Vascular Disorders and Thrombosis
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
what do organisms require to maintain homeostasis
circulatory system
what is the main function of the circulatory system
deliver nutrients and remove waste products from cells
what is the purpose of lymphatics
drain the extracellular space
arteries are under
high pressure
arteries move blood
away from the heart
veins move blood
towards the heart
the circulatory system is composed of
blood
central pump (heart)
vascular network
lymphatic vessels empty back into the blood via
thoracic duct
arteries have
large lumen
thick vessel walls
why is it important for arteries to have thick vessel walls
must withstand large pressure and stretch/recoil to keep continuous flow of blood
what do the artery vessel walls have in them
tensile (strength)
elastin (elasticity)
t/f arteries have large resistance to blood flow due to having a large lumen
false, minimal resistance
arterioles have
narrow lumen
thick layer of smooth muscle
what is important about the smooth muscle in arterioles
constricts based on sympathetic/ parasympathetic stimulation
what is the main function of the narrow lumen in arterioles
provide resistance to circulatory system as blood moves further from heart
what are the three layers of vessels
tunica intima, tunica media, tunica adventitia
what is the function of capillaries
site of nutrient waste/ product exchange between blood and surrounding tissue
t/f capillaries are the most numerous vessel but only contains 5% of total blood volume
true
what are the three types of capillaries
continuous, fenestrated, discontinuous
RBC moving through capillaries single file allows for
time for exchange of nutrients and waste
what allows RBC to move single file through capillary
slow velocity of blood flow
small lumina
continuous capillaries have
