AP Bio unit 2 test (based off AP Classroom)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
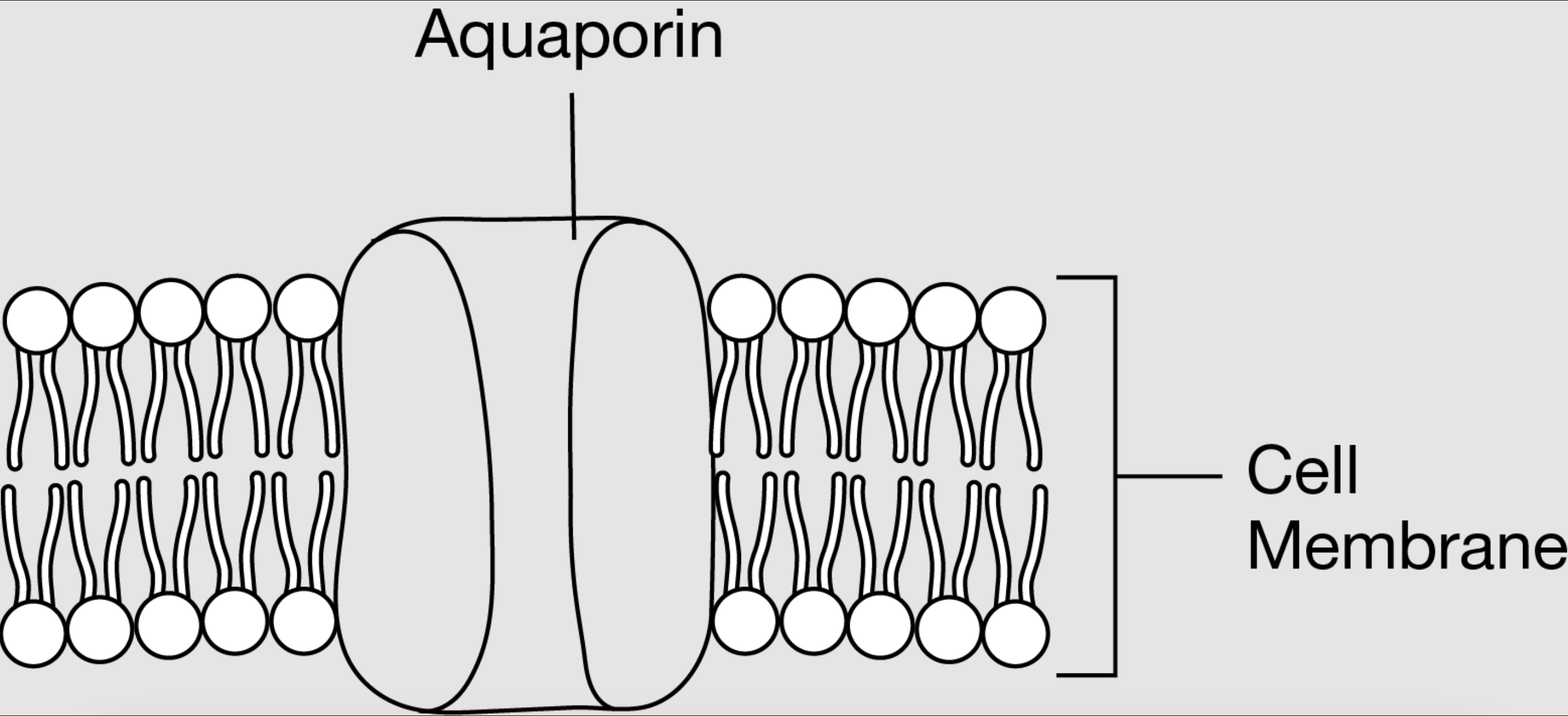
Water molecules will still be able to move across the cell membrane but at a slower rate.
Which statement best describes the effect on water transport across the cell membrane if the aquaporin in the figure ceases to function?
The bacterial cell, because it has the largest surface-to-volume ratio.
The bacterial cell is more efficient in the exchange of materials with the external environment. While the egg cell is much larger than the bacterial cell, the egg cell has a surface-to-volume ratio that is 33 times smaller than the bacterial cell's surface-to-volume ratio.
