BSC 2011 - Chapter 32: Animal diversity
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Characteristics of Animals
• Multicellular
• Heterotrophic
• Cells do not have cell walls
• Most have nerves, muscles, and the capacity to move at some point in the life cycle
• Ability to reproduce sexually
• Specialized sensory structures and nervous system
• Have blastula stage during development
All animals have a ________ stage during development.
blastula
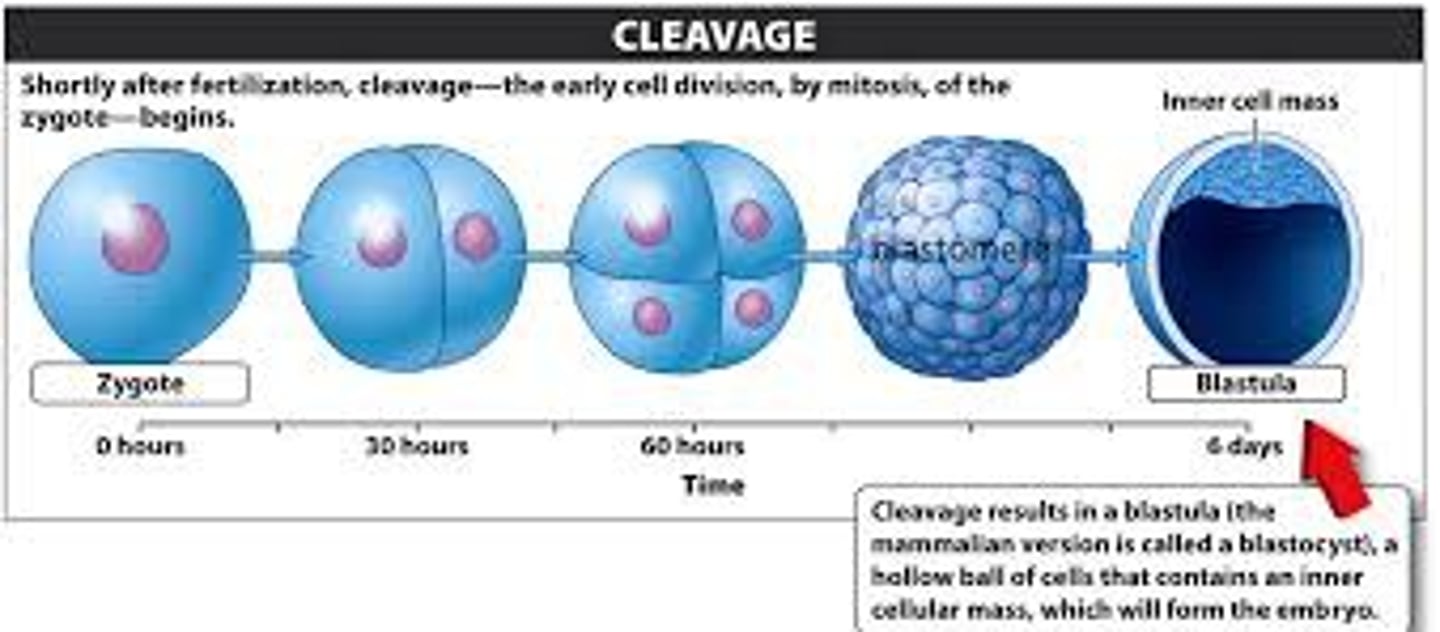
Blastula Stage
