Phonetics Exam 2
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
English has ____ consonant phonemes,
24
consonants are produced by…
vocal tract constrictions that involve the coming together of two articulators
vowels are less constricted
2 types of consonants
sonorant and obstruent
sonorant/resonant consonants
nasals, liquids, glides
Obstruent
stops, fricatives, affricates
**blocking air from flowing
T/F: Consonants cannot stand alone as an utterance, unlike some vowels
True
syllabic vowels and consonants
Vowels (+ a few consonants) that form the main part of a syllable
Prevocalic consonants
Consonants that occur before a vowel in a syllable
Postvocalic consonants
consonants following a vowel
consonats are classified by…
manner of production
place of articulation
voicing
Manner of production
refers to how the airstream is changed as the consonant is produced
Place of articulation
the place in the vocal tract where the constriction is located that produces a consonant.
Voicing
refers to whether the vocal folds vibrate when producing a consonant
Cognates
phonemes when they have the same manner and place and differ only in voicing
Ex) p/b, t/d, s/z, k/g, f/v —> goat/coat, ban/pan, ted/dead,
Vowels vs Consonants: Vowels
Produced with a relatively open vocal tract
Airstream is mostly unobstructed.
All vowels are voiced.
Different vowels are created by a change in tongue, lip, and tension occurring.
Classified by:
1. Tongue Height
2. Tongue Advancement (Frontness)
3. Tension
4. Roundedness
Sounds are acoustically most intense.
Functions as a syllable nucleus of the rime
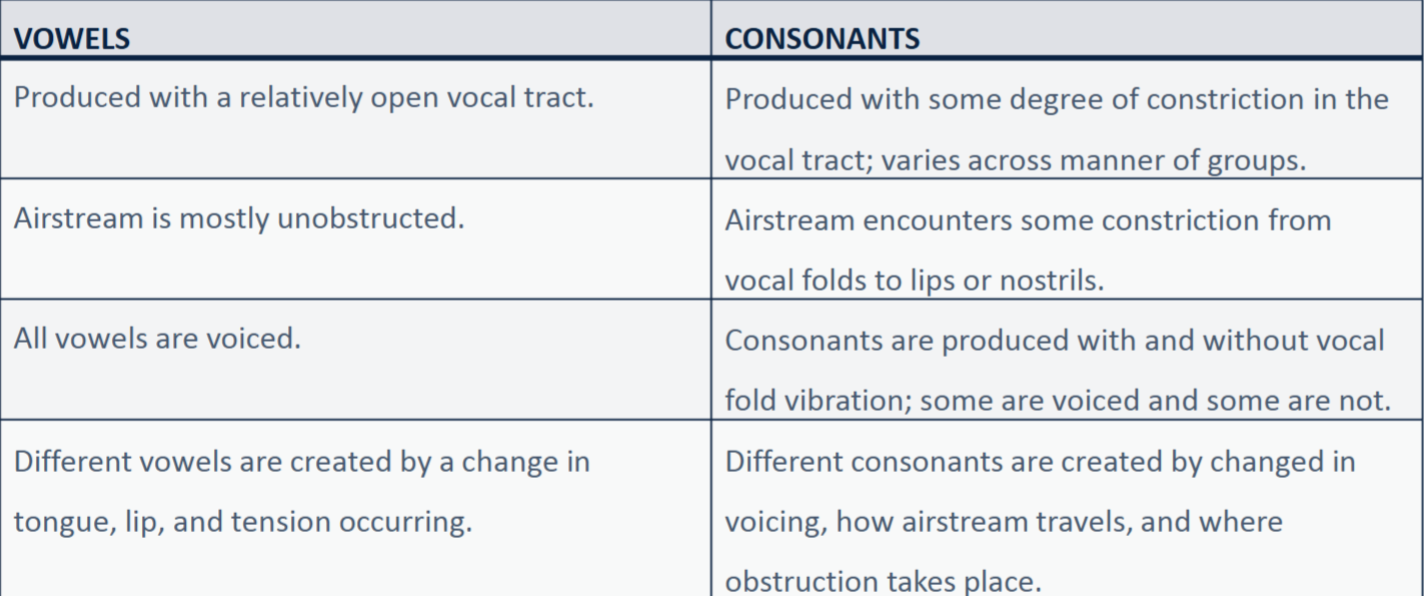
Vowels vs Consonants: Consonants
Produced with some degree of constriction in the vocal tract; varies across manner of groups.
Airstream encounters some constriction from vocal folds to lips or nostrils.
Consonants are produced with and without vocal fold vibration; some are voiced and some are not.
