Oxygen Transport
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Explain the relationship between diffusion and blood supply ?
High to low concentration, blood carries molecules / particle away, maintain concentration gradient
Haemoglobins
Protein with a quaternary structure
Each Haem group contain a ferrous ion ( containing metal )
What ion is contain in the haem group ?
Iron Fe 2+
What molecule is combine with an iron ion ?
each iron ion can combine with 1 oxygen molecule O2
What is the primary structure ?
Amino acid sequences in the four polypeptide chains
What is the secondary structure ?
Polypeptide chains coiled into a helix
What is the tertiary structure ?
Polypeptide chains are folded into a unique shape ) makes it able too carry oxygen )
What is the quaternary structure?
The 4 chains linked together . each chain is associated with a haem group.
Each molecule of haemoglobin can carry how many molecules of oxygen ?
4 molecules of oxygen = 8 total atoms
What does the protein structure determines ?
The O2 ( oxygen ) affinity
What do we called the molecule when oxygen binds to haemoglobin ?
Oxyhaemoglobin
What is the process call when the o2 and haemoglobin are binding ?
Loading or association
Where in the body does the binding of O2 and haemoglobin occurs ?
Alveoli/ other gas exchange surface
What is the process call when the O2 releases ?
Unloading or disassociation
Where in the body does the releasing of O2 occurs ?
It occurs at the respiring body tissues
What is the role of haemoglobin ?
To be efficient at transporting oxygen, the haemoglobin must :
Readily associate with O2 at the gas exchange surface
Readily dissociate from oxygen at the respiring tissues
How does the haemoglobin changes from deoxygenated to oxygenated ?
Haemoglobin changes its oxygen affinity under different conditions.
It does this by changing shape.
In the presence of CO2 , Hb binds more loosely to oxygen.
Will more readily dissociate with it.
What is step 1 of oxygen transport?
The 1 st O2 does not bind easily to the Hb. This is cuz the 4 polypeptide units are closely united.
Therefore, at low O2 con.c ( low partial pressure pO2 ) only little O2 binds to haemoglobin.
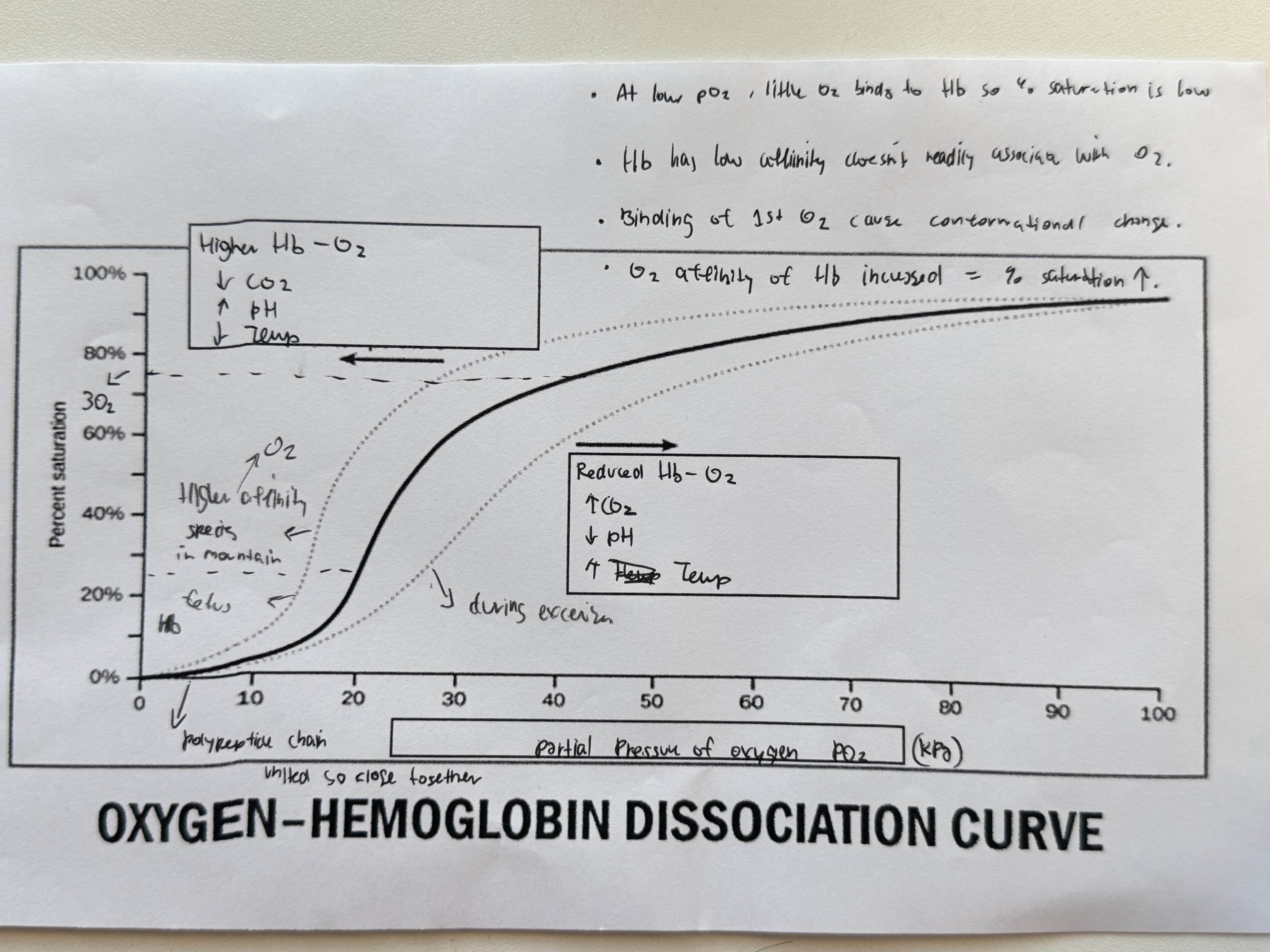
What does the start of the graphs show ?
