Unit 7: Industrial and Economic Processes
1/103
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
specific regions where manufacturing and production activities are concentrated, often characterized by factories, warehouses, and infrastructure to support economic activities.
Industrial belt
to reduce or eliminate industrial activity in a region, often leading to a decline in manufacturing jobs and economic shifts toward service-based economies. This shift impacts various economic sectors and patterns, environmental interactions, urban landscapes, trade dynamics, and globalization processes.
Deindustrialize

a region in the northeastern and midwestern United States that experienced significant industrial decline and economic downturn since the late 20th century. This area, once known for its booming manufacturing industry, now faces issues like factory closures, job losses, and urban decay, highlighting the shifts in industries and manufacturing practices within the country.
Rust belt

the economic division that involves the extraction and harvesting of raw materials directly from the natural environment. This includes activities like agriculture, forestry, mining, and fishing.
Primary sector

the part of the economy that transforms raw materials from the primary sector into finished or semi-finished goods through manufacturing, construction, and processing. Examples include turning timber into furniture, ore into steel, or crude oil into gasoline
Secondary sector

the part of the economy focused on providing services rather than goods, including activities like retail, healthcare, finance, entertainment in media, and education
Tertiary sector

the knowledge-based part of the economy focused on services that require a higher degree of education, like research and development, information technology, and financial planning. This sector is characterized by intellectual activities and specialized skills, driving innovation and economic growth in developed countries.
(Ex: Information technology, financial services, education, research and development, and consulting.)
Quatenary sector
the highest level of services involving the most influential economic influencers, like scientific research, top CEOS, and other jobs with specialized, high-skill labor, often seen as an extension of the quaternary sector (information/knowledge) but focused on elite expertise, encompassing roles in government, healthcare, education, and non-profits
Quinary sector
the phenomenon of how an initial economic input (like a new factory or government spending) creates a larger, ripple-effect increase in overall economic activity, jobs, and income for a region, as money circulates locally through spending and re-spending, fueling basic and non-basic industries
(Ex: A government spent on road construction, money will go to builders in wages. These builders spend some additional income on for example clothes, and also save some. The clothes seller earns more money, and spends some of this. The effect goes on.)
Multiplier effect
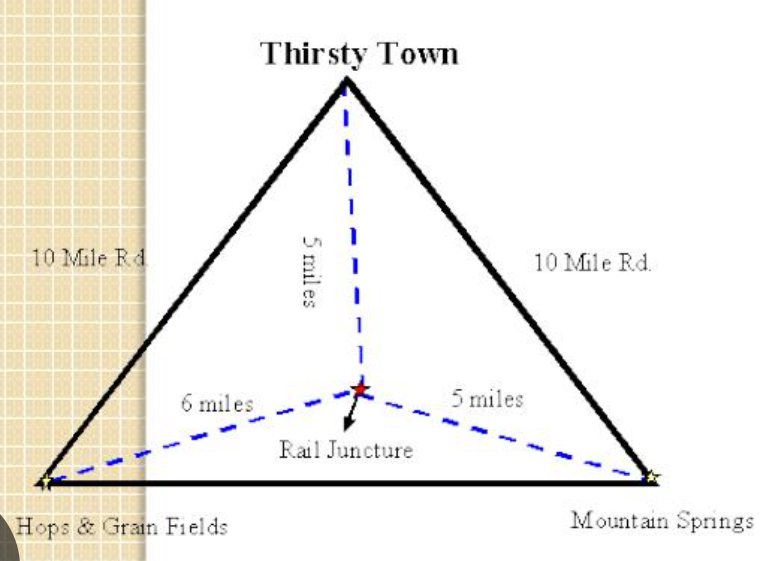
an economic principle that explains industries choose locations to minimize costs, focusing on transportation (raw materials vs. finished goods), labor (cheaper wages), and agglomeration (clustering benefits), aiming to maximize profits by finding the cheapest triangle of production, especially useful for bulk-losing (steel) or bulk-gaining (beverage) industries, though globalization challenges its simplicity.
Least cost theory

a location where goods are transferred from one mode of transportation to another, facilitating the movement of cargo in trade. These points are crucial for economic activity as they often occur at ports or airports, where shipping containers are transferred between ships, trucks, and trains.
Break-of-bulk point
Raw materials weigh less than the finished product so they locate near the market (consumers) to limit transportation costs for heavier, larger finished goods
Bulk-gaining
Raw materials weigh more than the finished product so factories locate near the source of input materials (like mines and forests) to cut costs on transportation and handling
Bulk-reducing
What happens when the finished goods are too fragile to transport (like potato chips)?
Based on least cost theory, the chips would locate near the raw materials since potatoes are heavier than the bags of chips HOWEVER since the potato chips are fragile, it's more ideal to locate near the market since nobody wants bags of crushed potato chips.
the benefits (like lower costs, shared labor, specialized suppliers, innovation) that companies gain by clustering together in a specific area
Agglomeration economies
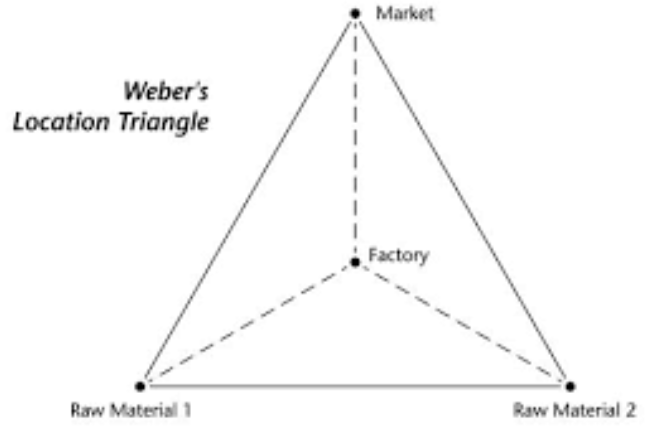
visualizing the optimal factory placement by connecting two raw material sources and one market, forming a triangle, to minimize transport costs, considering factors like material weight (bulk-reducing/gaining) and labor/agglomeration benefits
Locational triangle
a measure of the total economic output of a country, including the value of all goods and services produced by its citizens both within and outside the country\'s borders. It is one of the primary indicators used to assess the size and performance of a national economy.
GNP (Gross National Product)

the total monetary value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders in a specific time period, typically measured annually.
GDP (Gross Domestic Product)
the total income earned by a nation's residents and businesses, including any income earned abroad, over a specific period, usually a year. This encompasses all income generated within a country's borders, plus net income received from abroad, providing a broader perspective on economic well-being and prosperity.
GNI

