Funktionella grupper: struktur och namn
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
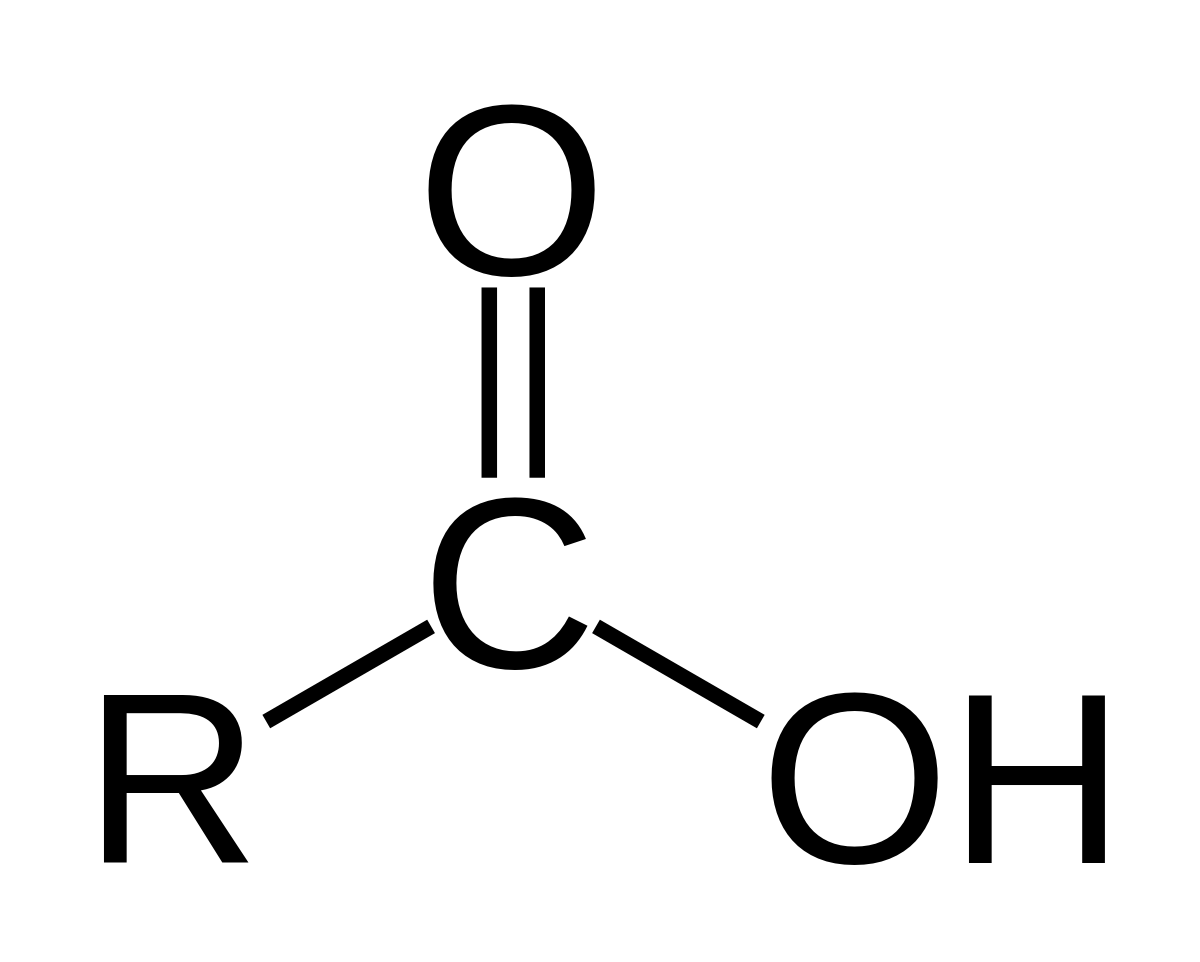
very polar but weak acid
Carboxylic acid/Karboxyl syra
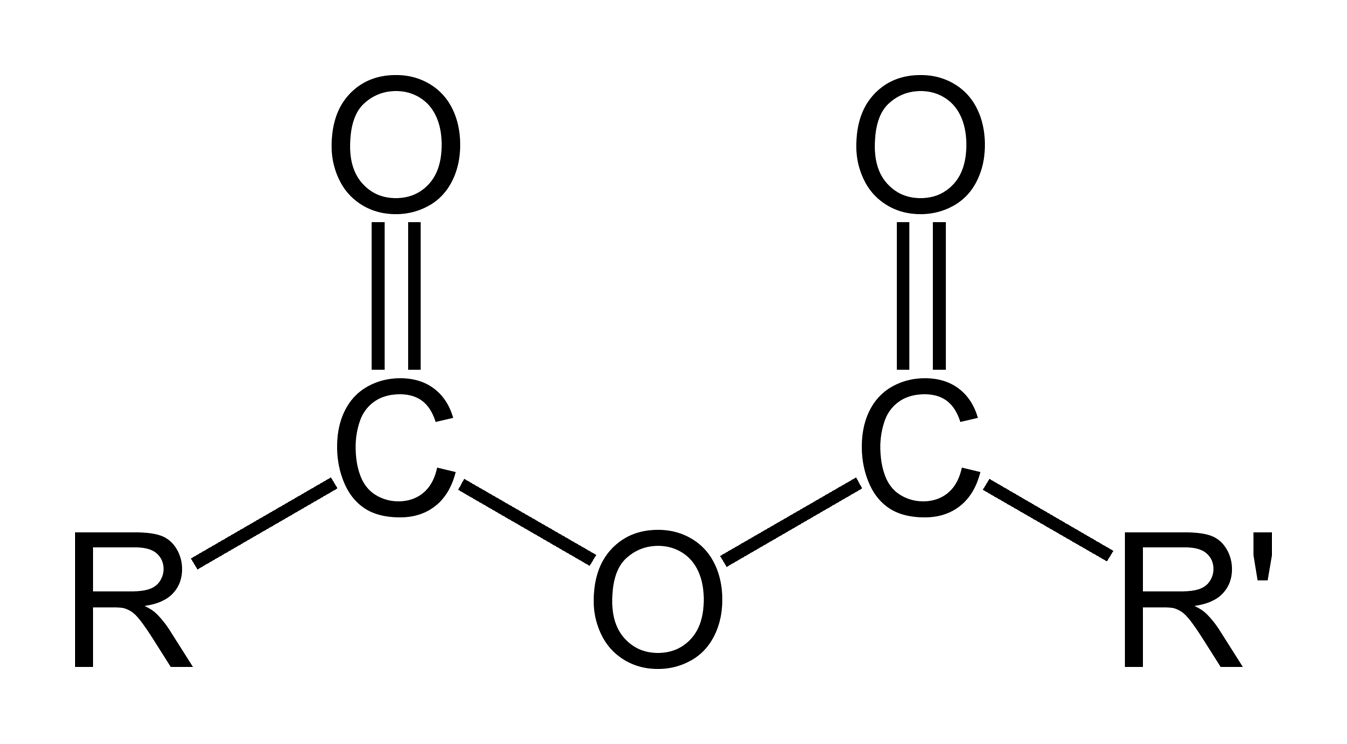
compounds formed by removing water from acids
