Muscular System- Year 1 Midterms
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
are responsible for all types of body movement
Muscles
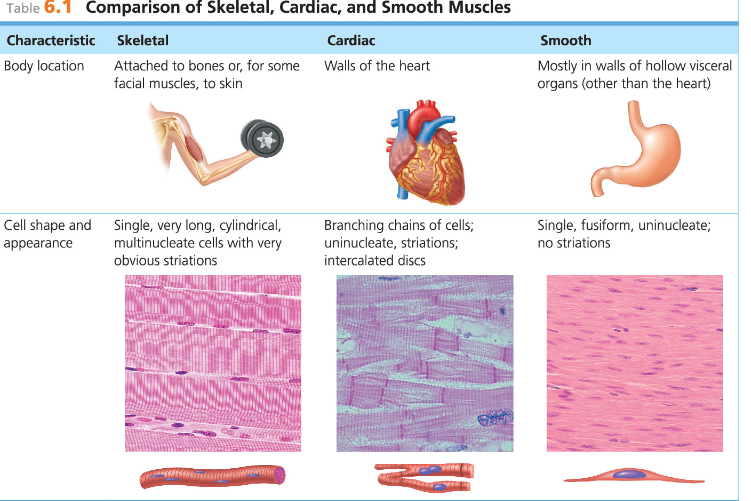
Three basic muscle types are found in the body
Skeletal, Cardiac, Smooth muscles
___ and ________are elongated (muscle cell = muscle fiber)
Skeletal and smooth muscle cells
Contraction and shortening of muscles are due to the movement of
microfilaments
Prefixes that refer to “muscle”
myo- and mys-
Prefix that refers to “flesh”
sarco-
Study These
Ok
Study these
Ok
Study these
Ok
Most skeletal muscle fibers are attached by _____ to bones
tendons
Skeletal muscle cells are look:
Large, cigar-shaped, and multinucleate
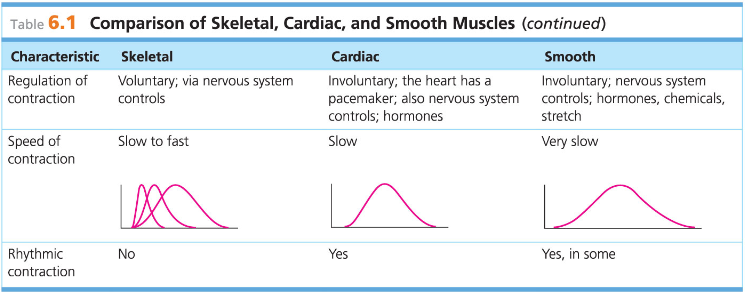
Skeletal muscle is also known as ____ because of its obvious stripes
Striated muscle
Skeletal Muscle is also known as_____ because it is the only muscle tissue subject to conscious control
voluntary muscle
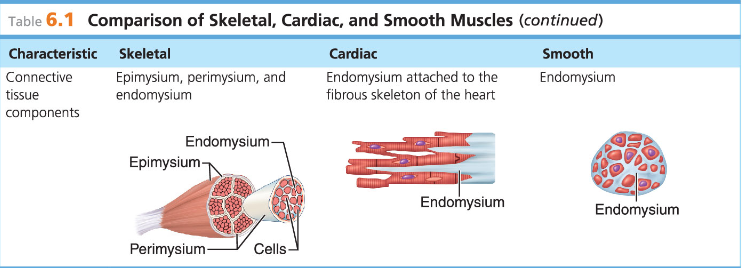
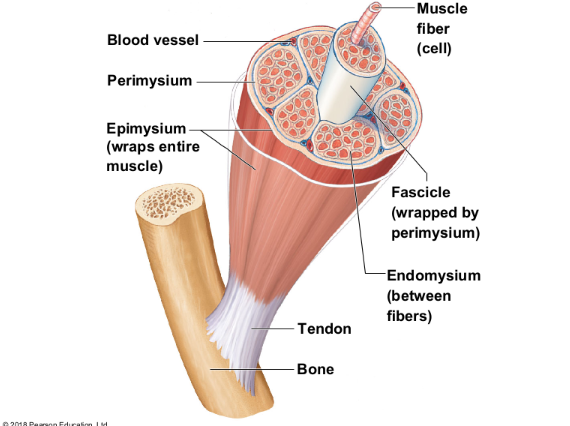
Skeletal muscle cells are surrounded and bundled by
connective tissue
Skeletal muscle connective tissue: encloses a single muscle fiber
Endomysium
Skeletal muscle connective tissue: wraps around a fascicle (bundle) of muscle fibers
Perimysium
Skeletal muscle connective tissue: covers the entire skeletal muscle
Epimysium
Skeletal muscle connective tissue: on the outside of the epimysium
Fascia
study the muscle types
ok
The ________ of skeletal muscle blends into a connective tissue attachment
epimysium
epimysium: cordlike structures
Mostly collagen fibers
Often cross a joint because of their toughness and small size
Tendons
epimysium: sheetlike structures
Attach muscles indirectly to bones, cartilages, or connective tissue coverings
Aponeuroses
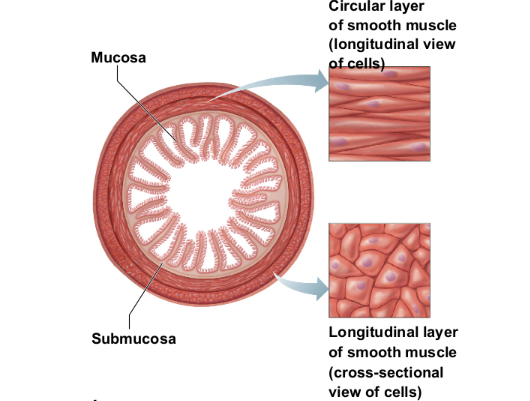
No striations
Involuntary—no conscious control
Found mainly in the walls of hollow visceral organs
(such as stomach, urinary bladder, respiratory
passages)
