Calorimetry - Redox rxn
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Temperature Equilibrium
It is the final temperature that objects in contact will reach when they are in thermal equilibrium
Formulas for Temperature Equilibrium
Q꜀ₒₒₗ = - Qₕₒₜ
M꜀Cp꜀ (Tf - Ti)꜀ = - MₕCpₕ(Tf-Ti)ₕ
Calorimetry
The science of the accurate measurements of amounts of heat and the accompanying temperature changes of an observed body when it releases or absorbs heat
The measurements of the amounts of heat transferred to or released from a substance underlying physical or chemical process
Calorimeters
Calibrated Devices
Exothermic Reaction
The heat produced by the reaction is absorbed by the solution, which increases its temperature.
Endothermic Reaction
The heat required is absorbed from the solution, which decreases temperature
Constant-pressure calorimeter/ coffee-cup calorimeter
a simple device used to measure the heat of a chemical reaction at constant pressure
two nested styrofoams
frequently used in determining the specific heat of solids or in studying reactions in aqueous solution.
the pressure inside the calorimeter is basically equal to the pressure of the surroundings.
Formulas for Coffee-cup Calorimeter
Qᵣₓₙ + Qₛₒₗᵤₜᵢₒₙ = 0
Qᵣₓₙ = - Qₛₒₗᵤₜᵢₒₙ
Qₘₑₜₐₗ = - Qᵥᵥₐₜₑᵣ
Q = MCpΔT
Constant-Volume Calorimeter/ Bomb Calorimeter
is a type of calorimeter that operates at a constant volume
Formulas for Bomb calorimeter
Qᵣₓₙ = - (Q꜀ₐₗ + Qᵥᵥₐₜₑᵣ )
Q = MCpΔT
Q꜀ₐₗ = C꜀ₐₗ ΔT
Ccal
heat capacity of the calorimeter
Enthalpy
Chemical Energy involved in the heat flow of chemical reaction between the reactants and products
The change in enthalpy (ΔH)
is the amount of heat flow in a system for reactions carried out at constant pressure.
Enthalpy of Combustion
KJ/mol
Redox Reaction
Comes from the two words Reduction - Oxidation reactions
Cations
is a positively charged ion, formed when an atom loses one or more electrons
Atomic number
Represents the number of protons in an atom
Anion
is a negatively charged ion, Formed when an atom gains one or more electrons
Redox Reactions
is a type of chemical reaction wherein there is a transfer of electrons from one substance to another causing a change in their oxidation states.
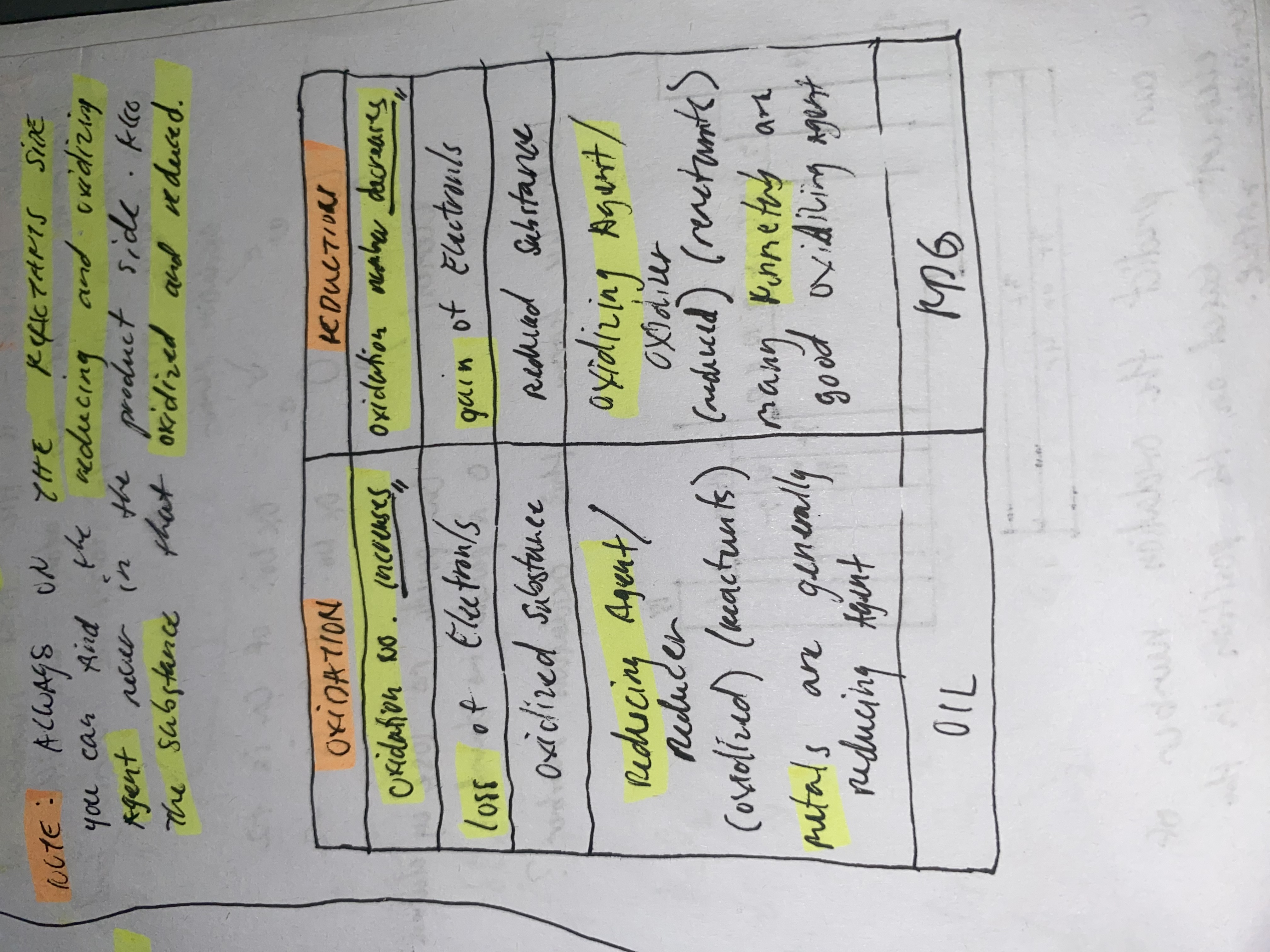
Reduction
is the gain of electrons in chemical reactions
more negatively charged
Decreases oxidation number
Oxidation
is the loss of electrons in a chemical reaction
more positively charged
Increases oxidation number
Reducing Agent
oxidized substance
donates electrons
Oxidizing agent
reduced substance
accepts electon
Always in Reactants side
Where can we find the reducing/oxidizing agent as well as the oxidized/reduced substance?
Memorize
Oxidation number
is the total number of electrons that an atom will either gain or lose in order to form a chemical bond with another atom.
metals
cations
tends to lost electrons to become positively charged
nonmetals
anions
tends to gain electrons to become negatively charged
Group 18
noble gas have zero oxidation number