UA PSIO EXAM 3
1/231
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
232 Terms
3 Types of Muscle
Skeletal, Cardiac, Smooth
Basic function of all muscles
Generate tension
Functions of Skeletal Muscle
Locomotion, facial expression, posture and body position, regulation of body temp
Skeletal muscle contraction is voluntary or involuntary?
voluntary
T or F: All skeletal muscles are automatic
False, some are automatic but we can change their ability like the diaphragm
Muscles ____ on bones
pull
Origin
the place where the muscle starts on a bone
Insertion
the place where the muscle ends on a bone
Muscle Action
The insertion moves towards the origin
Flexion
Decreasing the angle between two bones
Extension
Increasing the angle between two bones
Plane where extension and flexion mostly occur:
Sagittal plane
T or F: In standard anatomical position everything is extended
False, the feet arent
Abduction
Moving away from the midline of the body
Adduction
Moving toward the midline of the body
Abduction and Adduction occurs on which plane?
frontal plane
Reverse muscle action (RMA)
when the insertion is anchored, the origin moves towards the insertion
Agonist
muscle primarily responsible for movement
Antagonist
muscle which opposes the action of the agonist
Synergist
assists the agonist in making a movement more efficient
Fixator
special synergists which help to prevent movement at muscle origin
Lever
a rigid bar that is free to move around a fixed point, the rigid bar in this case is bone.
Fulcrum
the fixed point around which a lever can move, in this case a joint
muscles act to facilitate movement at a _____ by exerting force on the ____ to move a load
fulcrum, lever
First Class Levers (LFE)