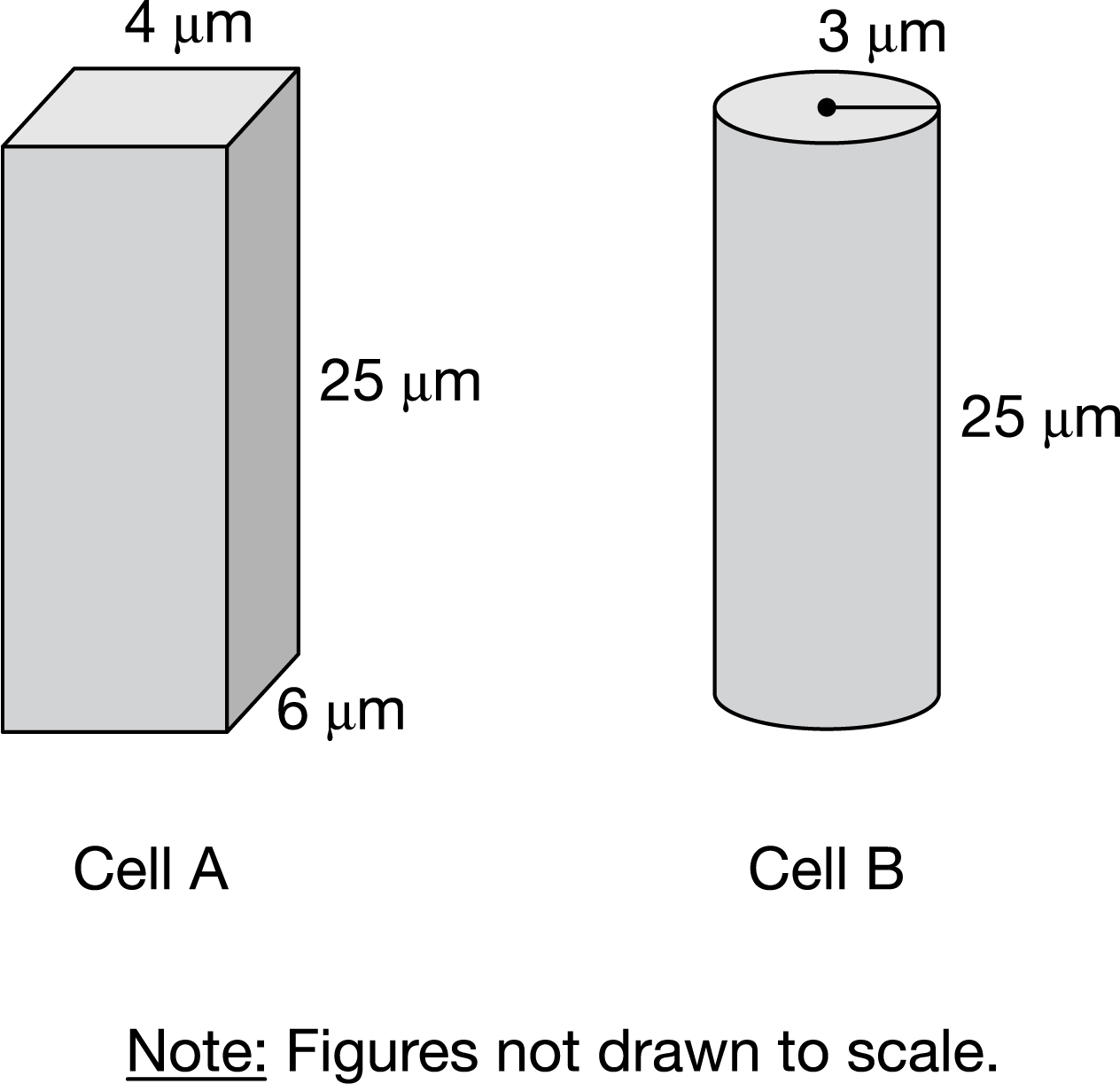
A spherical bacterial cell has a radius of 3 |um The human egg cell has a radius of 100 |um.
Which statement correctly indicates the cell that is able to more efficiently exchange materials with the external environment and provides a correct explanation?
Cell A, because it has the larger surface-area-to-volume ratio.
Of the two cells represented in the figure, Cell A has the larger surface-area-to-volume ratio of 0.91 compared to a surface-area-to-volume ratio of 0.75 for Cell B. Cell A would likely exchange substances with the surrounding environment at a greater rate.
Two different models of a living cell are represented in the figure.
Of the two cells represented in the figure, which would likely be more efficient at exchanging substances with the surrounding environment?
