biological molecules
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
how is the small intestine adapted for its function?
large surface area provided by villi and microvilli
lots of capillaries
thin wall - short diffusion distance
lacteals -absorption of fats
what is the role of the rectum?
stores faeces
what is ingestion?
when food enters the mouth
what is absorption?
the movement of soluble food through the wall of the small intestine into the blood stream
what is assimilation?
when small food molecules are used to build large ones
what is excretion?
the removal of waste products of metabolism
what is egestion?
the removal of faeces from the anus
what is the word equation for photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide + water (+light energy0 —> oxygen and glucose
what is the balanced symbol equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2+6H20 —> 6O2 + C6H12O6
what is a limiting factor?
factor in a reaction which is in shortest supply
lack of this factor is the reason why the rate of reaction no longer increases
what are the limiting factors of photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide
light intensity
temperature
increasing any of the above will increase the rate of photosynthesis until another factor becomes limiting
why is the rate of photosynthesis low in the morning?
temperature is the limiting factor
low temperatures inhibit enzyme activitty
carbon dioxide levels are high
why is the rate of photosynthesis high at midday?
high temp maximises enzyme activity
co2 is the limiting factor as its in the shortest supply
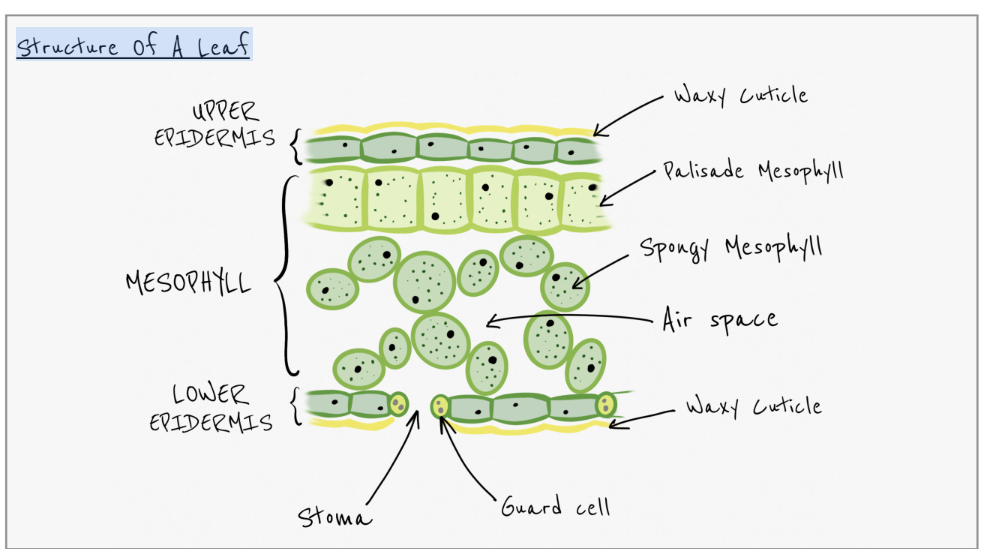
how is the leaf adapted to their role?
thin and broad (large surface area)
why do chloroplasts appear green?
chlorophyll absorbs red/blue light
reflects green light
why do different coloured lights affect the rate of photosynthesis?
green is reflected (not absorbed) = low rate of photosynthesis
blue and red is absorbed - results in faster rate of photosynthesis
what does the plant use glucose for?
making cellulose cell walls
making proteins and DNA
making starch for storage
making sucrose for transport
what is the role of nitrate in plants?
making amino acids and proteins
making DNA
growth
deficiency symptom = stunted growth
what is the role of magnesium ions in plants?
making chlorophyll
deficiency symptom = yellow leaves
how is the waxy cuticle adapted for its role?
prevents evaporation of water and stops pathogen entry
how is th3 upper epidermis adapted for its role?
transparent to allow light to enter the leaf
how is the palisade mesophyll adapted for its role?
contains lots of chloroplasts for photosynthesis
how are the air spaces in spongy mesophyll adapted for their role?
allow gases to diffuse
how is the xylem adapted for its role?
allows entry of water and mineral ions by transpiration stream
how are the guard cells adapted for its role?
control opening and closure of stomata
how is the stomata adapted for its role?
allow co2 t0 enter, o and h20 to leave