Opening of the mouth (not very common movement) sorta like a scissor movement
Second Class Levers (FLE)
Lifting up on your toes and concentric movement of the calf kinda like a wheelbarrow
Third Class Levels (FEL)
Most common type of lever system in the body like how tongs work
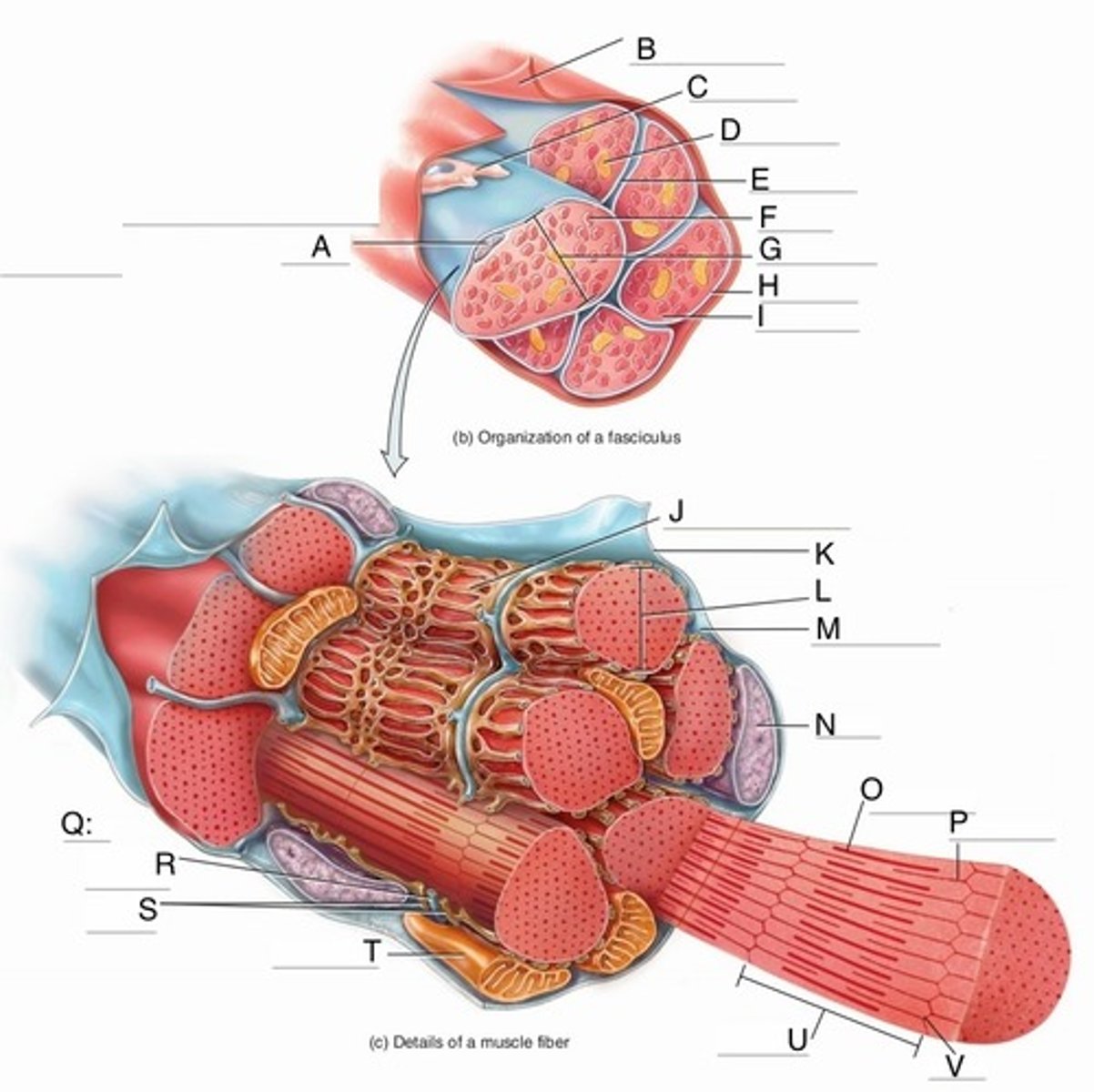
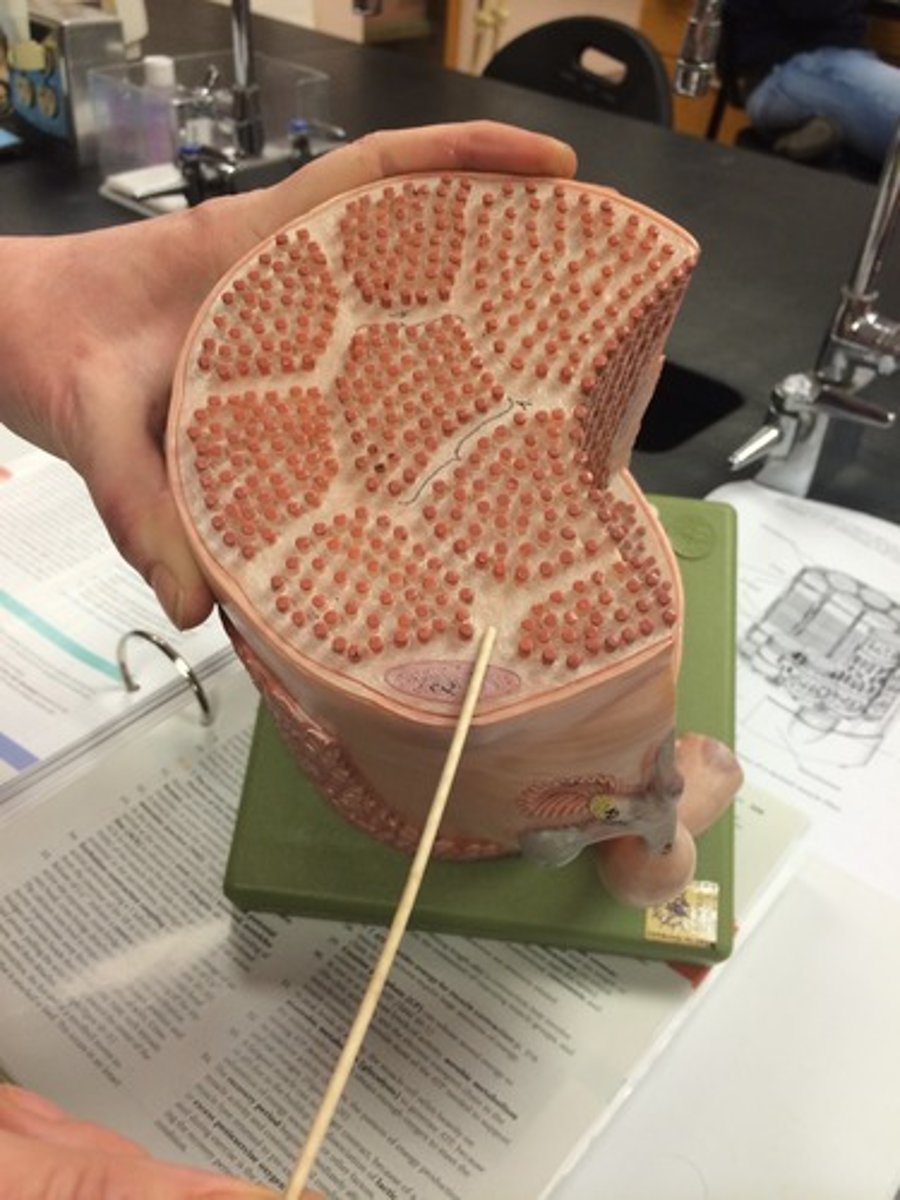
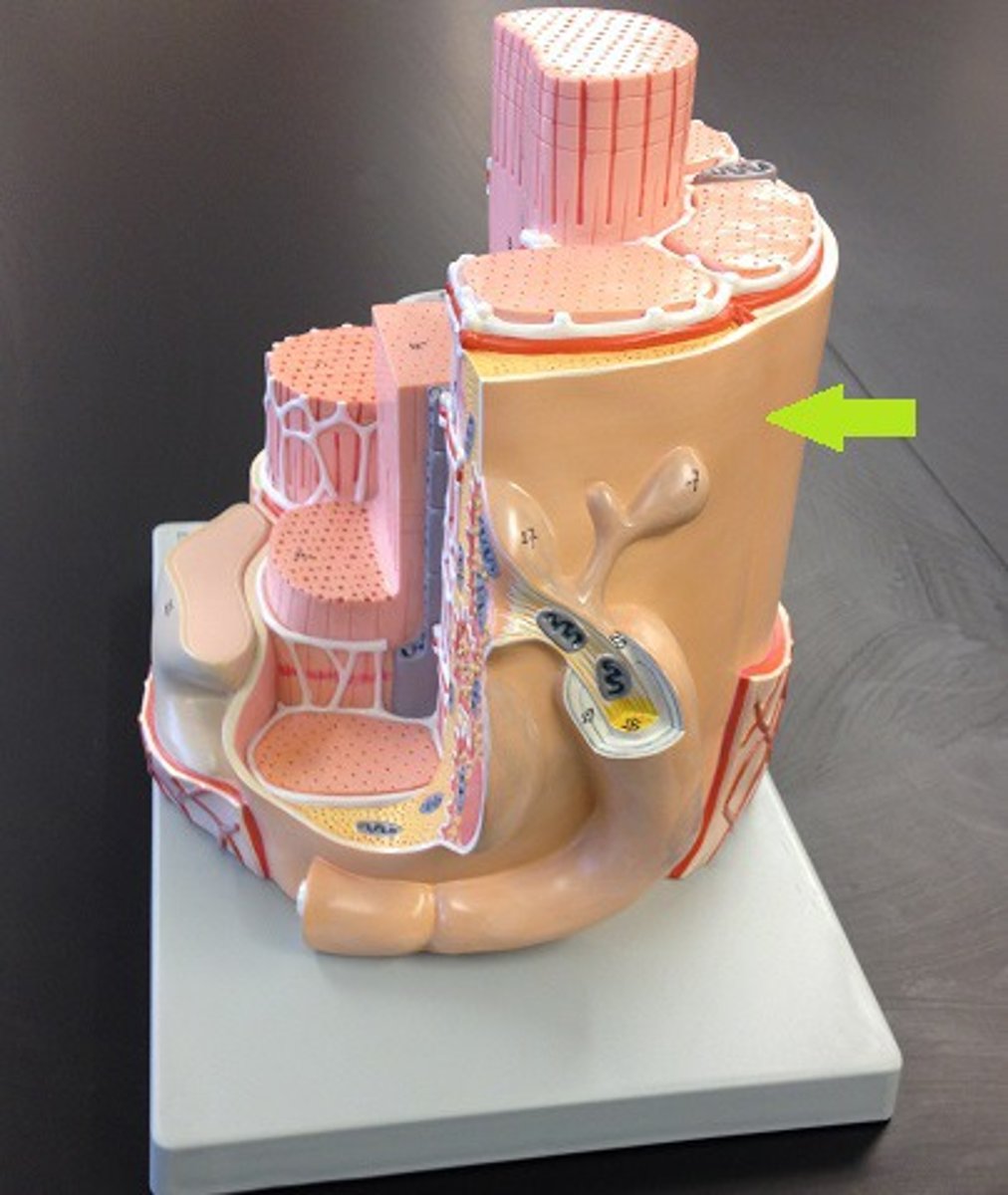
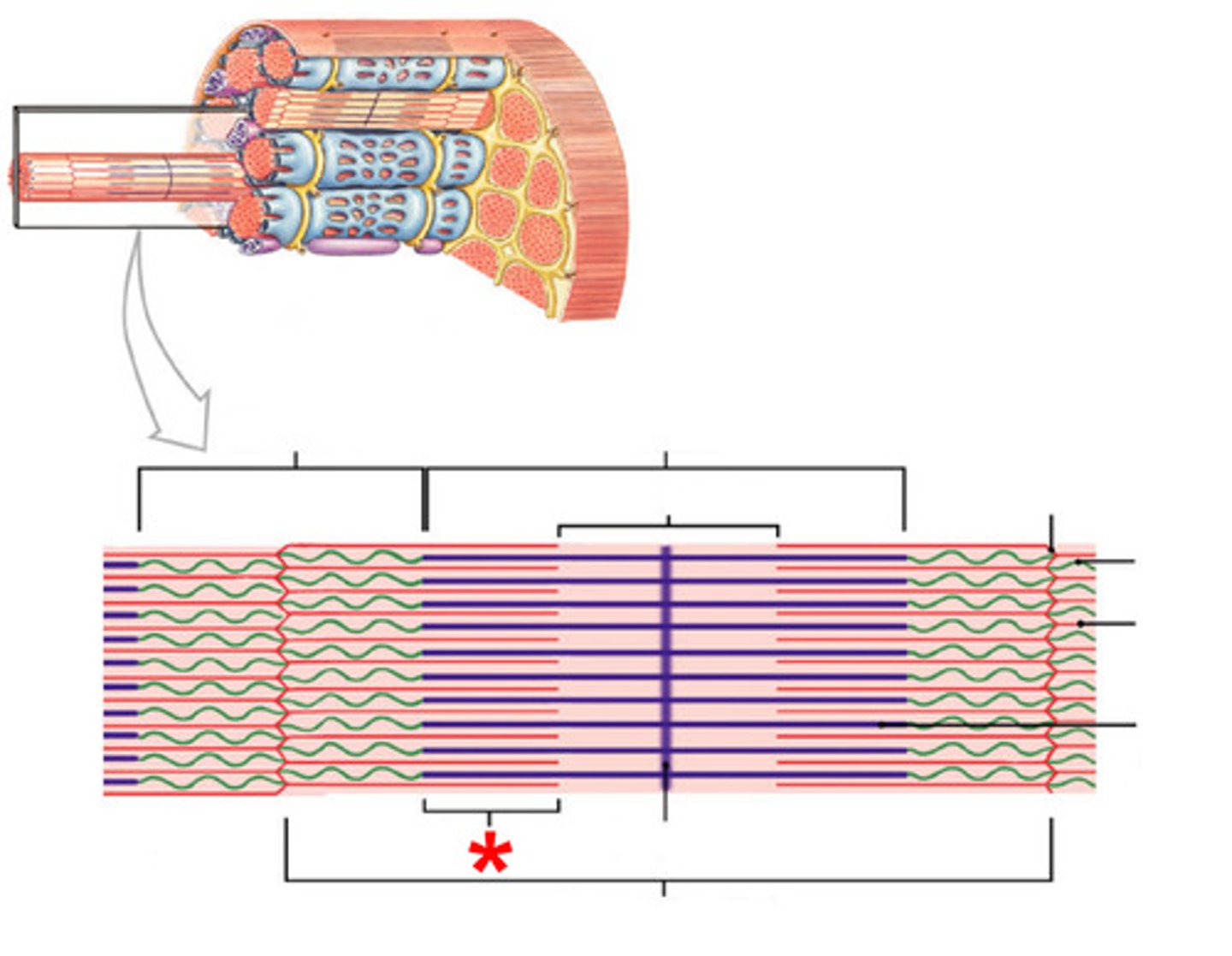
Structural organization of skeletal muscle (deep - superficial)
muscle fibers, fascicles, muscles, groups of muscles
Muscle fibers
individual muscle cells made of myofibril can span 100 micrometers in diameter covered by endomysium
fascicles
bundles of muscle fibers covered with perimysium
Muscles
bundles of fascicles covered by the epimysium
Muscle fibers cannot undergo ____ after birth
mitosis
Hypertrophy
increase in cell size
Hyperplasia
