AP Psychology semester one exam
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
161 Terms
empiricism
the view that knowledge originates in experience and that science should rely on observation and experimentation
structuralism
An early school of psychology that used introspection to explore the structural elements of the human mind. introduced by Edward Titchener
Functionalism
a school of psychology that focused on how our mental and behavioral processes function and how they enable us to adapt, survive, and flourish. Introduced by William James
Behaviorism
the view that psychology (1) should be an objective science that (2) studies behavior without reference to mental processes. most researcher psychologists today agree with (1) but not (2)
Humanistic Psychology
historically significant perspective that emphasized the growth potential of healthy people and the individual’s potential for personal growth
Cognitive neuroscience
the interdisciplinary study of the brain activity linked with cognition (thinking, memory, language etc)
psychology
the science of behavior and mental processes of people and organisms. Wilhelm Wundt established the first psychology lab in Leipzig, Germany.
psychometric
the scientific study of the measurement of human abilities, attitudes, and traits
developmental psychology
the scientific study of physical, cognitive, and social change throughout lifespan
Socrates and Plato
the mind is separable from the body and continues after the body dies. Knowledge is innate
Aristotle
derived principles from careful observations. Knowledge is not preexisting. It grows from experiences stored in our memories.Rene
Rene Descartes
agreed with Socrates and PLato about the existence of innate ideas and mind’s
William Wundt
established the first psych lab in Germany
Edward Titchener
Cornell professor who introduced the school of structuralism by using introspection to search for the mind’s structural elements
William James
Harvard philosopher-psychologist who introduced the school of functionalism by considering the functions of our thoughts and feelings. Wrote the textbook Principles of Psychology and tutored Mary Calkins
Mary Calkins
student of William James who became the first female president of the American Psychological Association. She also became a pioneering memory researcher.
Margaret Floy Washburn
became the first woman to receive a PhD in Psychology. She also studied animal behavior
Max Wertheimer
developed the Gestalt perspective
Behavioral Perspective
school of thought based on how we learn observable responses and experiences. Key people include John Watson & B. F. Skinner
Psychoanalytic/Psychodynamic Perspective
school of thought based on how behavior springs from unconscious drives and conflicts. Key person is Sigmund FreudS
Humanistic Perspective
school of thought based on how we strive for personal growth. Key people include Carl Rogers & Abraham Maslow
Cognitive Perspective
school of thought based on how we encode, process, store, and retrieve information. Key person is Jean Piaget
Biological/Neuroscience Perspective
school of thought based on how the body and brain enable emotions, memories, and sensory experiences
Evolutionary Perspective
the school of thought based on how evolution influences behavior. Key person is CHarles Darwin
Social-Cultural Perspective
school of thought based on how behavior and thinking vary across situations and cultures. Key person is Alfred Bandura
Gestalt Perspective
the school of thought based on the “organized whole”. Key people include Hohler, Wertheimer, and Koftka
case study
an observation technique in which one person is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
Longitudinal Study
studying a person or event over a long period of time (ex. the effetcs of medications on kids)
Cross sectional study
a study in which people of different ages a
Ex-post facto study
studying something after it happened naturally. look at the effect, seek the cause. (ex. birth defects)
operational definiton
specifically names the operations (steps or procedures) that the experimenter must use to control or measure the variables in the experiment. This allows the experiment to be replicated
Replication
repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding extends to other participants and circumstances
confounding variable
a factor other than the IV that might produce an effect in an experiment (ex. the temperature of the room, external noises)
Mode
the measure of central tendency that is most frequently occurring score(s) in a distribution
Mean
the measure of central tendency that is the arithmetic average of a distribution
Median
the measure of central tendency that is the middle score in a distribution (falls at thee 50th percentile). Half the scores are above it, half the scores are below it
Range
the measure of variation that is the difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution. Expressed as a singular number
standard deviation
a computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score
normal curve (normal distribution)
a symmetrical, bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many types of data; most scores fall near the mean (68% fall within one standard deviaton of it) and fewer near the extremes
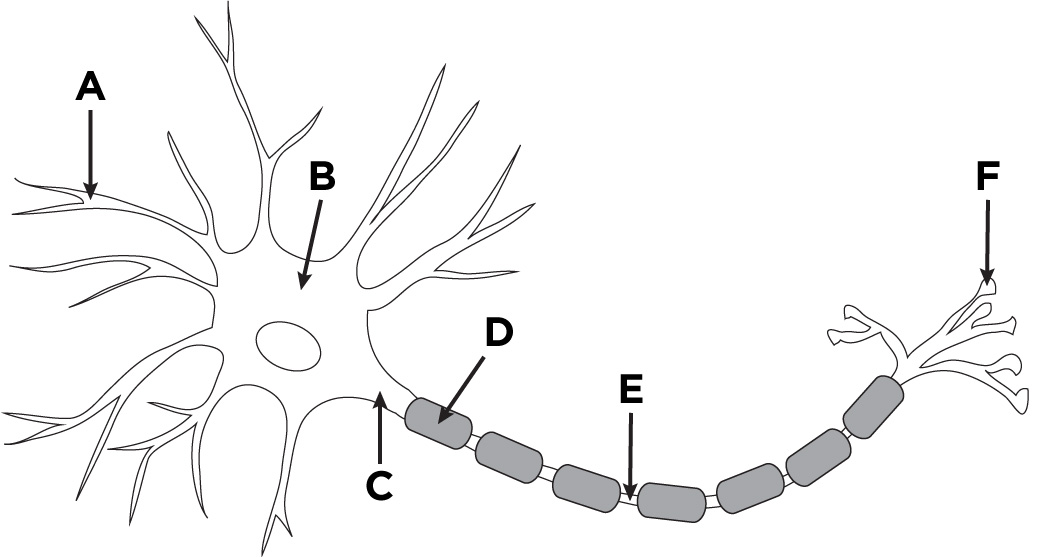
dendrites
what is A?