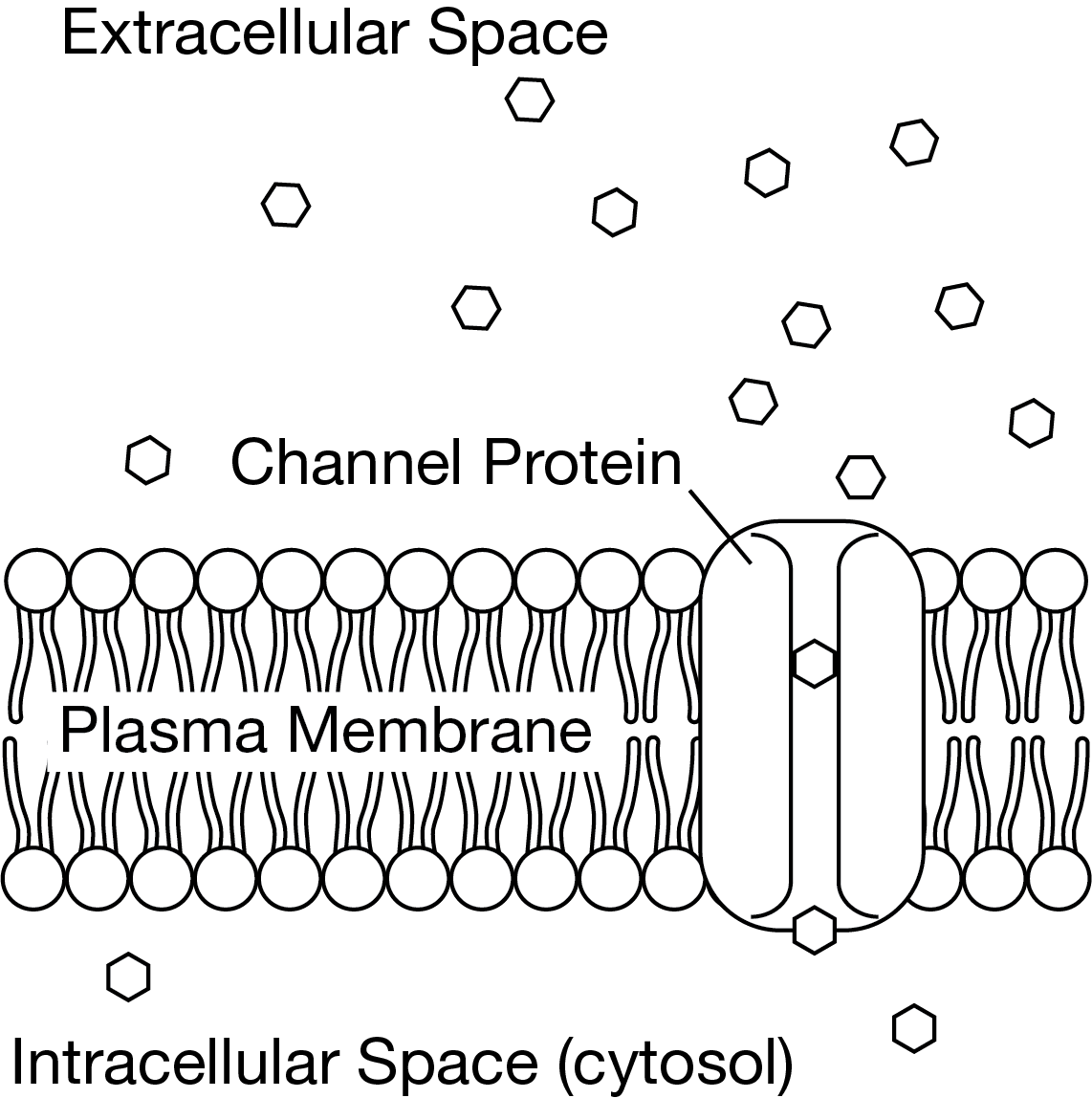
Add more of the proteins to the plasma membrane and measure the rate of the particle movement.
Figure 1 shows a model of how a channel protein influences the movement of a particle across a cell’s plasma membrane.
Figure 1. A section of a cell’s plasma membrane, showing a channel protein and a concentration gradient across the membrane
An investigator wants to understand whether a newly found membrane protein is involved in membrane transport of a certain particle. Which investigation will help determine whether the new membrane protein is a channel protein involved in membrane transport?