Increase in cell number
Satellite cells
undergo mitosis after birth for aid in muscle regeneration
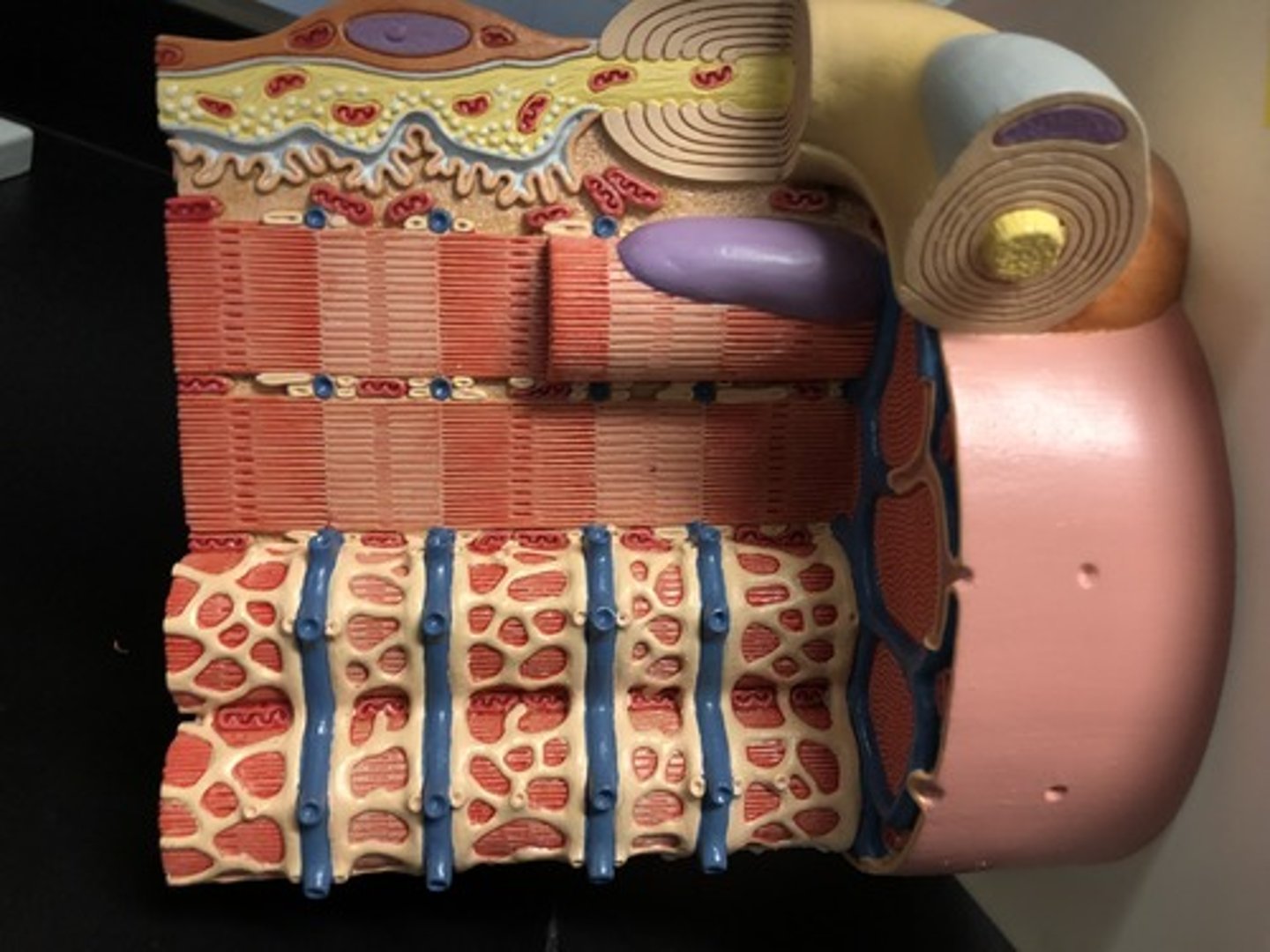
Functional units of organization
Conduction, Control, Contraction (CCC)
Conduction of electrical signals
Sarcolemma surrounds cytoplasm, T-tubules arise from sarcolemma
Control of muscle contraction
sarcoplasmic reticulum stores calcium, close proximity to t-tubules, surrounds myofibrils
Contraction
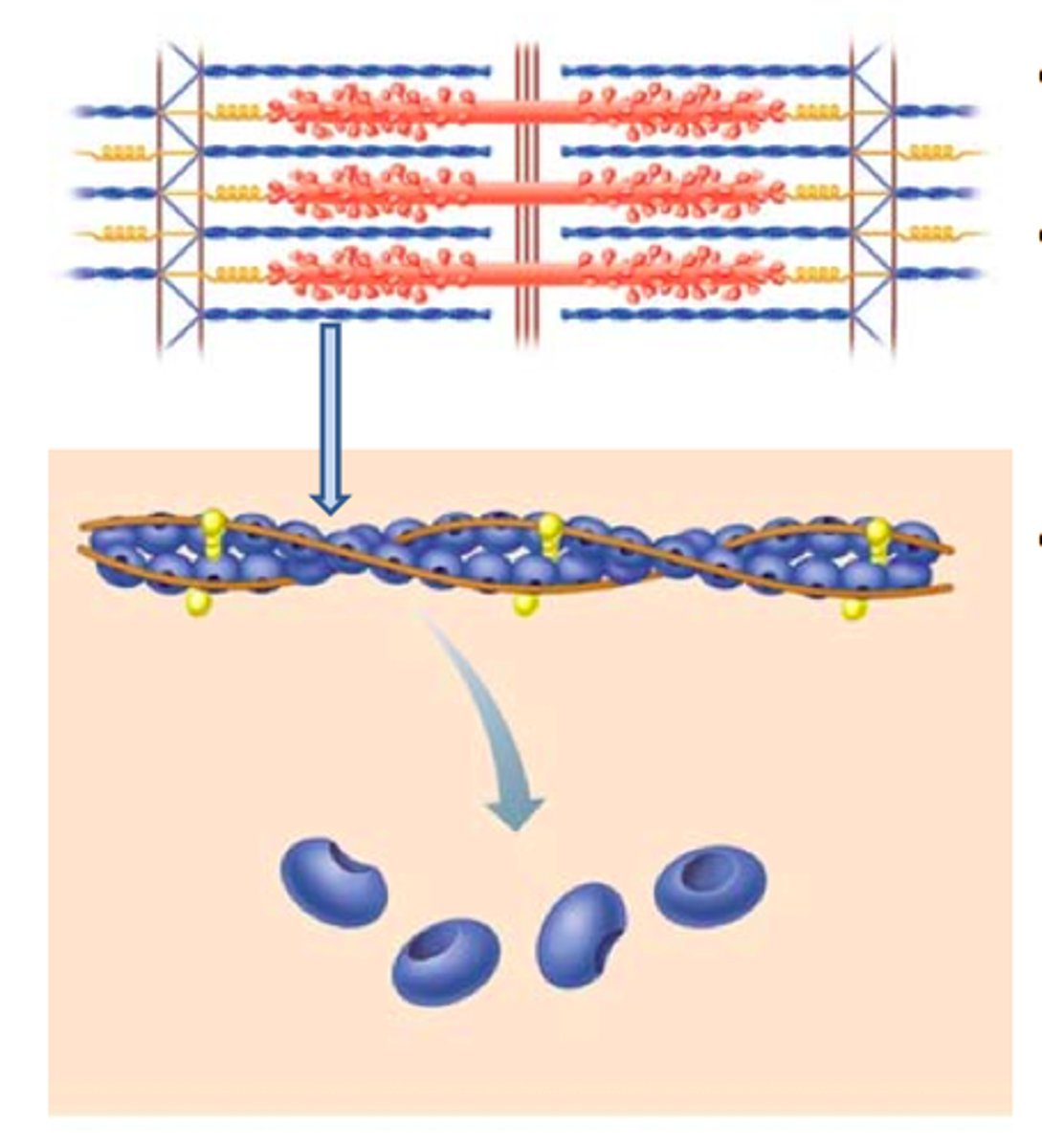
myofibrils, long bundles of protein filaments of actin and myosin organized into units called sarcomeres
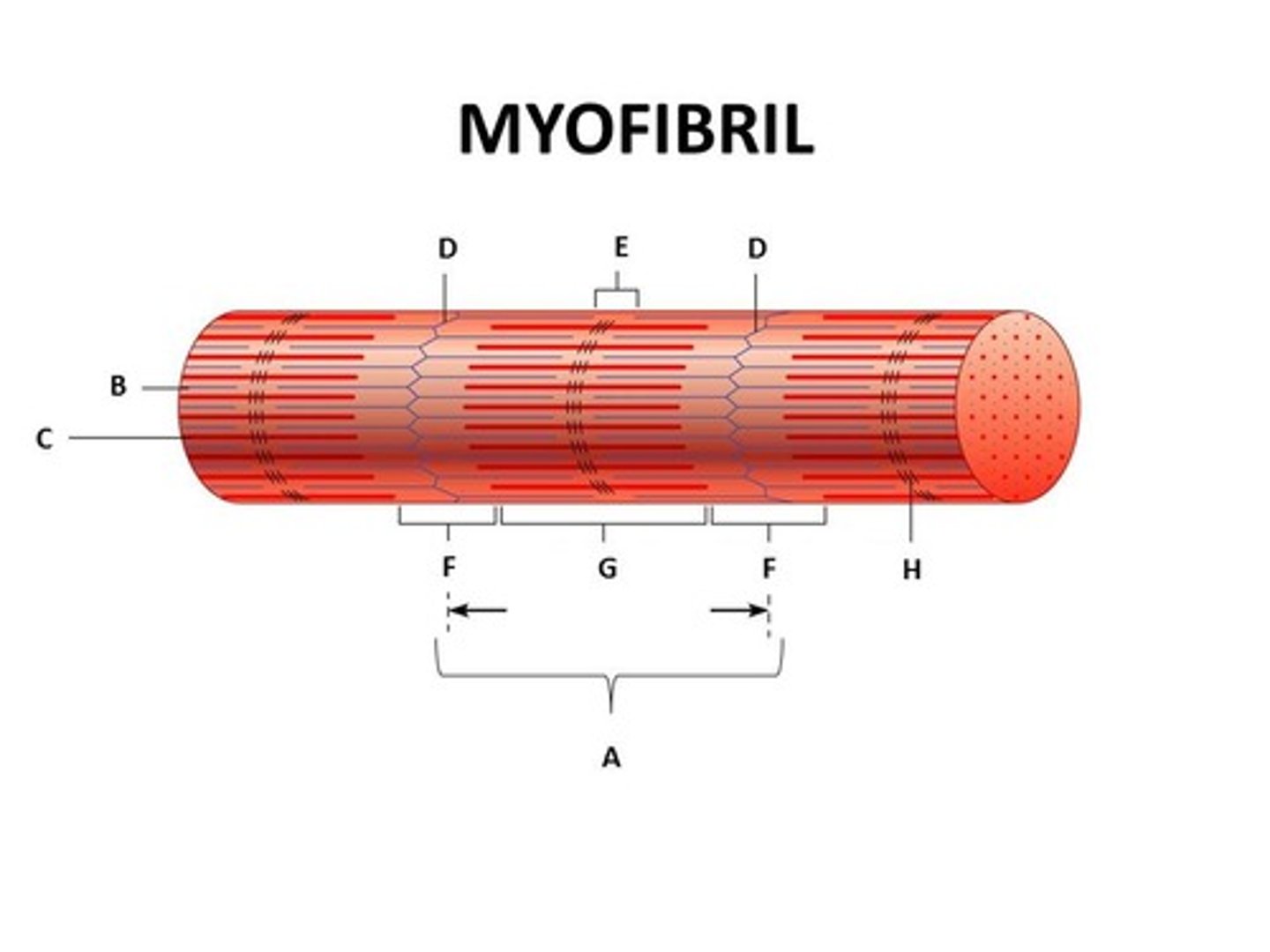
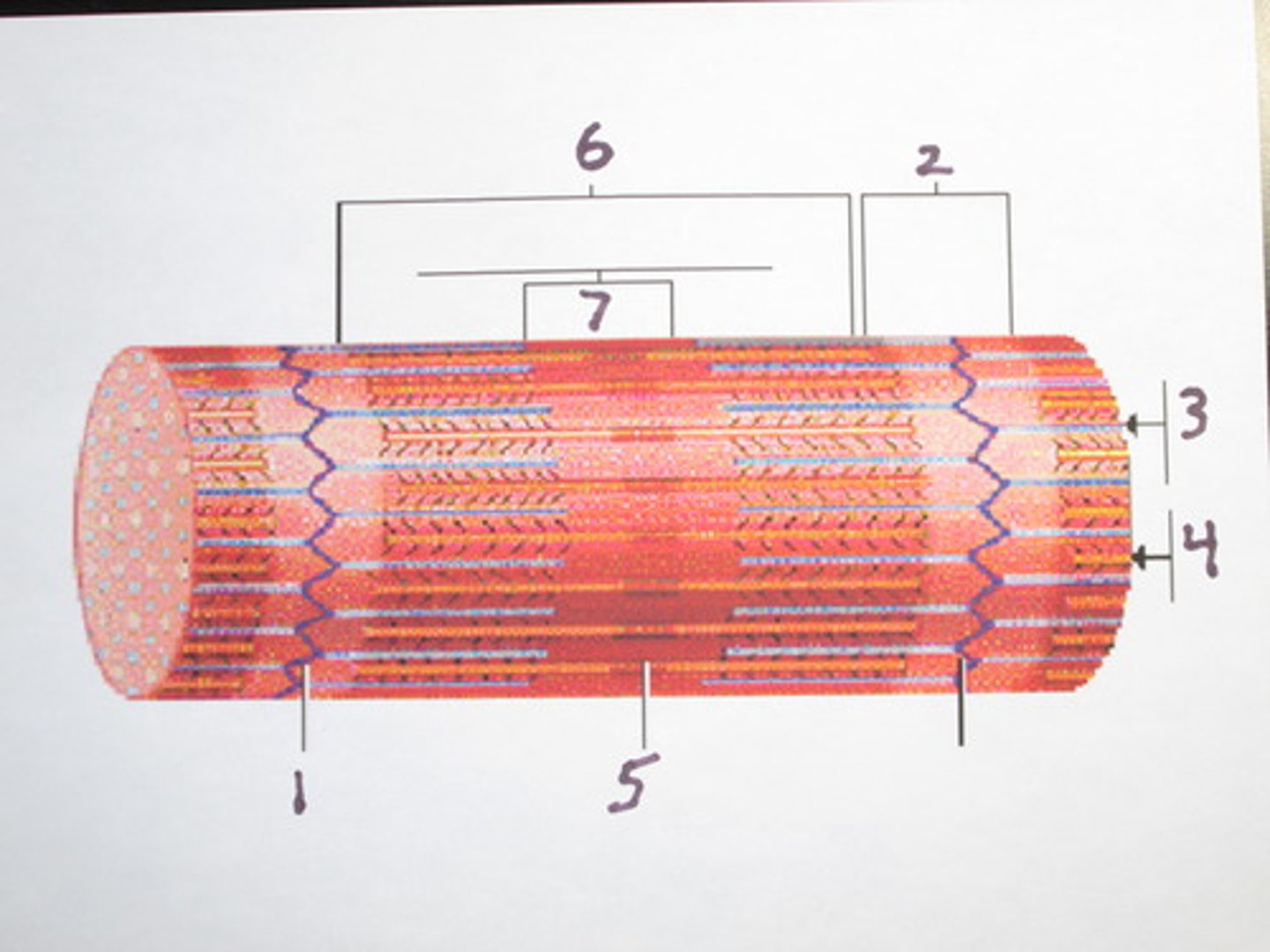
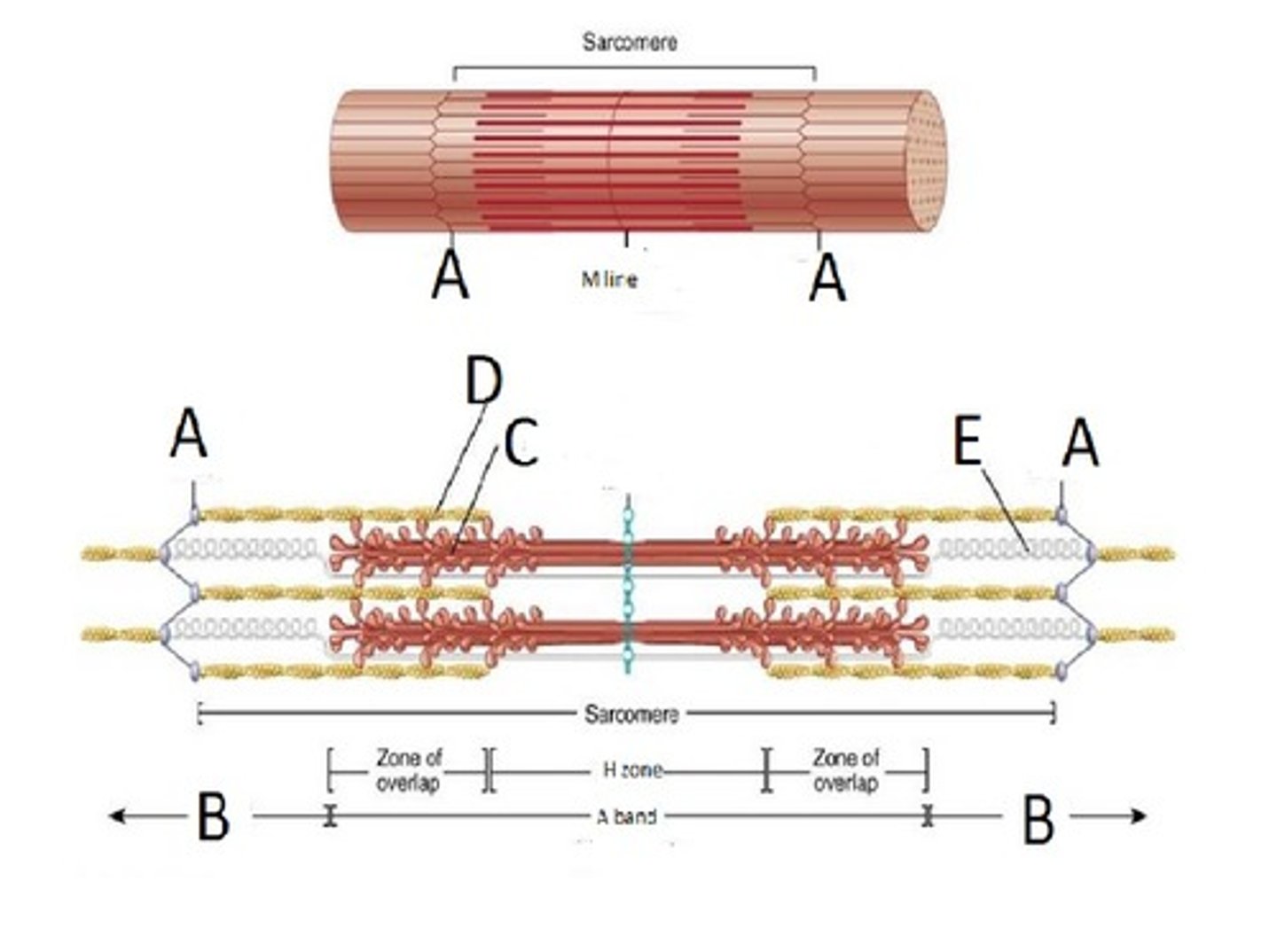
Sarcomere
functional unit of muscle contraction
D
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
(Organelle of the muscle fiber that stores calcium.)