Different consonants are created by changed in voicing, how airstream travels, and where obstruction takes place
Classified by:
A. Voicing
B. Place
C. Manner
Sounds are acoustically less intense
Functions as a syllable onset, coda of the rime
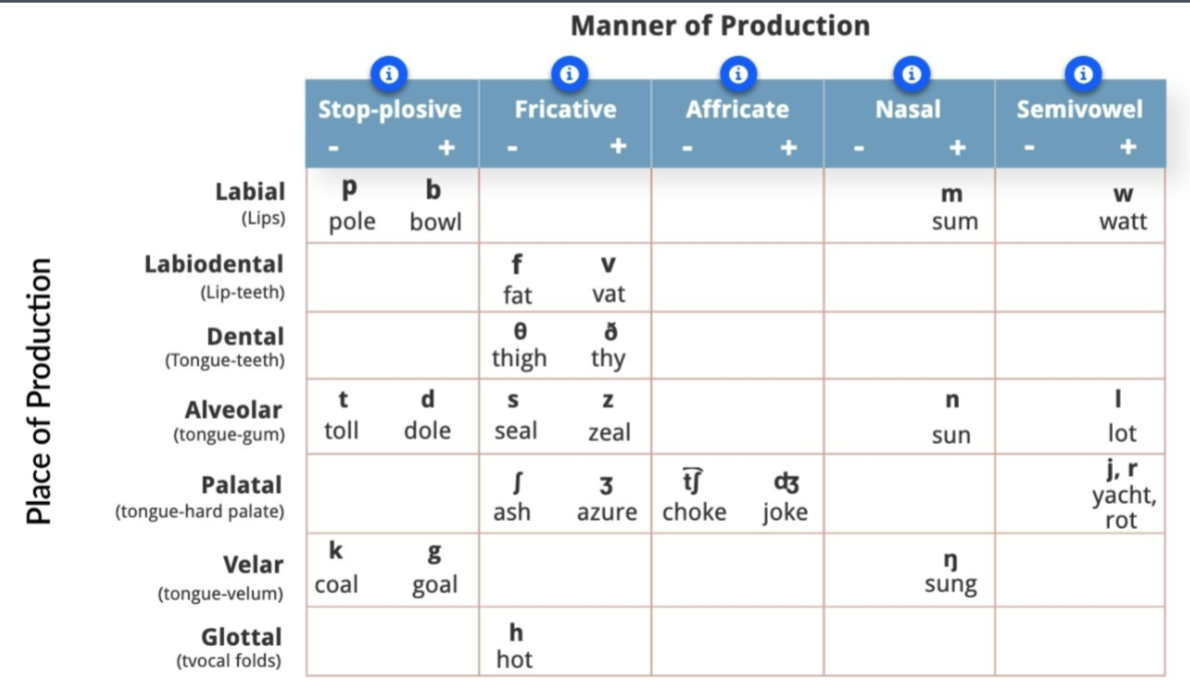
Place and Manner of Production Chart
Note: /r/ is Spanish trill, /ɹ/ is English “r” sound
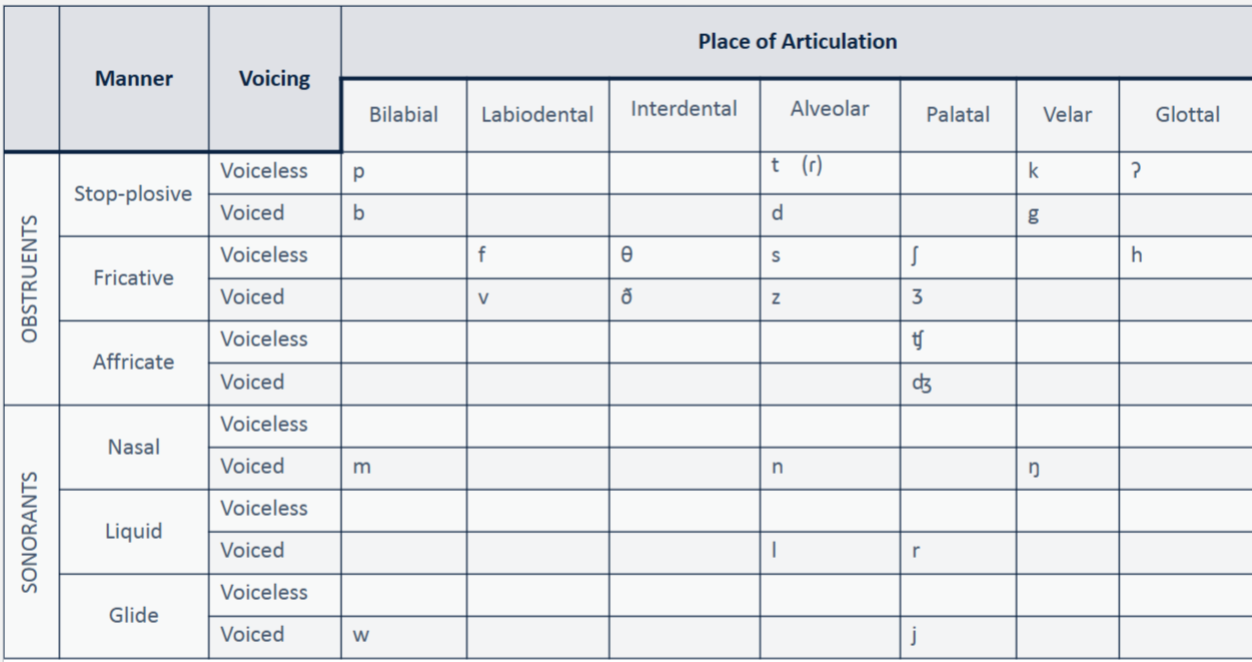
Class of Consonants
Stops/Plosives
produced by blocking the airstream behind the
point of constriction
air is then released, resulting in a burst of sound (consonant phoneme is produced)
Stops have the shortest duration of the English phonemes
voiced vs voiceless stops
Voiced stops
produced by the release of the constricted articulators
Voiceless Stops
produced by both vibrations in the vocal folds and the release of the constricted articulators
Resonance
depends on shape of vocal tract
listeners can tell difference in place of articulation of phonemes bc of the difference in this
Stop Consonants /p/ and /b/
cognates
Voiced bilabial stop: /b/
Voiceless bilabial stop: /p/
Stop Consonants: /t/ and /d/
cognates
Voiced alveolar stop: /d/
Voiceless alveolar stop: /t/
Stop Consonants: /k/ and /g/
cognates
Voiced velar stop: /g/
Voiceless velar stop: /k/
Nasal Consonants
/m/ /n/ /ŋ/
produced by lowering the velum to allow the airstream to emerge from the nasal cavity and blocking airstream from emerging from oral cavity
all are voiced
3 places of articulation (same as stops): bilabial, alveolar, or velar.
Nasal Consonants: /m/
voiced bilabial nasal
Nasal Consonants: /n/
voiced alveolar nasal
Nasal Consonants: /ŋ/
can NOT be syllabic
Voiced velar nasal: /ŋ/
Fricative Consonants
obstruents