an economic theory that states that in the long run, exchange rates should adjust so that identical goods have the same price in different countries when expressed in a common currency. This concept is essential for understanding economic development as it provides a more accurate measure of living standards and economic productivity across nations by accounting for differences in cost of living and inflation rates.
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
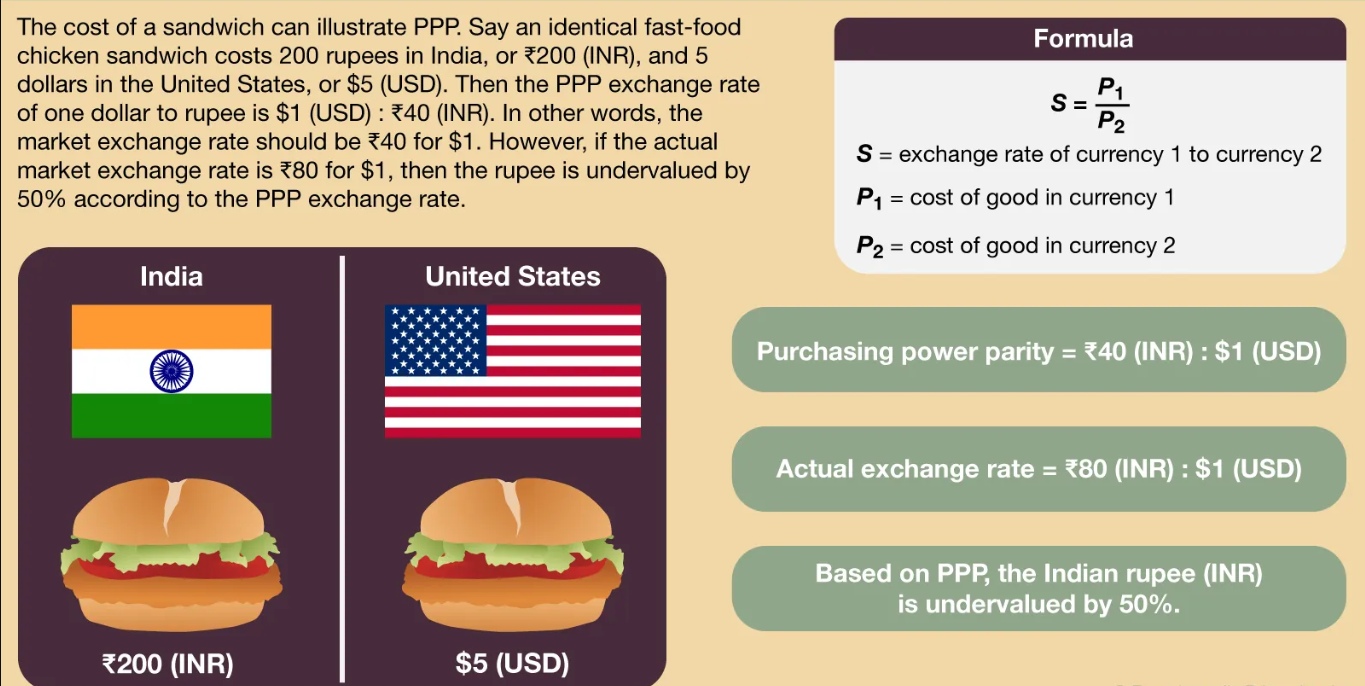
the formal sector involves legal, taxed, government-monitored jobs (like doctors, teachers, corporate roles) with benefits and structure, while the informal sector includes unregulated, untaxed activities (street vending, unregistered services, illegal work) lacking protection, often prevalent in less developed countries (LDCs) and difficult to measure, impacting GDP/GNI data and urban planning
Formal vs Informal sector
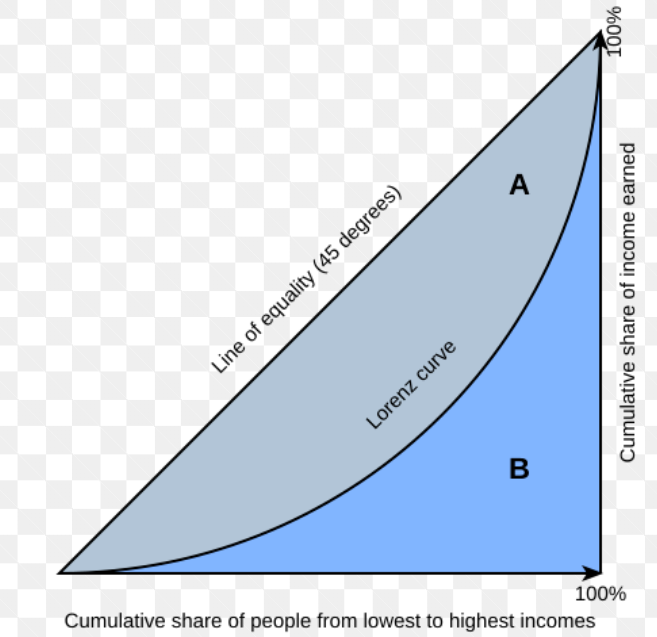
a statistical measure used to represent income inequality within a population, ranging from 0 to 1, where 0 indicates perfect equality and 1 indicates maximum inequality. This coefficient helps in understanding the distribution of wealth in a society and is essential for analyzing socio-economic development as well as urban disparities.
Gini coefficient
a composite measure that reflects inequalities in gender-based outcomes across three key dimensions: reproductive health, empowerment, and labor market participation. It highlights disparities between genders, providing insights into the social and economic development of countries. A higher GII indicates greater inequality between men and women, which can signal issues related to gender equity and overall development levels.
GII (Gender Inequality Index)
a composite statistic used to measure and rank countries based on their levels of human development. It takes into account three key dimensions: life expectancy at birth, education level, and per capita income. This index provides a more nuanced view of development than traditional economic measures by emphasizing the well-being and quality of life of individuals.
HDI (Human Development Index)
a range of financial services, including small loans and savings accounts, aimed at individuals and small businesses who lack access to traditional banking systems. This financial approach is particularly significant in supporting low-income populations, especially women, by empowering them economically and enabling entrepreneurial activities that can lead to improved living standards.
Microcredit/Microfinance
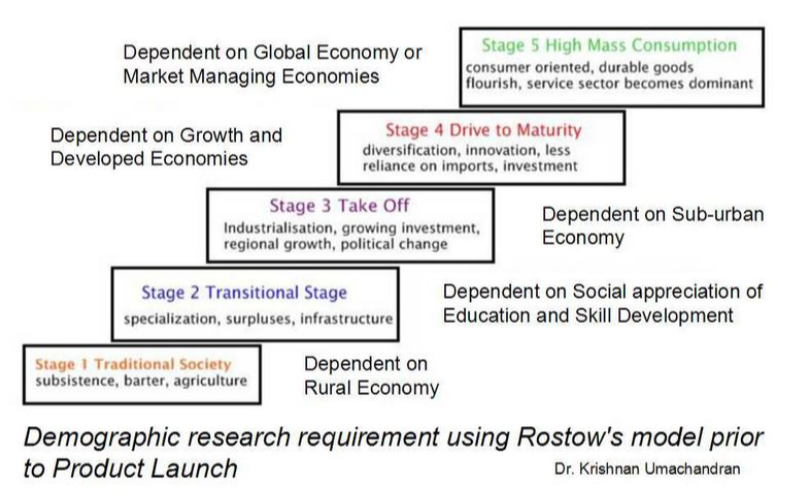
describes a linear path of development with five stages: Traditional Society, Preconditions for Take-off, Take-off, Drive to Maturity, and Age of High Mass Consumption, showing how countries transition from agrarian to industrialized, consumer-focused economies, emphasizing infrastructure, technology, and shifts in economic activity from primary to secondary to tertiary sectors.
Stages of economic growth model

