W2L2- The Genetic Code
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
what does transcription produce
mRNA as the template for protein synthesis
which strand is mRNA the same as
same as coding strand apart from T is U in mRNA
which strand is used by RNA-Pol3 to produce mRNA
template strand is physically used bby RNA-PolIII to produce mRNA
what did Watson and Crick say in their 1953 second paper
seems likely that the precise sequence of the bases is the code which carries the genetical information
mostly theory at this point but was confirmed later on by many other scientists
What was the goal of the Matthaei and Nirenberg experiment (1961)?
To decipher the first 'word' (codon) of the genetic code by determining which amino acid was specified by a known synthetic RNA sequence.
What key component did they use as the 'messenger' molecule in Matthaei and Nirenberg experiment?
Poly-U (Polyuridylic acid), a synthetic RNA molecule consisting only of repeating Uracil (U) nucleotides. This meant the only possible codon was UUU.
What type of system was used to carry out protein synthesis?
A cell-free system derived from E. coli, which contained all the necessary machinery (ribosomes, tRNAs, enzymes) but lacked its own native mRNA, allowing them to control the genetic message.
What were the results of the experiment when poly-U was added to the system?
The system only synthesized a polypeptide when the radioactive amino acid Phenylalanine was present, creating a protein called polyphenylalanine.
they used a radioactive version of each amino acid in different test tubes and only protein polyphenylalanine was produced
What was the definitive conclusion of the experiment?
The RNA codon UUU codes for the amino acid Phenylalanine.
how many amino acids does insulin have
110 amino acids
10^58 possible DNA sequences
why is it important that the genetic code is degenerate
provides a buffer against the harmful effects of mutations, protecting an organism's proteins from random changes in its DNA.
"Degeneracy" in this context means that most amino acids are coded for by more than one unique codon
64 codons but only 20 amino acids so significant redundancy
is there a correlation between frequency of AA use and number of codons encoding them
yes
the more frequent the aa use in protein, the higher the number of codons encoding them
leucine has 6 codons and takes up almost 10% of residues in proteins
tryptophan has one codon and takes up around 1% of residues in proteins
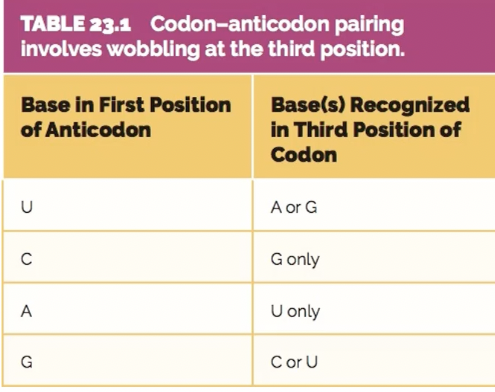
what is wobble pairing
where the base pairing between the tRNA anticodon and the mRNA codon is flexible at the third position of the codon.
This non-standard pairing means that a single type of tRNA molecule can recognise and bind to multiple, synonymous codons (codons that code for the same amino acid).
codon-anticodon pairing possibilties
tRNA anticodon first base/mRNA codon third base
U/ A or G
C/ G only
A/ U only
G/ C or U
how many examples of modified bases in tRNAs have been reported
81
what does modification of tRNA bases involve
usually involved direct alteration of the primary bases in tRNA
there are some exceptions in which a base is removed and replaced by another base
What is the degeneracy of the genetic code?
The feature where most amino acids are coded for by more than one unique codon.
The primary benefit of genetic code degeneracy.
It minimizes the impact of point mutations by increasing the chance that a base change will result in a silent mutation (coding for the same amino acid).
Definition of Wobble Pairing.
Flexible base pairing between the $\text{tRNA}$ anticodon and the mRNA codon at the third codon position and the first anticodon position.
who proposed the Wobble hypothesis
Francis Crick 1966
What does a tRNA anticodon base of Guanine (G) pair with in the mRNA third position?
Cytosine (C) or Uracil (U)
(G:U is a non-canonical wobble pair).
What does a tRNA anticodon base of Uracil (U) pair with in the mRNA third position?
Adenine (A) or Guanine (G).
Which modified tRNA base can pair with U, C, or A at the wobble position?
Inosine (I), which is derived from the modification of Adenine.
General role of chemical modification of tRNA bases.
To increase the accuracy (fidelity) and efficiency of protein synthesis, and to determine tRNA specificity for wobble pairing.
How does the modified base 2-thiouracil restrict pairing?
It restricts pairing to Adenine (A) alone, as it can only form one hydrogen bond with Guanine (G).
What kind of synthetic RNA did Matthaei and Nirenberg use?
Poly-U (Polyuridylic acid), which resulted in the protein polyphenylalanine.
The tRNA anticodon and mRNA codon bases are fixed for the first two positions. Which positions allow wobble?
The first base of the tRNA anticodon and the third base of the mRNA codon.