At low partial pressure of O2 , little O2 binds to Hb , so % of saturation is low.
Hb has a low affinity / does not readily associate with O2
What is step 2 of oxygen transport?
Binding of the first oxygen changes the quaternary structure of the Hb (a conformational change), making it easier for further oxygen molecules to bind.
The polypeptide chains become less tightly bonded and the haem groups are uncovered.
Therefore, only a small increase in oxygen partial pressure is needed for the second and third oxygens to bind.
This is called positive cooperativity (the curve steepens).
What is step 3 of oxygen transport?
Binding of the 1st O2 cause conformational change.
Oxygen affinity of Hb increased , so % saturation increases
What is step 4 of oxygen transport?
After binding of the third oxygen molecule, it is harder for the fourth to bind due to probability - three sites are already occupied, so it is less likely that an oxygen molecule will find a free site to bind to. The curve therefore flattens/ plateaus.
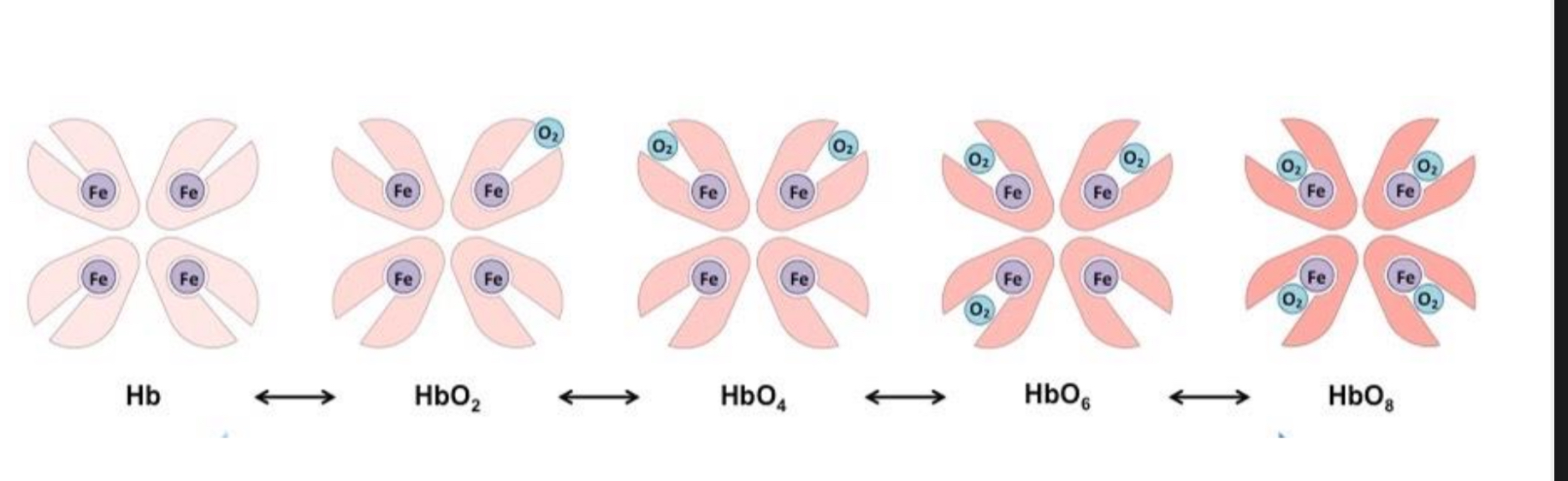
The process of oxygen transportation