a stage in the economic development model characterized by little foreign investment, high rates of subsistence farming, predominantly rural areas, and an economy that hasn’t begun development by modern metrics
Traditional Society

a stage in the economic development model proposed by economist Walt Rostow, which outlines the necessary conditions that must be established for a country to transition from a traditional society to a state of economic growth. This stage emphasizes infrastructure development, investment in education, and the adoption of new technologies as vital elements that enable a society to advance toward industrialization and sustainable economic progress.
Preconditions for Take-Off

the critical stage in economic development when a society begins to transition from pre-industrial to industrialized status, marked by rapid growth and increased investment in industries. During this phase, there is often a surge in manufacturing and infrastructure development, leading to higher levels of productivity and job creation. This concept is integral to understanding various theories of development, as it highlights the shift necessary for sustained economic progress.
Take-Off

the process of economic development where a society transitions from reliance on primary industries to more diversified and advanced sectors, leading to sustained economic growth. This concept emphasizes the importance of innovation, technological advancements, and infrastructure development as key drivers that propel economies into a more mature state, ultimately enhancing quality of life and productivity.
(Note: Four Asian Tigers means South Korea, Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Singapore)
Drive to Maturity

the final stage in the economic development model proposed by Walt Rostow, characterized by a high level of consumer goods and services available to the population. This stage indicates a society where consumption is not only widespread but also diverse, allowing individuals access to a variety of products that enhance their quality of life. This stage is also linked to advanced industrialization and technological progress, contributing to increased income levels and changing social structures.
High Mass Consumption
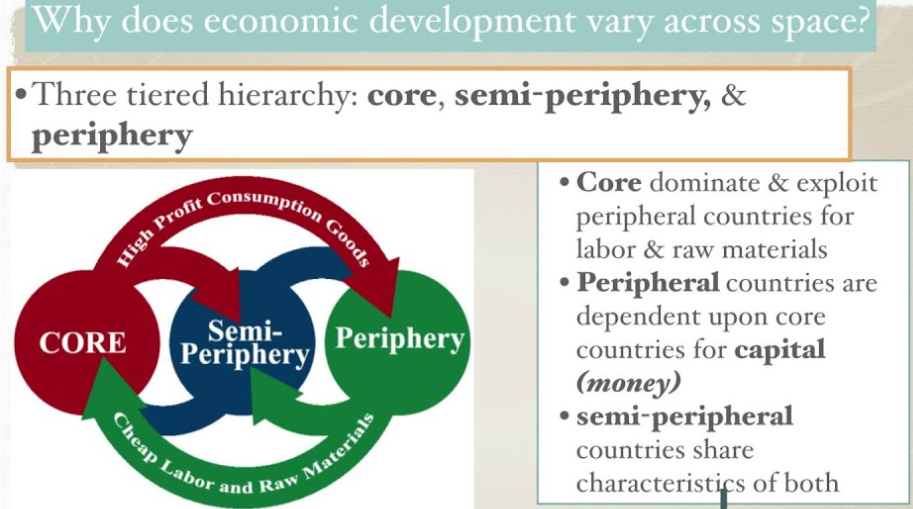
a socio-economic framework that categorizes countries into core, semi-periphery, and periphery based on their economic activities and global power dynamics. This theory emphasizes the interconnectedness of nations in a single global system, where wealth and resources flow from the periphery to the core, leading to unequal development and persistent disparities between countries.
World Systems Theory
the most economically developed nations that drive global economic activity and have a significant influence on international trade, politics, and culture. These countries typically possess advanced technological infrastructure, strong educational systems, and robust economies, which allow them to dominate the global market and engage in high-value production.
Core countries
nations that are in the middle tier of the world system, exhibiting characteristics of both core and periphery nations. These countries typically have a mix of industrialized and developing features, often playing a crucial role in the global economy by bridging the gap between the wealthier core nations and the less developed peripheral countries.
Semi-Periphery Countries
nations that are less economically developed and typically rely on agriculture and raw material exports. These countries often face challenges such as political instability, limited industrialization, and a lack of infrastructure, which can hinder their development compared to other nations. This status influences various aspects of their society, including economic opportunities for women, particularly in agricultural sectors.
Periphery Countries
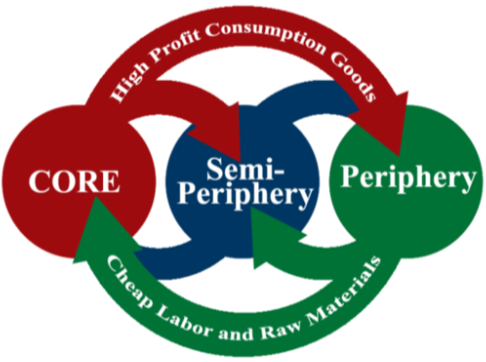
an economic and social theory that suggests that the development of some countries is contingent upon the exploitation and underdevelopment of others, particularly in the context of a global capitalist economy. It argues that resources flow from peripheral, underdeveloped countries to core, developed countries, leading to a cycle of dependency and hindering true development in those peripheral nations.
Dependency Model
independent organizations that operate outside of government control, typically focused on addressing social, environmental, humanitarian, or developmental issues. They play a vital role in global governance and often challenge state sovereignty by providing services, advocating for policy changes, and raising awareness about various issues and can influence decision-making processes and mobilize resources, making them key players in both local and international contexts.
NGO (non-governmental organization)
the heavy reliance a country’s economy has on exporting raw materials instead of manufactured goods, making it vulnerable to price swings and hindering diversified development, often linking to the core-periphery model where developing "periphery" nations supply cheap goods to "core" nations.
Commodity dependence