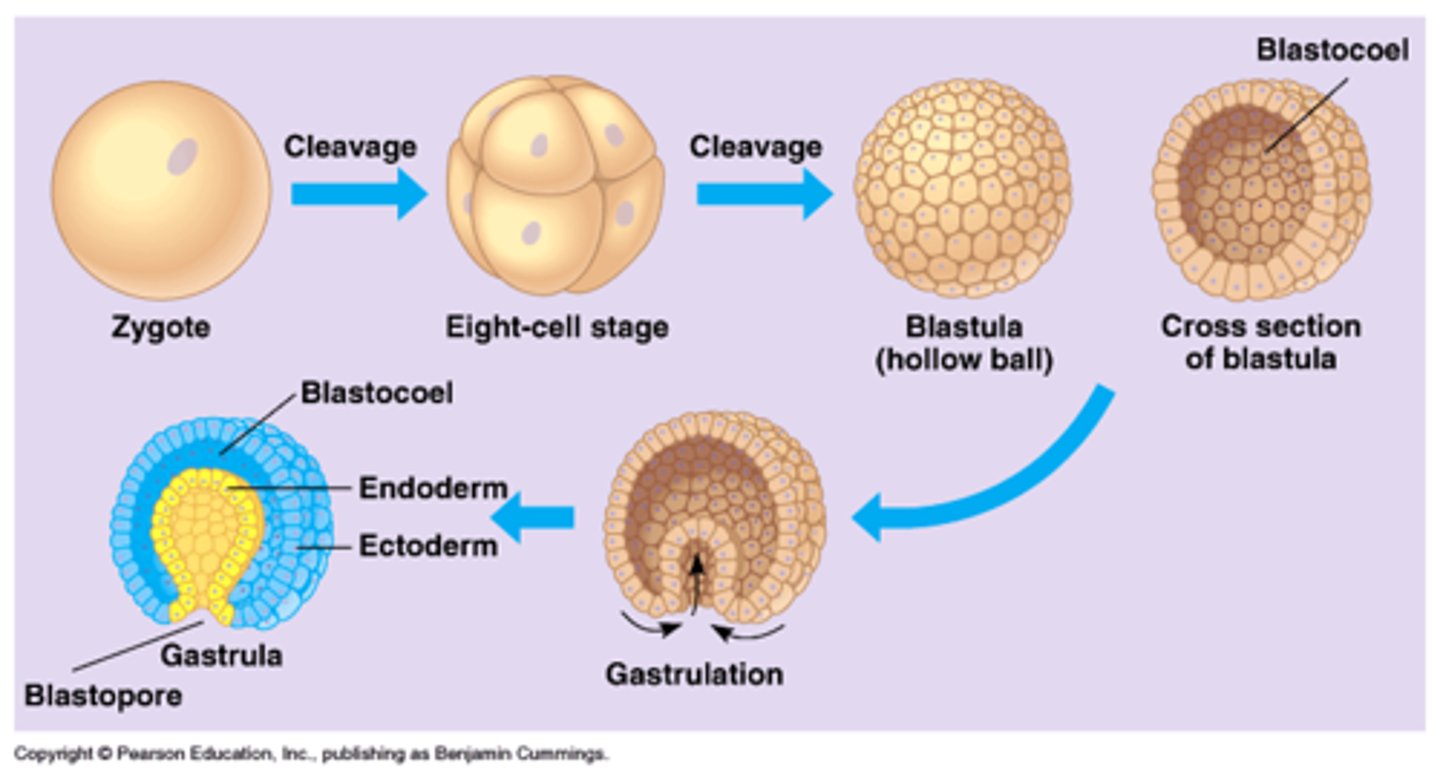
Cleavage
• The rapid series of mitotic cell divisions a zygote after fertilization
• Creates a ball of cells called a morula and eventually a blastula
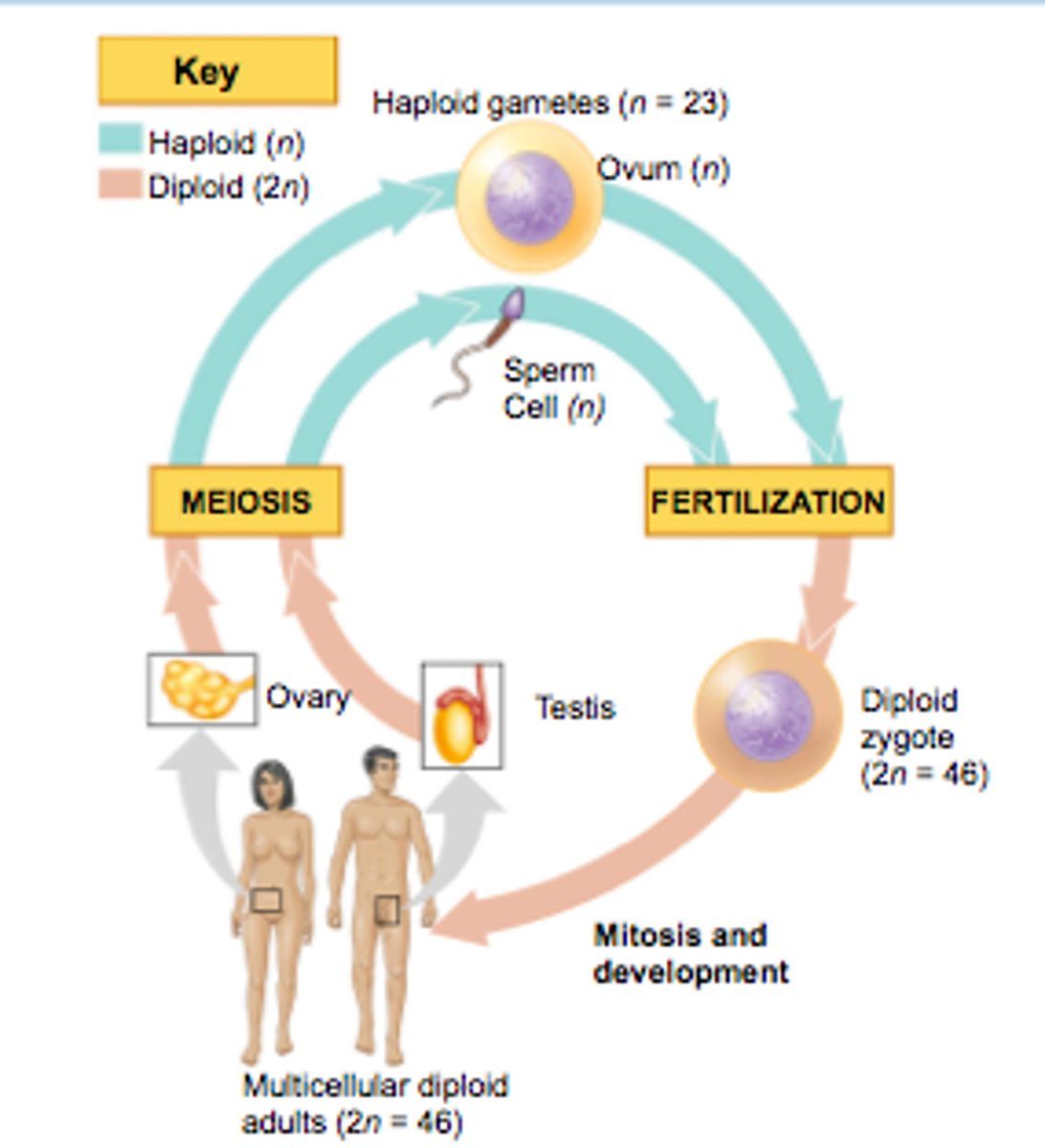
Animals display a _______ life cycle.