produced by forcing the airstream through a narrow constriction of the articulators or vocal folds
can be voiced or voiceless (more intense)
Fricative Consonants: /f/ and /v/
Cognates
Voiceless labiodental fricative: /f/
Voiced labiodental fricative: /v/
Fricative Consonants: /θ/ and /ð/
interdentals
Voiceless dental fricative: /θ/
Voiced dental fricative: /ð/
Fricative Consonants: /s/ and /z/
cognates
Voiceless alveolar fricative: /s/
Voiced alveolar fricative: /z/
Fricative Consonants: /ʃ/ and /ʒ/
cognates
Voiceless palatal fricative: /ʃ/
Voiced palatal fricative: /ʒ/
Fricative Consonants: /h/
Voiceless glottal fricative: /h/
greatly influenced by the vowel that follows
Affricate Consonants
a combination of a stop and fricative
the consonants consist of a plosive portion and a fricative portion during production
Affricate Consonants: /tʃ/ and /dʒ/
cognates
Voiceless palatal affricate: /tʃ/
Voiced palatal affricate: /dʒ/
Approximate Consonants (Semi Vowels)
a group of phonemes where the articulators only approximate a certain position within the oral cavity to produce the consonant
VP port closed
can be syllabic
Glides and Liquids
Palatal Approximate Consonants
/j/ and /ɹ/
NOT COGNATES
palatals because of the tongue's movement toward the palate
/j/ is a glide
/ɹ/ is a liquid
Glides
/w/ and /j/
Liquids
/ɹ/ and /l/
Vocalic
/r/ can differ based on its placement within the word.
A vocalic /r/ is classified by the vowel sound it follows.
Prevocalic
Prevocalic /r/: the sound at the beginning of the word such as rake, ram, rice, race.
Labiovelar
the involvement of the lips and velum in its production
/w/ is a glide labiovelar
Alveolar
the tongues movement toward the alveolar ridge during articulation
/l/ is a liquid alveolar