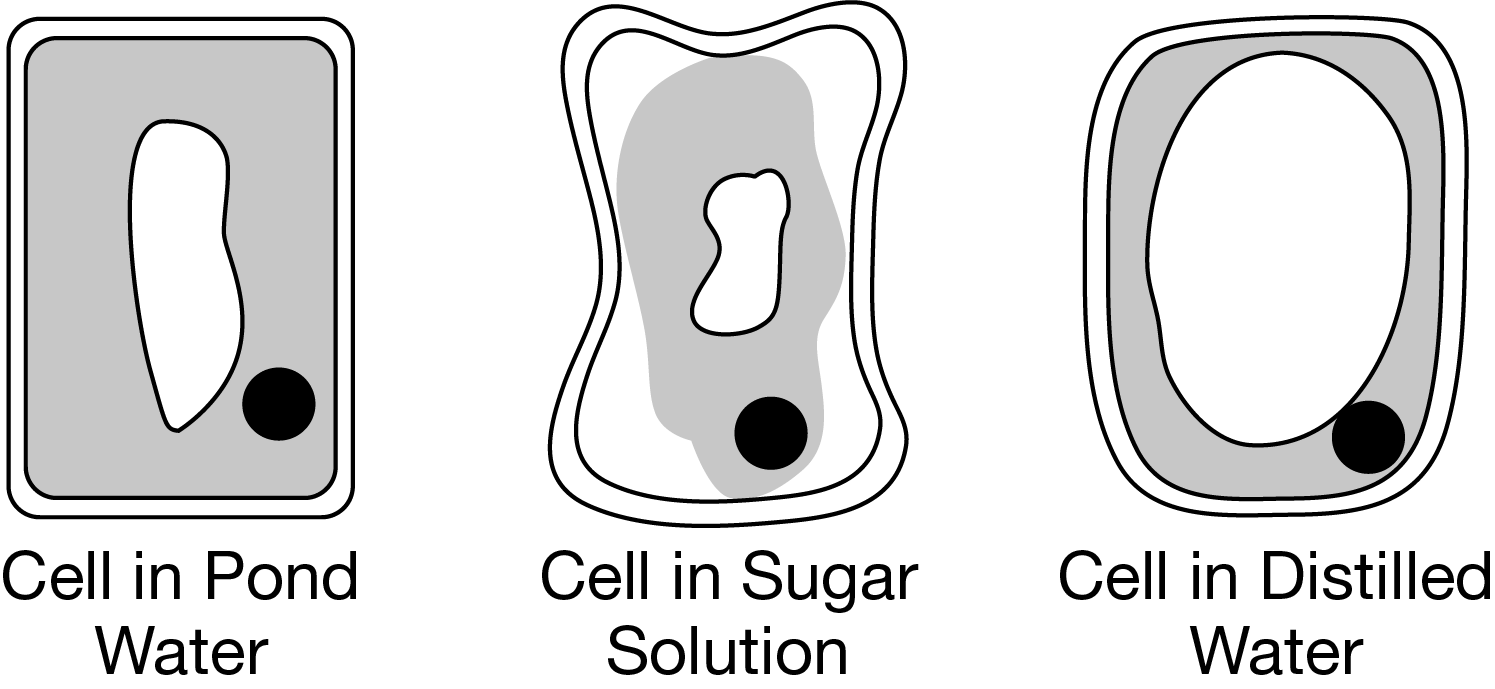
There was a net movement of water out of the cell suspended in the sugar solution and a net movement of water into the cell suspended in the distilled water.
The plasma membrane that surrounds a living cell is typically permeable to water but not sucrose. In the experiment represented in Figure 1, there was a net movement of water out of the cell suspended in the sugar solution, causing the cell to appear shriveled, and a net movement of water into the cell suspended in the distilled water, causing the cell to appear inflated.
In an experiment, cells were isolated from an aquatic plant and suspended in pond water, a sucrose sugar solution, or distilled water. All of the cells were then viewed under a microscope. Compared with the cell in the pond water, the cell in the sugar solution appeared shriveled, and the cell in the distilled water appeared inflated. The results of the experiment are represented in Figure 1.
Which of the following statements best explains the observations represented in Figure 1 ?