Acid anhydride/Syraanhydrid
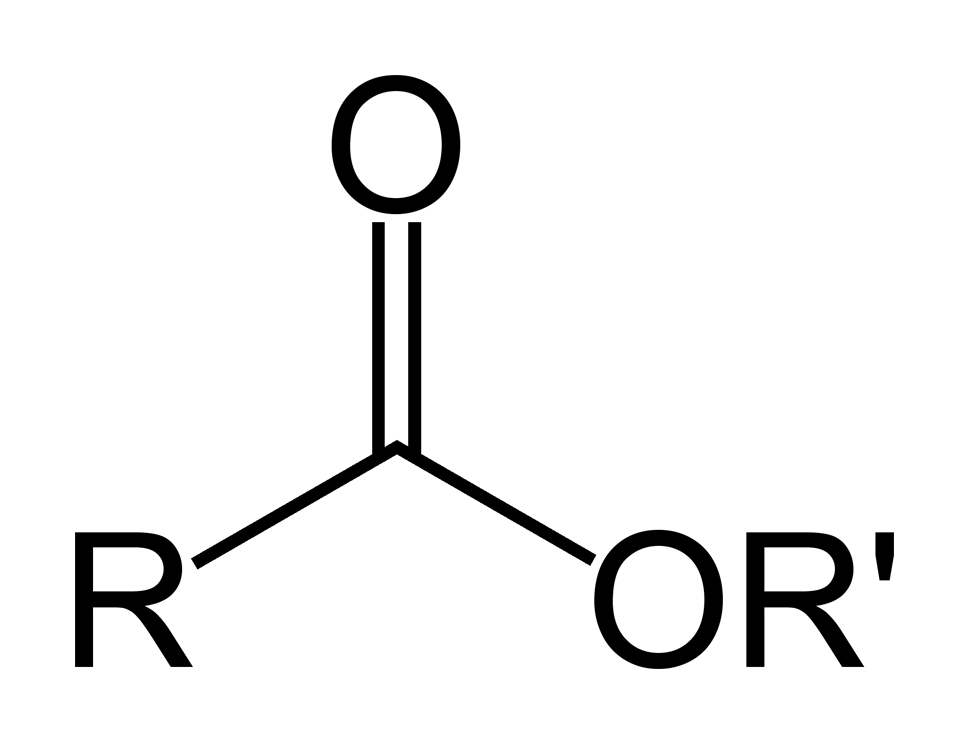
derived from carboxylic acids, OH-group is replaced with OR’-group
Ester
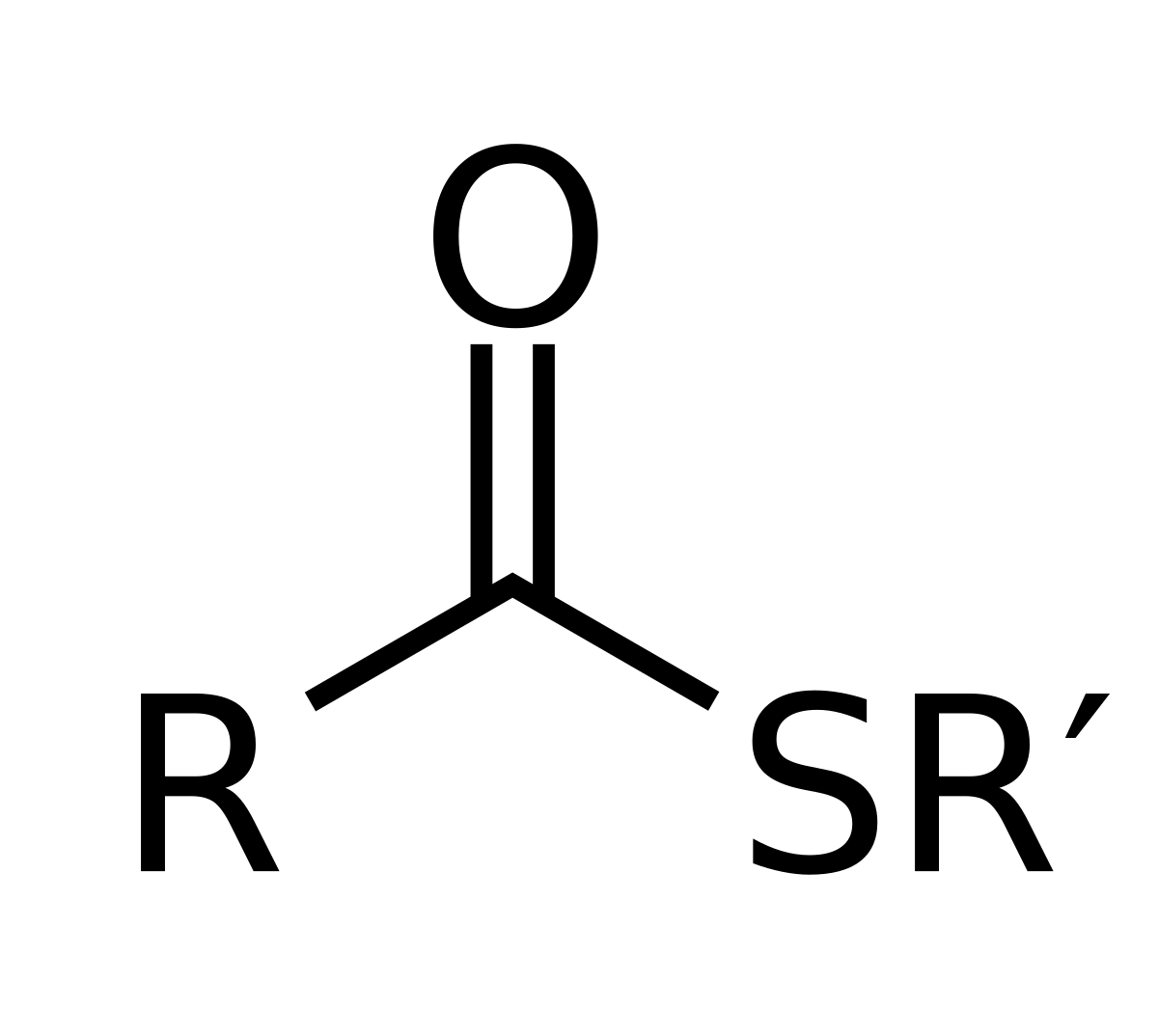
Created by reacting a carboxylic acid with a thiol, active acyl group carrier
Thioester/sulfurester