Spindle-shaped fibers that are uninucleate
Contractions are slow and sustained
Smooth muscle
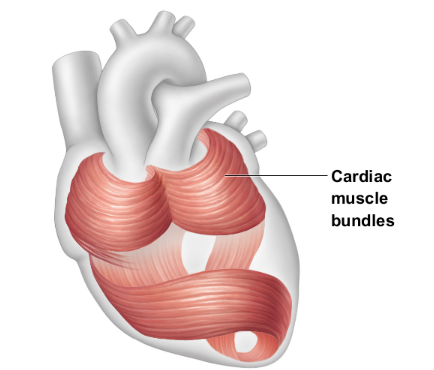
Striations
Involuntary
Found only in the walls of the heart
Uninucleate
Branching cells joined by gap junctions called intercalated discs
Contracts at a steady rate set by pacemaker
Cardiac muscle
Maintain posture and body position, Stabilize joints, Generate heat
skeletal muscle
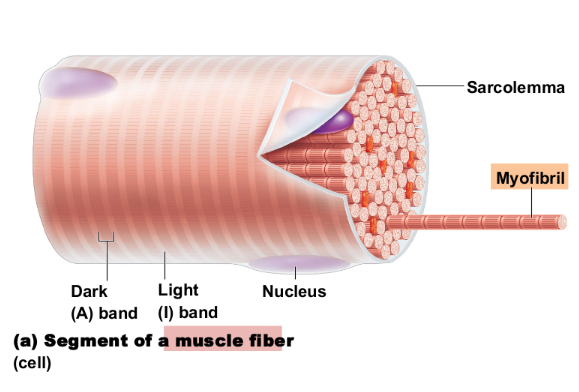
Microscopic Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle: specialized plasma membrane
Sarcolemma
Microscopic Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle: long organelles inside muscle cell
Myofibrils
These bands give the muscle its striated (banded) appearance
Light (I) and dark (A) bands
Banding pattern of myofibrils:
Contains only thin filaments
Z disc is a midline interruption
Light (I) band
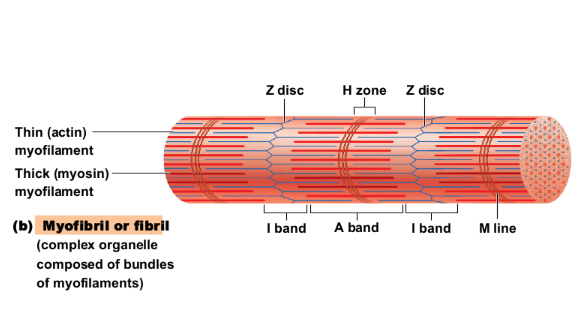
Banding pattern of myofibrils:
Contains the entire length of the thick filaments
H zone is a lighter central area
M line is in center of H zone
dark (A) bands
Microscopic Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle:
contractile unit of a muscle fiber
Structural and functional unit of skeletal muscle
Sarcomere
Myofilaments produce banding (striped) pattern: Thick filaments
myosin filaments
Myofilaments produce banding (striped) pattern: Thin filaments
actin filaments
Composed of the protein myosin
Contain ATPase enzymes to split ATP to release energy for muscle contractions
Possess projections known as myosin heads
Myosin heads are known as cross bridges when they link thick and thin filaments during contraction
myosin filaments
_______ are known as cross bridges when they link thick and thin filaments during contraction
Myosin heads
Composed of the contractile protein actin
Actin is anchored to the Z disc
At rest, within the A band there is a zone that
lacks actin filaments called the H zone
During contraction, H zones disappear as actin
and myosin filaments overlap