a company hires an external firm (often in another country) for tasks or services, usually to cut costs (like cheaper labor) or boost efficiency by focusing on core work, playing a big role in globalization, shifting jobs, and changing economic landscapes. This approach has become a significant feature of the global economy, as businesses seek to optimize their operations by leveraging lower labor costs and specialized expertise found abroad.
Outsourcing
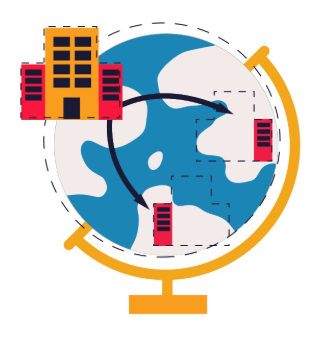
the practice of relocating business processes or production to another country, often to reduce costs or increase efficiency. This strategy is commonly used by companies seeking lower labor costs, tax benefits, or access to specialized skills.
Offshoring
outsourcing means hiring an external company (a third party) for a job, regardless of location, while offshoring means moving work to another country, which can be done by your own company (in-house) or by an outsourced firm
Difference between outsourcing and offsourcing
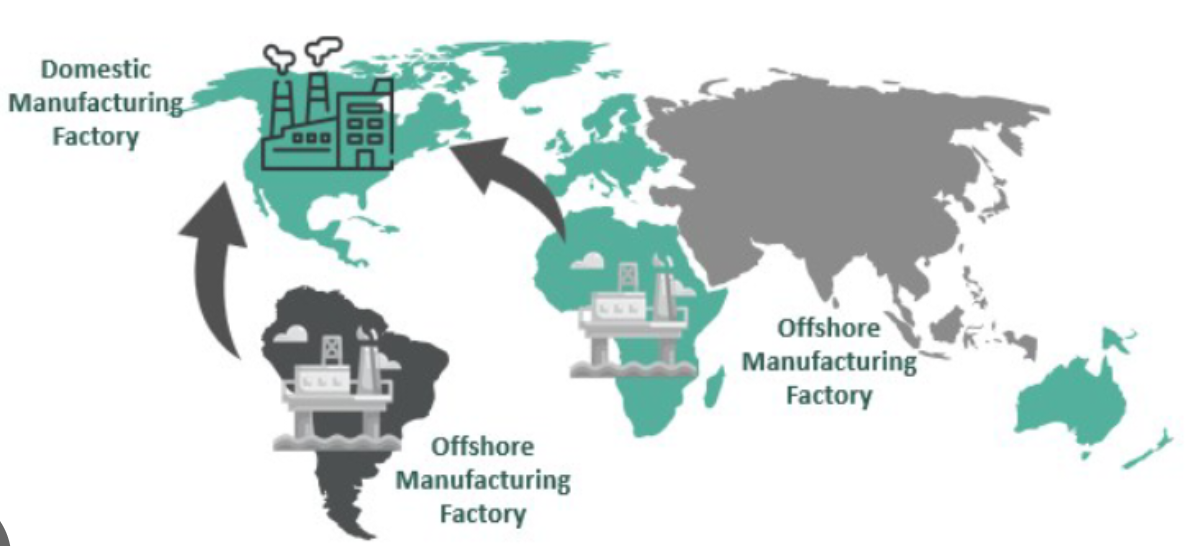
bringing manufacturing or business operations back to the home country after they were previously moved overseas (offshored) for lower costs, driven by factors like supply chain risks (e.g., COVID), rising foreign wages, automation, and government incentives, impacting global trade, employment, and economic geography.
Reshoring
describes how globalization shifted manufacturing jobs from developed countries (MDCs) to developing countries (LDCs) for cheaper, less-skilled labor, creating a global factory system where high-skill tasks (R&D, management) stay in MDCs, while low-skill assembly/production moves to LDCs, profoundly restructuring global economies and labor relations.
New international division of labor
basic economic activities bring money into a region from outside (exports like car manufacturing, tourism, tech), driving growth, while non-basic activities circulate money within the local area (services like grocery stores, dentists, local restaurants) and support the basic sector, creating the economic base of a city
Basic v. non-basic economic activity
designated areas within a country that offer favorable conditions for foreign and domestic companies to manufacture and export goods. These zones typically provide tax breaks, regulatory exemptions, and streamlined customs procedures to attract foreign investment, thereby promoting economic growth and job creation in developing countries as part of their integration into the global economy.
a designated area within a country where economic regulations differ from those in the rest of the country, typically with the aim of attracting foreign investment and boosting economic activity. SEZs often provide tax incentives, less stringent regulations, and improved infrastructure to encourage businesses to set up operations within these areas, making them significant in the context of global trade and economic shifts.
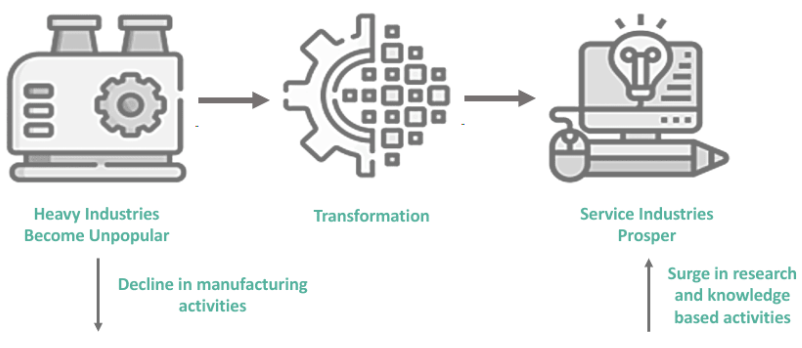
a society characterized by the shift from a manufacturing-based economy to one focused on services, information, and technology. In this type of society, the economy is dominated by sectors such as finance, healthcare, and education, while the traditional industrial jobs decline. This transformation has significant implications for population composition, including changes in workforce demographics and urbanization patterns.
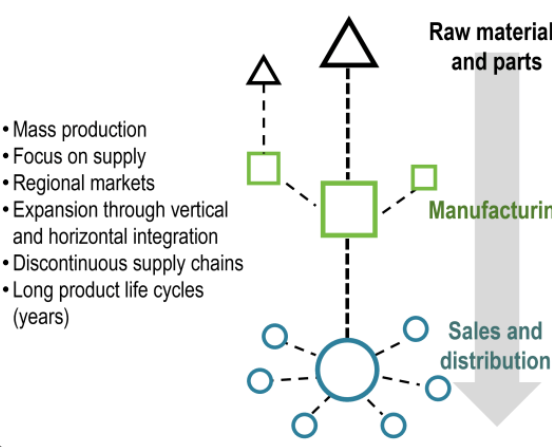
the system of mass production and consumption that emerged in the early 20th century, characterized by assembly line manufacturing, standardized products, and a focus on high wages for workers.
This replaced older methods by using low-skilled labor for simple, repetitive tasks to create large quantities of uniform products cheaply
This model revolutionized the industrial landscape by making goods more affordable and accessible to a broader audience, thereby shaping consumer culture and global economic practices.
Fordism
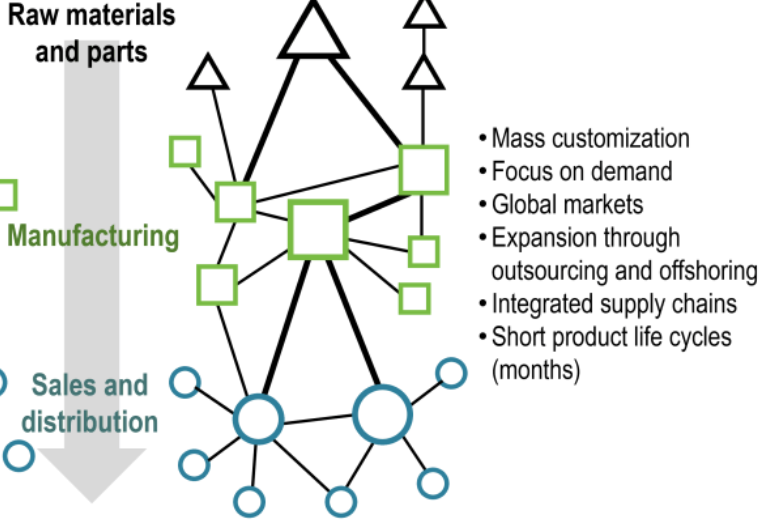
the shift from mass production (Fordism) to flexible, specialized, and decentralized production, focusing on customized goods, lean manufacturing (just-in-time), skilled workers, and globalized supply chains, driven by changing consumer demands and technology, leading to new industrial regions and uneven development
Skilled Labor: Requires multi-skilled workers who can adapt, unlike the unskilled assembly-line labor of Fordism.
New Industrial Regions: Fosters specialized clusters (like Silicon Valley) and knowledge-sharing, but also contributes to deindustrialization in older areas.
Post-fordism
businesses will shift production or locate facilities where they can achieve the highest net profit by substituting one production factor (like costly labor or high-rent land) with another (like cheaper labor, automation, or land) to minimize expenses and maximize gain, influencing location decisions
the economic theory, often linked to Harold Hotelling, explaining how businesses (especially competitors) position themselves spatially (e.g., near each other) to maximize their market share, influencing each other's locations to gain customer access
specialized areas or regions that focus on the development and promotion of high-tech industries and advanced technology.
Technopoles
specific areas or regions that are identified as having the potential for significant economic development and growth, driven by concentrated investment, innovation, and infrastructure. These areas act as engines of economic activity, attracting businesses and labor, and fostering regional development that can spill over into surrounding areas.
the positive economic ripples that spread out from a central area of economic growth (a "growth pole" or "technopole"), creating opportunities for surrounding, even distant, regions,
the negative economic impacts on one region (the periphery) caused by strong growth in another (the core), where resources like skilled labor, capital, and opportunities are drained from the periphery to the core, increasing regional inequality
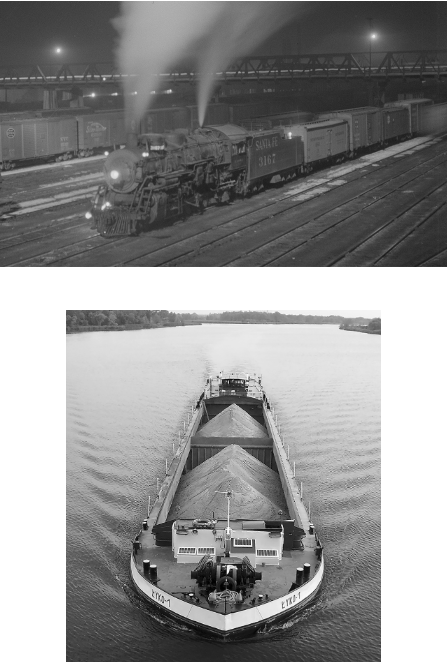
Compare the two images. What do the technologies shown demonstrate about the Industrial Revolution?
The increased transportation technology has enabled the diffusion and expansion of industrial activities.
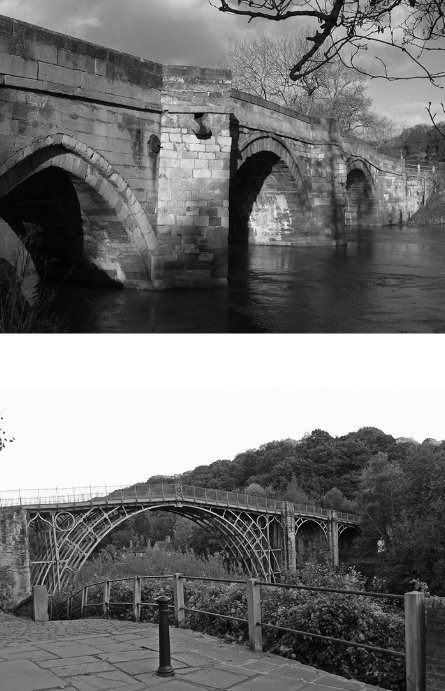

