Point mutations
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Point mutations change
a single nucleotide
Point mutations cause changes, types of point mutations
in protein-coding sequences can lead to changes in the protein sequence
• “silent” mutations do not change the protein sequence (e.g. variation in the 3rd base of many codons)
• “missense” mutations change the amino acid sequence
• conservative mutations change to a similar amino acid
• “nonsense” mutations create a stop codon
Point mutations can be caused by
DNA polymerase errors
• Select the wrong nucleotide
• Failure to remove incorrect nucleoside during proofreading
Mismatches can be caused by
tautomers
regular vs tautomer form
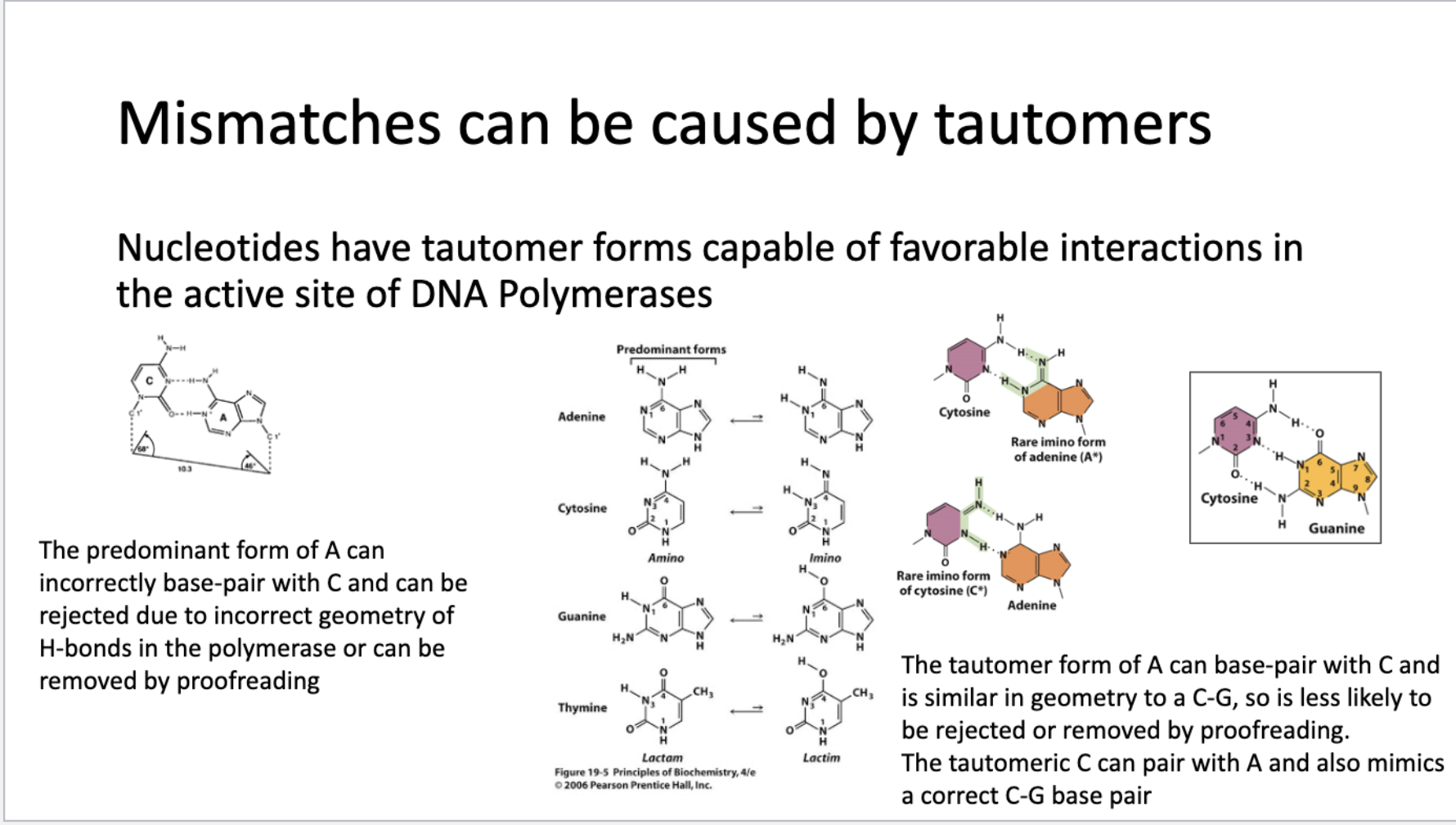
Nucleotides have tautomer forms capable of favorable interactions in the active site of DNA Polymerases
The predominant form of A can incorrectly base-pair with C and can be rejected due to incorrect geometry of H-bonds in the polymerase or can be removed by proofreading The tautomer form of A can base-pair with C and is similar in geometry to a C-G, so is less likely to be rejected or removed by proofreading.
The tautomeric C can pair with A and also mimics a correct C-G base pair
regular vs tautomer form 1
Nucleotides have tautomer forms capable of favorable interactions in the active site of DNA Polymerases
regular vs tautomer form 2
The predominant form of A can incorrectly base-pair with C and can be rejected due to incorrect geometry of H-bonds in the polymerase or can be removed by proofreading
The tautomer form of A can base-pair with C and is similar in geometry to a C-G, so is less likely to be rejected or removed by proofreading.
tautomer C
The tautomeric C can pair with A and also mimics a correct C-G base pair
regular vs tautomer form picture
Mismatches can be caused by 2
tautomers
Nucleotide tautomers increase the likelihood of mutations during DNA replication
Nucleotide tautomers are capable of favorable interactions in the active site of DNA Polymerases
Tautomers are short-lived and can switch back to the dominant form before or after incorporation into the synthesized strand
If a tautomer is added to the nascent strand and the polymerase moves on, it will return to the dominant form. The mismatched base pair will cause an irregularity in the DNA double helix that cannot be fixed by DNA polymerase but can be detected by repair machinery.
tautomers increase likelihood of
Nucleotide tautomers increase the likelihood of mutations during DNA replication
nucleotide tautomers are capable of
Nucleotide tautomers are capable of favorable interactions in the active site of DNA Polymerases
tautomers lifespan
Tautomers are short-lived and can switch back to the dominant form before or after incorporation into the synthesized strand
what if tautomer is added
If a tautomer is added to the nascent strand and the polymerase moves on, it will return to the dominant form.
The mismatched base pair will cause an irregularity in the DNA double helix that cannot be fixed by DNA polymerase but can be detected by repair machinery.
Point mutations can arise due to
mutagens or spontaneous processes
• Cytosine is spontaneously deaminated to form uracil which will base-pair with A in transcription and replication
• Guanine is oxidized to 8-oxoguanine in the presence of reactive oxygen species (a normal byproduct of electron transport in metabolism). 8-oxoG can base-pair with C or A in transcription and replication
Point mutations can arise due to 1
mutagens or spontaneous processes
Point mutations can arise due to 2 cytosine
Cytosine is spontaneously deaminated to form uracil which will base-pair with A in transcription and replication
Point mutations can arise due to 3 Guanine
Guanine is oxidized to 8-oxoguanine in the presence of reactive oxygen species (a normal byproduct of electron transport in metabolism).
8-oxoG can base-pair with C or A in transcription and replication