Why do organisms need fewer than 61 unique tRNA types to translate all codons?
The Wobble Hypothesis allows a single tRNA to recognise multiple codons due to flexible base pairing at the third position.
What is the benefit of chemically similar amino acids having related codons?
It minimizes the effects of mutation. If a mutation occurs, the resulting amino acid is likely to be chemically similar, preserving protein function.
Identify the two Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) listed as an example of chemical similarity.
Leucine (Leu) and Valine (Val). Both are Hydrophobic (nonpolar).
What is the role of modified bases in the $\text{tRNA}$ anticodon?
They affect the pattern of wobble pairing and are important in determining tRNA specificity.
Which mRNA codon bases can Inosine pair with at the wobble position?
Uracil (U), Cytosine (C), or Adenine (A). This allows the tRNA to recognize three out of the four bases.
How does the modified base 2-thiouracil restrict tRNA pairing?
It restricts pairing to Adenine (A) alone, because only one hydrogen bond can form with Guanine (G).
What does tRNA specificity' mean in the context of base modification?
It refers to the precise set of mRNA codons a particular tRNA anticodon is able to successfully recognise and bind to.
does the universal genetic code have alterations in other species
yes - some sporadic alterations
changes in universal genetic code have occured in some species
these changes are more common in mitochondrial genomes, where a phylogenetic tree can be constructed for the changes
paramecium uses STOP codons as amino acid coding codons
wholesale reassignments where in all mitochondria a STOP codon is translated into tryptophan
sense codon reassignment
What is the typical function of the UGA codon?
It is usually one of the three stop codons that terminates protein synthesis.
How can novel amino acids be inserted at certain stop codons?
The insertion requires the action of an unusual tRNA in combination with several proteins, such as SelB protein which binds to mRNA and helps tRNA get into ribosome
Which novel amino acid is inserted at some UGA codons?
Selenocysteine
In the ciliate Euplotes crassus, what two amino acids does the UGA codon specify?
Selenocysteine and Cysteine.
The chemical modification of tRNA anticodon bases is a strategy to determine what?
The pattern of wobble pairing and consequently, tRNA specificity.
what is a suppressor tRNA
A tRNA with an mutation in its anticodon
recognises a stop codon (nonsense mutation) and inserts an amino acid instead of release factor, allowing the ribosome to read through the termination signal and complete the protein.
polypeptide chain is extended beyond the termination codon
results in nonsense suppression at a site of nonsense mutation
What is the primary function of a Suppressor tRNA?
To read through a stop codon (nonsense mutation) by inserting an amino acid, synthesizing a polypeptide longer than the wild type.
Why is efficient suppression for suppressor tRNA considered deleterious?
It results in readthrough past normal termination codons, extending the resulting protein when it shouldn't be.
Suppressor tRNAs compete with which wild-type molecules?
They compete with wild-type tRNAs that have the same anticodon (to read the corresponding codon(s)).
At what frequency is the UGA stop codon 'leaky' and misread by Trp-tRNA?
1% to 3% frequency.
Define Missense suppression.
It occurs when a mutant tRNA recognizes a different codon from usual, so that one amino acid is substituted for another, correcting a missense mutation.
What is the key difference between Missense suppression and Nonsense suppression?
Missense suppression corrects a mutation that substituted one amino acid for another.
Nonsense suppression corrects a premature stop codon.
Define Recoding in the context of the genetic code.
Events that occur when the meaning of a codon or series of codons is changed from that predicted by the genetic code.
What type of molecular interactions are altered during a Recoding event?
Altered interactions between aminoacyl-tRNA and mRNA that are influenced by the ribosome.
Besides the mRNA sequence, what else influences the reading frame in recoding?
The ribosomal environment, including tRNAs
Name three types of Recoding illustrated in the diagram.
Read-through, Bypassing, and -1 Frameshifting.