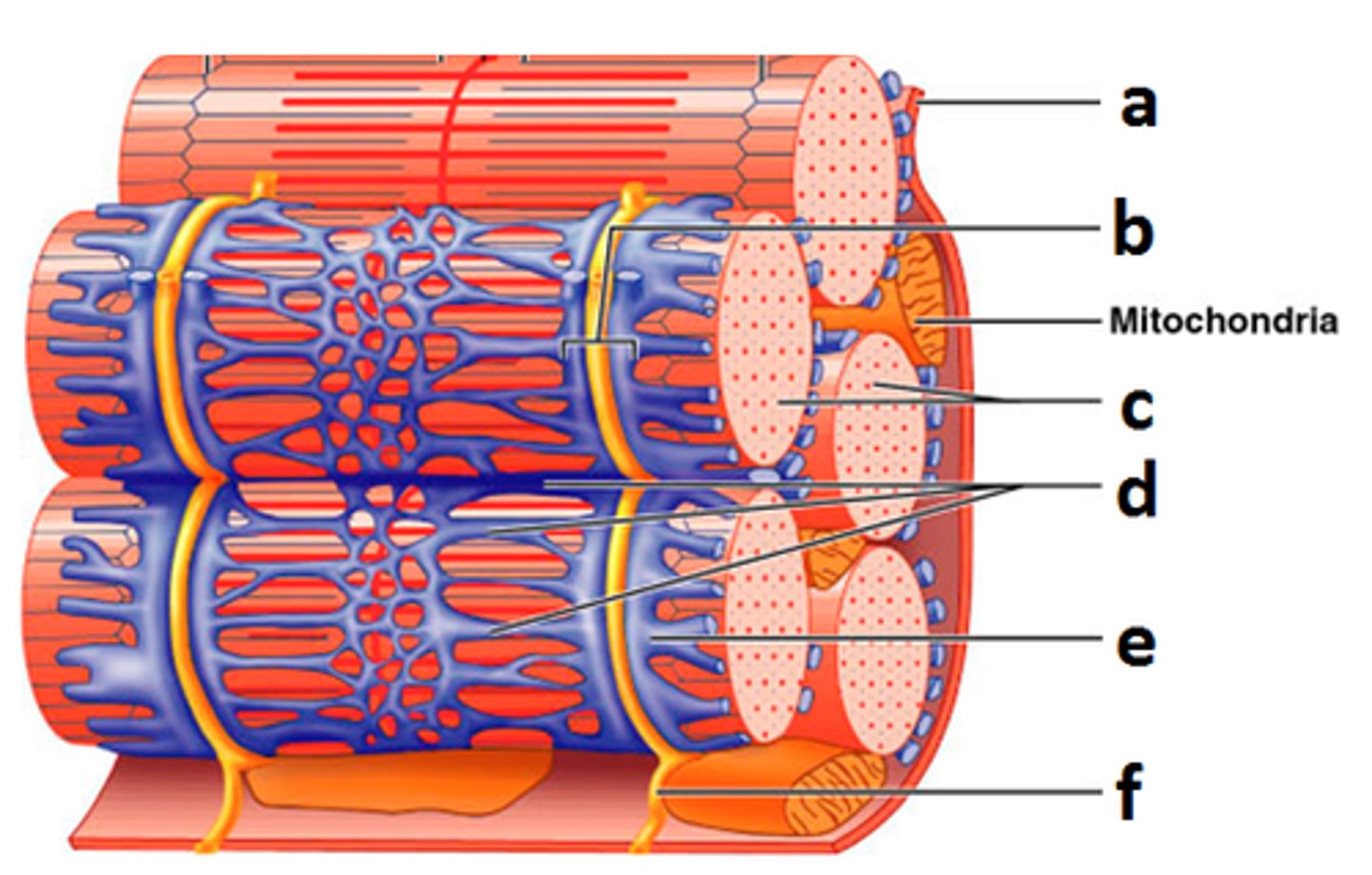
Triad
Contains T-Tubule and Terminal Cisternae
T
Mitochondrion
Myofibril
tightly packed filament bundles found within skeletal muscle fibers
Sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of a muscle cell
Sarcolemma
muscle cell membrane
Purple Blob
Nucleus (Control center of the cell)
Thick Filament
the thick myosin strands
Thin filament
thin strands of actin, troponin, and tropomyosin
Z-Disc
Separates the sarcomeres from each other Z line
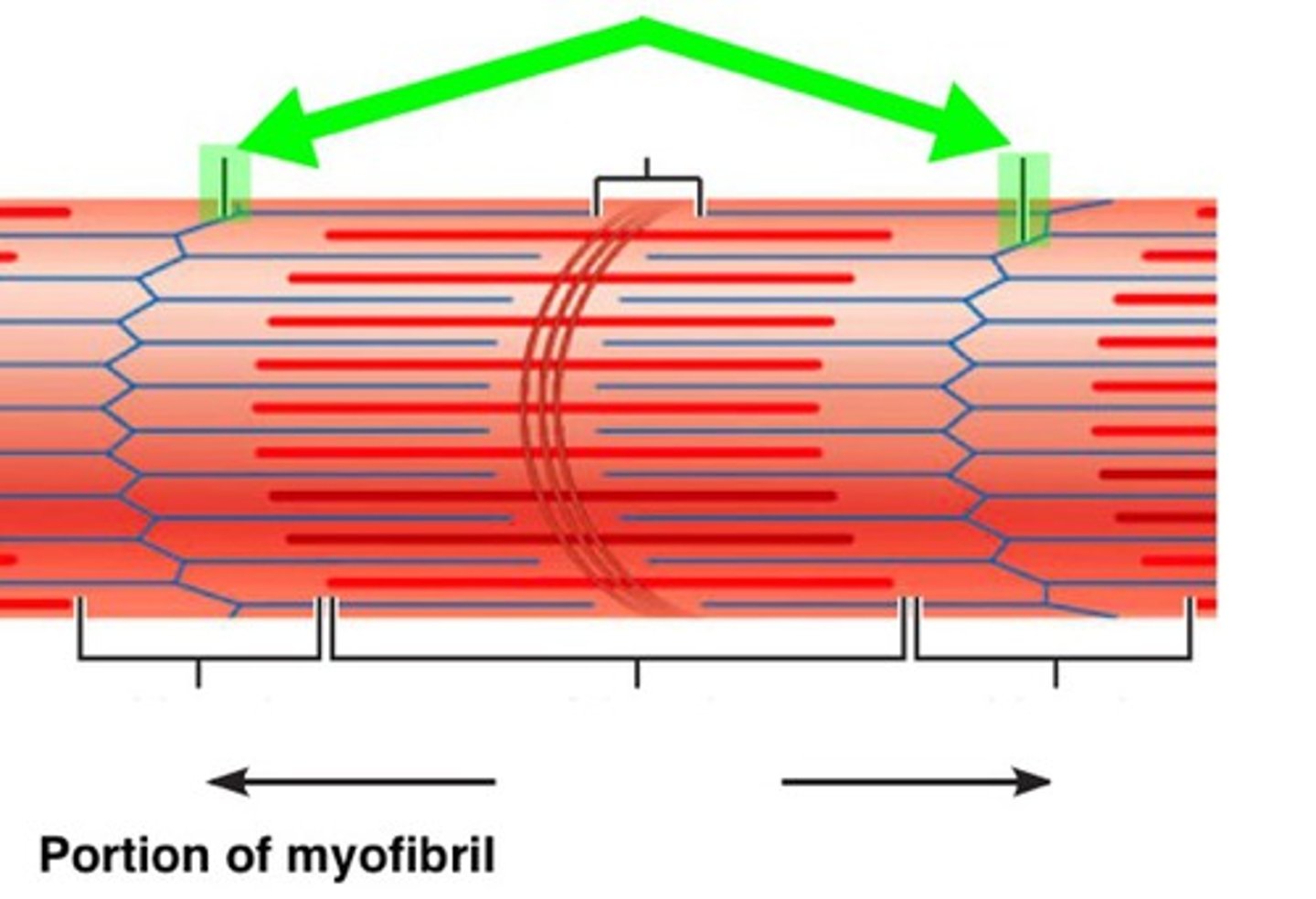
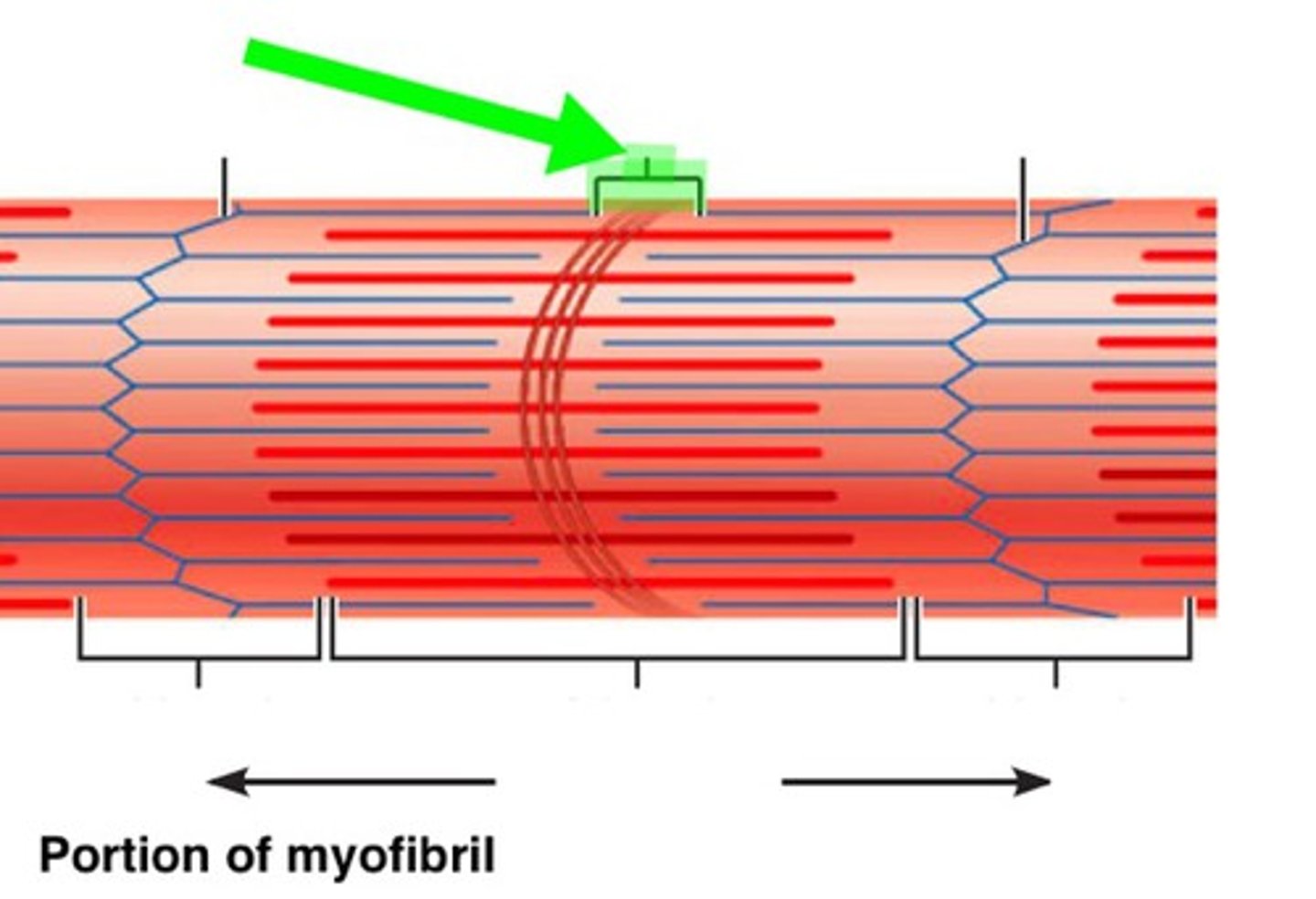
E
M-Line (middle)
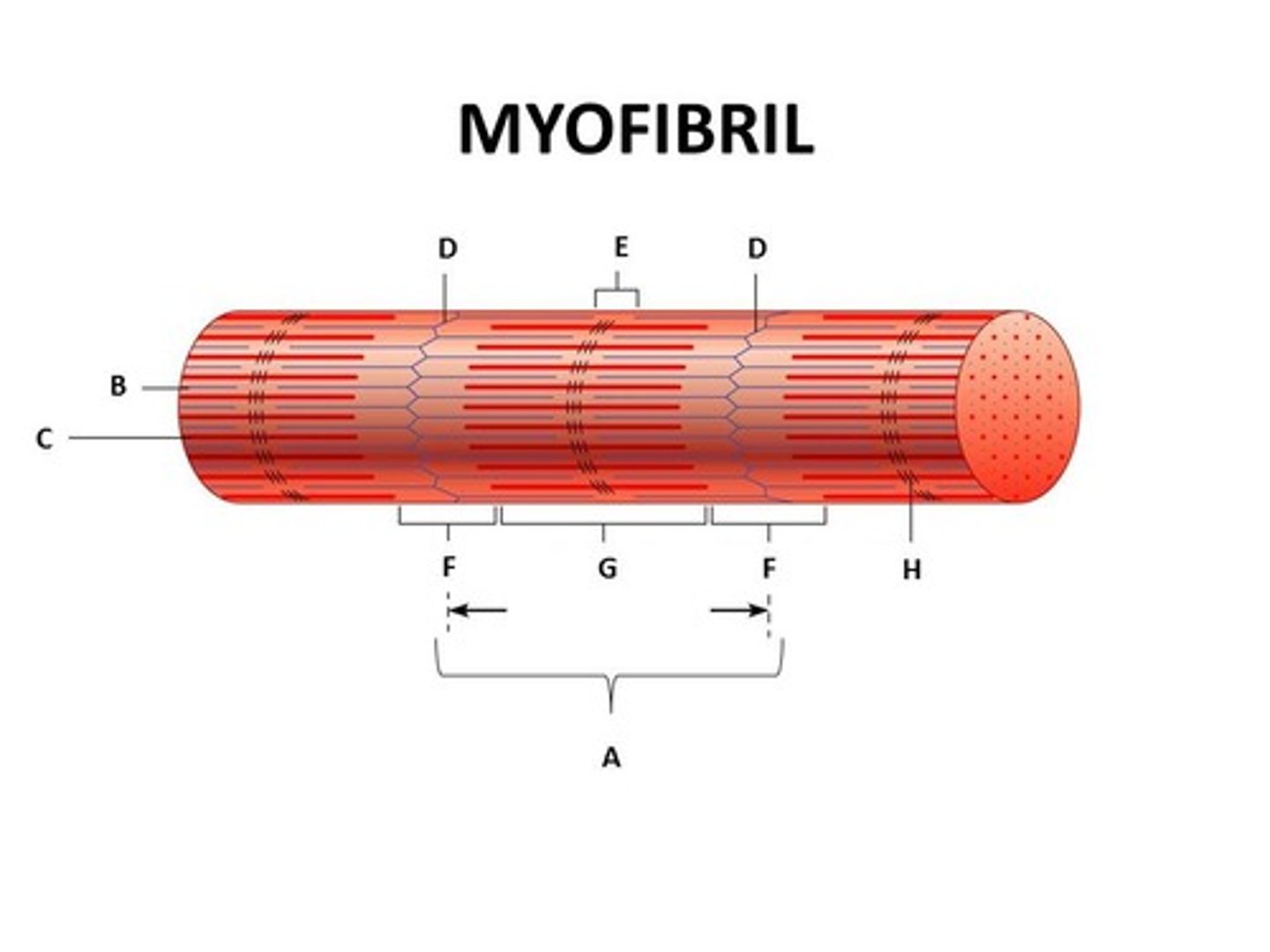
H-Zone