continuous endothelium
basement membrane
what is the function of continuous capillaries
passage of small molecules
exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
where can continuous capillaries be found
brain
lung
muscle
bone
fenestrated capillaries have
discontinuous endothelium
continuous basement membrane
what is the function of fenestrated capillaries
exchange of slightly large products
basement membrane being continous in fenestrated aids in
keeping certain products within the lumen due to negative charge
fenestrated capillaries are found in
renal glomeruli
intestinal villi
endocrine glands
chorid plexus
ciliary body of eye
discontinuous capillaries have
discontinuous endothelium and discontinuous basement membrane
what is the function of discontinuous capillaries
maximum passage of molecules from vascular lumen to extracellular space
discontinuous capillaries are found in
liver
spleen
bone marrow
veins are composed of
collagen, little smooth muscle and elastin
veins have
thinner vascular wall
blood passage through veins depends on
valves to prevent backflow
contraction on skeletal muscle
increased pressure gradient
veins typically ___ rather than contract
distend
veins typically hold how much of the total blood volume
65%
what is the purpose of elastin
gives elasticity to vessels
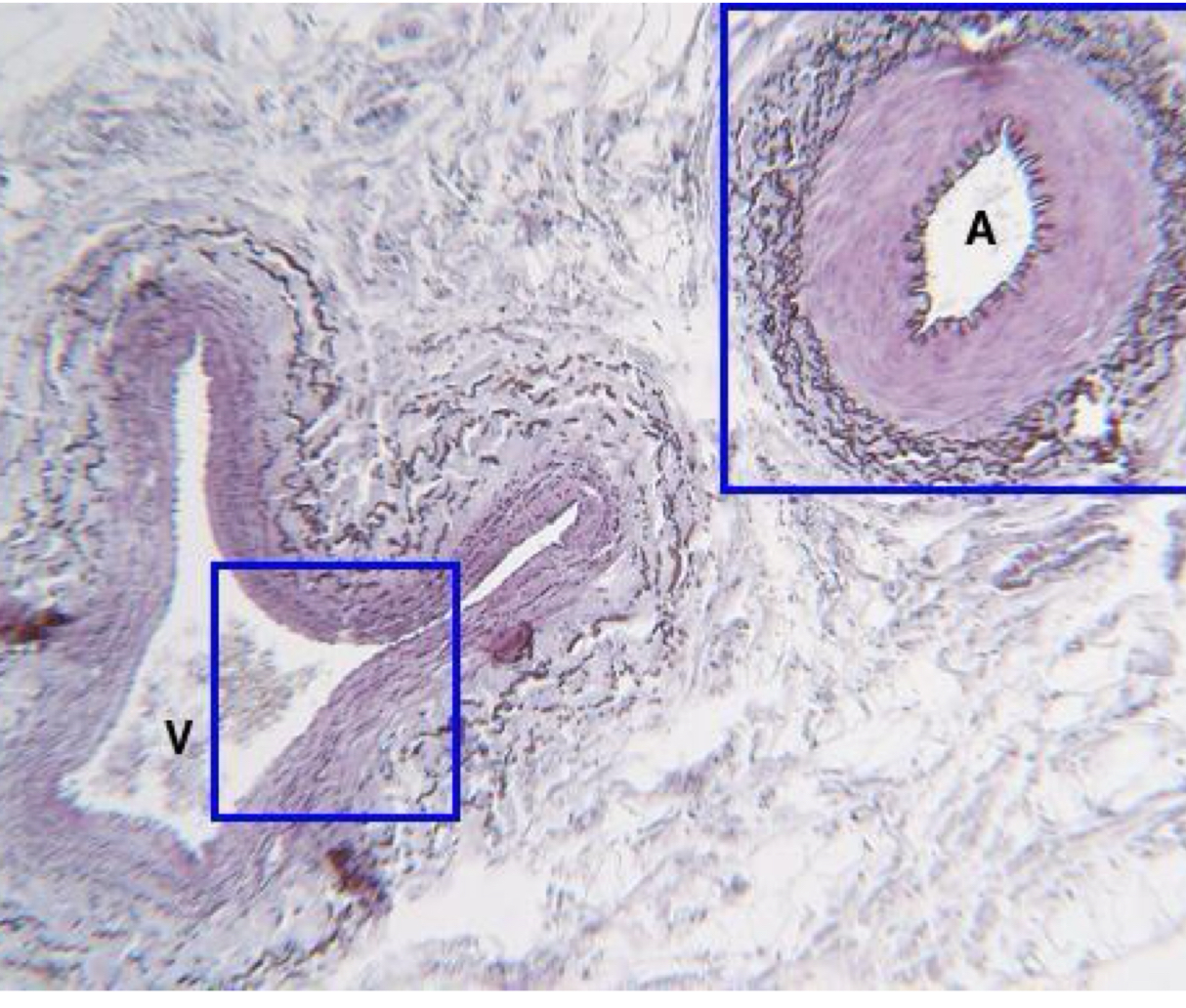
what is being shown on the right **
artery
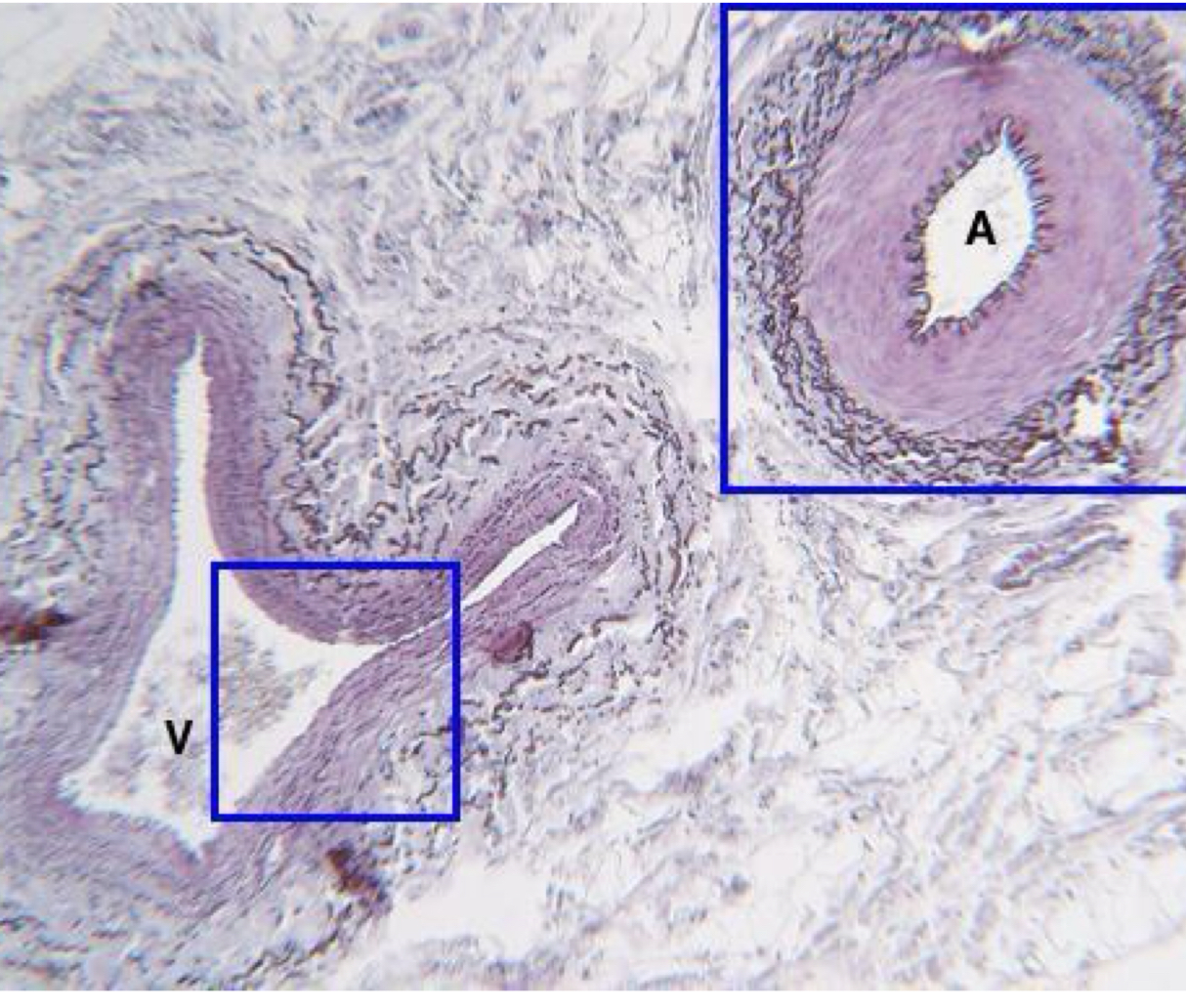
what is being shown on the left **
vein
which layer of the vessel is the endothelium with elastin
tunica intima
which layer of the vessel is the smooth muscle
tunica media
which layer of the vessel is the connective tissue
tunica adventitia
lymphatic vessels have
overlapping endothelial cells with large interendothelial gaps
t/f lymphatic vessels are distensible and a low pressure system like arteries