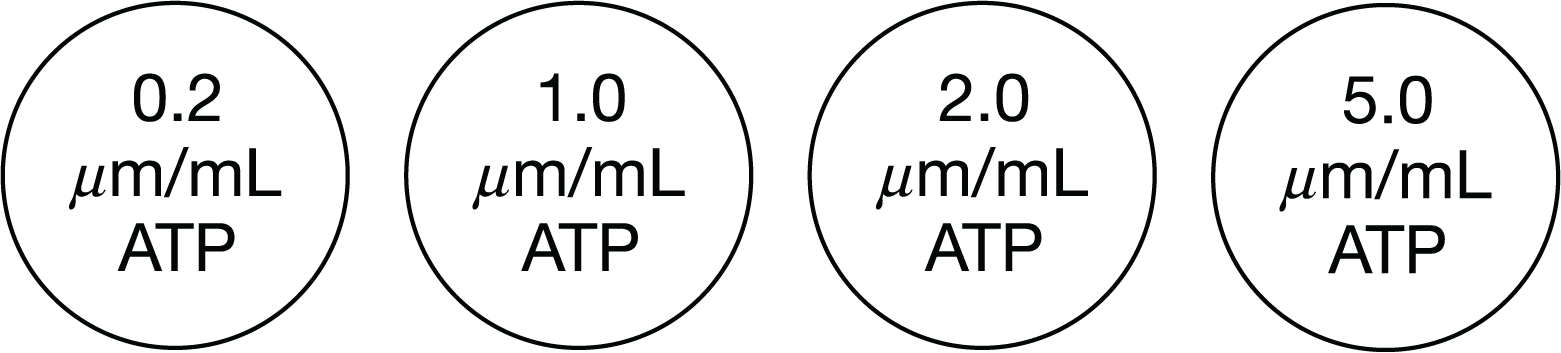
Incubate samples containing 1.0 |um/mL of ATP at four temperatures other than 25 Celsius.
This procedure combines the optimal ATP concentration for transport with data for transport rates at four other temperatures.
The transport of a substance across a plasma membrane of a specific organelle requires energy. The rate at which the transport takes place also depends on temperature. A scientist isolated the specific organelle and then used the following treatments to determine the conditions that will result in the maximal transport. All treatments contained the extracted organelle and were maintained at 25 Celsius.
The data from this experiment indicate that maximal rate of transport of protein X at 25 Celsius occurs at an ATP concentration of 1.0 |um/mL
Which procedure should be done next to gather data needed to meet the scientist’s objective?
In both plant cells and fungal cells, the cell wall surrounds the outside of the cell membrane.
In both plants and fungi, a major function of the cell wall is to confer structural rigidity to the cell. Thus, in both cell types, the cell wall’s location is similar. This is evidence supporting the alternative hypothesis proposed above.
Plant cell walls are composed of cellulose, while fungal cell walls are composed of chitin. A group of scientists hypothesize that this difference means the cell wall has largely different functions in plant cells and fungal cells. Alternatively, another group of scientists hypothesize that despite their biochemical differences, plant and fungal cell walls serve similar functions.
Which of the following observations would best support the alternative hypothesis described above?
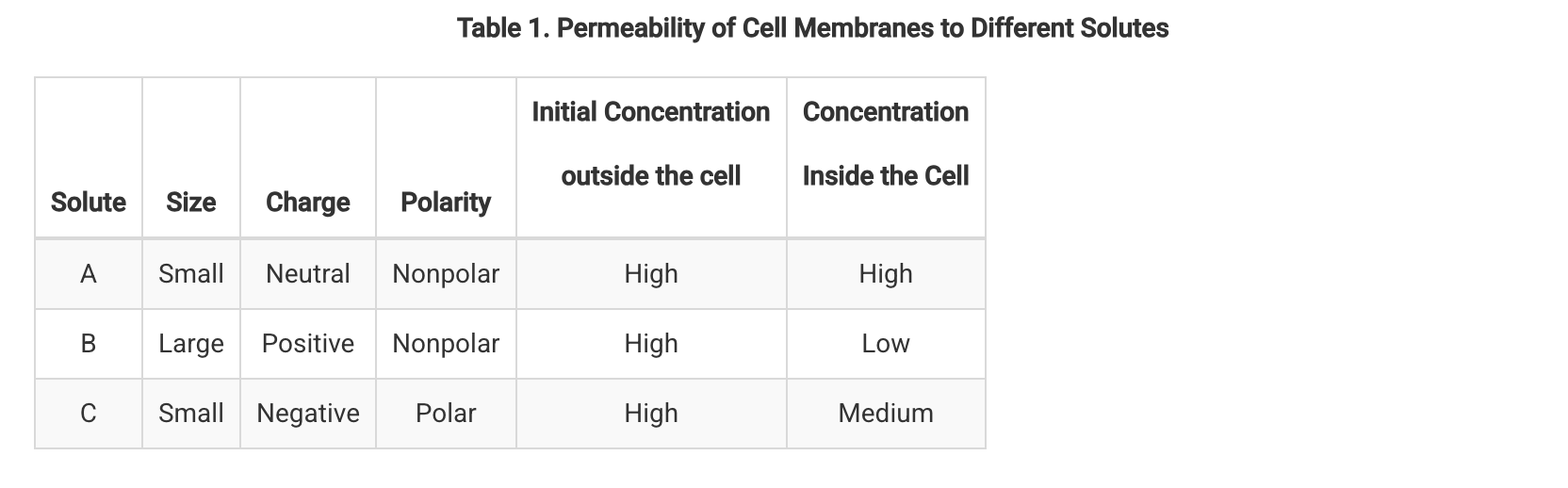
Small, nonpolar solutes showed the greatest increase in internal concentration, while large, nonpolar solutes showed little to no increase.