cell body/soma
what is B?
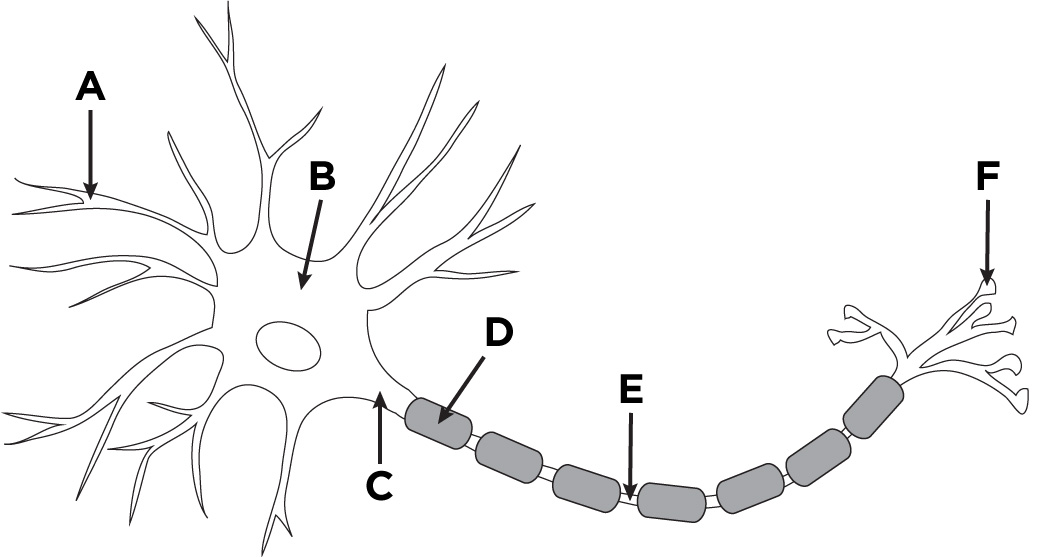
axon
what is C?
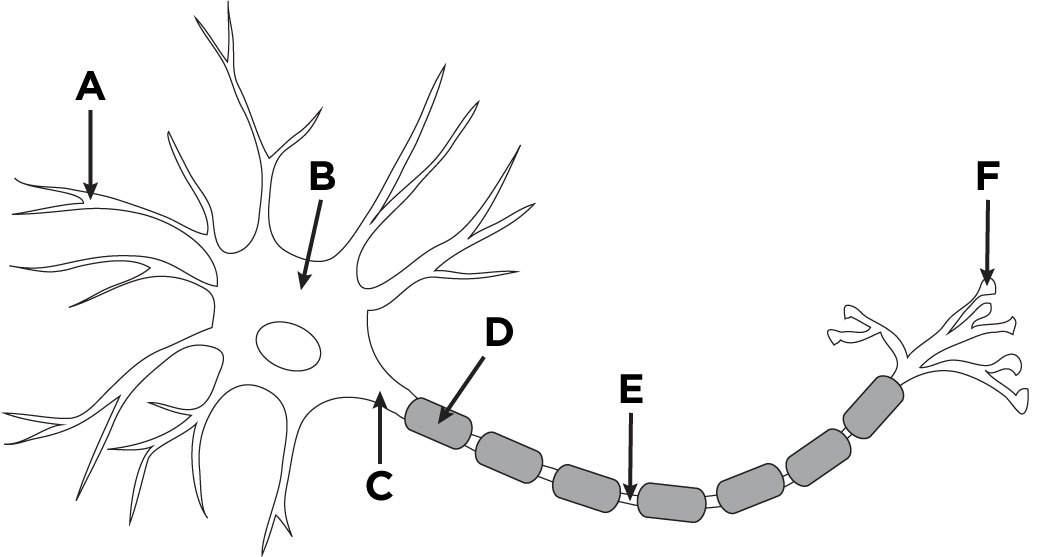
myelin sheath
what is D?