In the context of industrialization, how does the use of the building materials in Image 1 compare to the use of building materials in Image 2 ?
The development of the metals industry led to the construction of higher and longer bridges, a reduced need for stone as a building material, and rapid industrialization.
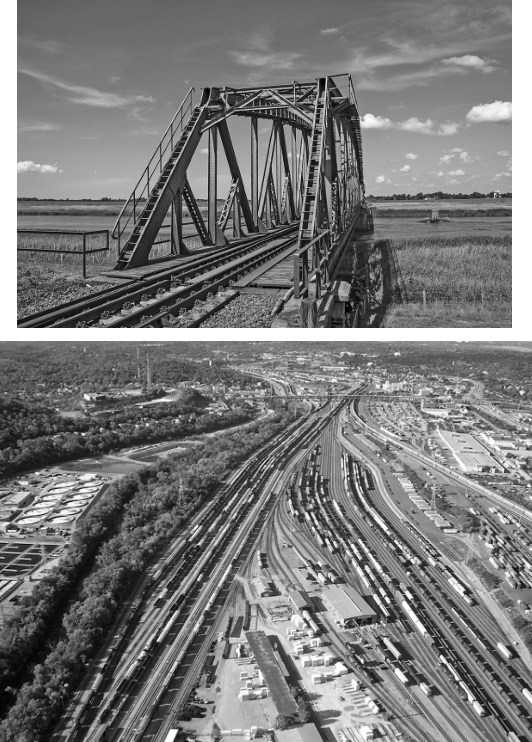