The data show that solute characteristics affect membrane passage, with small, nonpolar solutes having different penetration rates than large, polar ones. These observations support the concept of selective permeability.
Researchers exposed identical cells to solutions containing different solutes. Each solution had a higher concentration of the solute outside the cells than inside the cells. The solutes varied in size, charge, and polarity. After a set time, the researchers measured the concentration of each solute inside the cells to determine the permeability of the cell membranes to each solute. The results are shown in Table 1.
Based on the data in Table 1, which of the following statements best supports the hypothesis that only certain types of molecules can move freely across the cell membranes?
The drug is a small nonpolar molecule.
Small nonpolar molecules freely pass across the plasma membrane. If the drug is a small nonpolar molecule, this supports the alternative hypothesis.
A team of biologists develop a new drug, and one team member hypothesizes that the drug is incapable of freely passing across the plasma membrane and requires the help of membrane proteins to enter cells. Alternatively, another biologist on the team hypothesizes that the drug can diffuse passively across the plasma membrane like and can.
Which of the following, if true about the drug, best supports the alternative hypothesis that the new drug will exhibit simple diffusion across plasma membranes?
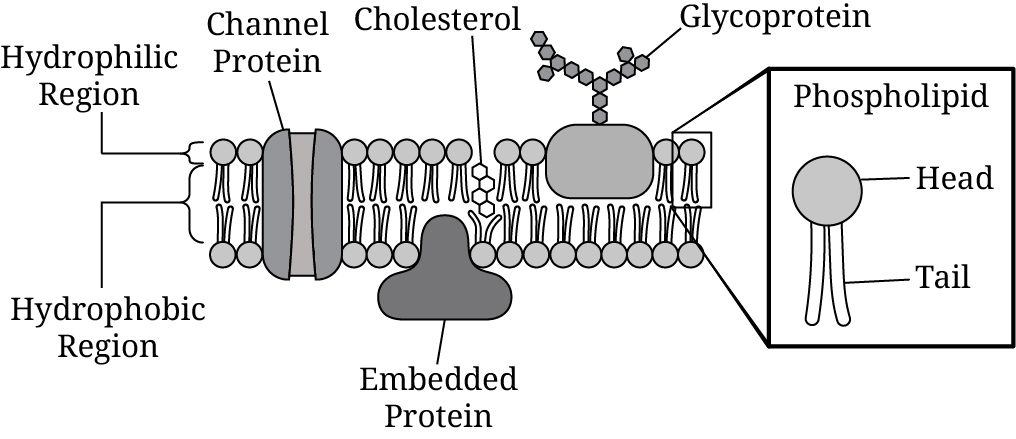
Based on Figure 1, which of the following membrane components are most likely nonpolar?
The phospholipid tails and cholesterol
The electrochemical gradient will change because the ATPase will stop functioning.
ATPase requires the use of ATP to move ions from one side of a cell membrane to another. The amino acid cysteine is important to the function of ATPase. A change in the cysteine prevents the ATPase from functioning.
Which of the following best describes what will happen to the movement of ions if there is a change in the cysteine of ATPase?
The membrane potential will be disrupted by an increase in K+ concentration inside the cell.
The intracellular K+ concentration will increase because the Na+ - K+ pump will continue to transport K+ into the cell without any diffusing out of the cell. As a result, the cell’s membrane potential will be disrupted.
A cell’s membrane potential is maintained by the movement of ions into and out of the cell. A model showing the influence of membrane proteins on the movement of sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) ions across the plasma membrane is presented in Figure 1.
Based on the model presented in Figure 1, which of the following outcomes will most likely result from a loss of protein function?
Which of the following statements best predicts the effect of increasing the permeability of the mitochondrial membranes to large molecules?
ATP production will decrease because of an increase in the occurrence of uncontrolled chemical reactions.