Vocabulary & Radioactive Decay
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is an isotope?
Atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of
neutrons.
What determines nuclear stability?
The ratio of neutrons to protons (n:p ratio). Small nuclei are stable near 1:1, while larger
nuclei need more neutrons to offset proton-proton repulsion.
Why do isotopes undergo radioactive decay?
To achieve a more stable neutron-to-proton ratio when the nucleus lies outside the band of
stability.
What force holds the nucleus together?
The strong nuclear force, which counteracts proton-proton repulsion.
How many stable isotopes exist naturally on Earth?
About 250, all with atomic numbers below lead (Pb). Beyond Pb, all isotopes are radioactive.
What is fission?
The splitting of a large unstable nucleus into smaller nuclei, releasing large amounts of
energy.
What is fusion?
The combining of small nuclei into a larger one in a highly exothermic process, as occurs in
stars.
What is radioactive decay?
The transformation of an unstable atomic nucleus into a more stable one through the emission
of radiation.
Rank the typical energies involved in nuclear, chemical, and intermolecular processes.
Nuclear reactions: millions to billions of kJ/mol; chemical bonds: hundreds to thousands of
kJ/mol; intermolecular forces: tens of kJ/mol.
What type of kinetics describes radioactive decay?
First-order kinetics — the decay rate depends only on the amount of the radioactive nucleus
present.
What is half-life?
The time required for half of a sample of a radioactive isotope to decay.
After 3 half-lives, what fraction of the original sample remains?
One-eighth (12.5%).
What occurs during alpha decay?
The nucleus emits a helium-4 particle (two protons and two neutrons).
Effect: Atomic number decreases by 2, mass number decreases by 4.
What occurs during beta-minus decay?
A neutron is converted into a proton, and an electron (β⁻) is emitted.
Effect: Atomic number increases by 1; mass number unchanged.
What occurs during beta-plus decay (positron emission)?
A proton is converted into a neutron, emitting a positron (β⁺) and a neutrino.
Effect: Atomic number decreases by 1; mass number unchanged.
What occurs during gamma decay?
The nucleus releases excess energy as a photon (γ-ray) without changing its atomic or mass
numbers.
Which type of decay has the highest penetration power?
Gamma decay.
²³⁸₉₂U →
Alpha Decay (loss of a helium nucleus)
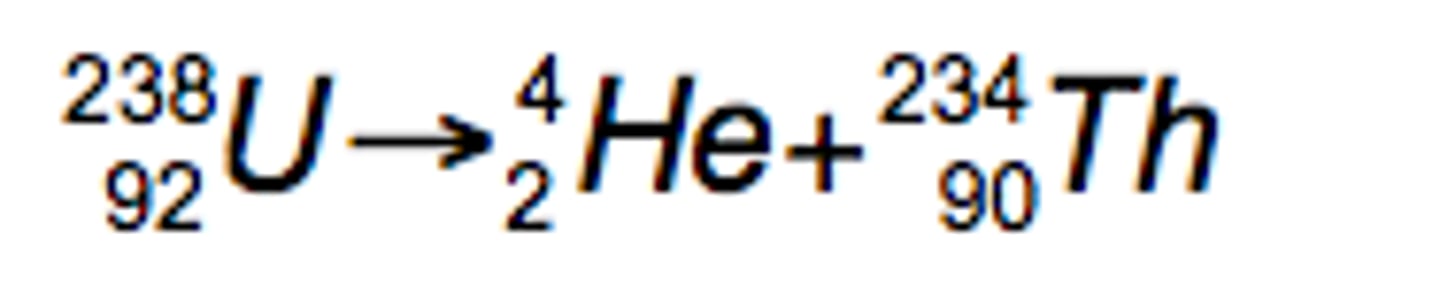
Strontium-89 (mass number 89, atomic number 38) decays into yttrium-89 (mass number 89, atomic number 39) and an electron.
Beta-minus decay (neutron converted to proton, electron emitted)
Sodium-22 (mass number 22, atomic number 11) decays into neon-22 (mass number 22, atomic number 10) and a positron
Beta-plus decay (positron emission)
Cobalt-60 (mass number 60, atomic number 27) decays into nickel-60 (mass number 60, atomic number 28) and emits a gamma photon
Gamma decay (photon emission, no change in mass or atomic number)
Polonium-210 (mass number 210, atomic number 84) decays into lead-206 (mass number 206, atomic number 82) and a helium-4 nucleus
Alpha decay
A radioisotope has a half-life of 12 days. If you start with 640 mg, how much remains after 24 days?
Two half-lives → 160 mg remain
A radioisotope has a half-life of 5 hours. If you start with 800 g, how much remains after 10 hours?
Two half lives → 200g remain
A substance with a half-life of 4 days starts at 100 g. How much remains after 8 days?
25 g
A sample of ¹⁴C with a half-life of 5730 years decays for 11,460 years. What fraction remains?
1/4 (25%)
If 25 g of a radioisotope remain after 3 half-lives, what was the original mass?
25 g × 2³ = 200 g