The two images illustrate advancements in technology resulting from the Industrial Revolution. Comparing the images, which of the following statements best illustrates an impact of the Industrial Revolution on society?
The invention of the steam engine and the construction of steel bridges to carry trains across various physical features led to ever-increasing demand for the materials and labor to build more trains and tracks.
The port of Los Angeles is the busiest port in the United States and a major break-of-bulk point. Which of the following statements correctly explains why Los Angeles is a break-of-bulk point?
The port can accommodate large container ships that can be unloaded quickly so that containers can be transferred onto carriers that use California’s highway and rail systems.
Which of the following best explains the relationship between GDP per capita and world system theory?
There is an uneven distribution of economic development and geographical division of labor in the world.
Which of the following explains the spatial patterns of economic development for most countries in Southeast Asia, including Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, and Vietnam?
Most Southeast Asian countries are considered to be part of the semiperiphery because of the extensive growth of the secondary economic sector.
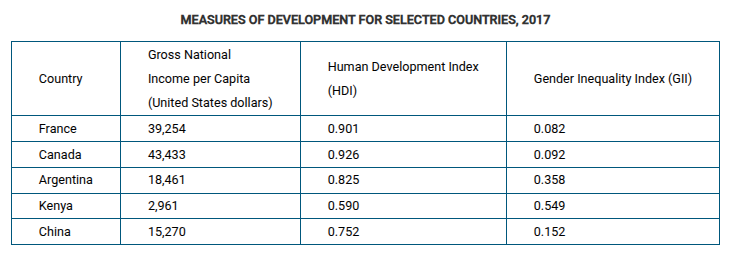
Which of the following statements explains one of the limitations associated with utilizing the measures of development shown in the table above?
All the statistics aggregate data to the country level. Frequently, there is a great deal of variation in development within countries that is hidden by aggregated data.
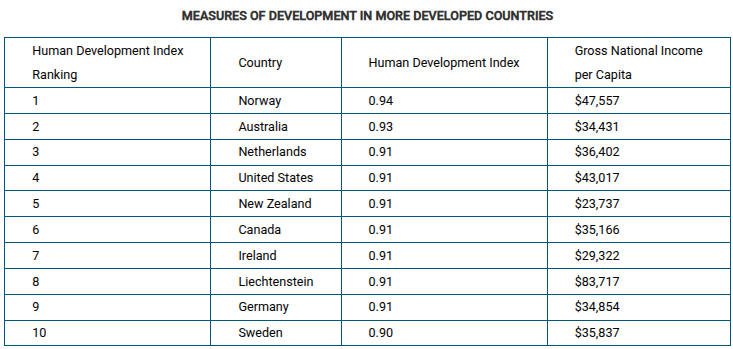
Using the data in the table, which of the following explains a limitation of using gross national income (GNI) per capita as the only measure of a country's level of development?
A country can have a high level of economic and social development that is not reflected in annual production and trade data.
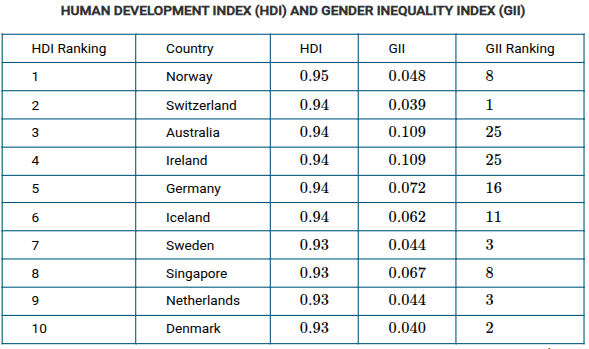
Based on the data in the table, which of the following statements is accurate?
Increased levels of economic development often conceal gender inequities.
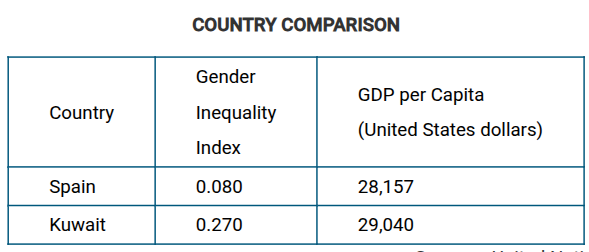
Which of the following statements is most consistent with the data shown in the table?
There are a large number of women in the Spanish legislature, but few women have been elected in Kuwait.
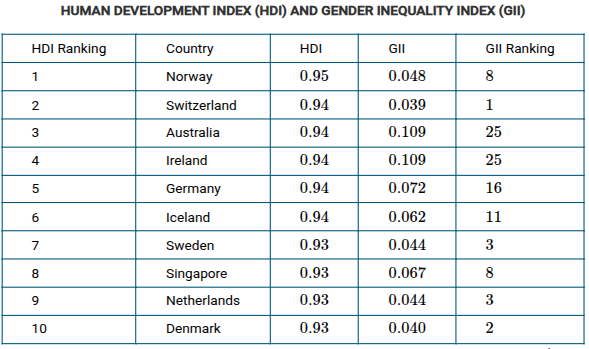
Which of the following conclusions is best supported by the data shown in the table?
Countries with the highest HDI rankings do not necessarily have the highest rates of women’s labor-market participation.
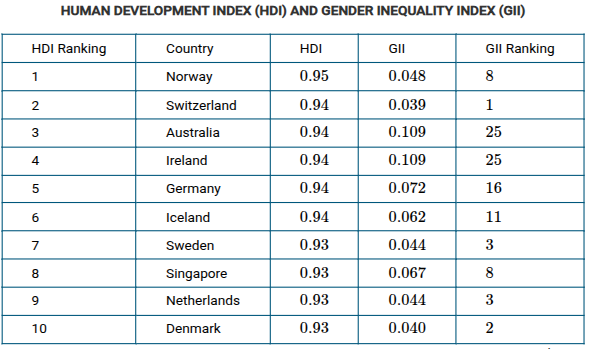
Australia, Ireland, and Germany have the highest GII values in the table shown. What do these countries' high GII values indicate when compared to their HDI values?
These countries have less gender equality despite high levels of education and health care.
Which of the following statements explains a weakness in Rostow's stages of economic growth model?
The model is based on successive stages that countries must pass through independently until they reach high mass consumption without taking into account that countries are interdependent.
Which of the following explains a limitation of the three-tiered structure of Wallerstein’s world systems theory?
The model locks most countries into the development model of core, semiperiphery, and periphery with little opportunity for peripheral economies to advance into the wealthy core.
Which statement explains one way in which the transformation of India’s economy contradicts Wallerstein’s world system theory?
Using a development strategy to avoid economic dependency, India has been able to develop its own industries and participate fully in the global economy.
Which of the following best explains a benefit of membership in the European Union?
Member states form a single market, which creates a powerful economic bloc.
Which of the following concepts explains the decision to relocate market-oriented factories in the United States from the Midwest and Northeast to locations in the southern United States or Mexico?
Comparative advantage, because products can be made more efficiently in the southern United States and Mexico. Operating costs and wages are lower, and the manufactured products are easily transported to major United States markets.
Which of the following best explains a trading relationship between two countries based on comparative advantage?
Each country specializes in the type of good for which it has the lowest opportunity cost, resulting in a higher global output of both types of goods.
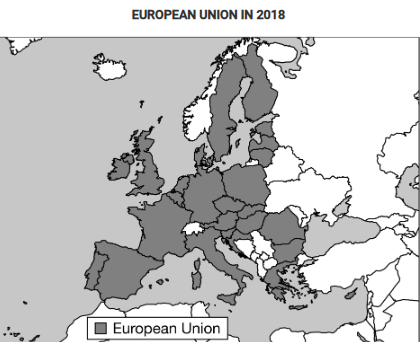
Which of the following statements best explains a limitation of the political map shown in conveying economic information?
In the context of free trade, the borders between the member states are irrelevant.
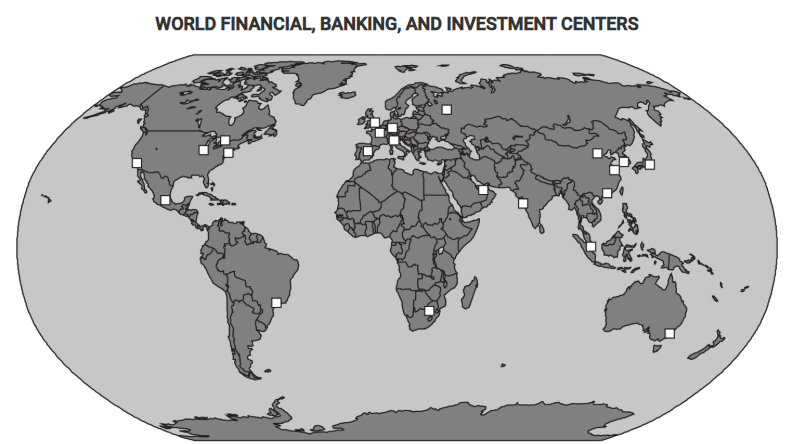
The map shows the locations of world financial, banking, and investment centers. Which of the following best explains a limitation of the map’s representation of global economic patterns?
The map does not show the growth of investment in businesses in less developed countries.
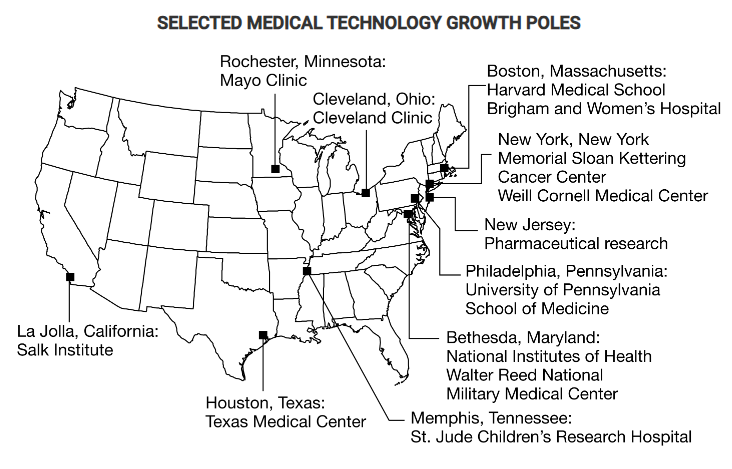
The map shows medical technology growth poles in the United States. Which of the following statements best explains a limitation of the map in showing the geographic context of these growth poles?
Each growth pole location is supported by an international network of researchers and multinational corporate partners.
Which of the following explains a significant obstacle to sustainable development in more developed countries?
The reliance on fossil energy sources for electric generation and vehicle fuel has depleted resources globally and contributed to atmospheric pollution in cities.
The country of Costa Rica has protected 25 percent of its land in the form of national parks or other protected areas. Which of the following best explains the desired effect of Costa Rica's process of land preservation?
Costa Rica's national parks and preserved areas are intended to promote international ecotourism and support the country's sustainable local economic development.
Which of the following explains a negative effect that can occur in countries that depend on ecotourism as a pathway to sustainable economic development?
The development of ecotourism can attract multinational tourism corporations that take their earnings out of the country while attracting tourists who impact the local environment.