gametic
Gametic Life Cycle
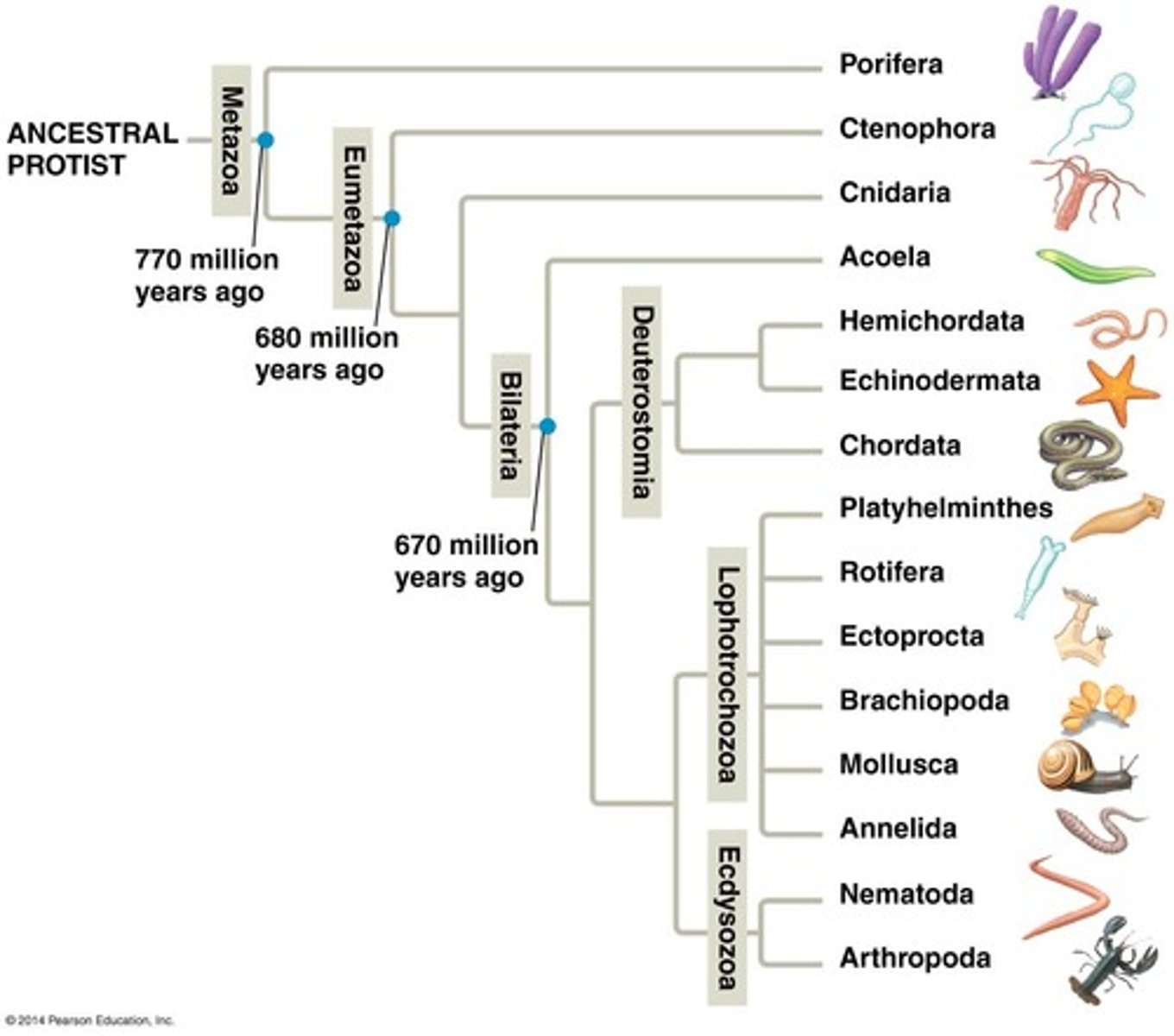
The Animal Kingdom is ____________.
monophyletic
Most likely ancestor of the Animal Kingdom is a ________ ___________ _______ similar to choanoflagellates.
colonial flagellated protist
Edicarian biota
The earliest fossils of macroscopic animals
Large increase in animal diversity during the ________ period.
Cambrian period (541-485 MYA)
Factors that largely increased animal diversity during the Cambrian period
1. Favorable environmental conditions (e.g. increased O2 and O3)
2. Evolution of Hox gene complex
3. Evolutionary "arms race" between predator and prey
Hox genes
A group of genes that control the basic body plan of an embryo
• Regulate development of entire segments of the body
• Each homeobox gene has a major responsibility for the development of a particular region in the body
• Allowed for new morphologies
Animals are usually diploid except for ______ phase.
gamete
Mesozoic Age
The age of dinosaurs
Cenozoic Age
The age of mammals

Animal classification is largely based on...
