BMAT Flashcards
1/215
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
216 Terms
Type 1 diabetes
Pancreas can not produce enough insulin
Process of genetic engineering
1. Useful gene is cut from one organism's DNA using enzymes
2. This is then inserted into the vector's DNA using ligase enzymes
4 examples of genetic engineering
1. Bacteria producing human insulin
2. GM crops
3. Sheep producing drugs in their milk
4. Inserting healthy genes to replace faulty genes in inherited disorders
When must genetic engineering occur and why
Early stage of development so the organism develops to express the desired gene
3 pros of genetic engineering
1. Uses in medicine
2. Improve growth rates of crops
3. Provide more vitamins through crops
3 cons of genetic engineering
1. Effects flower and insects
2. Low success rates in animals
3. Creates a selection pressure, which can lead to more resistant pests
3 cons of selective breeding
1. Reduces gene pool
2. High chance of inbreeding
3. Increase chance of recessive inherited disorders
Stomach
1. Pummels food with muscular walls
2. Produces pepsin
3. HCL to kill bacteria and give right pH for enzymes
Pancreas
Produces digestive enzymes to the small intestine
Gall bladder
Stores bile and releases it to the small intestine
Liver
Bile is produced
Large intetsine
excess water absorbed from food
Rectum
Faeces is stored and let pout through the anus
Peristalsis
Involuntary waves of muscle contraction that keep food moving along in one direction through the intestine
When blood glucose levels are too high
1. Pancreas releases insulin
2. Insulin binds to the target organ and causes glucose to move from the blood into respiring muscle cells and for excess glucose to be converted into glycogen stored in the liver
3. This reduces the blood glucose level
When blood glucose levels are too low
1. Pancreas produces glucagon
2. Binds to lover cells causing glycogen to be broken down into glucose
3. Glucose is then released back into the blood
Treatment for type 1 diabetes
1. Insulin injections
2. Diet and exercise
3. Future: genetic engineering pancreatic cells
Type 2 diabetes
Body cells no longer respond to insulin
If water content is too high
1. Receptor in the brain detects it is too high
2. Co ordination centre receives this info and coordinates a response
3. Pituitary gland releases less ADH so less water is reabsorbed into kidney tubules
If water content is too low
1. Receptor in brain detect it is too low
2. Co ordination centre receives this info and coordinates a response
3. Pituitary gland releases more ADH so more water is reabsorbed into kidney tubules
If body temp is too high
1. Temp receptors detect it is too high
2. Thermoregulatory centre receives this info and triggers effectors
3. Hairs lie flat
4. Sweat is produced by sweat glands and evaporates
5. Vasodilation, more blood flows to surface of the skin
nano
10^-9
micro
10^-6
milli
10^-3
centi
10^-2
deci
10^-1
kilo
10^3
mega
10^6
giga
10^9
Salivary glands
Produce Amylase
Homeostasis
Maintenance if content internal environment
If body temp is too low
1. Temp receptors detect it is too low
2. Thermoregulatory centre receives this and triggers effectors
3. hairs stand up to insulate
4. vasoconstriction
5. shivering
Thyroxine:
1. Where is it produced?
2. Role?
1. Thyroid gland
2. Regulating things like rate of metabolism, heart rate and temp
Adrenaline:
1. Where is it produced?
2. Role?
1. Adrenal glands
2. Prepare for fight or flight
FSH:
1. Where is it produced?
2. Role?
3. Stimulates/inhibits which other hormones?
1. Pituitary gland
2. Causes egg to mature in the follicle
3. Stimulates ovaries to produce oestrogen
Oestrogen:
1. Where is it produced?
2. Role?
3. Stimulates/inhibits which other hormones?
1. Ovaries
2. Lining of uterus to grow
3. Stimulates LH, inhibits FSH
LH:
1. Where is it produced?
2. Role?
3. Stimulates/inhibits which other hormones?
1. Pituitary gland
2. Stimulates the release of an egg at ovulation
3. None
Progesterone:
1. Where is it produced?
2. Role?
3. Stimulates/inhibits which other hormones?
1. Ovaries by remaining follicle
2.Maintains lining of the uterus in second half of the cycle
3. Inhibits LH and FSH
How are hormones used to reduce fertility?
1. Oestrogen-- prevents the release of an egg, as it inhibits FSH and prevents eggs maturing
2. Progesterone-- stimulates growth of thick mucus which prevents sperm getting through
Water cycle
1. Evaporation-- from land and sea
2. Transpiration-- released from plants
3. Condensation-- water vapour rises and condenses into clouds
4. Precipitation-- rain or snow into land
Cathode
-ve electrode
Anode
+ve electrode
Electrolyte
ionic aqueous compound
Why is dc not ac used in electrolysis?
In ac, the current would keep changing directions and would lead to an uneven distribution of ions in the electrodes
What occurs at the cathode?
Cations receive e- so are reduced
What occurs at the anode?
