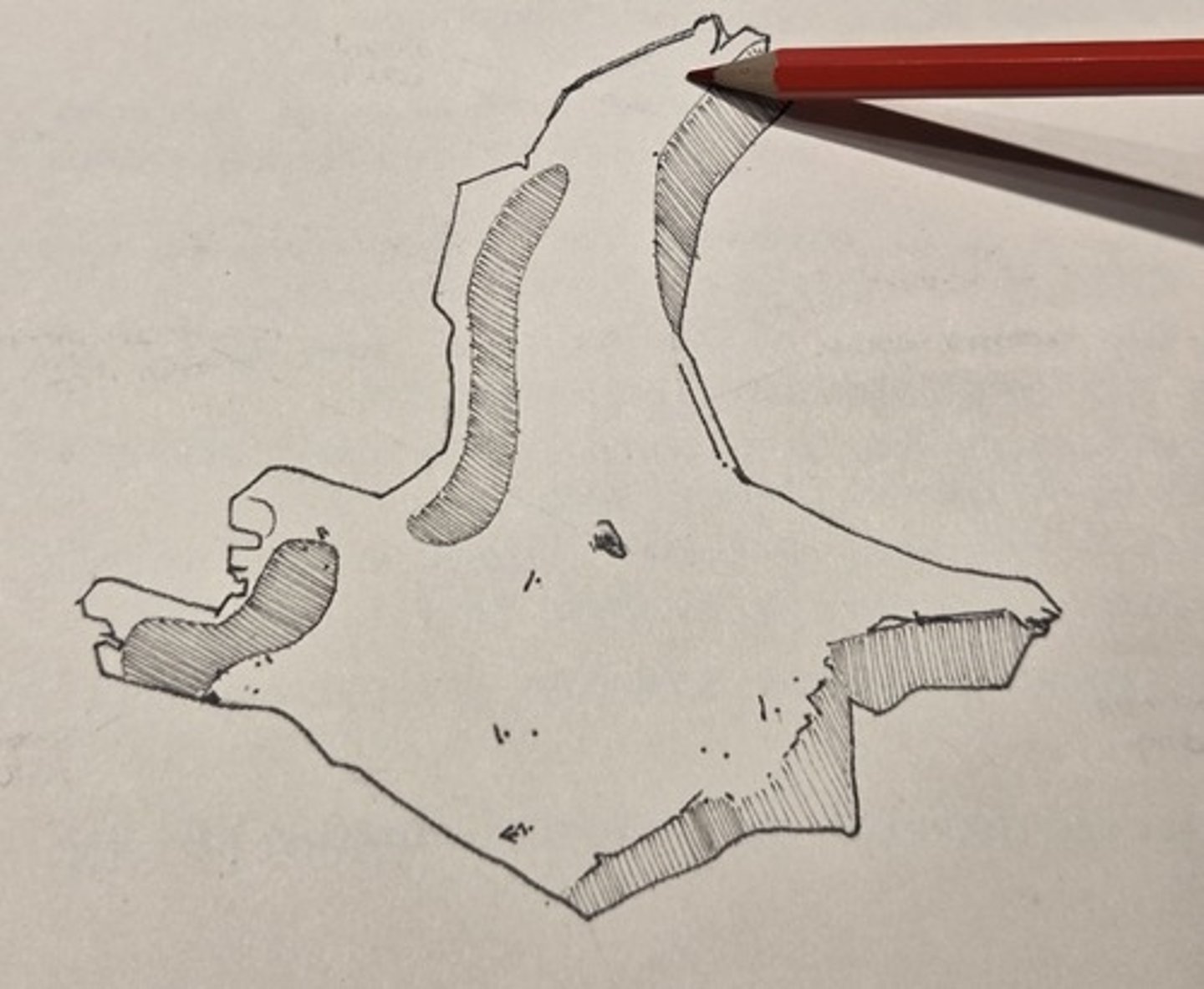
zygomaticofacial foramen
perforates the covex lateral surface of the zygomatic
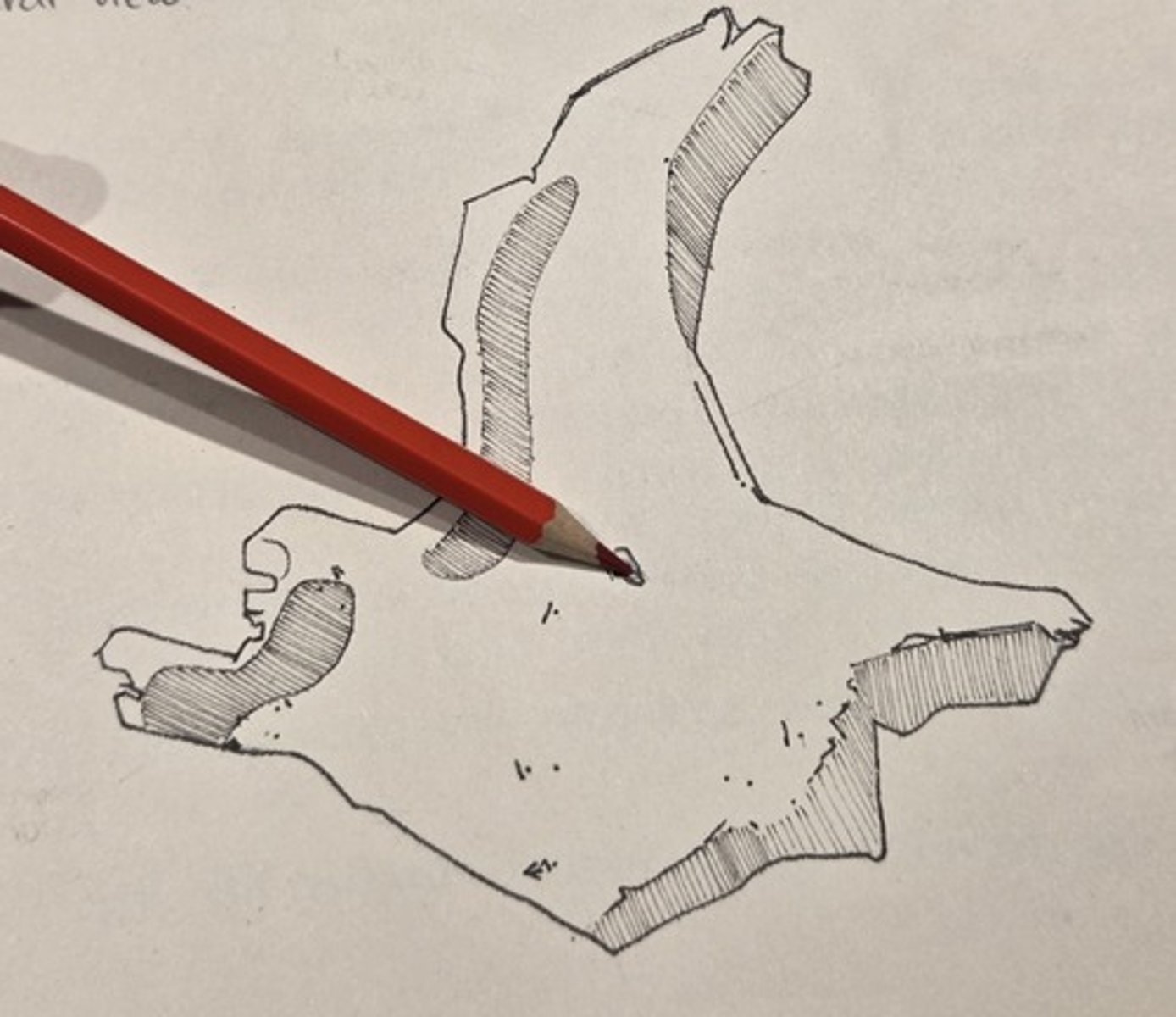
maxillary process
extends toward the midline, forming the inferolateral orbital margin
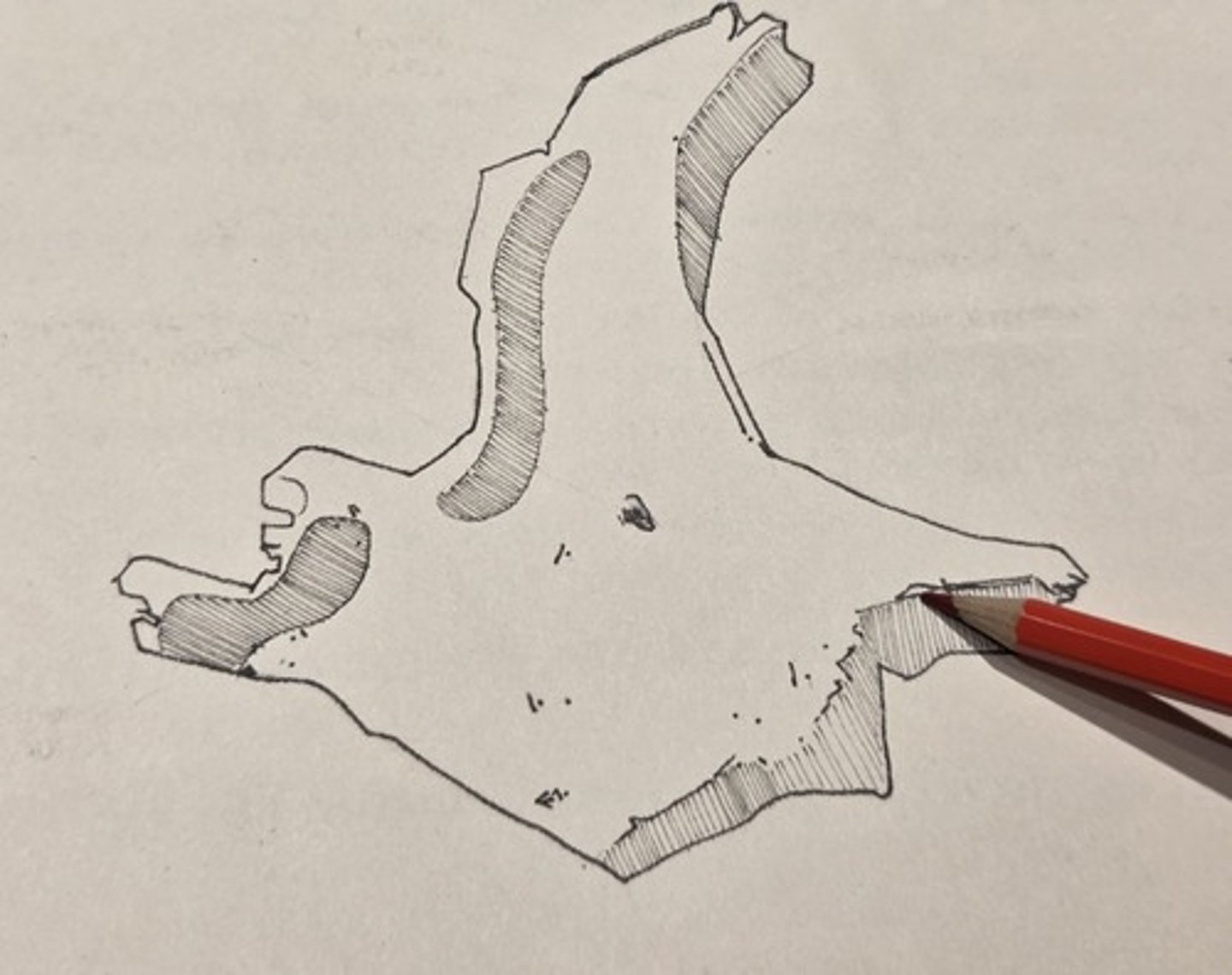
masseteric origin
the roughened, expanded inferior edge of the bone, extends from the zygomaticomaxillary to the temporozygomatic suture
