Oceanography (units 1 and 2)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What did Kepler discover?
Planetary motion
What did Galileo discover?
Mass and acceleration
What did Newton discover?
The laws of gravity, and calculus
What ship first measured the depths of the ocean?
The Challenger (1872)
What does SONAR stand for?
SOund NAvigation Ranging
What was said by Carl Sagan?
“The cosmos is all there is, all there ever was, and all there ever will be.”
What is the Principle of Horizontality?
Beds that are made when a river deposits material will always be horizontal
How are crossbeds made?
As ripple marks form with the current, the pattern they make as they move are called crossbeds
Explain Fire Hose logic
A liquid will travel through a smaller opening faster than a bigger opening to maintain a constant speed
What makes metamorphic rocks hard?
Increased heat and pressure
What are striations?
Parallel scratches on mountains caused by glaciers
What does time have to do with the stability of an element?
The less time it takes for an element to go through radioactivity, the less stable it will be.
When did the Precambrian period occur?
4.6 BILLION years ago
When did the Paleozoic period occur?
541 MILLION years ago
When did the Mesozoic period occur?
252 MILLION years ago
When did the Cenozoic period occur?
66 MILLION years ago
What is the Inner Core made of?
Solid metal (iron and nickel)
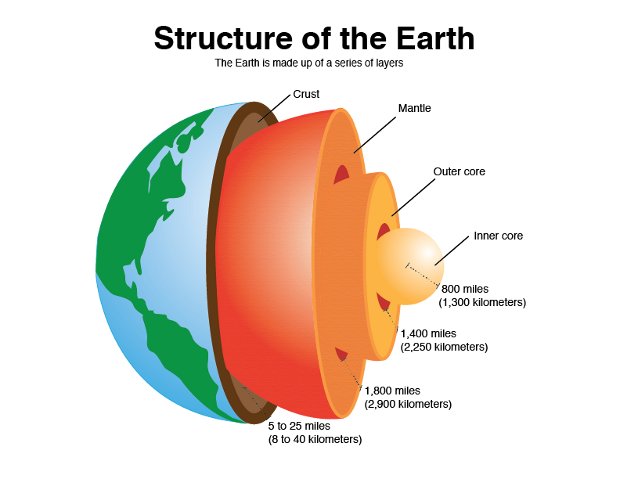
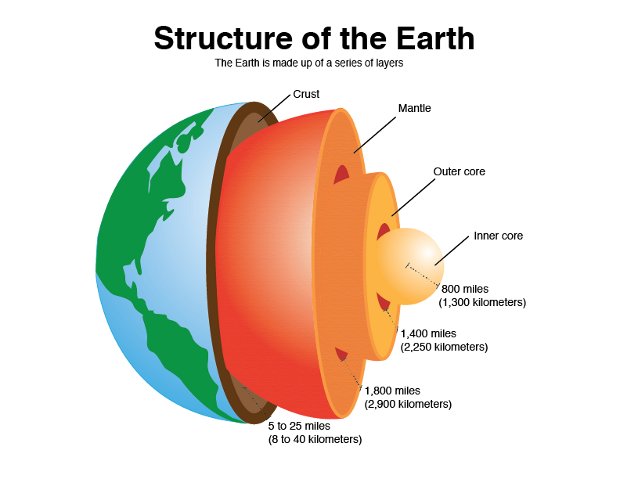
What is the Outer Core made of?
Liquid metal (iron and nickel)
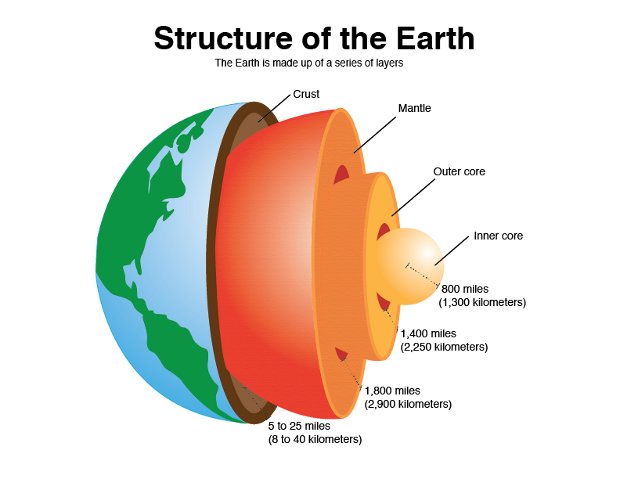
What is the Mantle made of?
iron silicon and oxygen (very ductile)
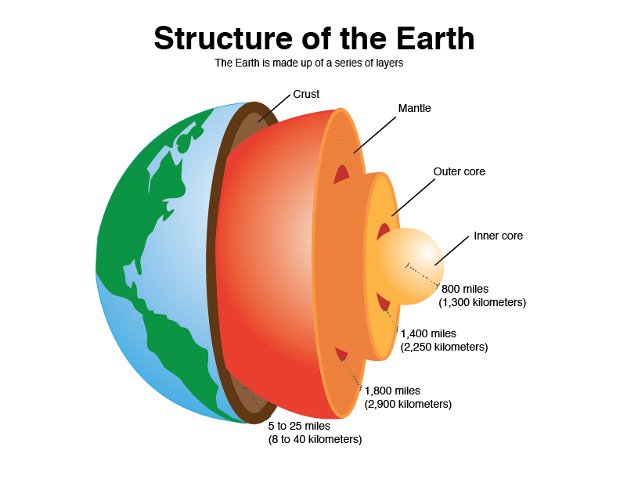
What is the Crust made of?
elements and minerals (low density)
What is isostacy?
Isostasy is the equilibrium of the Earth's crust, where pieces of the crust float on the mantle (balancing out weight in water)
***What is the Cork Concept?***
Things high in density sink
***What is the Glass Blower Concept?***
Hot things bend, cold things snap
What is the Oceanic Lithosphere made of?
Basalt- dark-colored, thin, fine-grained, dense igneous
What is the Continental Lithosphere made of?
Granite- light-colored, thick, low density, coarse, igneous
Explain ocean basins
An oceanic lithosphere is thinner and higher in density than continental, so it sinks until its weight has been displaced (isostacy)
Name evidence for Continental Drift
the countries fit, glacial deposits, fossil assimilation, rock types matching
What was Continental drift renamed as in 1960?
Sea-floor spreading
Name evidence for Sea-Floor Spreading
Mid-Oceanic Ridge, earthquake patterns, trenches and volcanos
How is Oceanic Lithosphere created?
Deep earthquakes ram material into the ground→liquid rock forms creating→volanos that make basalt
What are Hot Spots?
Magma Chambers in the Lithosphere that melt into the Asthenosphere, creating hot rock that comes up through a volcano
What happens to a magma chamber as the Lithosphere moves?
The chamber stays still but the volcano moves on the lithosphere, leading the chamber making a new volcano
What is Convection Current?
density driven current

What is Slab Pull?
gravity pulling down, splitting the Earth, digging trenches further
Name examples of convergent plate boundaries
Pacific, Nasca, South American, and North American plate boundaries
If an earthquake is hot, will it be powerful or weak?
weak; glass blower concept
***SuperBall concept***
A hot temperature correlates to fast molecular energy
As density decreases, what does volume do?
Increase
What does volcanism do for the M.O.R?
It increases volume and lowers the density causing magma to rise
How deep is the oceanic lithosphere?
70km
What does litho stand mean?
rock
what does astheno stand mean?
weak
what does meta stand for?
change
what does morphic mean?
shape