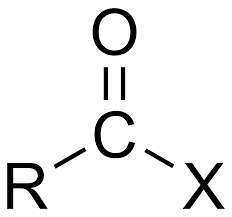
OH-group is replaced by a halide
Acid halides/Acyl halides/ Syra eller acylhalider
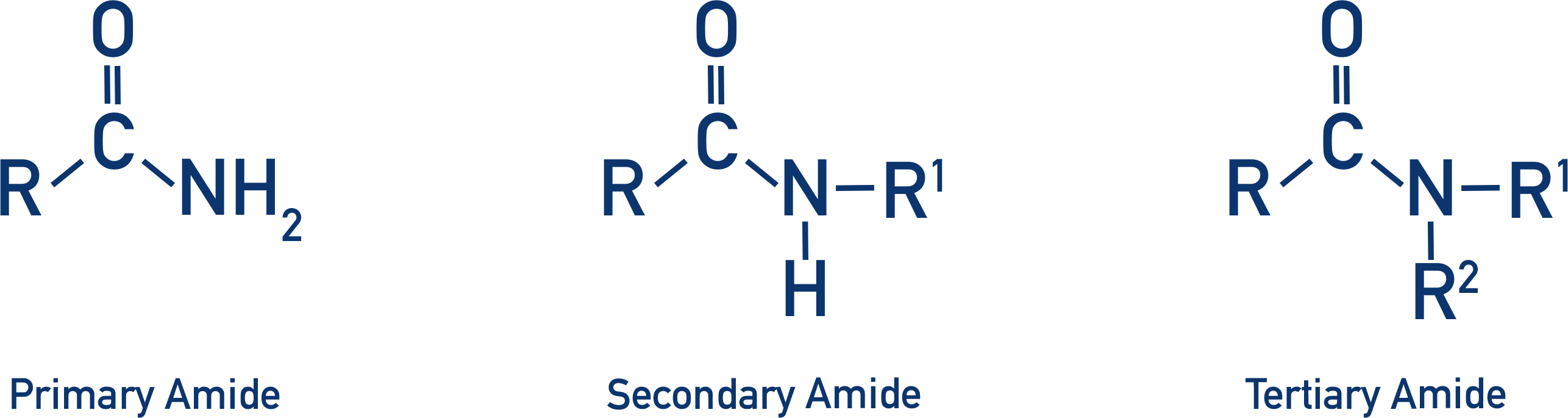
an acyl group (R–C=O) linked to a nitrogen atom
Amides/Amider
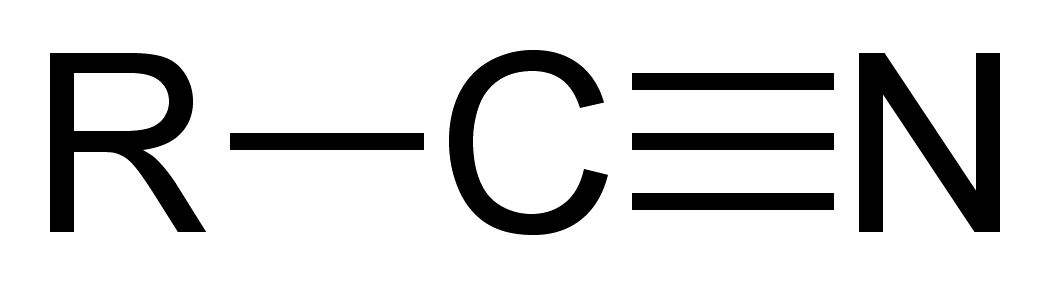