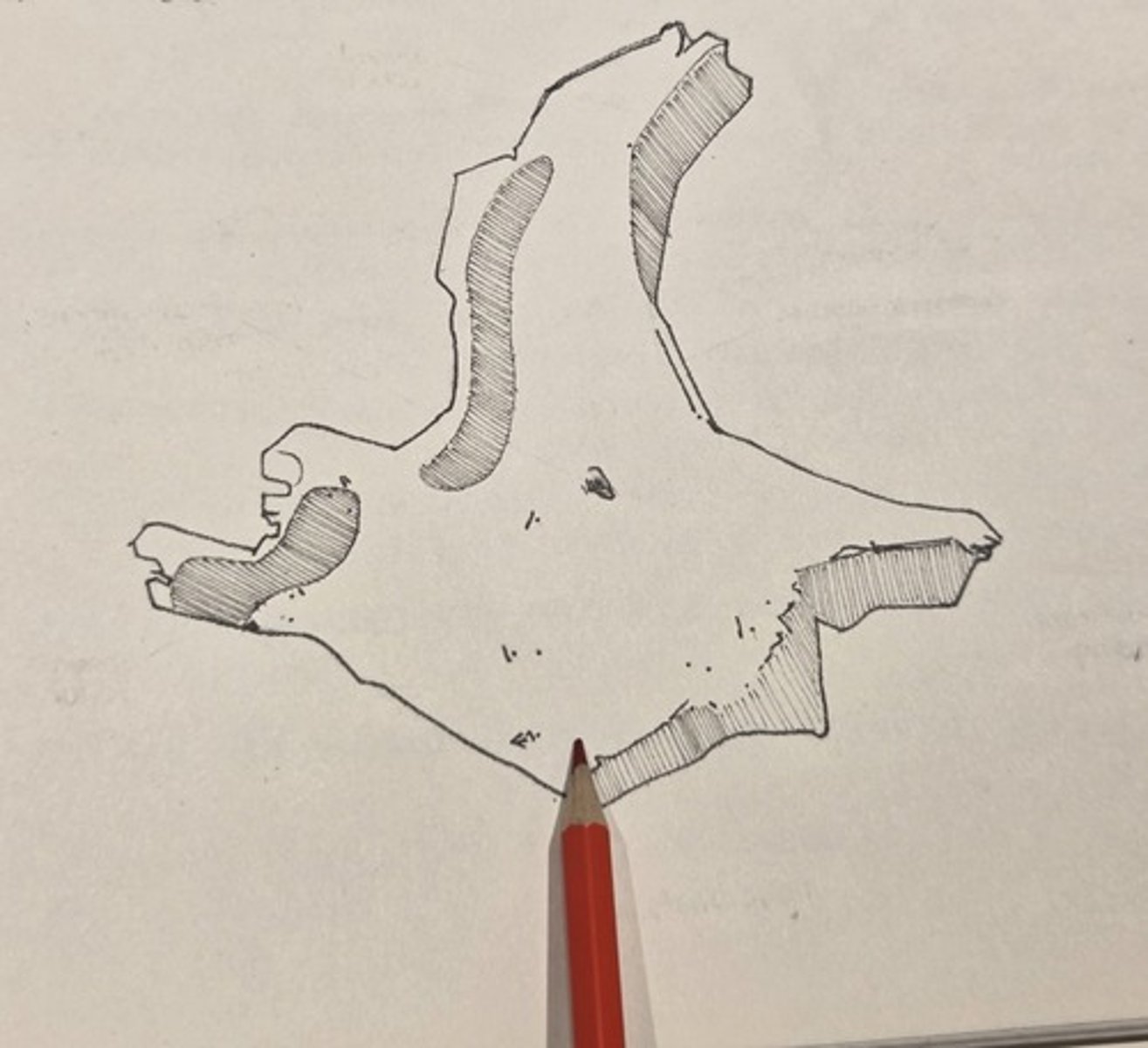
temporal process
extends posteriorly to join the zygomatic process of the temporal bone
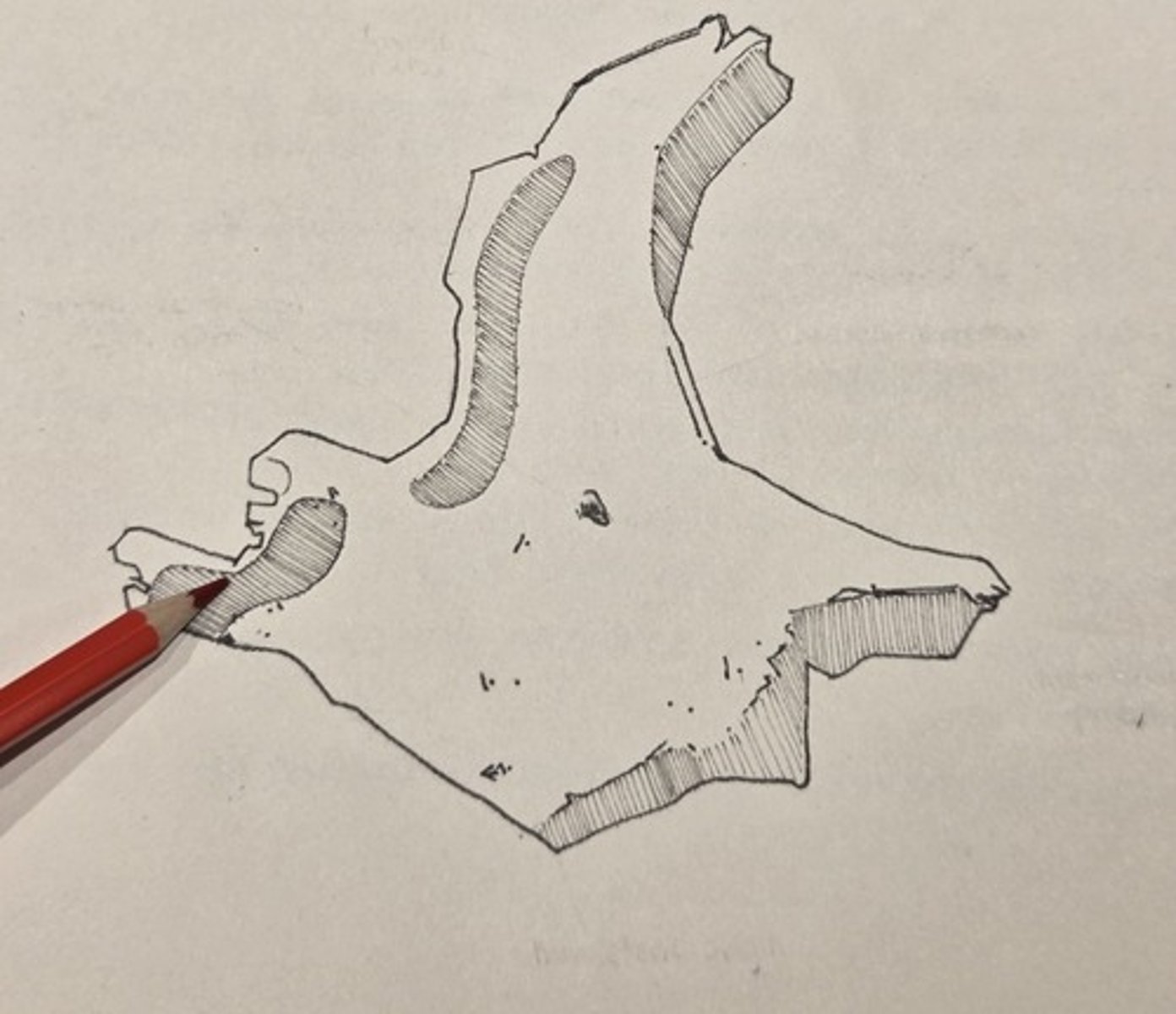
Alae (wings)
either side of a deep midline furrow on the superior surface of the vomer. This part of the bone is the thickest and sturdiest and is tightly appressed to the sphenoid

perpendicular plate
the vomer is a thin verticle sheet of bone on the midline below the Alae