thick filaments only
Zone of Overlap
where thick and thin filaments overlap
G
(A BAND) dark area; extends length of the thick filaments
1
(I BAND) light area, contains only thin filaments
E
(Titin Filament) Stabilizes the thick protein, span from Z-M
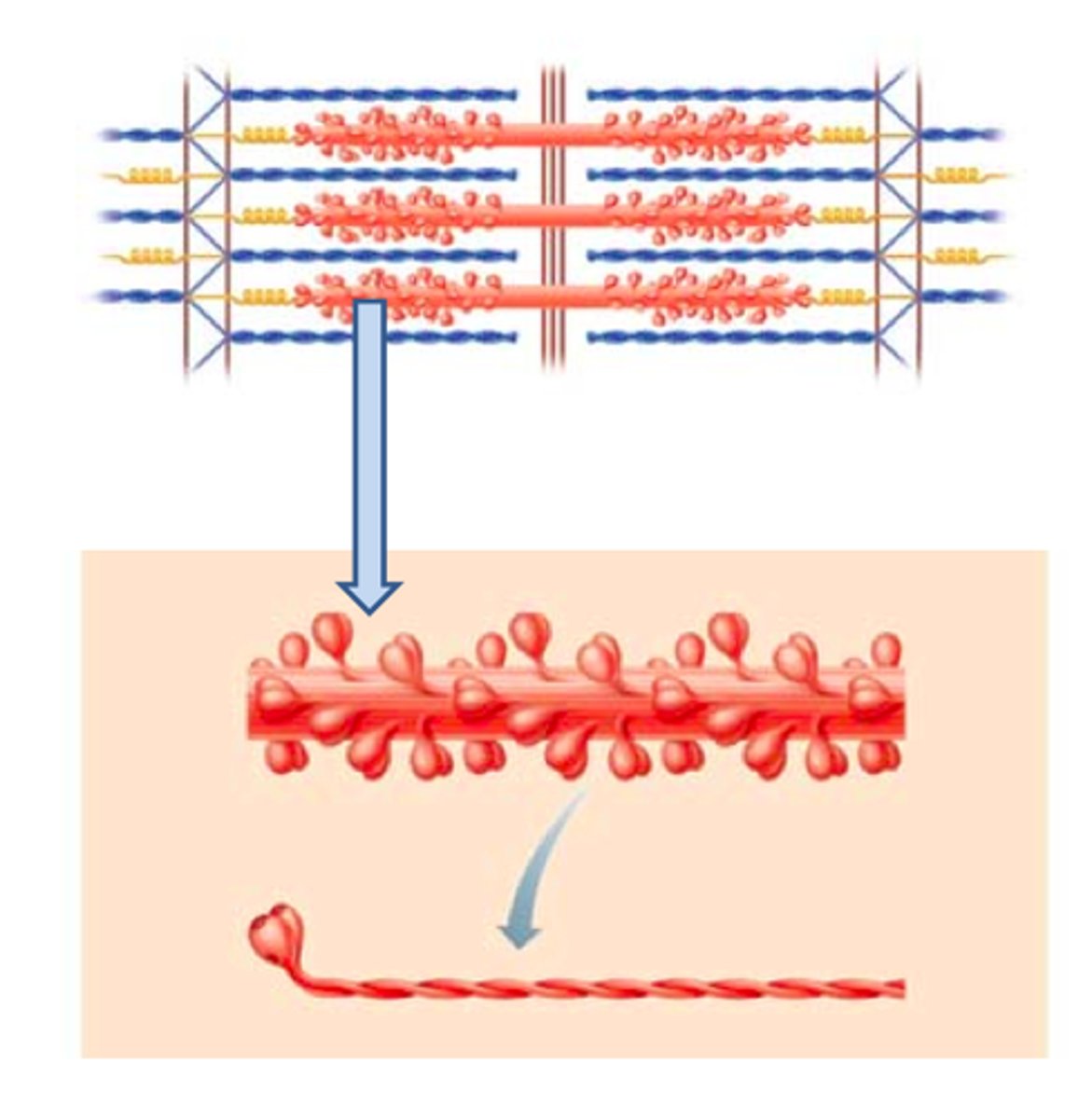
Crossbridge
Myosin heads bind to actin
Sliding Filament model of Muscle Contraction
1. Myosin 'heads' bind to actin to form a 'crossbridge'
2. Conformational change, energized by ATP hydrolysis, causes thin filaments to slide along thick filaments
3. Myosin head groups release, form new crossbridges, and the sliding cycle repeats...
As thick/thin overlap increases?