a cyano group = carbon atom triple-bonded to a nitrogen atom
Nitriles/Nitriler
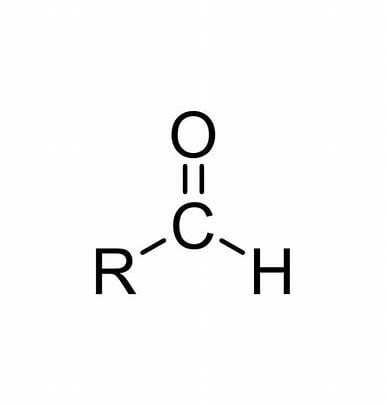
Carbonyl/Acyl group with a single bonded H
Aldehydes/Aldehyder
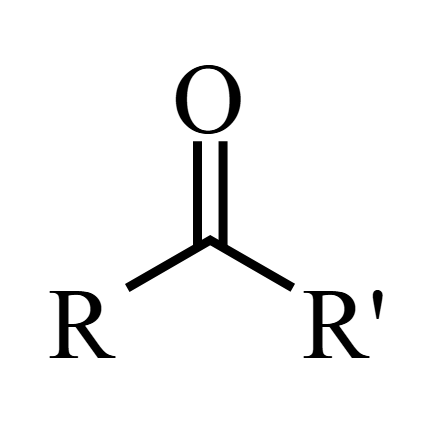
polar and reactive
Ketones/Ketoner
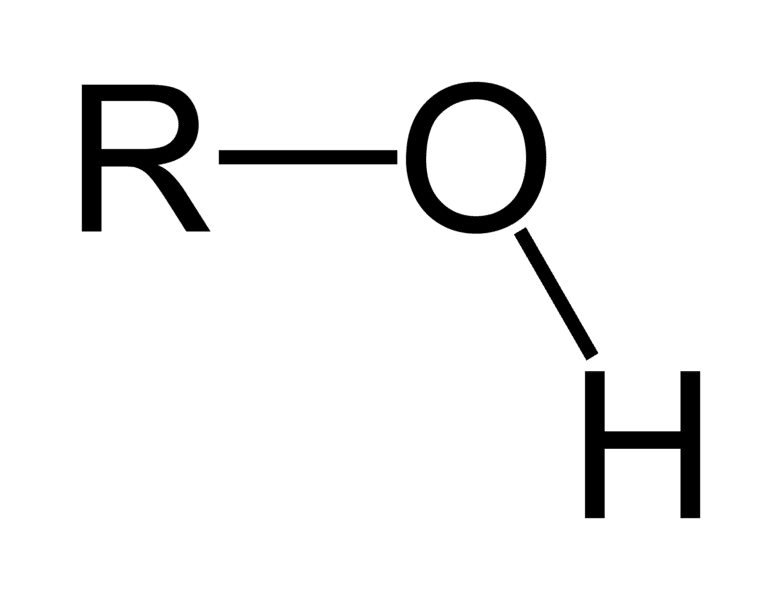