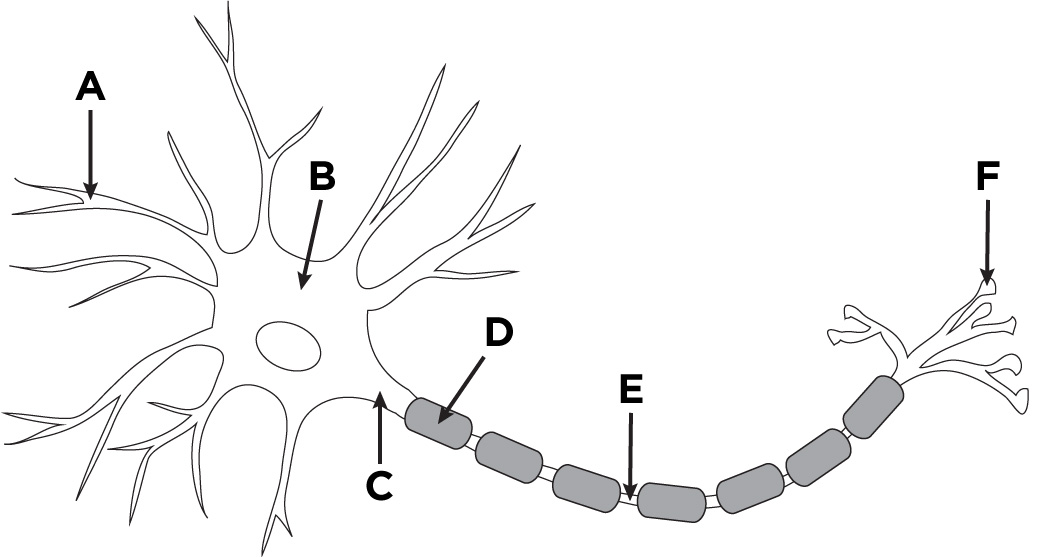
Nodes of Ranvier
what is E?
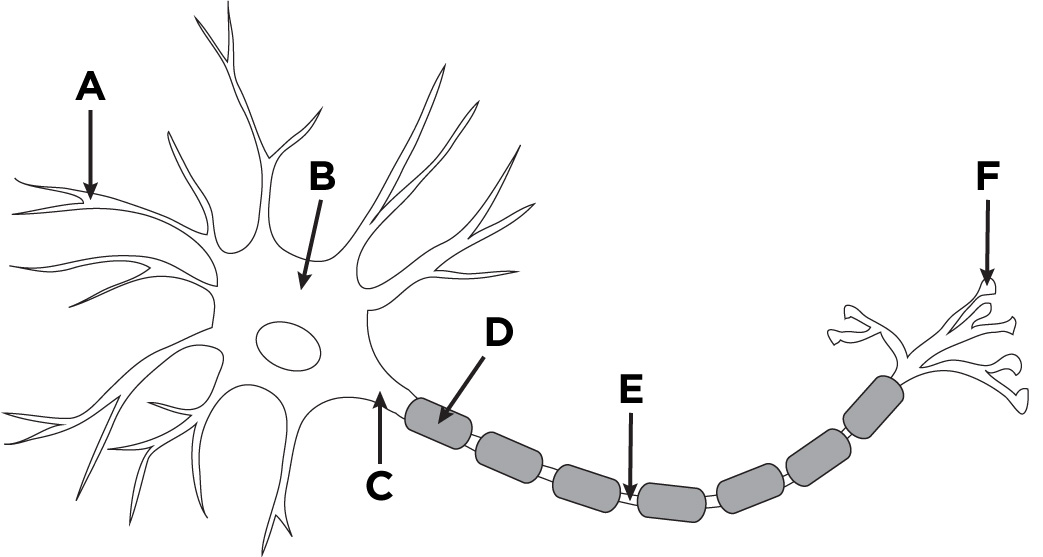
terminal branches of axon
what is F?