I band length decreases, A band length remains constant, H zone length decreases, Zone of overlap increases
Muscle Proteins
Contractile, Regulatory, Structural
Contractile proteins
Actin, Myosin
Regulatory Proteins
Troponin, Tropmyosin
Structural Proteins
Titin, dystrophin, myomesin, nebulin, alpha-actinin
Actin
Found in thin filament, has myosin binding sites for crossbridge formation
Myosin
found in thick filaments, has myosin head that binds to the myosin binding sites for crossbridge formation
Thin Filaments
composed of two strands of actin + regulatory proteins
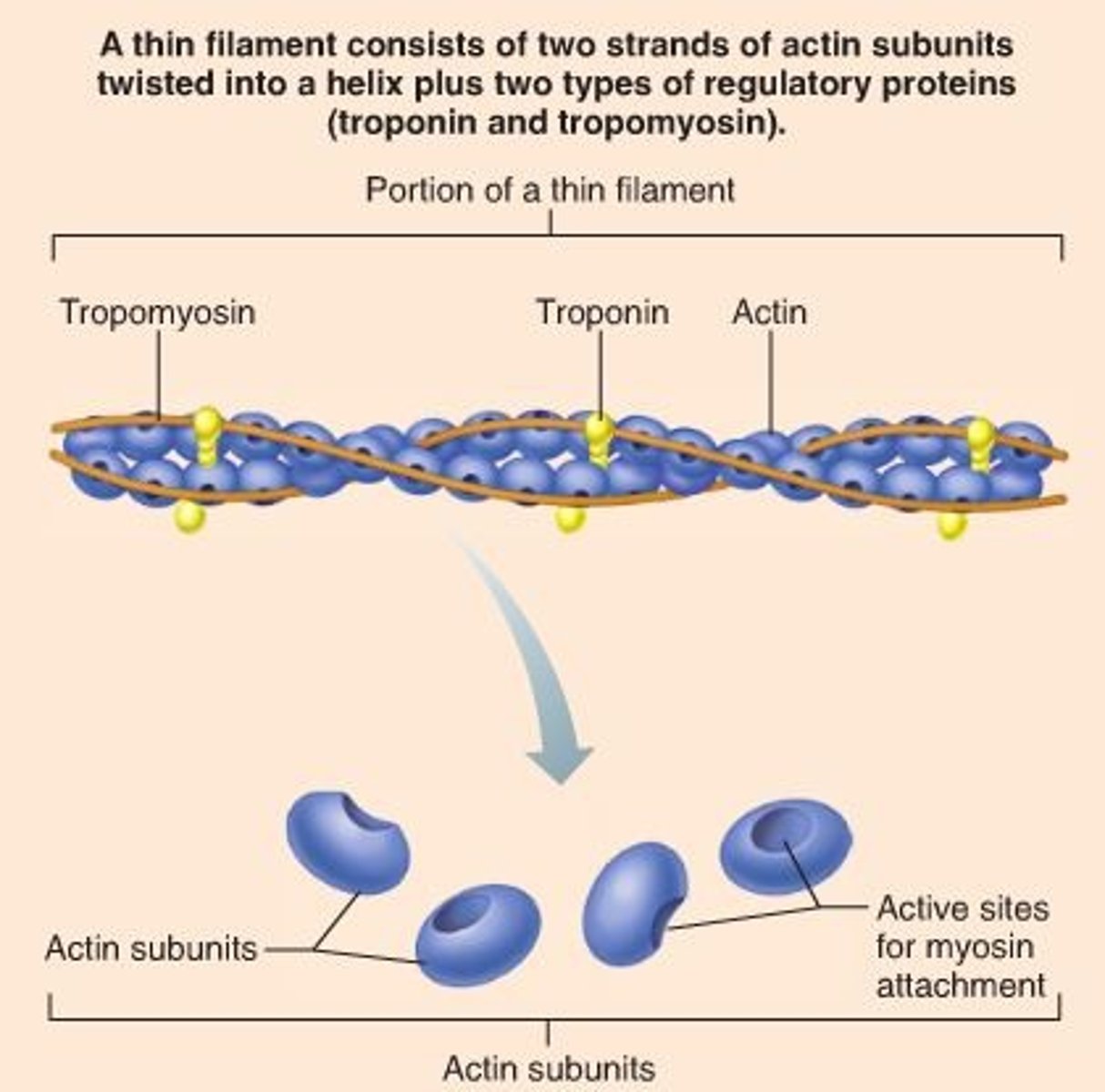
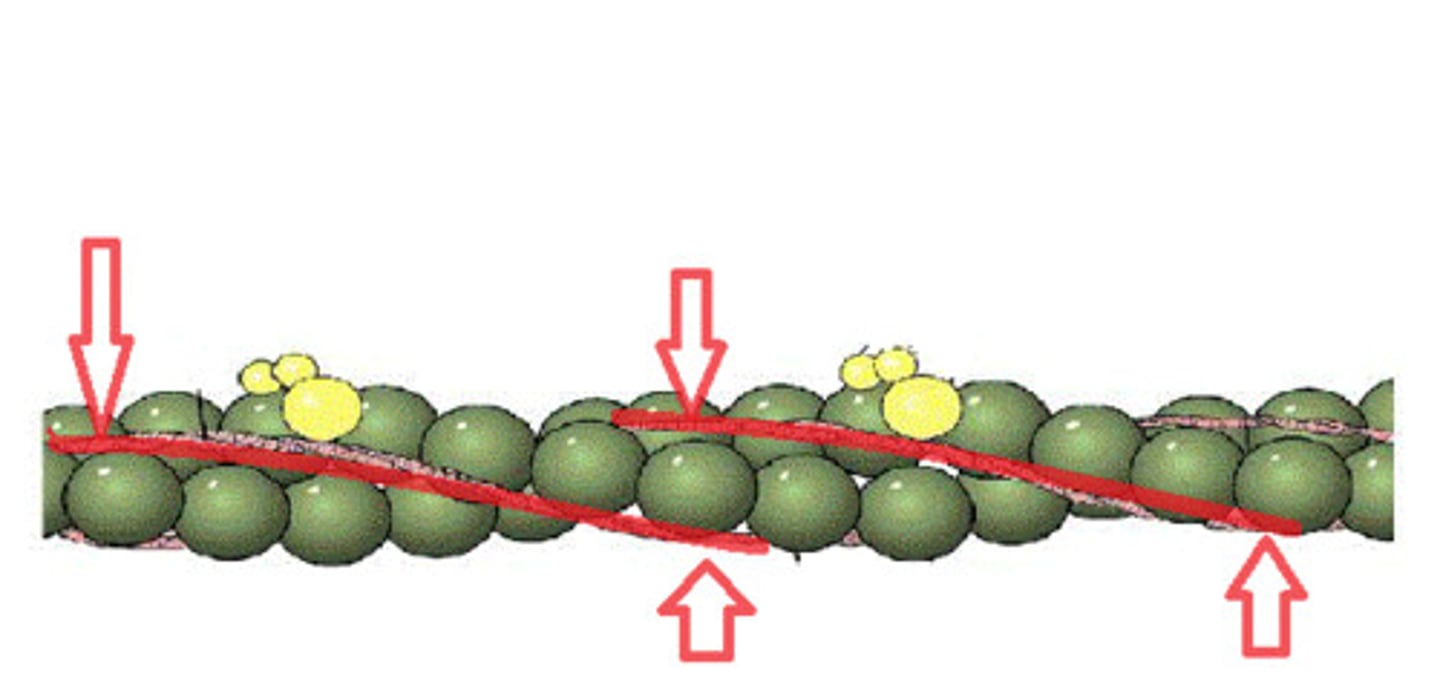
Tropomyosin
Found in thin filaments, covers the myosin binding sites when relaxed
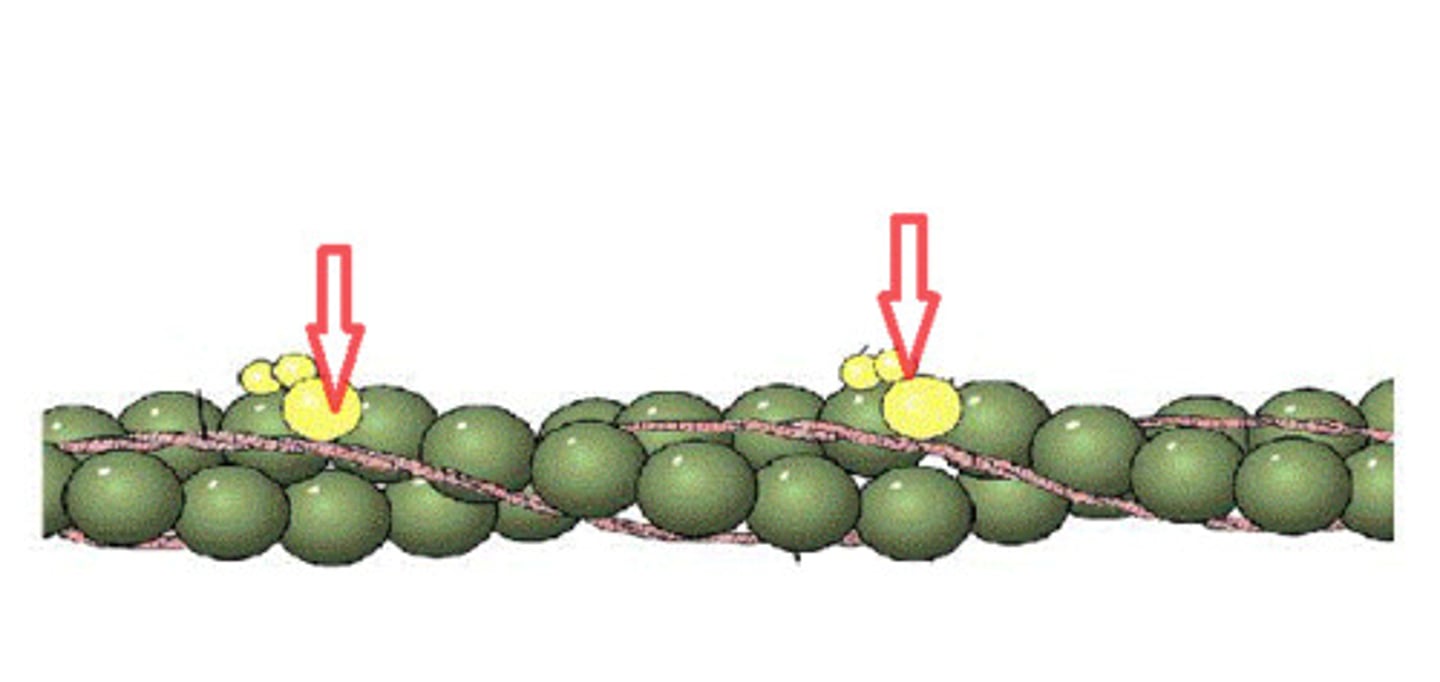
Troponin
found in thin filaments, holds tropomyosin in place when relaxed, calcium binds to troponin to shift tropomyosin away from binding sites to allow crossbridge formation
Thick filament
made of myosin, myosin head has ATPase activity when bound to actin, spans the distance between and overlaps thin filaments
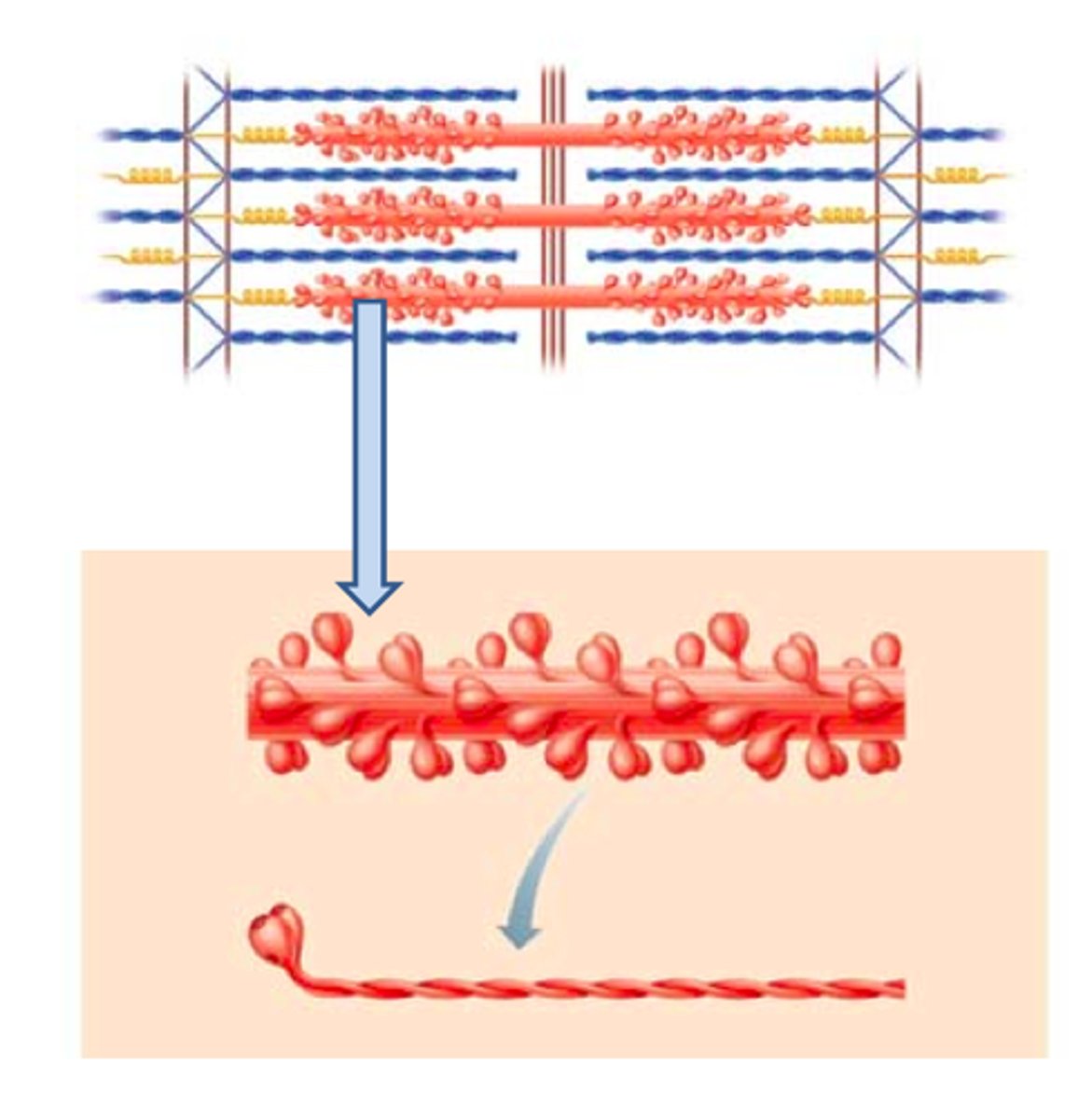
Titin
spans half of each sarcomere from Z disc to M line
stabilizes the position of the thick filament; gives muscle its elasticity and extensibility; and helps the sarcomere return to resting length after contraction
Dystrophin
Cytoskeletal protein that links the thin filament to the sarcolemma, helps transmit tension from sarcomeres to tendons
Nebulin
spans the length of thin filaments, anchors thin filament to z-disc
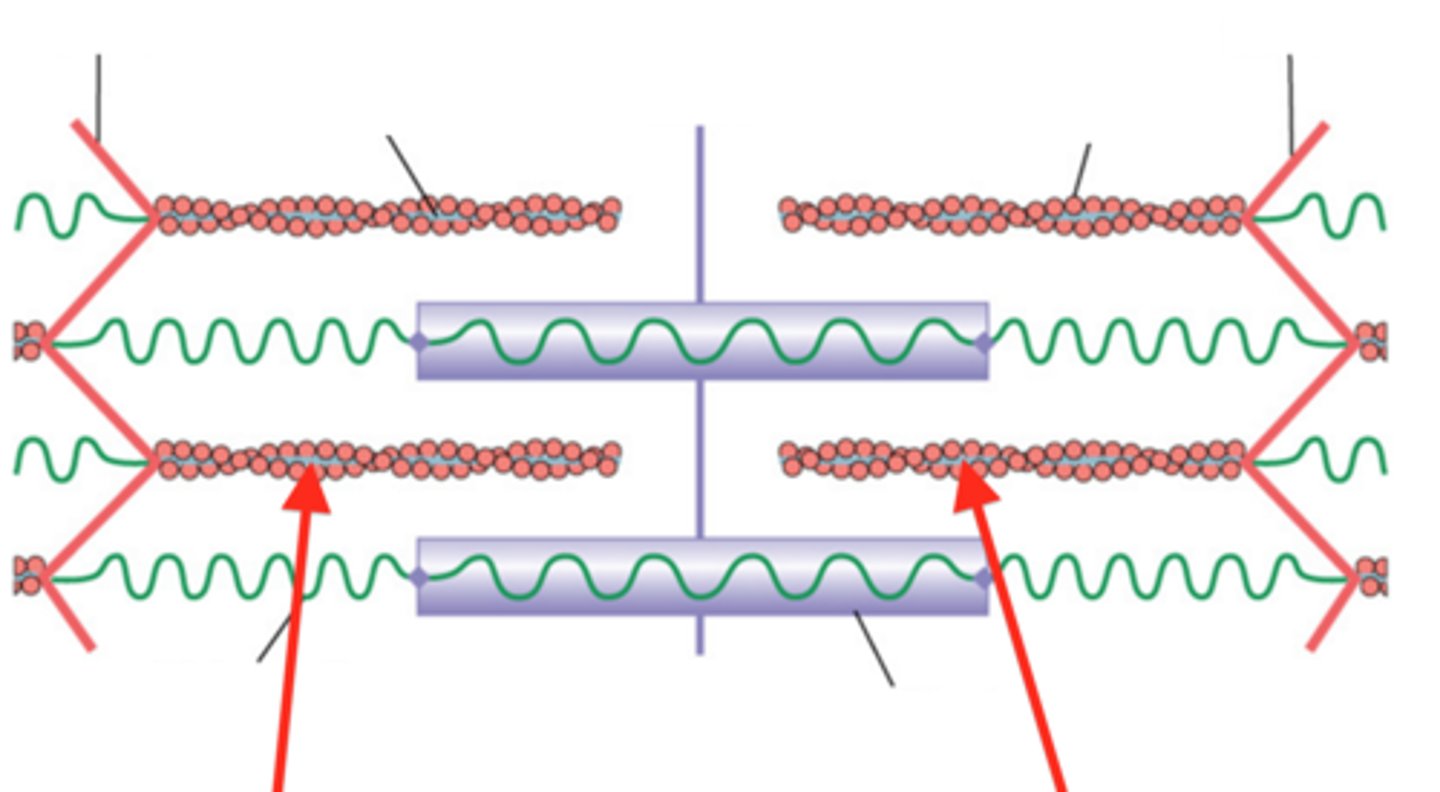
Alpha-actinin
- found in the Z disc
- binds to actin molecules of the thin filaments and to titin

Myomesin
-found in the M line
-binds to titin and thick filaments to connect them together at the M line

Crossbridge Cycling
begins when myosin binding sites on actin filaments become exposed (Ca 2+ serves as the signaling molecule)
How does the myosin head get ready before a muscle contraction starts?
ATP Binds to the myosin head, ATP changes to ADP and Pi, cocks back like a pistol ready to shoot
Contraction Cycle Step 1
Myosin binding sites on actin become exposed when Ca2+ binds to troponin
Contraction Cycle Step 2
Myosin heads bind to actin forming crossbridges
Contraction Cycle Step 3