Has a OH-group (hydroxyl group)
Alcohol/Alkohol
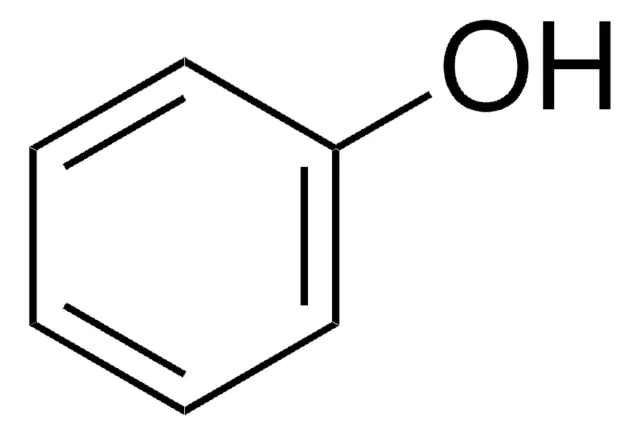
Aromatic ring/cylohexane with a hydroxyl group
Phenols/Fenoler
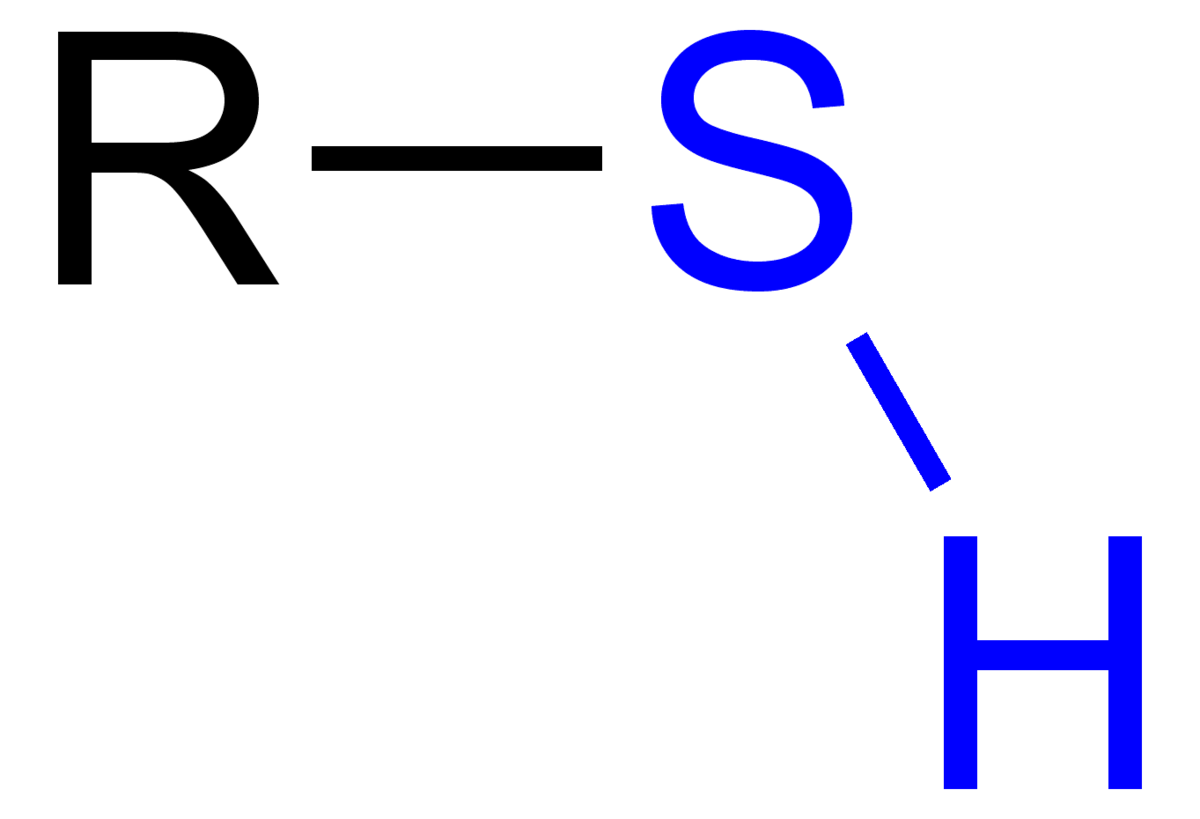
Contains a sulfhydryl (-SH) functional group, where sulfur is bonded to a hydrogen.
