Structure 1.4 - 1.5 definitions review (IB HL Chemistry)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Relative Atomic Mass
The mass of an atom is measured on a relative scale
• The reference point of the scale is the carbon-12 isotope. It is
considered the standard with 12 units.
• The relative atomic mass (Ar) is the weighted average of one atom of
the element
Relative Formula Mass (Mr)
• The sum of the weighted average of the masses of the atoms in a
formula unit relative to one-twelfth of an atom of carbon-12.
• It does not have units
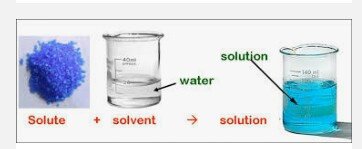
Components of a Solution
Solvent: A substance that has other substances dissolved in it (Does the dissolving).
Solute: Other substances present in a solution (Dissolve in solvent).
Hydrates
A hydrated salt is a compound that contains a fixed ratio of water
molecules within the crystalline structure of the compound. This water
of crystallization can be driven off by heating, resulting in an anhydrous
salt.
Titration
Titration is a laboratory procedure used to determine the
concentration of solution using a standardized solution (a.k.a. a
a solution whose concentration is known.)
Titrant: solution of known concentration in the burette
Sample: solution of unknown concentration in the flask
How Titrations Work
A base with known concentration is slowly added to the acid solution until all of the acids have been neutralized. At this endpoint, the solution changes color. The volume of base needed to reach the endpoint is used to calculate the concentration of the acid.f
Standard Solution
• A solution of known concentration
Ideal Gases
An ideal gas consists of moving particles with...
a) negligible volume
b) no interparticle forces. All collisions between particles are
considered elastic.
Ideal Gases vs Real Gases
Real gases deviate from the ideal gas model, particularly at low
temperatures and high pressures
As pressure increases...
• the gas occupies less space, and the particles occupy a greater
proportion of the space ∴ Their volume is no longer negligible
• the volume decreases, the particles approach one another and
attractive forces increase between particles
Ideal Gases vs Real Gases
Real gases deviate from the ideal gas model, particularly at low temperatures and high pressures
At low temperatures, the kinetic energy of the particles decreases, and the strength of the interparticle forces increase
Molar Volume of an Ideal Gas
The molar volume of a gas is a constant at a specific temperature and pressure. At STP (standard temperature and pressure) one mole of a gas has a volume of 22.7 dm3 mol-1 (this number is in the data booklet)
@STP
T = 273 K (0°C)
P = 100 kPa
Solutions
A solution is a homogenous mixture of at least two substances in one
phase (the components are uniformly mixed giving an appearance that
there is one visible “part”.)
Solutions can be solids, liquids, or gases
Boyle’s Law
The volume of a gas is always the same as the volume of the container
because particles spread fully….
• Pressure results from particles colliding with the walls of a container
• Pressure increases when the frequency or energy of collisions increases
Boyle’s Law: the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume
If the temperature is held constant, increasing volume of a fixed mass of
gas decreases its pressure
Charles’s law
The volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (a.k.a temperature in kelvin).
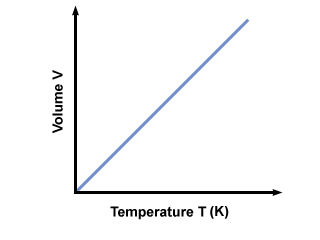
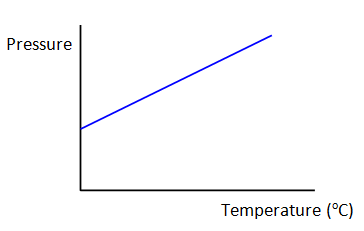
Gay-Lusaac’s Law
As Temperature increase…
Kinetic energy of particles increases
Particles move faster and collide with the walls of the container more frequently and with higer energy
The pressure of a gas is directly proportional to absolute temp
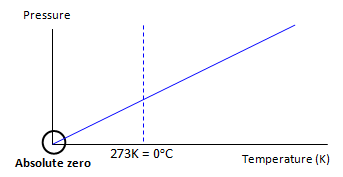
Empirical formula
The empirical formula of a compound gives the simplest ratio of each
element present in that compound.
• Formulas of all ionic compounds are empirical
Molecular formula
The molecular formula gives the actual number of atoms of each
element present in a molecule. It is a multiple of the empirical formula.
i.e Glucose CH20 & C6H12O6
Mole Definition
Mole definition: mass of a substance that contains as many particles
as there are atoms in 12 g of carbon 12