Each image shows a different way that products of the Industrial Revolution were transported. Which of the following statements best compares the impacts of the two forms of transportation?
Both forms of transportation accelerated production and distribution of goods.

Which of the following changes in global economic patterns occurred because of the innovations depicted in the two images?
Early adopters of the two innovations began to increase colonization in search of new sources of raw materials for manufacturing goods.
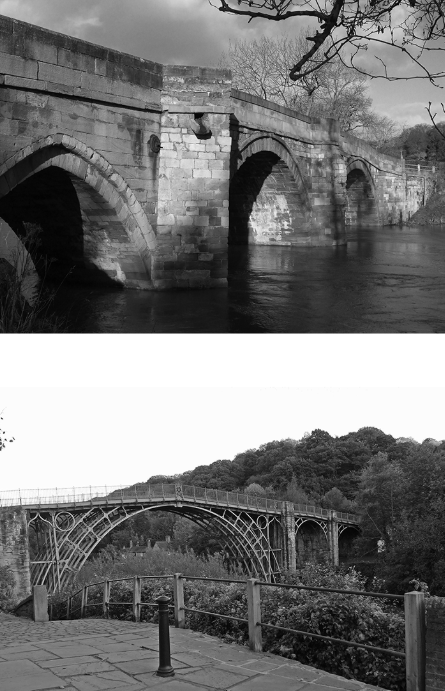