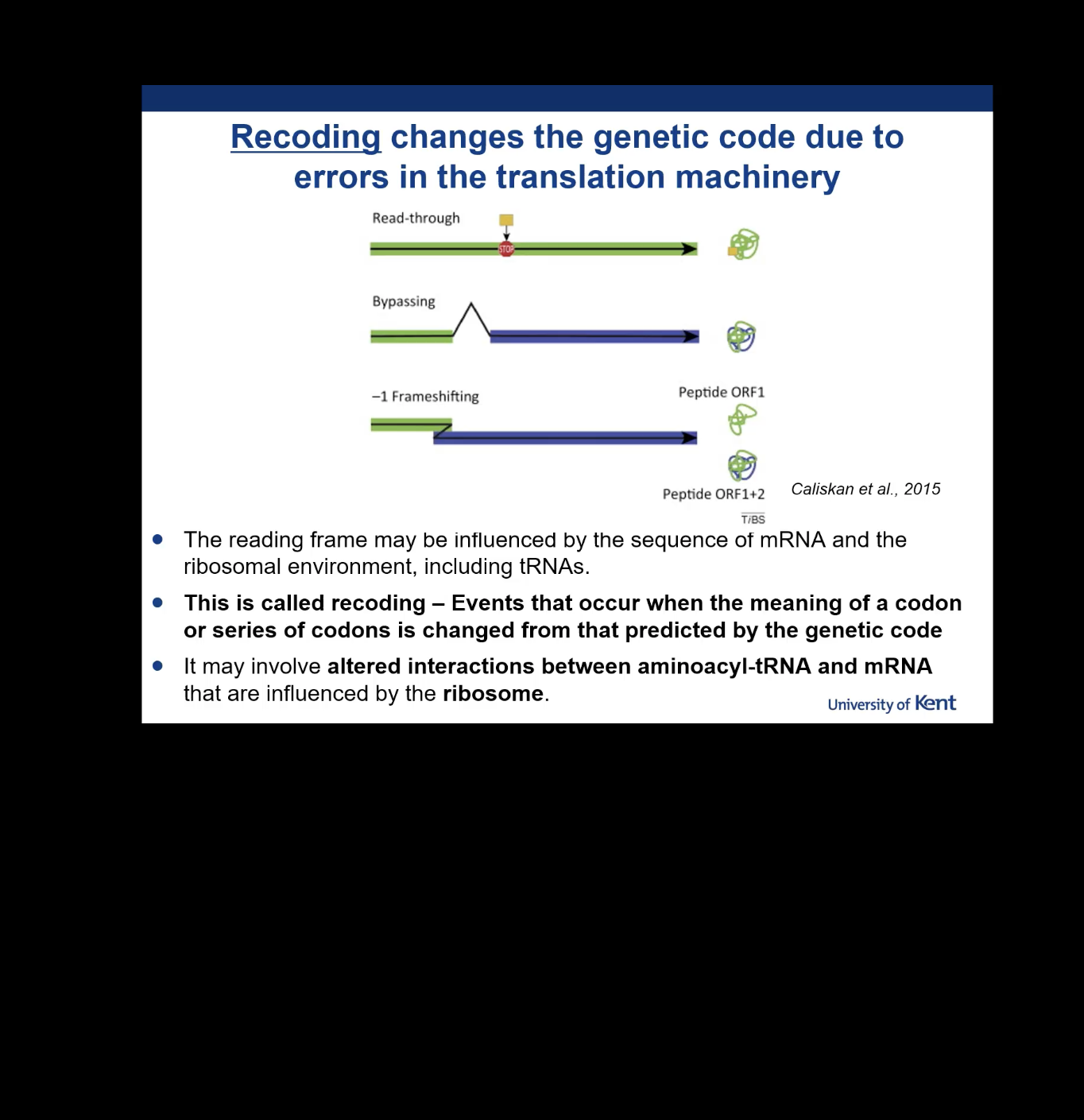
What is the result of read-through recoding?
The ribosome reads past a stop signal (like a stop codon), extending the polypeptide.
What causes Programmed -1 frameshifting in viruses (e.g. SARS-CoV)?
So-called slippery sequences, heptamer (7-nucleotide) stretches, often AAA/UUU triplets.
In Programmed -1 frameshifting, the ribosome will either backtrack or do what?
Skip (+1) 1 nucleotide or backtrack (-1) nucleotide
What does a slippery sequence allow a tRNA to do, thus changing the reading frame?
It allows the tRNA to shift by one base after it has paired with its anticodon.
Programmed -1 frameshifting is caused by what kind of mRNA sequence?
Slippery sequences (heptamer/7-nucleotide stretches), often AAA/UUU triplets.
What two actions can the ribosome perform at a slippery sequence to cause a frameshift?
It will either backtrack -1 or skip +1 1 nucleotide.
What is the biological significance of programmed frameshifting?
Translation of some genes (like in viruses) depends upon the regular occurrence of this event for correct protein expression.
Which frameshift type is required for expression of the tyb gene of the yeast Ty element?
A +1 frameshift.
What is the mechanism of programmed frameshifting in the yeast Ty-element?
A tRNA slips one base in pairing with a codon, causing a frameshift that can suppress termination.
efficiency is usually ~5%
What is the primary function of this frameshifting in the Ty-element?
Producing the correct ratio between Tya (GAG structural viral protein) and Tyb (Pol-related polymerase).
What is the typical efficiency of this programmed frameshifting in the Ty-element?
The efficiency is usually ~5%
What are the two protein products generated by alternative modes of translation in the Ty-element?
The Tya protein or the Tya-Tyb fusion protein.
What molecular process happens to the RNA inside the VLPs (viral like particles) for programmed frameshifting in the yeast Ty-element
It gets reverse-transcribed into DNA (cDNA; complimentary DNA).
What happens to the new double-stranded cDNA generated from the RNA? Yeast Ty gene
It reintegrates into another part of the genome.