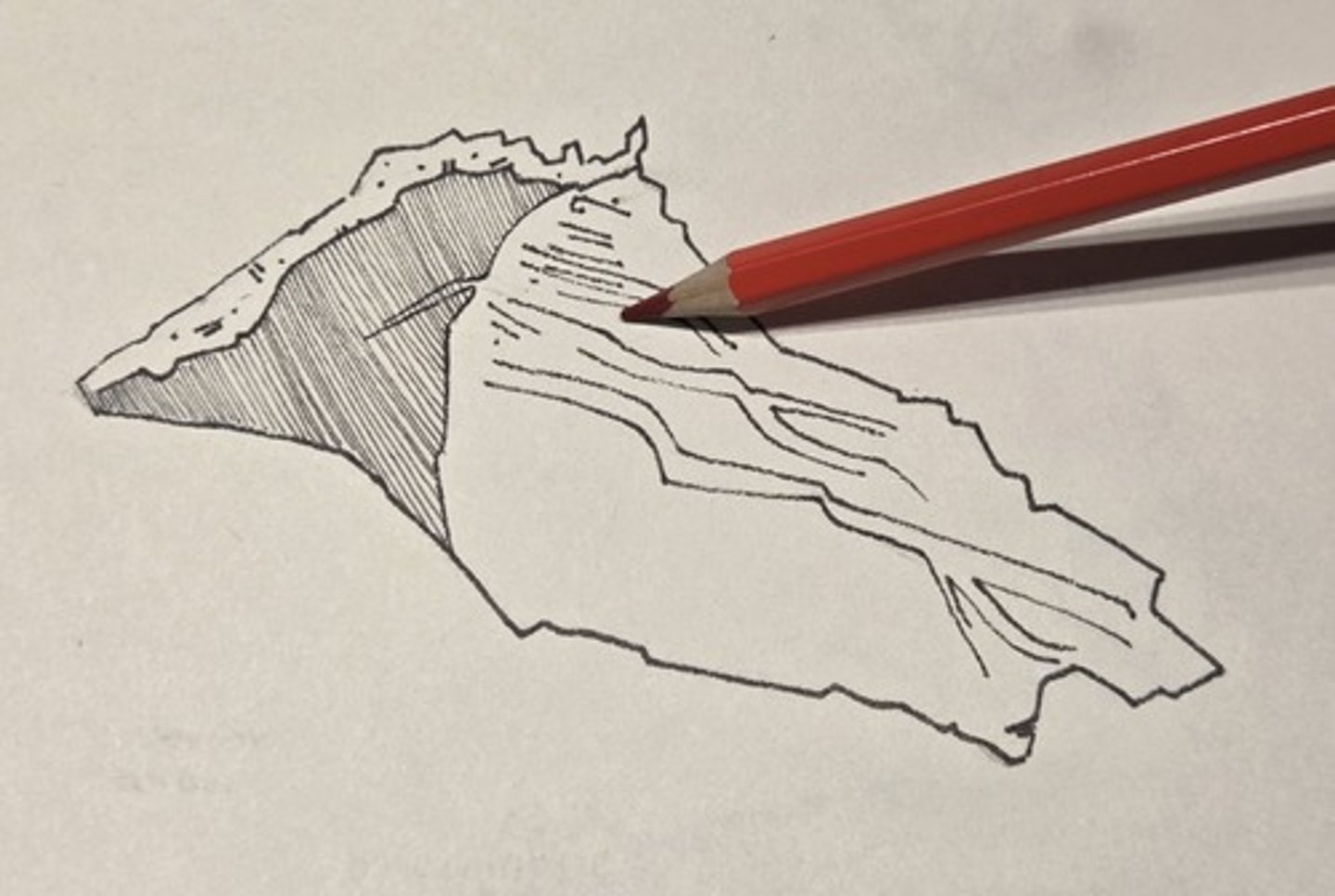
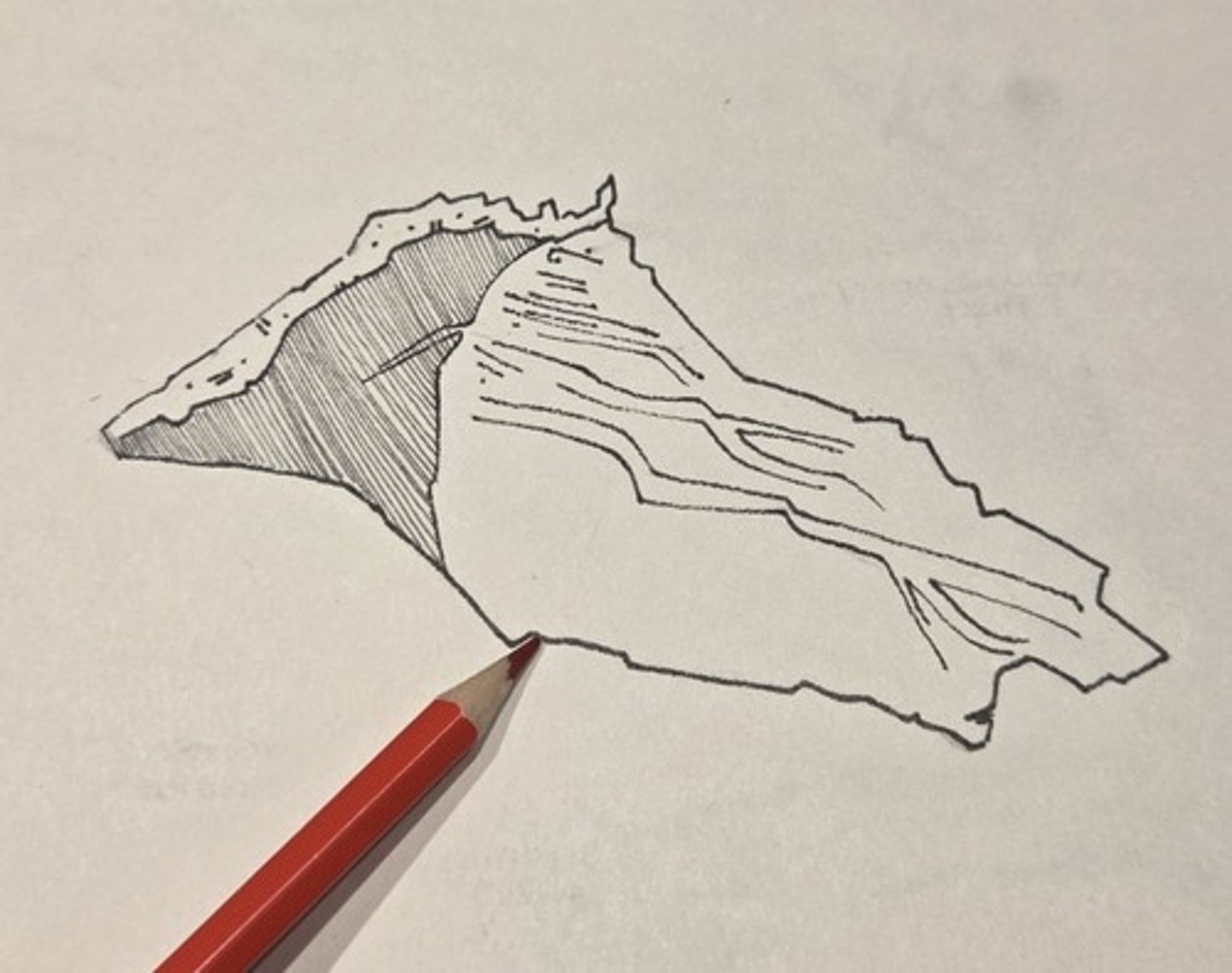
posterior border
nonarticular part of the vomer that divides the posterior nasal aperture into two halves
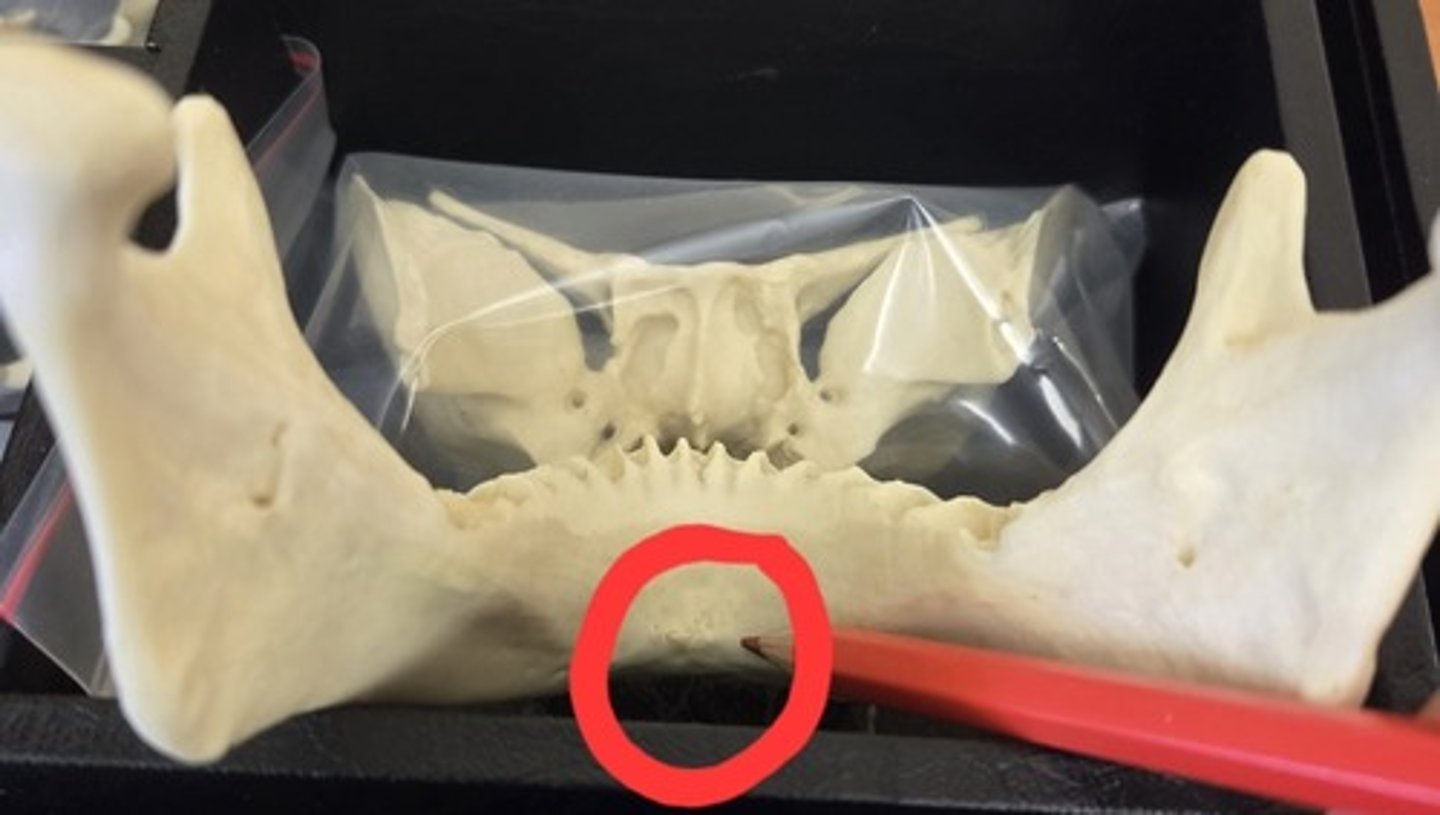
mental spines
are small ridges on the inner surface of the mandible; serve for attachment of certain chin muscles
mylohyoid groove
crosses the medial surface of the ramus, running anteroinferiorly from the edge of the mandibular foramen