Thiols (mercapto)
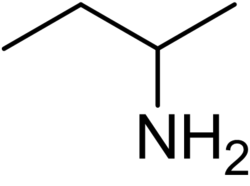
Contain a nitrogen atom bonded to carbon and/or hydrogen atoms
Amines
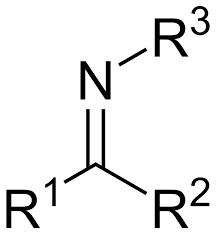
compounds featuring a carbon-nitrogen double bond
Imines
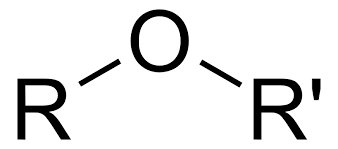
Oxygen bonded to two carbons
Ether/Eter
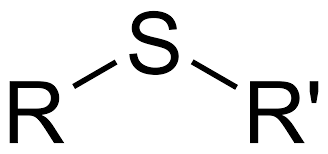
a thioether
Sulfides/sulfider
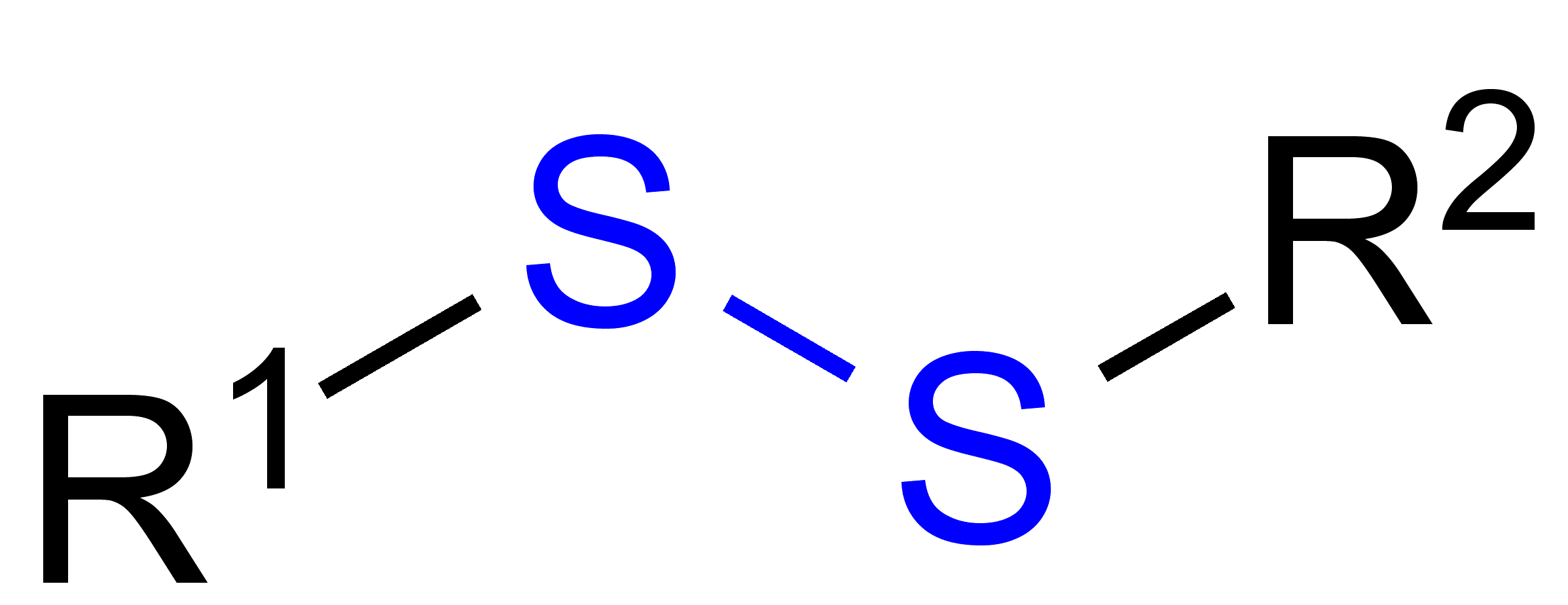
Disulfides
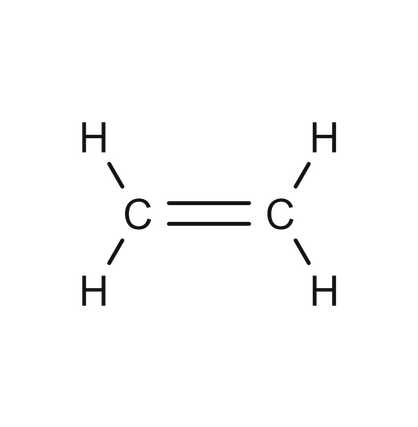
Double bonded carbon chain
Alkenes/Alken
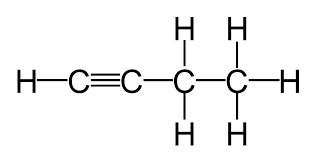