Which of the following best explains how the diffusion of industrialization relates to the two images shown?
The stone bridge predates the Industrial Revolution. The technology for steel bridgework became available through the diffusion of steel manufacturing processes.
Which of the following explains the development patterns for a country that has a large proportion of its economy engaged in the secondary economic sector?
The country has access to shipping lanes and inexpensive transport options that lead to establishment of factories close to raw materials or to markets, depending on the manufacturing process.
Which of the following best explains the relationship of a country's economic sector employment to its development level?
Core countries have the highest percentage of workers in the tertiary sector and the lowest percentage of workers in the primary sector because of the economic emphasis on services.
The higher gross domestic product per capita in some less developed countries such as Brazil, South Africa, and Malaysia is best explained by increases in the value of the country’s
manufacturing output and service industry employment
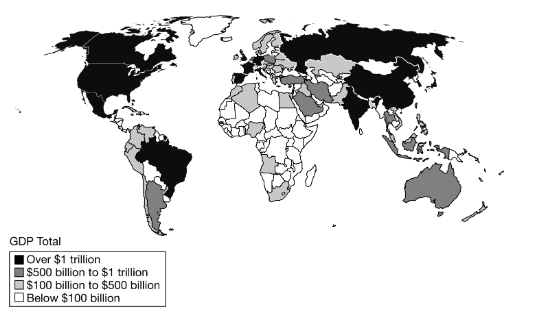
The map shows gross domestic product (GDP) by country. Which of the following factors best explains a limitation of GDP by country in comparing the level of productivity among countries?
Different population sizes, such as China, Japan, and the United States
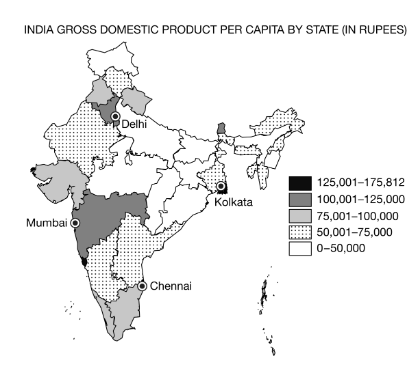
Explain how the map represents an incomplete picture of the economy in India.
The data do not measure the informal economy, which in regions with high employment in agriculture could be significant.
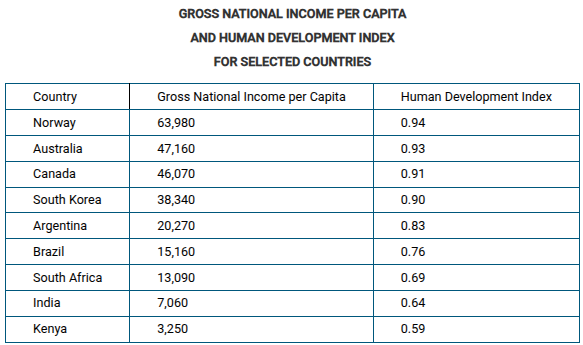
Based on the data in the table, which of the following statements explains a limitation of using gross national income per capita compared to the Human Development Index as a measure of development?
Using gross national income per capita as a measure of development puts too much importance on economic production as the sole measure of development.
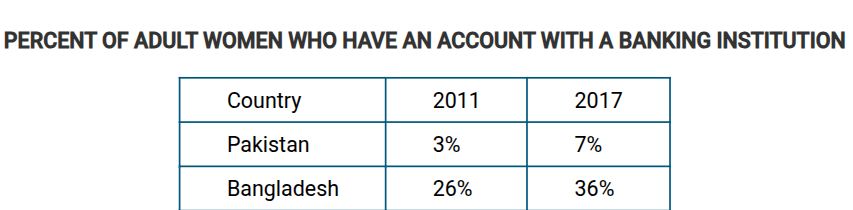
By tradition it is uncommon for women to hold personal bank accounts in Pakistan, and until the 1990s this was much the same in Bangladesh. Which of the following best explains the significant change in the percent of women with bank accounts in Bangladesh?
The increased access to microlending institutions for women, such as the Grameen Bank
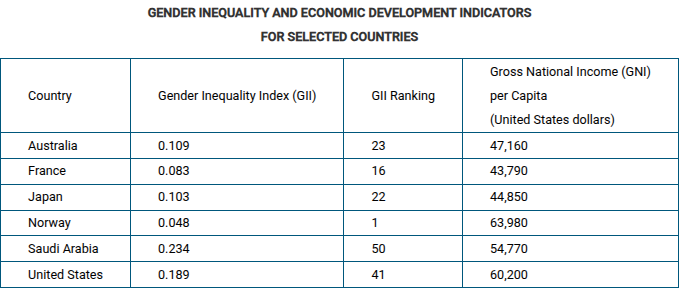
Which of the following statements explains the data relationship between the statistics shown in the table?
A high level of economic development does not guarantee that women will have an equitable position in society.
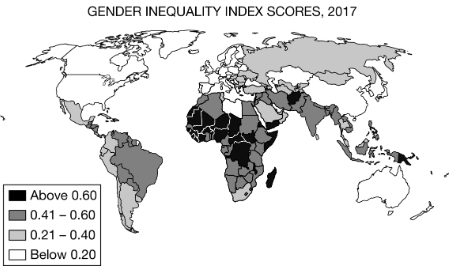
In a number of countries there remains significant inequality between men and women. Based on a comparison of the patterns on the map, which of the following statements draws an accurate conclusion?
Women in Libya have more equality with men than do women in other African countries.
Rostow’s stages of development can easily be applied to countries such as the United States and Japan, but not so easily to countries such as the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Bolivia, because the theory
places emphasis on developed nations having less developed nations to exploit for resources
Which of the following explains the most significant weakness of Wallerstein’s world system theory?
World system theory provides little explanation about how a country like South Korea could rise from a peripheral country to a core economy.
Which of the following best explains a political-economic weakness or limitation of Rostow’s stages of economic growth?
Rostow made the inaccurate assumption that all countries want modernization as defined in the model and would pass through the outlined stages in order.
Chile is able to grow and harvest grapes and strawberries in the months of October through April, while in the United States such fruit is harvested from April through October. The United States has a much larger manufacturing capacity and ships durable goods such as cars and trucks to Chile. These examples can best be explained by
the economic principle of comparative advantage
Which of the following explains how microlending policies can lead to interdependence in the world economy?
Increased funding opportunities for individuals in less developed countries have led to increased economic stability on a local level and trade opportunities with other countries.
In 2008, a debt crisis within the United States housing market triggered a global economic crisis. Which of the following best explains how this process occurred?
Because the global financial system is interconnected, banks in other countries were negatively affected by the crisis in the United States.
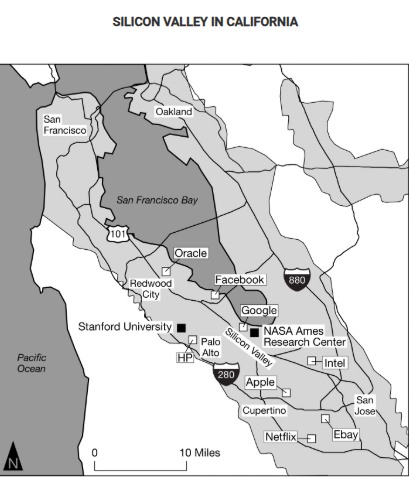
California’s Silicon Valley is an example of a high-technology region. Which of the following would best accompany the map shown to help explain the origins of this high-technology region?
A description of how the area’s research institutions, including Stanford University and the NASA Ames Research Center, served as growth poles for development

The image shows an open-pit coal mine in the United States. Which of the following best explains a limitation of the image in analyzing economic patterns of coal mining?
It does not indicate patterns of restructuring that have resulted in a decrease in coal mining jobs.