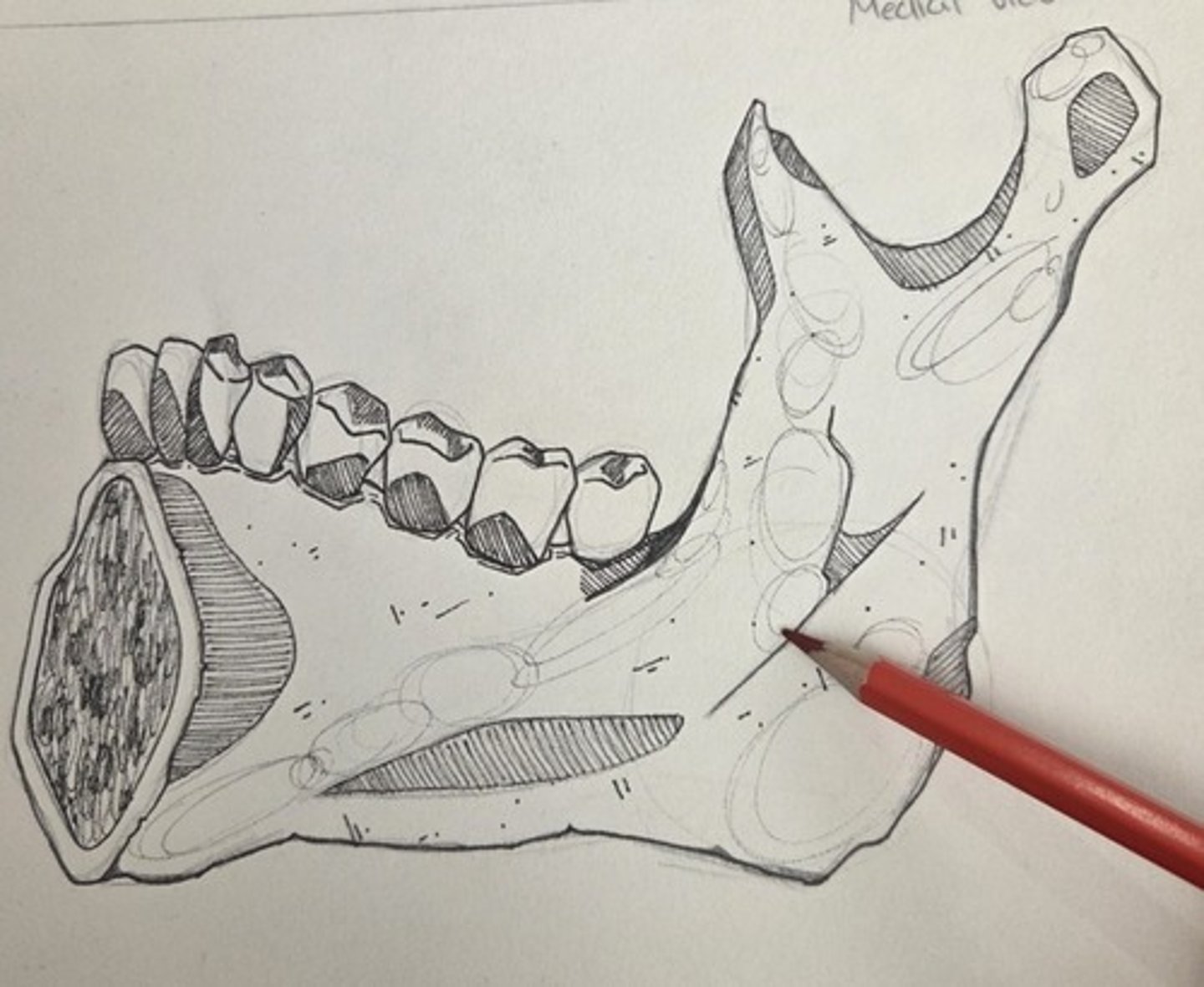
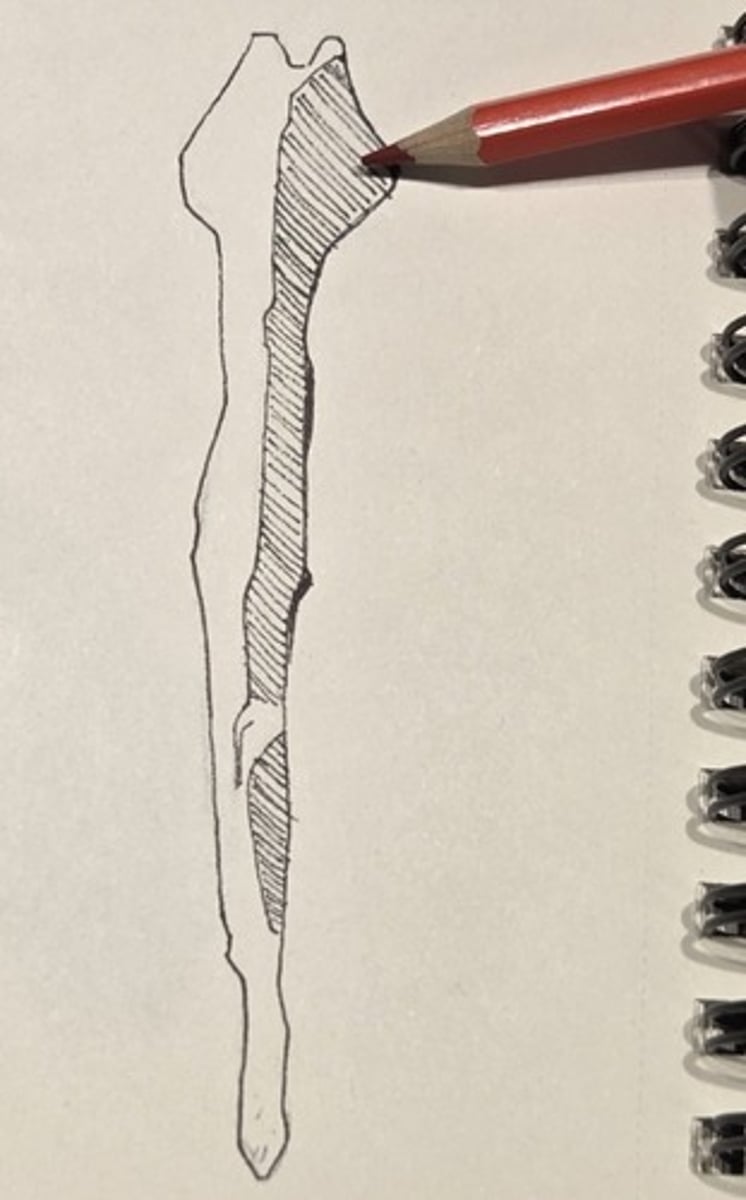
Body
the thick, bony part of the mandible that anchors the teeth
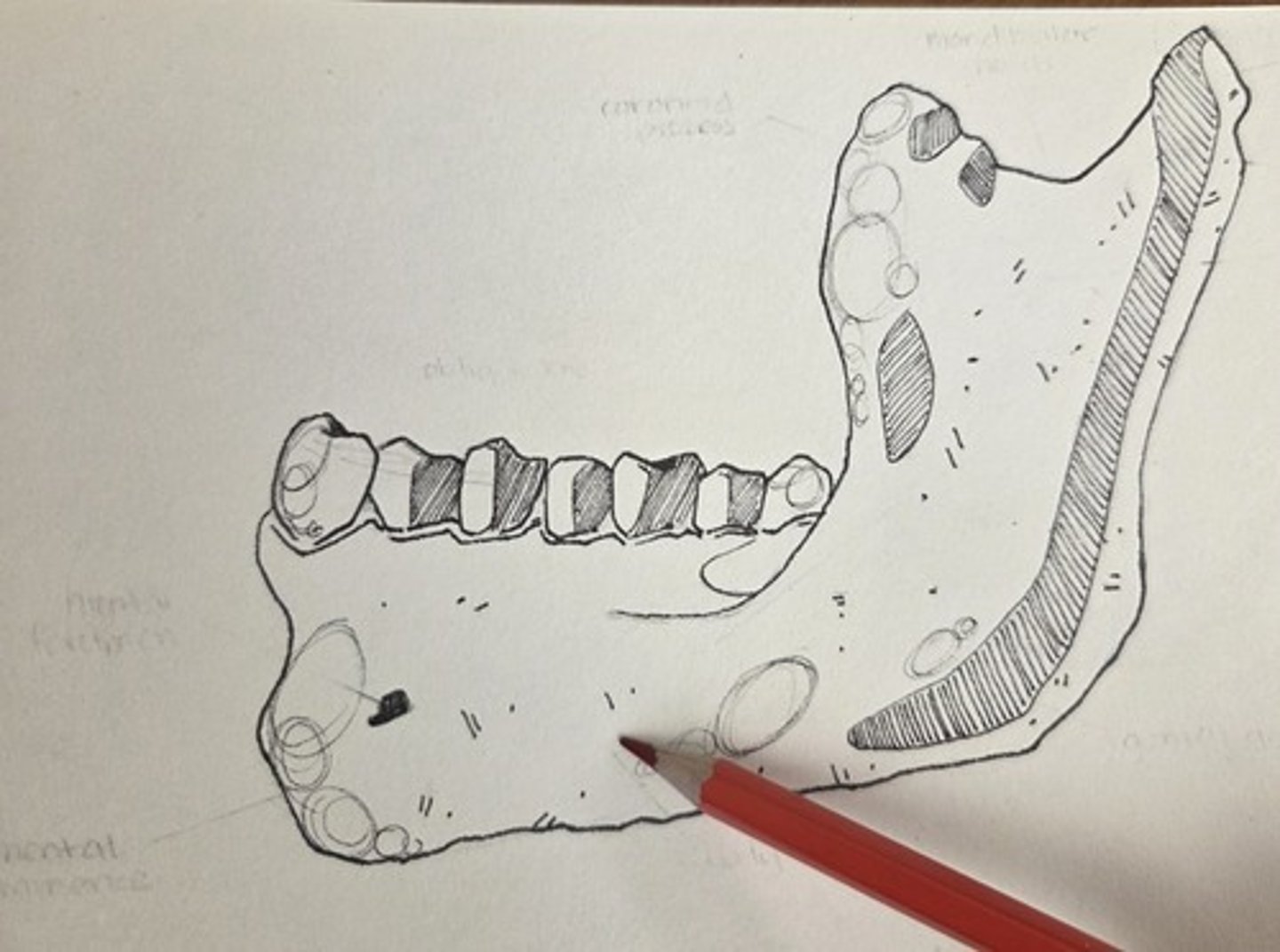

mental eminence
the triangular eminence, or bony chin, at the base of the corpus in the anterior symphyseal region
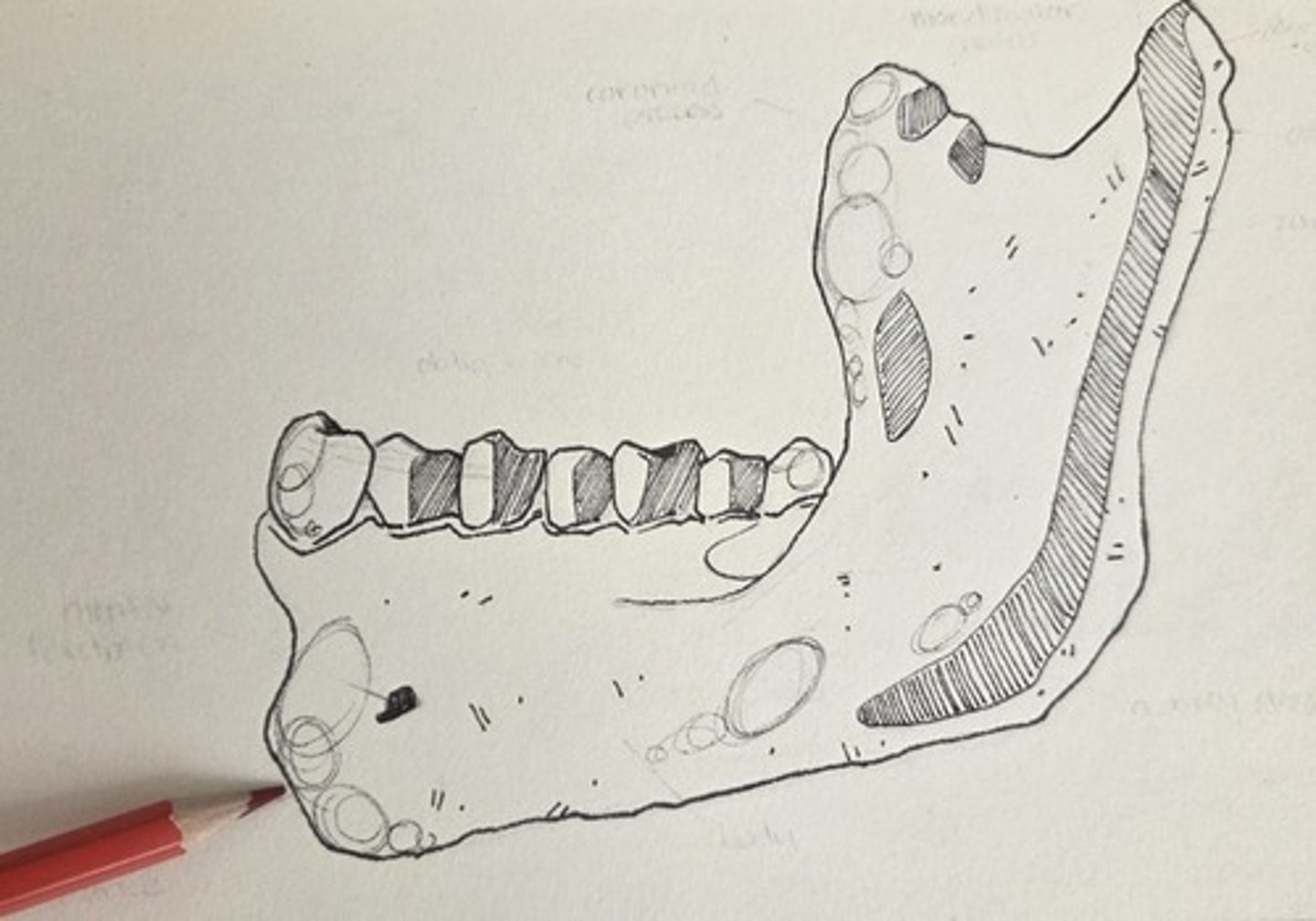
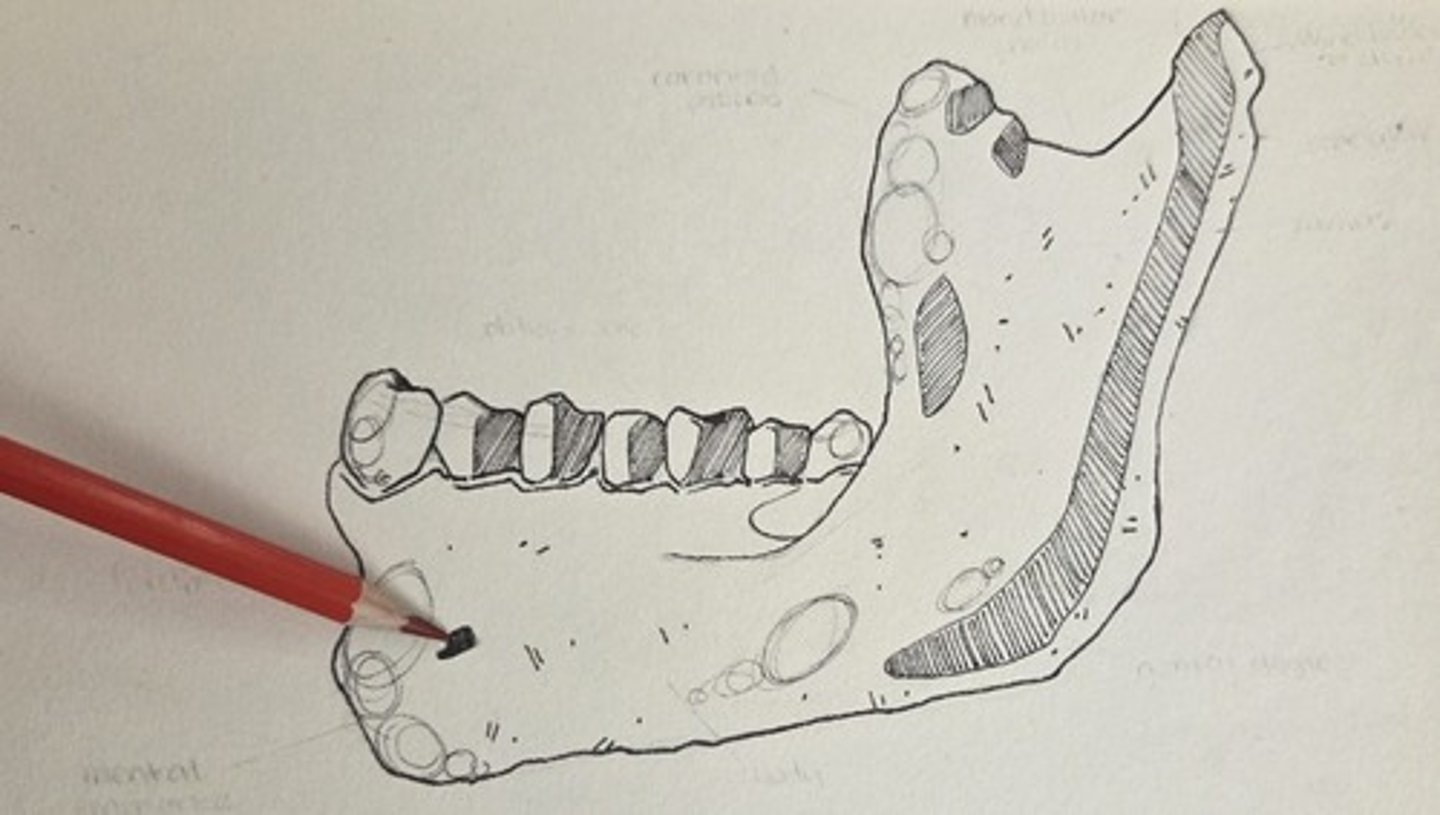
mental foramen