Triple bonded carbon chain
Alkynes/Alkyn
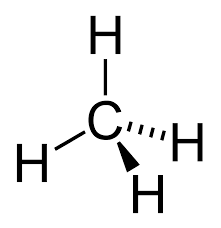
Single bonded carbon chain
Alkane/Alkan
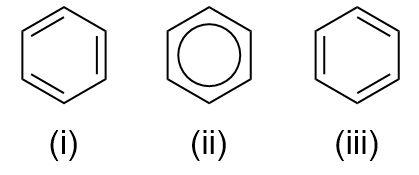
Arene/Aromatisk ring
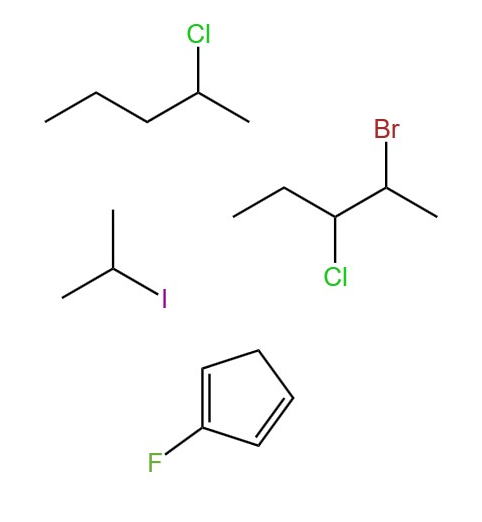
halogen bonded to a carbon chain (alkyl group)
halo alkane