4U Bio: Unit 1 - Biochemistry
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is a biological molecule?
A molecule that makes up living things
What does the biological function of a molecule depend on?
Type of bonds between atoms
Shape of molecule
What does intra- mean?
Within
What does inter- mean?
Between
(T/F) Electrons are shared in covalent bonds
True
What is a Hydrogen bond?
A type of dipole-dipole force between a positive H atom and a negative O/N/F ion from ANOTHER MOLECULE
Is a Hydrogen bond an intramolecular bond?
No.
water is the universal _____
solvent
What is adhesion?
Water molecules sticking to other substances
What is cohesion?
Water sticking to other water molecules
(T/F) water is more dense in solid form.
False
Why is water’s specific heat capacity important?
Harder to change its temperature, meaning it can store and release heat in the winter.
Ratio of C:H:O in carbohydrates
1:2:1
What is an isomer?
Molecules that have the same formula with different arrangements
What are 3 monosaccharides with the formula C6H12O6 ?
Glucose, fructose, and galactose.
What is the chemical formula for ribose?
C5H10O5
Where does the difference between glucose and galactose occur?
On the 4th carbon
What is the difference between glucose and galactose?
Glucose’s 4th carbon has hydroxyl (OH) at the top.
Where does the difference between alpha and beta carbohydrates occur?
The first carbon
What is the difference between alpha and beta carbohydrates?
Alpha carbohydrates have the OH-group at the bottom
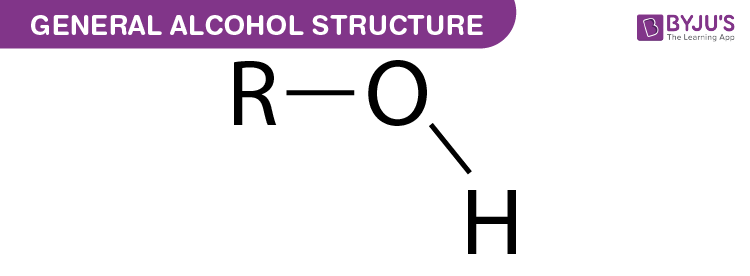
What is this functional group called?
Hydroxyl
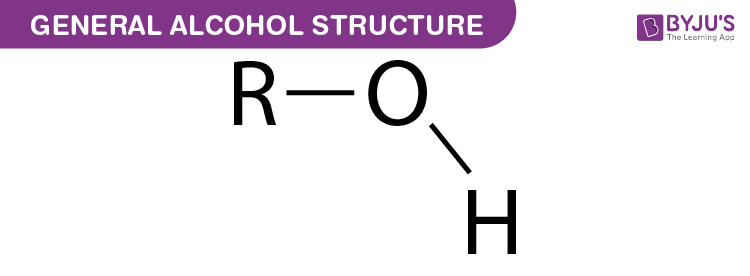
What joins two sugar molecules in a disaccharide?
A glycosidic bond/linkage
What causes a glycosidic bond?
Synthesis reaction between two Hydroxyls
What is always a product of dehydration synthesis?
Water.