the large, sometimes multiple foramen located on the lateral corpus surface, near mid-corpus, below the premolar region
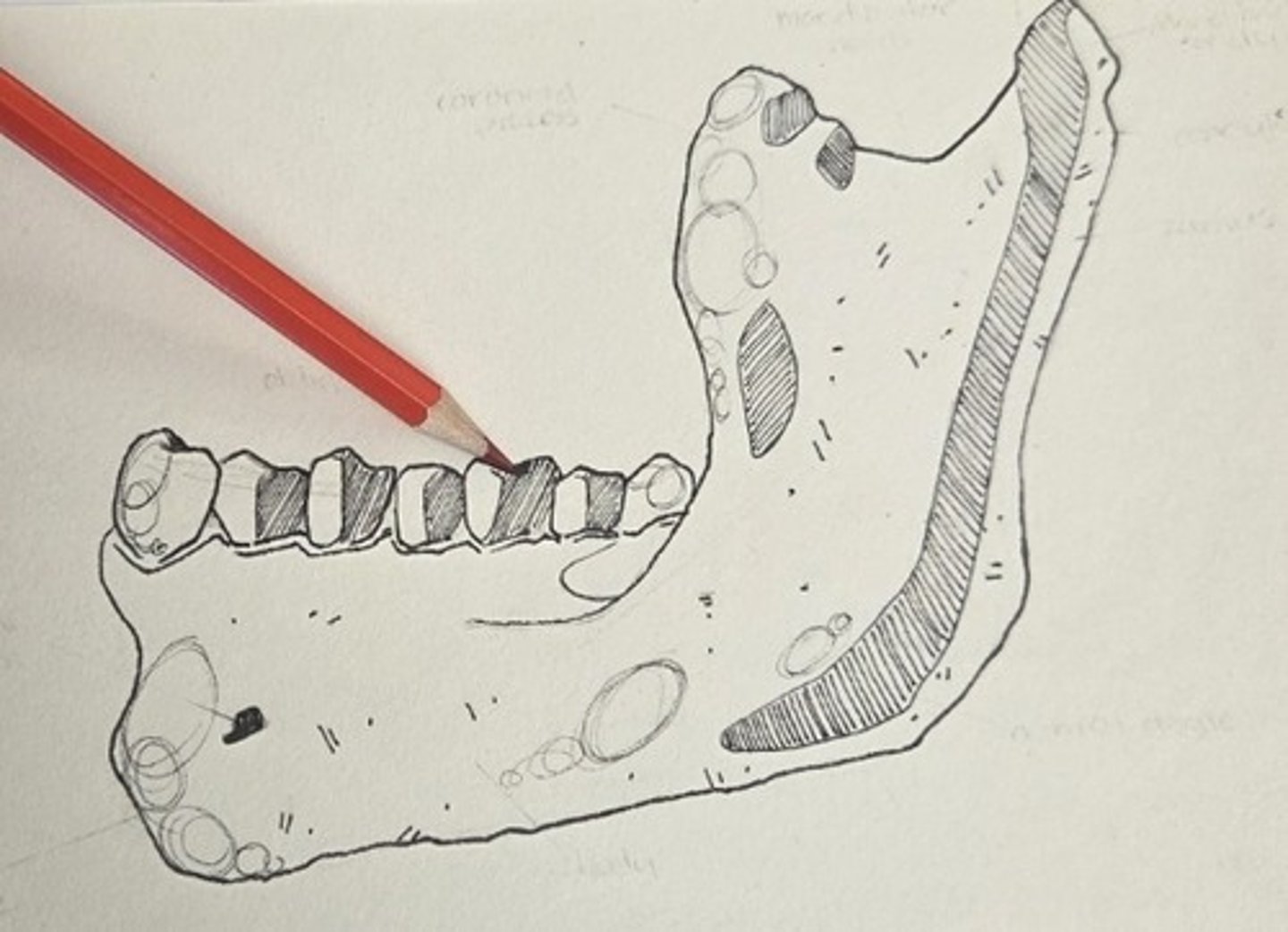
oblique line
a weak eminence that passes from the root of the ramus to the area at the rear of the mental foramen
ramus
this vertical part of the mandible rises above the level of the teeth and articulates with the cranial base
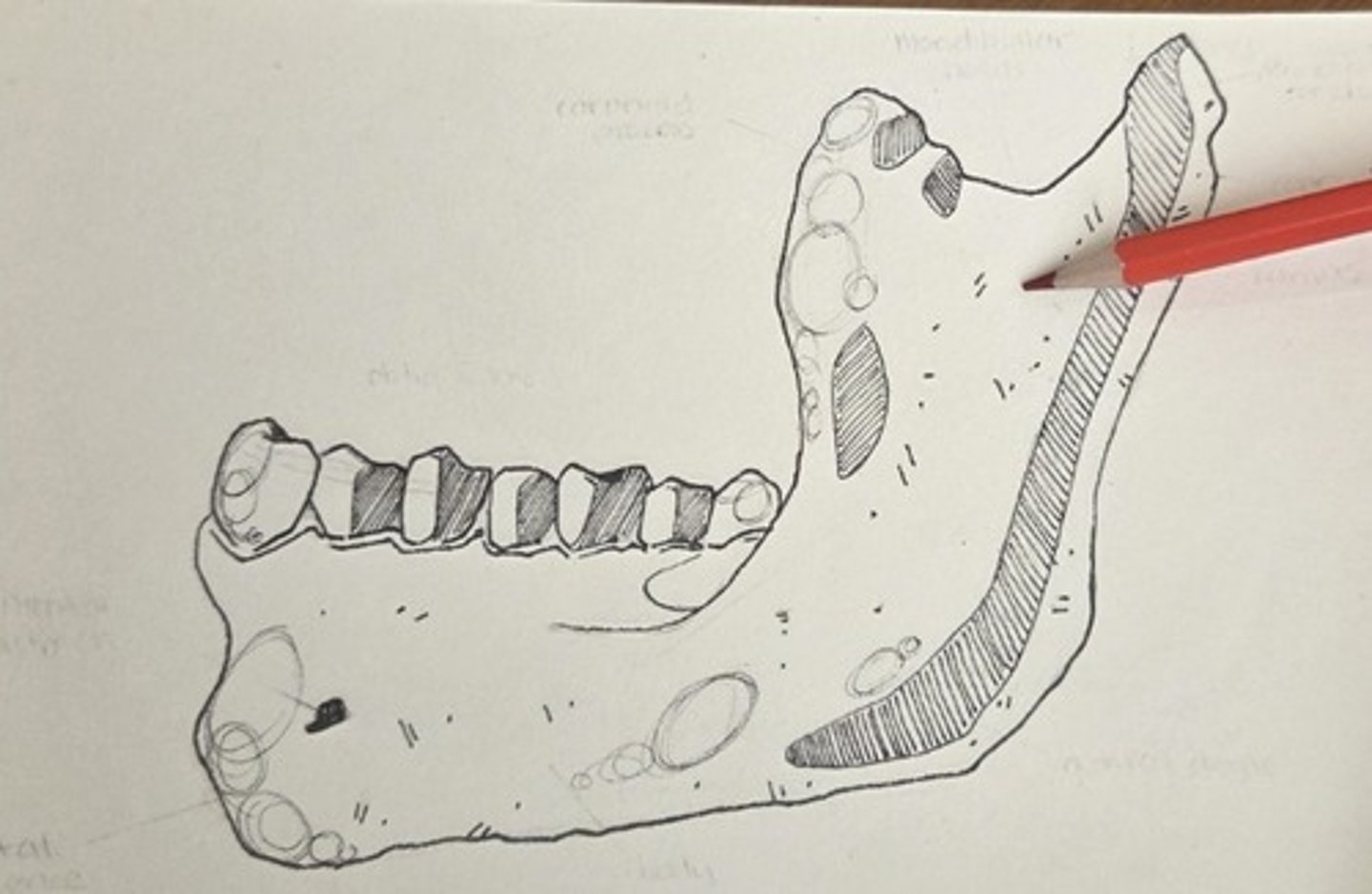