false, like VEINS
what is required to move lymph through lymphatic system
valves
contraction of skeletal muscle
what is the function of endothelium
fluid distribution
inflammation
immunity
agiogenesis
hemostasis
normal endothelium is
antithrombotic and profibrinolytic
what does antithrombotic mean
regulates hemostasis and prevents clot formation
what does profibrinolytic mean
helps break down complexing of fibrinogen into fibrin
single layer of endothelial cells lines
all components of the circulatory system
what is rete mirabile
specialized vascular networks formed by arterial blood vessels through center of large venous sinuses
what is the function of rete mirabile
countercurrent exchanger
-regulate temp
-ionic contraction gradients
-O2/CO2 exchange
-equalize blood pressure
where are rete mirabile located
around right and left internal carotid arteries
along cranial floor
what is the interstitium
space between parenchymal and stromal cells and microcirculation
what is the function of the intersitium
provide pathways for microvasculature, lymphatic vessels, nerves, and trafficking leukocytes
module systemic physiologic properties exerted by parenchymal glands
general fluid pool providing cushioning effects for organs
structural framework for cell survival
what is the extracellular matrix
structural, adhesive, and absorptive components WITHIN the interstitium
ECM is composed of
type I collagen
glycoproteins
glycosaminoglycans
proteoglycans
type I collagen provides
structural framework for ECM
what do glycoproteins provide for ECM
sites of attachment for structural proteins
site of adhesion for transmigrating leukocytes
what do proteoglycans do for the ECM
hydrophilic, bind to large amounts of water
components of the ECM are produced by
parenchymal cells
fibroblasts
glial cells (CNS)
macrophages
trafficking leukocytes