1. Presence or absence of different tissue types
2. Type of body symmetry
3. Patterns of embryonic development
Bilateral animals
• Has a dorsal (top) side
• Has a ventral (bottom) side
• Has a right and left side
• Has anterior (head) and posterior (tail) ends
• Has cephalization (the development of a head)
Tissues
Collections of specialized cells isolated from other tissues by membranes
Porifera (Sponges)
• No symmetry
• No tissues
Eumetazoa
• Radial or bilateral symmetry
• More than one type of tissue that develop from 2 or 3 germ layers
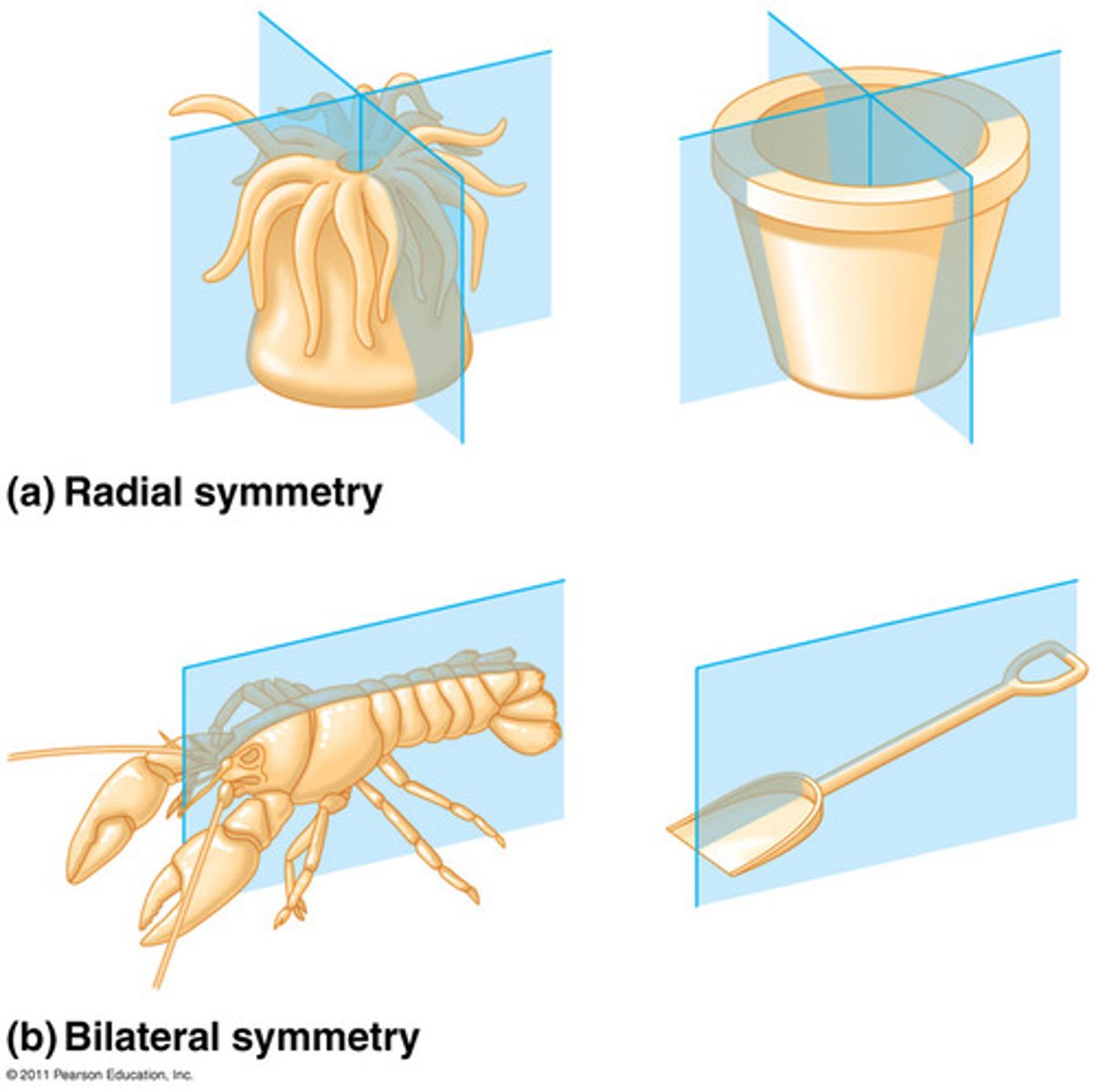
Radial animals
• Have radial symmetry
• Have two germ layers (diploblastic)
• Develop tissues but no organs