mandibular condyle
the large, rounded, articular prominance on the posterosuperior corner of the ramus
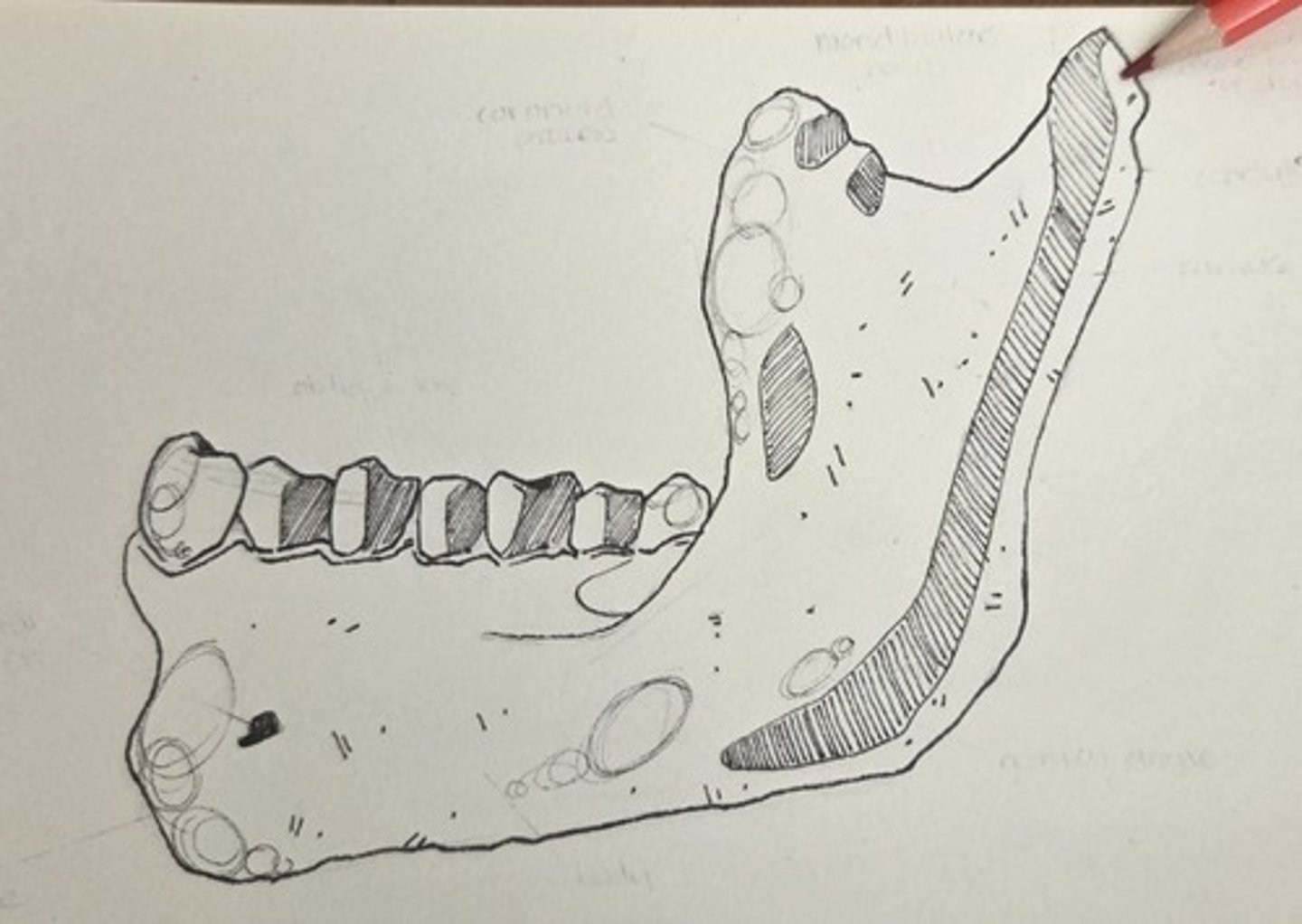

condylar neck
the area just anterioinferior to the condyle
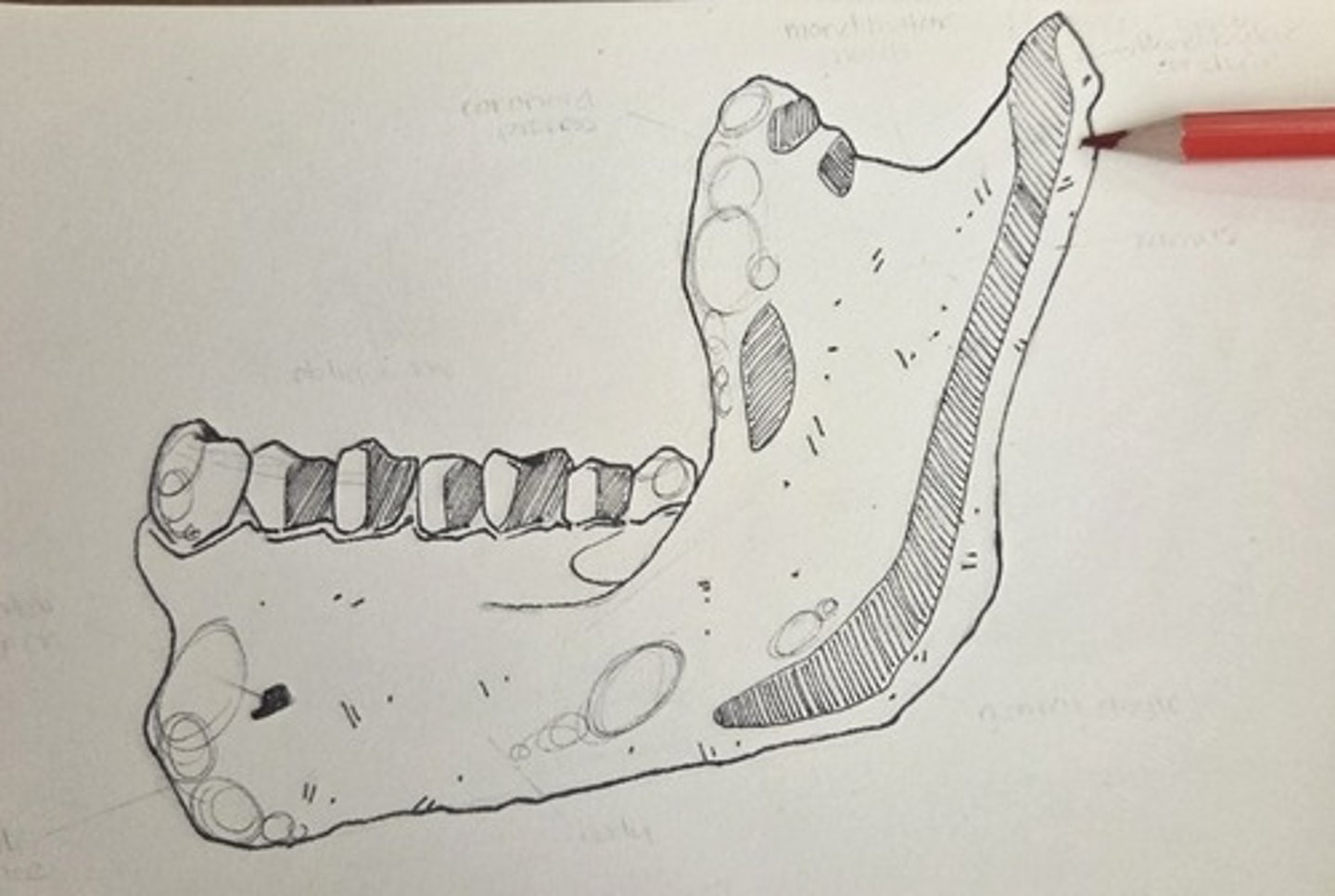
coronoid process
the ramus is thin and triangular, varying widely in shape
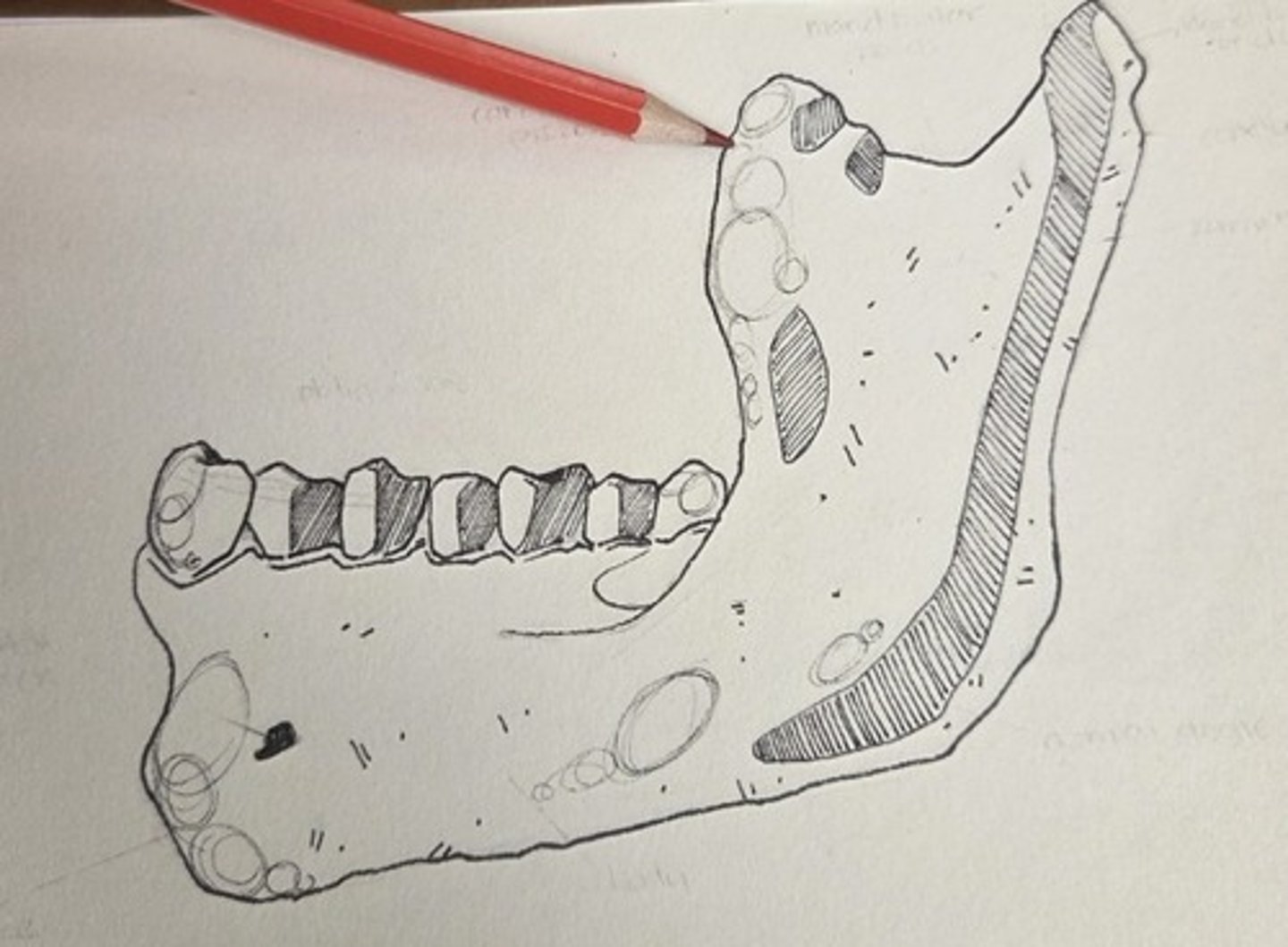
mandibular notch
the notch between the condule and the coronoid process
