AP Bio Unit 7 || Population Genetics and Hardy Weinberg
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Gene Pool
Genetic Makeup of a population
Microevolution
Small scale genetic changes of a population, driven by random occurences
Random Occurences in mircoevolution
Mutations, genetic drift, gene flow/migration, and natural selection
Mutations
Mutations result in genetic variation in organisms
forms new allels/phenotypes
faster reproduction rate = more mutations in the gene pool
Genetic Drift
Chance events that cause changes in allele frequencies from one generation to the next
2 types of genetic drift
bottleneck and founder effect
Bottleneck effect
Occurs when a population encounters a non-selective disaster (floods, famine, fires, ect.), drastically reducing genetic diversity. The surviving gene pool may no longer represent the original population.
Founder Effect
Occurs when a few individuals of a population become isolated from the main population. A new gene pool is established and it is not representative of the main population.
Gene Flow
The movement of allels between populations due to migration of individuals or gametes.
Relative Fitness
Number of offspring an individual produces compared to the average number of offspring
Reproductive success is measured by ______ ______.
Relative fitness
Three modes of natural selection
Directional selection
Stabilizing Selection
Disruptive selection
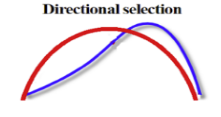
Directional selection
Selection towards one extreme phenotype
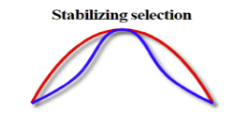
Stabilizing selection
Selection towards the mean and against extreme phenotypes
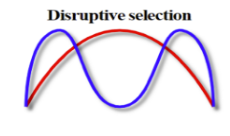
Disruptive selection
Selection against the mean toward extreme phenotypes
Sexual selection
A form of natural selection where traits are favored because they increase an individual’s chances of mating rather than survival. (Peacock’s tail).
Hardy Weinberg Equillibrium
Asses if natural selection or other factors are acting on a population’s evolution at a locus; determines what the allele frequencies would be if the population was NOT evolving. If the calculated values match the actual values, then the population is not evolving.
Five conditions must be met to establish Hardy Weinberg Equillibrium
No mutations: No new alleles added to the gene pool
Random Mating: Individuals pair randomly without any preference for specific traits
No natural selection: All individuals have an equal chance of surviving and reproducing, regardless of their traits
Large population size: The population is large enough to prevent genetic drift (random changes in allele frequencies)
No gene flow
Hardy-Weinber Equation
p² + 2pq + q² = 1
p² = percentage of homozygous dominant individuals (AA)
2pq = percentage of the heterozygous genotype (Aa)
q² = percentage of the homozygous recessive genotype (aa)
p + q = 1
p is the frequency of the dominant allele
q is the prequency of the recessive allele
Dogs ___ to assert their ____.
PEE … DOMINANCE