myosin heads pivot toward the center of the sarcomere (power stroke)
Contraction Cycle Step 4
As myosin heads bind ATP, the cross bridges detach from actin
Contraction Cycle Step 5
cross-bridge detachment; ATP binds to myosin head; link to actin broken
Contraction Cycle Step 6
the contraction cycle repeats until the myosin binding sites on actin are no longer available
Rigor Complex
the attached head group after the power stroke
Rigor Mortis
the rigor of death that happens due to lack of ATP to detach the crossbridge
T or F: ATP is not needed to detach the crossbridge
FALSE, ATP is needed
Crossbridge Neural Control (SOE)
Excitation, Excitation-Contraction Coupling, Contraction, Relaxation
Excitation (SOE)
electrical signal transmitted from motor neuron to skeletal muscle fiber
Excitation-Contraction Coupling (SOE)
Ca2+ is released from sarcoplasmic reticulum
Contraction (SOE)
Ca2+ binds to troponin on the thin filament, forms crossbridges
Relaxation (SOE)
removal of CA2+
The Electrical Signal
CNS sends an electrical impulse to the Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ) to the muscle fibers
Neuromuscular transmission
transmitting an electrical impulse from the motor neuron to muscle fibers across the NMJ
Neuromuscular Junction
synapse where a motor neuron transmits a signal to a skeletal muscle fiber, causing it to contract
Motor End Plate
specialized region of sarcolemma with receptors that respond to neurotransmitters
Neuromuscular transmission at the NMJ step 1
Action potential arrives at the synaptic end bulb of a motor neuron and causes opening of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
Neuromuscular transmission at the NMJ step 2
Synaptic vesicles containing acetylcholine (ACh) undergo exocytosis
Neuromuscular transmission at the NMJ step 3
ACh is released into the synaptic cleft and binds to ACh receptors on the motor end plate
Neuromuscular transmission at the NMJ step 4
ACh receptors open and allow Na+ to enter the muscle fiber, generating an action potential on the sarcolemma
Neuromuscular transmission at the NMJ step 5
ACh is quickly broken down to acetate and choline by acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
Release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum step 1
Action potential runs along sarcolemma and continues into T-Tubules