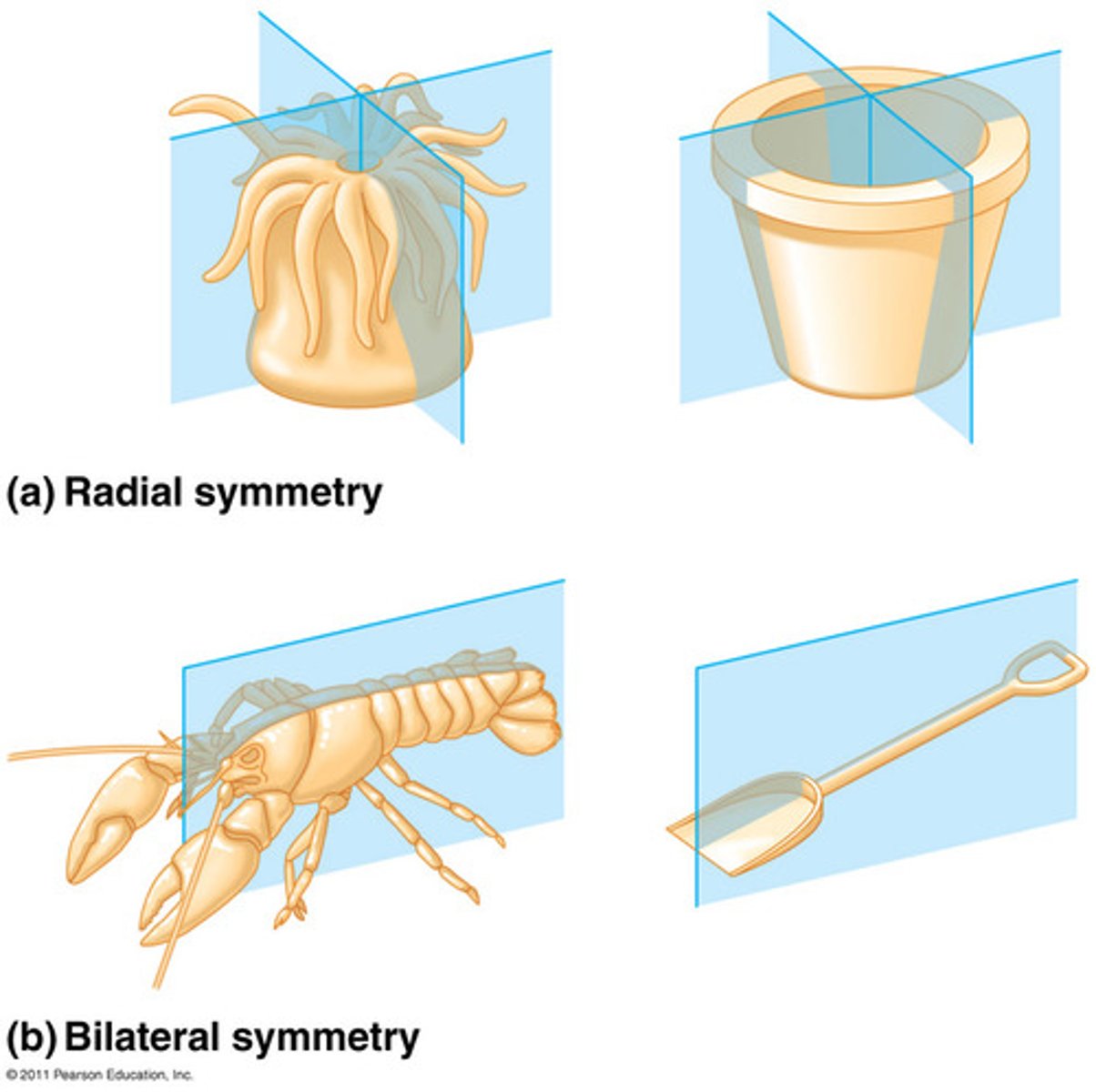
Bilateral animals
• Have bilateral symmetry
• Have three germ layers (triploblastic)
• Develop tissues and organs
• Most possess a body cavity (coelom)
Acoelomates
Triploblastic animals that lack a true body cavity/coelom
Coelom
A fluid-filled body cavity that is completely lined by mesoderm (the middle tissue layer of an embryo)

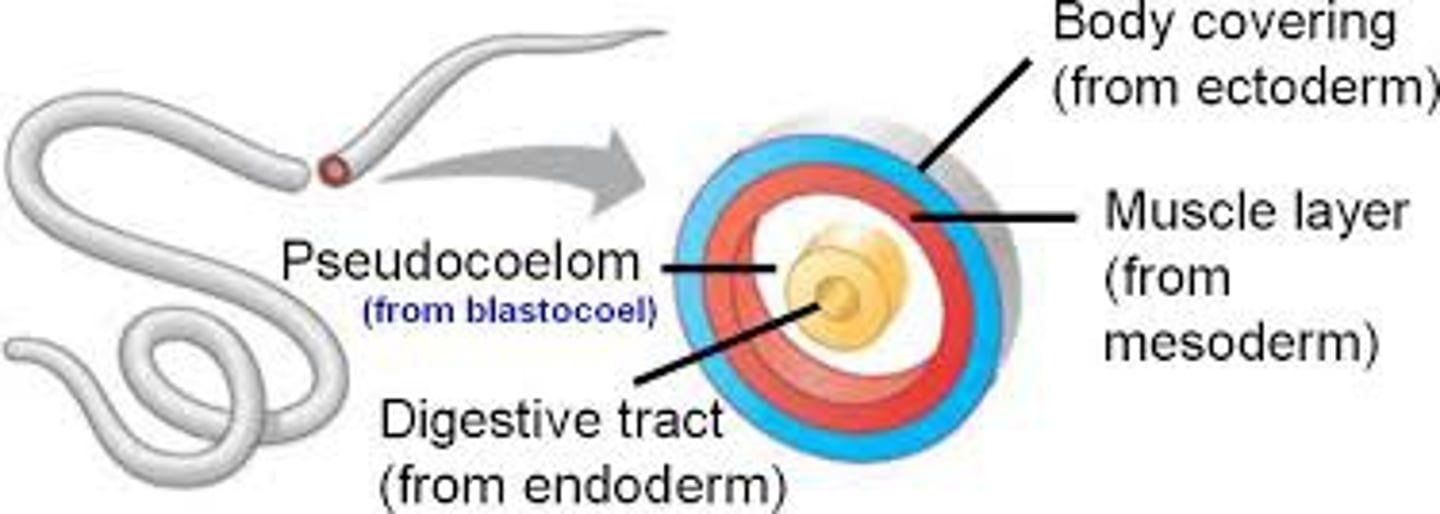
Pseudocoelom
• Forms between the mesoderm and endoderm layers
• Only partially lined by mesoderm
• Functions like a true coelom
Protosome
• Blastopore forms the mouth
• Cleavage is spiral
• Cleavage determinate --> Cell fate is set
Deuterostome
• Blastopore forms the anus
• Cleavage is radial
• Cleavage indeterminate --> Cell fate is flexible or totipotent
Other methods of animal classification
• Presence of exoskeleton
• Development of notochord
• Presence or absence of segmentation (traced to changes in Hox genes)
Modern animal phylogeny is based on __________ and ________ data.
morphology; molecular data
Ecdysozoa
• Named for ecdysis (molting)
• All secrete a non-living cuticle
• Strongly supported as a separate clade by molecular evidence
Lophotrochozoa
• Have a trochophorelarva or a lophophore
• Lophophore: horseshoe-shaped crown of tentacles used in feeding
• Trochophore larvae have a band of cilia
Animal numbers
• ~1.3 million species identified
• Thought to be up 3-30 million extant species