Periodic Table - Chemistry
1/61
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Where are the group numbers located?
Vertical
Where are the period numbers located?
Horizontal
Where does the staircase start?
Group 13-16
What are properties of metals?
Luster (shiny), flexible as solids, conductor of heat and electricity, solid at room temperature, ductile, malleable
What are examples of metals?
Lithium, Barium
What are metalloids?
A mix of metals and non-metals, solids at room temperature, brittle, semi-conductor, acts more like nonmentals
What are examples of metalloids?
Carbon, Radon
What are nonmetals?
Colorful, brittle, hard or soft, poor/ non conductors, dull
What are examples of nonmetals?
Boron, Polonium
What are Alkali metals?
Very reactive, whole group has the same props, soft, slivery solids
Where are Alkali metals located?
Group 1, s-block
What are the valence electrons of Alkali metals?
1
What is the predicted charge of Alkali metals?
+1
What are Alkali Earth metals?
High melting/ boiling points, low density, not as reactive as Alkali metals, reactive with water, slivery-white apperance
Where are Alkali Earth metals located?
Group 2, s-block
What are the valence electrons of Alkali Earth metals?
2
What is the predicted charge of Alkali Earth metals?
+2
What are Halogens?
All states of matter: gas (g), liquid (l), solid (s), reactive, found in salts in nature, makes acid when bonded with hydrogen
Where are Halogens located?
Group 17, d-block
How many valance electrons are in Halogens?
7
What is the predicted charge in Halogens?
-1
What are Noble Gases?
Colorless, orderless, tasteless, inflammable gases, unreactivity
Where are Noble Gases located?
Group 18, p-block
How many valance electrons are in Noble Gases?
8
What is the predicted charge of Noble Gases?
None
What are transition metals?
Hard, dense, solids, good conductors, not as reactive as transition metals, colorful
Where are transition metals located?
d-block
How many valance electrons are in transition metals?
Varies
What is the predicted charge of transition metals?
Varies
What are inner transition metals?
Highly dense, radioactive
Where are inner transition metals located?
f-block
How many valance electrons are in inner transition metals?
N/A
What is the predicted charge of inner transition metals?
N/A
What does ductile mean? (Metals)
It means a material can be stretched into thin wires without breaking
What does malleable mean? (Metals)
It means a material can be hammered or tolled into thin sheets without breaking
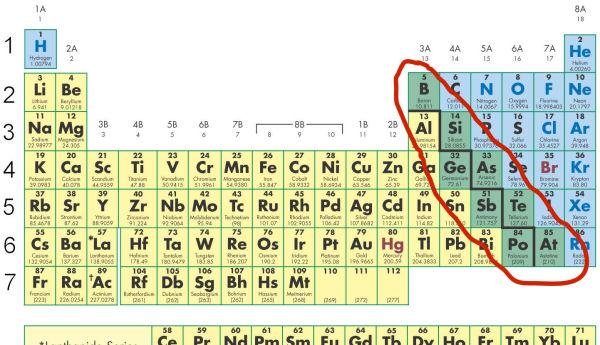
Where are metalloids located?
On the staircase
What is the atomic radius?
The distance from the center of an atom’s nucleus to the edge of its valence electrons. It shows how big an atom is
What is density?
How much mass something has compared to its volume. It tells you how tightly packed the matter is inside an object or substance
What is electronegativity?
The ability of an atom in a compound to attract a shared pair of electrons
What is the melting point?
The temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid
What is the period trend of the atomic radius?
Decreases
What is the group trend of an atomic radius?
Increases
What is the period trend of density?
None
What is the group trend of density?
Increases
What is the period trend of electronegativity?
Increases
What is the group trend of electronegativity?
Decreases
What is the period trend of ionization energy?
Increases
What is the group trend of ionization energy?
Decreases
What is the period trend of a melting point?
None
What is the group trend of a melting point?
Decrease
What is a period?
A horizontal row of elements that have the number of electron shells, and the number of protons increase as you go left to right
What is a group?
A vertical column where its elements have similar chemical properties because they have the number of valence electrons
What does periodic mean?
Properties repeat in a regular pattern when arranged by atomic number on the periodic table
What is an ion?
An atom that has gained or lost electrons, giving it a charge
Why is atomic radius’s period trend decreasing?
Increase nuclear charge that would increase the FOA (force of attraction) and pull the valence electrons closer, making the atom smaller
Why is atomic radius’s group trend increasing?
Additional electrons shells are filled that are higher in energy, and thus farther away from the nucleus, distance is changing
Why does the period trend increase in Ionization?
Increased charge increased by the number of protons + electrons which increases the FOA needed to move the electron
Why does the group trend decrease in Ionization?
The electron is getting further away due to the electron being further from the nucleus, which leads to a weaker shield around the valance electron, making it easier to move it. Decreasing the FOA needed to remove it
Why does the period trend increase from electronegativity?
Increases its nuclear charge due to an increase of protons and electrons, making it harder for them to attract a shared pair of electrons. The FOA pulls them closer together
Why does the group trend decrease for electronegativity?
Increased atomic radius and weakened electron shield around valence electrons due to the number of protons and electrons going up, decreasing the FOA needed to remove those valence electrons
Why are noble gases not considered for electronegativity?
They have full outer shells, leading to them being very stable
What is ionization?
The minimum energy required to remove an electron