Anions give away e- so are oxidised
When there is an aqueous compound, which ions are attracted to:
1. Cathode
2. Anode
1. H+ ions
2. Halide ions, and if not then OH- ions
Electroplating process
1. The cathode is the object being electroplated
2. The anode is the metal you want to coat the object in
3. The electrolyte is a solution of the metal that you want to coat it with
Hydrogen test
Burning splint gives a squeaky pop
Oxygen test
Relights a glowing splint
Carbon dioxide test
Limewater turns cloudy
Chlorine test
Damp blue litmus paper is bleached
Carbonate test
Use dilute acid, effervescence and turns limewater cloudy
Halides test
add silver nitrate:
1. Cl= white ppt
2. Br= cream ppt
3. I= yellow ppt
Sulfate test
Add barium chloride with dilute HCl, white ppt of barium sulphate forms
Silver + NaOH
White ppt
Calcium + NaOH
white ppt
Magnesium + NaOH
white ppt
Copper + NaOH
Blue ppt
Iron (II) + NaOH
Green ppt
Iron (III) + NaOH
Brown ppt
Lithium flame test
Crimson red flame
Sodium flame test
Yellow orange flame
Potassium flame test
Lilac flame
Calcium flame test
red organe flame
Copper flame test
Green precipitate
Presence of water test
Add anhydrous copper (II) sulphate, turns from white to blue
Origins of CO2 in atmosphere
Respiring organisms
Decay of dead organisms
Dissolved CO2 escaping from the sea
Combustion
Origins of CH4 in the atmosphere
Cow farming
Landfill
Anaerobic organisms
Effects of CO2 and CH4
The more long wave radiation absorbed
Global warming
How is CO formed?
incomplete combustion
Problem with CO?
Stronger affinity to Hb than O2, so prevents O2 being effectively transported around the body
SO2 produced by
fuels with impurities being burnt
Problems with SO2
Dissolves in rain to form acid rain
Problems with Nitrogen oxides
can cause breathing difficulties
Why is chlorine added to water?
kill bacteria
Why is fluorine added to water?
prevent tooth decay
How can insulators be charged?
friction
How does charging occur between two insulators?
Friction causes electrons to be transferred from one insulator to the other
Uses of static electricity
1. Paint sprayers
2. Dust precipitators
3. Defibrillators
Hazard of electrostatics
1. Sparking
How does sparking occur?
Air between two charged objects becomes ionised due to a large voltage and can start conducting charges
What is earthing?
Excess charge is removed from the object by connecting it to the ground with a wire
Fuse
stops current flowing through the circuit when it gets too high
Diode
only allows current to flow in one direction
LED
only allows current to flow in one direction, and emits light when there is a current
Thermistor
changes resistance based on temp
LDR
changes resistance based on light levels
AC vs DC
DC= only flows in one direction
AC= alternates direction
Conductors vs insulators
Conductors= allows the movement of electrons in solids
Insulators= poor conductors of electricity
Current is...
flow of charge
current=
charge/time
Voltmeters are always connected in
parallel
Ammeters are always connected in
series
resistance=
Voltage/current
V-I graph for a fixed resistor
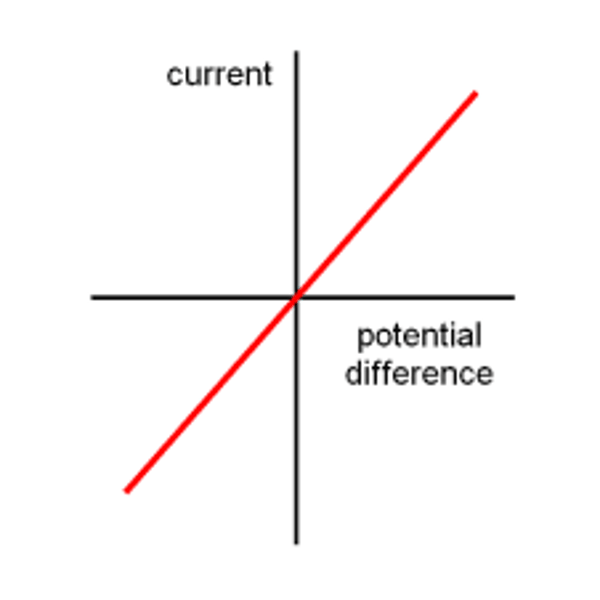
V-I graph for a filament lamp
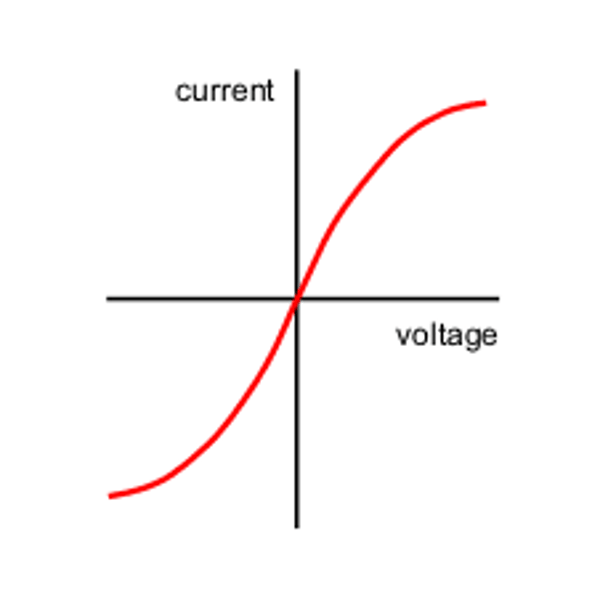
Why does resistance increase as temperature increases?
Waste energy causes ions to vibrate more, which opposes the flow of charge
Negative temperature coefficient thermistor
Resistance decrease as temp goes up
ideal diode
Perfect conductor in one direction and perfect insulator in the other