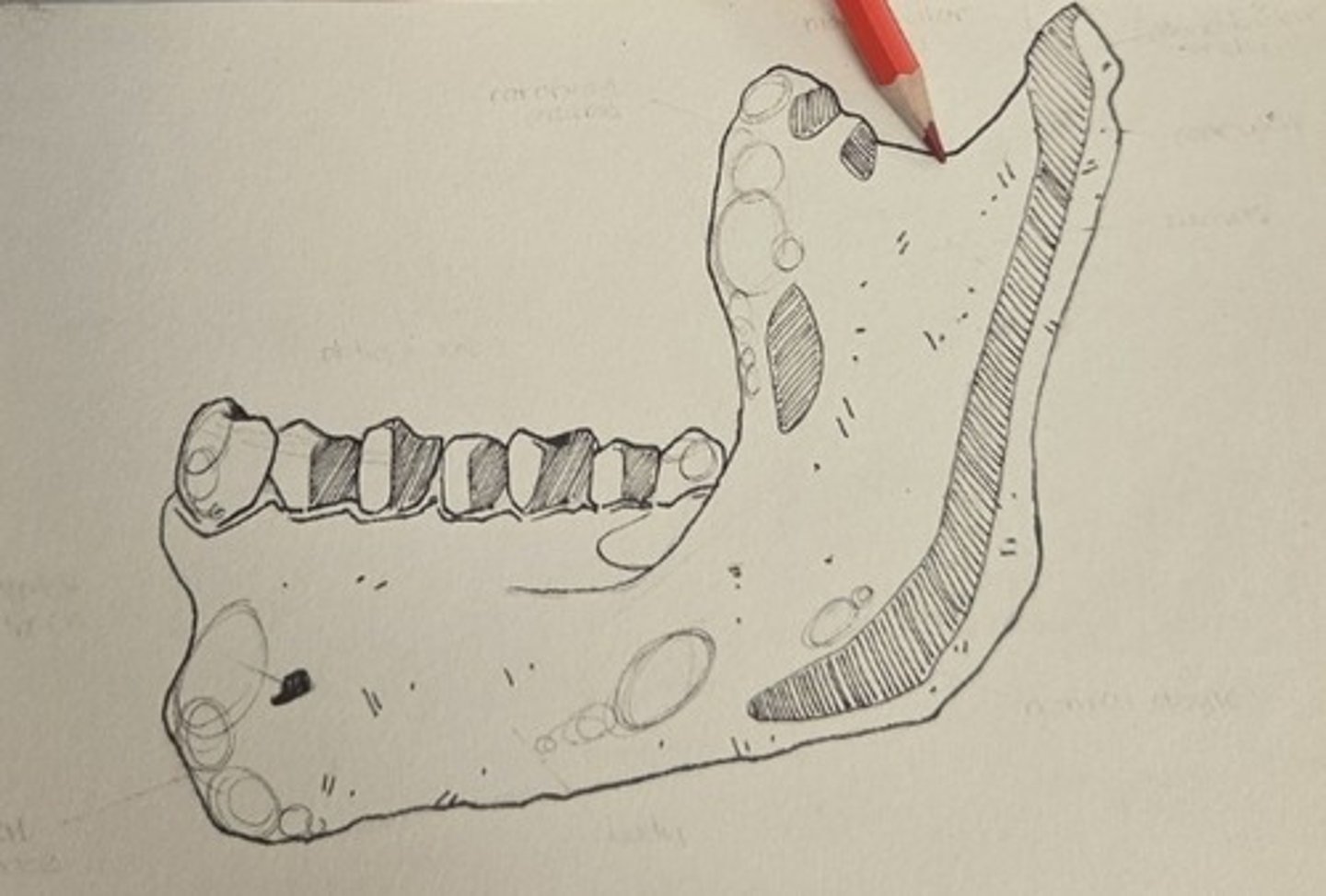

gonial angle
rounded posteroinferior corner of the mandible

nasal foramen
perforates the facial surface and transmits a vein
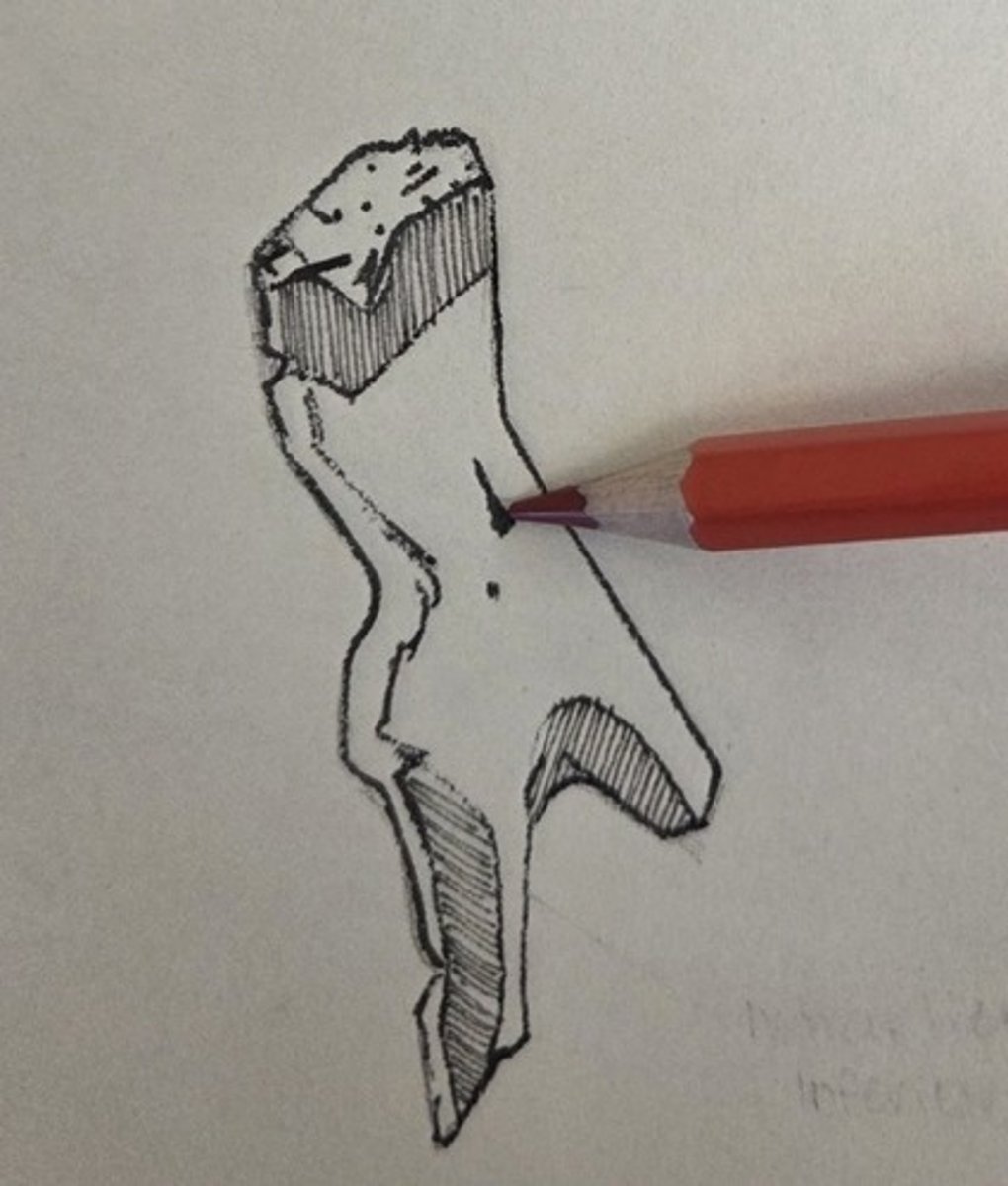
posterior lacrimal crest
vertical crest on the medial orbital wall that bounds the posterior half of the lacrimal groove
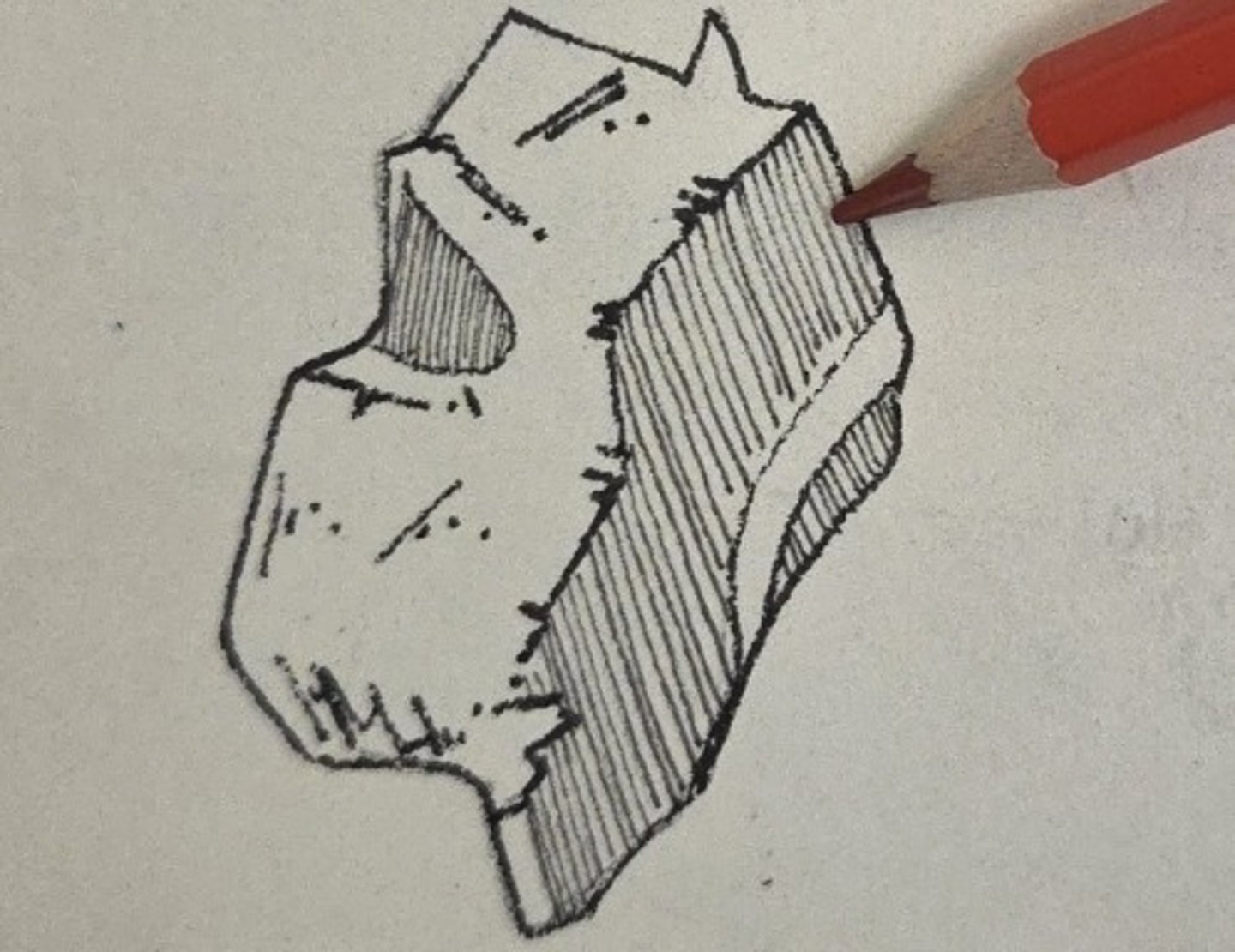
lacrimal groove
forms the posterior portion of the superior end of the lacrimal canal
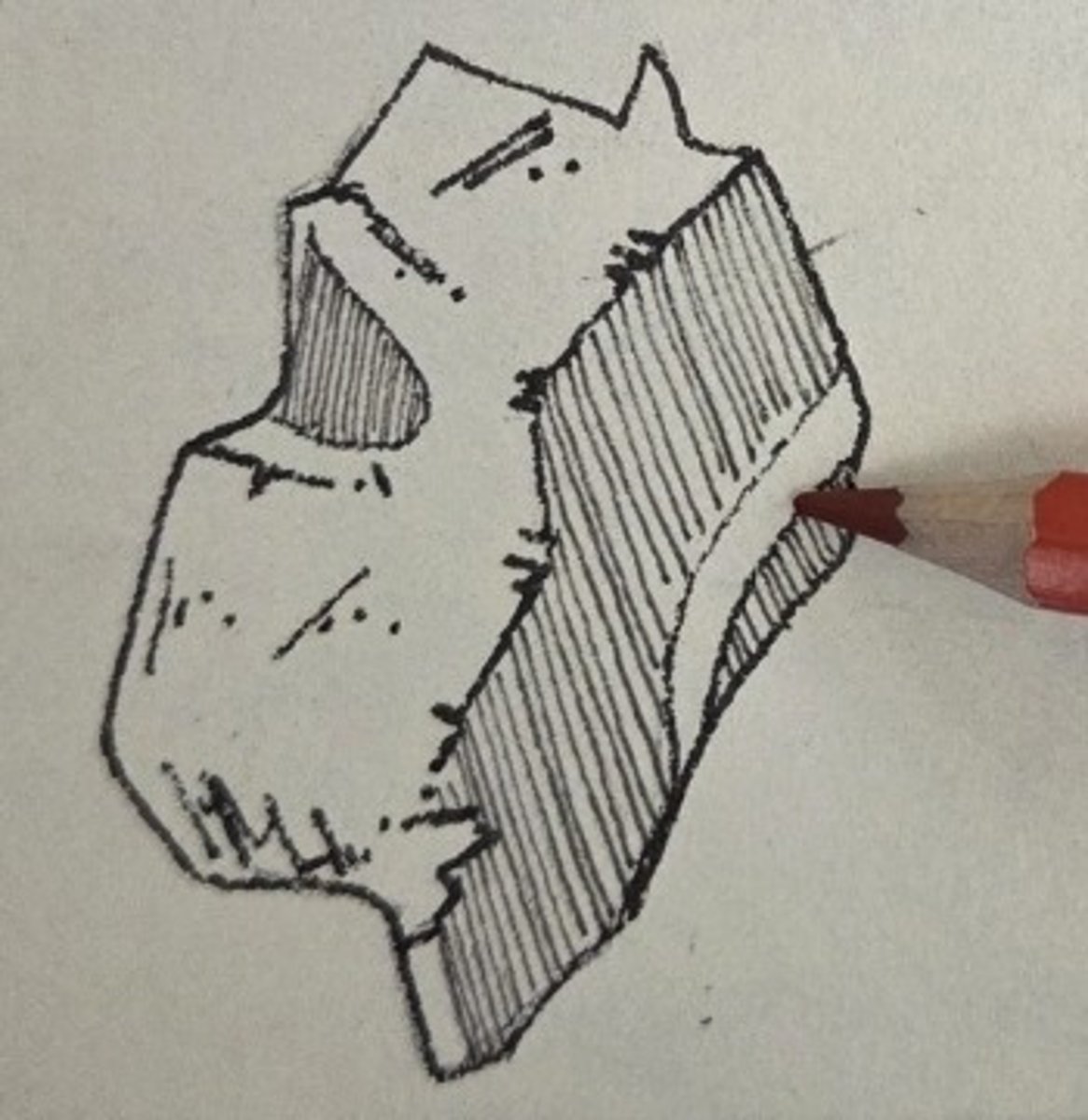
Lamina
a thin, vertical, undulating sheet of bone extending medially and inferiorly from the maxillary process
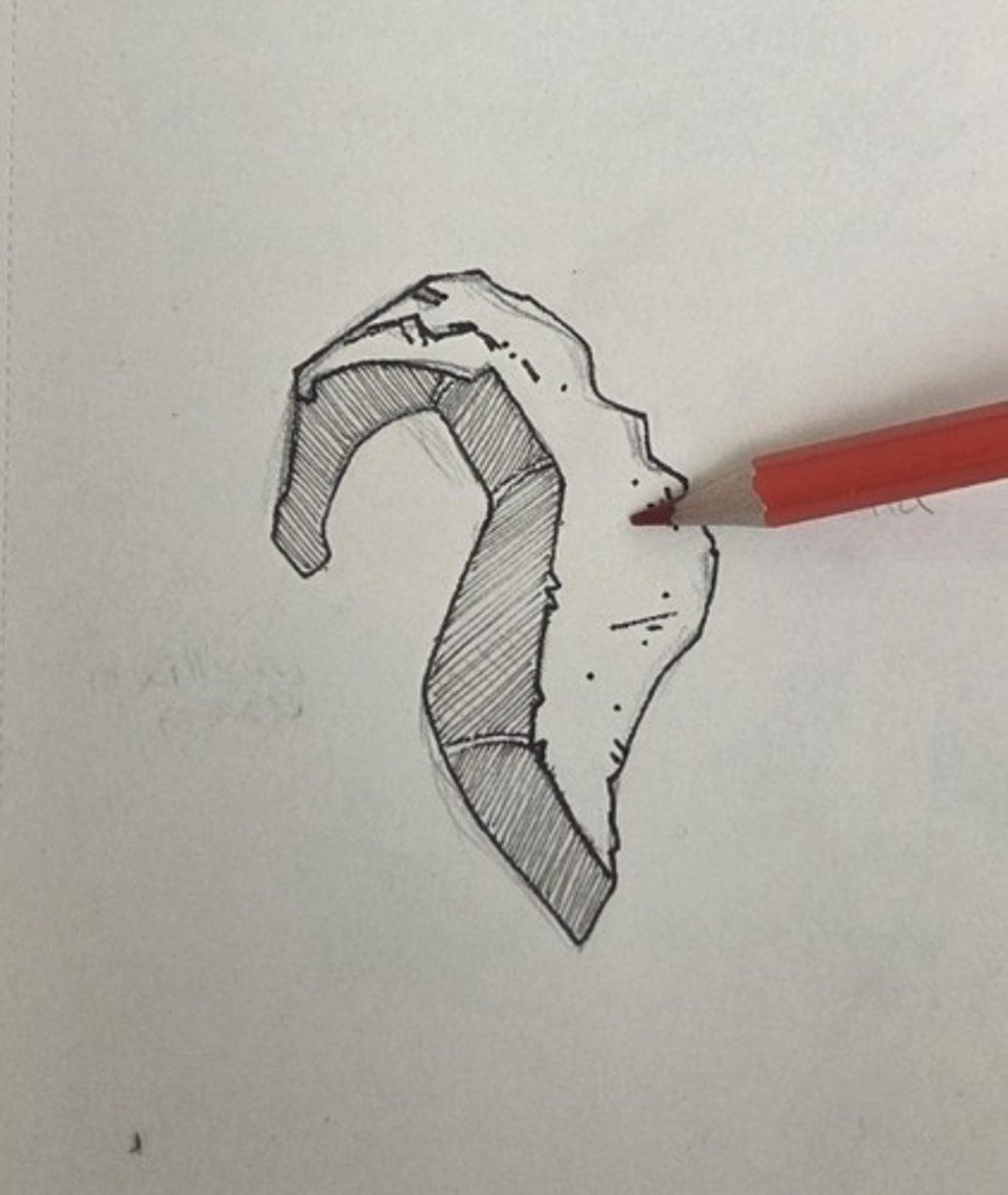

maxillary process
the delecate hook of the bone extending toward the medial surface of the maxilla
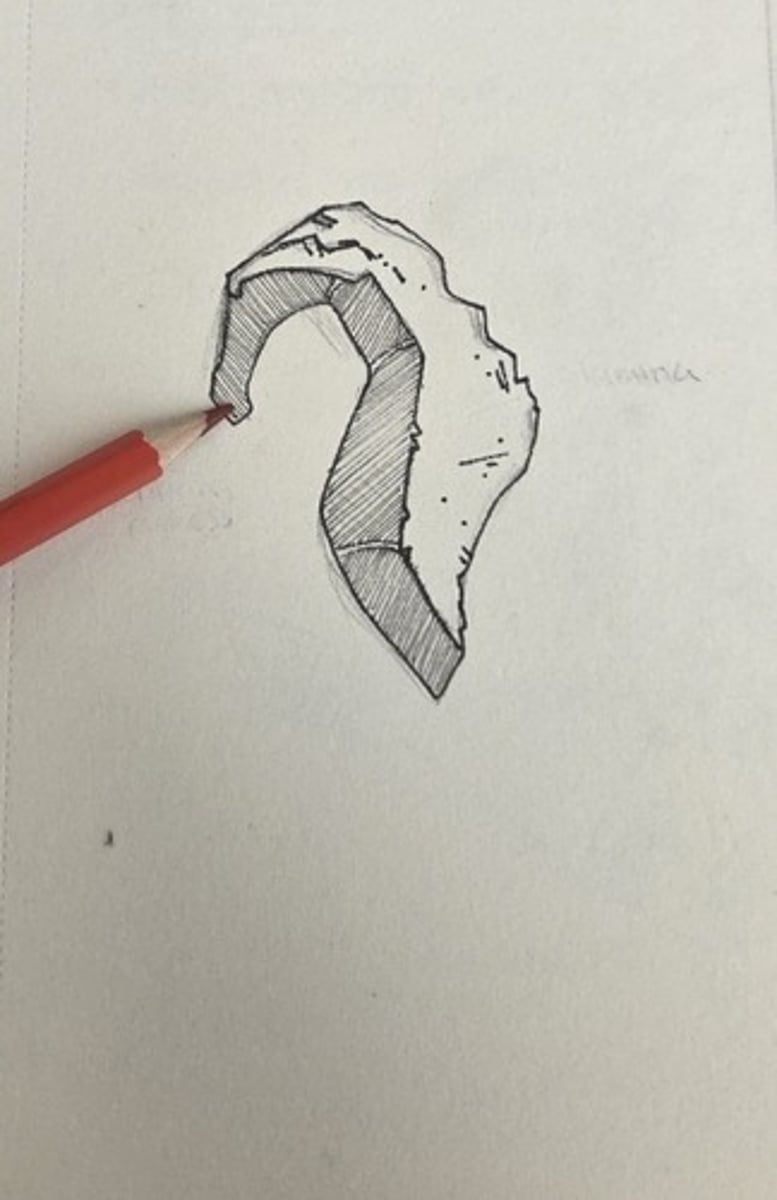
ethmoid process
the inferior concha is just posterior to the lacrimal process