Optics Final Exam Concepts
1/229
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
230 Terms
What are the 5 types of Monochromatic Aberrations we learned about?
i) Spherical Aberrations
ii) Coma
iii) Radial Astigmatism
iv) Curvature of field
v) Distortion
Which Monochromatic Aberrations occur with points ON axis?
i) Spherical Aberrations
Which Monochromatic Aberrations occur only with points OFF axis?
i) Coma
ii) Radial Astigmatism
Which aberrations can be minimized with a small diameter aperture stop?
i) Spherical Aberrations
ii) Coma
Which lens designs have the most Coma?
Meniscus Lenses
Which lens designs have the least Coma?
Plano and Biconvex
Which monochromatic aberration occurs from tilting the lens?
Radial Astigmatism
In radial astigmatism, which principal meridian experiences the greater increase in magnitude of refracting power? aka, which is greater, KT or KS?
Tangential, KT>KS
Which effective power, ET or ES, has the greater magnitude? at any angle other than 0.
Tangential, ET > ES
If the tangential is the horizontal meridian, which line image will form closer to the lens?
Vertical
If the horizontal line image forms closer to the lens, which meridian is the tangential?
Vertical
If an object is displaced vertically, which meridian is the tangential? Sagittal?
Tangential = Vertical
Sagittal = Horizontal
If an object is displaced horizontally, which meridian is tangential? sagittal?
Tangential = Horizontal
Sagittal = Vertical
Which tilt is a lens tilted vertically (tilted about the horizontal)? Pantoscopic or Faceform?
Pantoscopic
Which meridian is Tangential in a Pantoscopic tilt? Sagittal?
Vertical; Horizontal
Which tilt is a lens tilted horizontally (tilted about the vertical)? Pantoscopic or Faceform?
Faceform
Which meridian is Tangential in a Faceform tilt? Sagittal?
Horizontal; Vertical
What helps us determine the front surface power of a given lens power that will completely eliminate radial astigmatism?
Tcsherning Ellipse
What is the range of lens powers that we can completely eliminate radial astigmatism?
Which type of lens power can we not completely eliminate radial astigmatism using a spherical front surface? (high hyperope/ high myope)
-25D to +10D;
High Plus Powered Lenses ( > +10D); High Hyperope
Which aberration occurs due to a flat object and a curved screen (curved conjugate image)?
Curvature of field
What is the name of a curved set of image points conjugate to a given object distance?
Petzval Surface
Which are the two most important aberrations to control in lens design (aka - which aberrations have the largest effect on a viewer viewing through spectacle lenses)?
i) Curvature of field
ii) Radial Astigmatism
What happens to curvature of field when you eliminate radial astigmatism of a spec using Tscherning Ellipse?
Curvature of field will be worsened
Which is the best lens design type?
Meniscus Lenses (Convex front, concave back) that reduce both radial astigmatism and curvature of field but don’t completely eliminate either
What distortion is caused by a plus lens at near?
pincushion (magnification of periphery > center)
What distortion is caused by a minus lens at near?
barrel (magnification of periphery < center)
What distortion is caused by a plus lens at distance?
Barrel
In a diverging system, H2 is (in front of/ behind) the system
in front of
In a diverging system, H2 is (in front of/ behind) F2
behind
In a converging system, H2 is (in front of/ behind) the system
Behind
In a converging system, H2 is (in front of/ behind) of F2
Front
f1 is the length from ___ to ___
H1 to F1
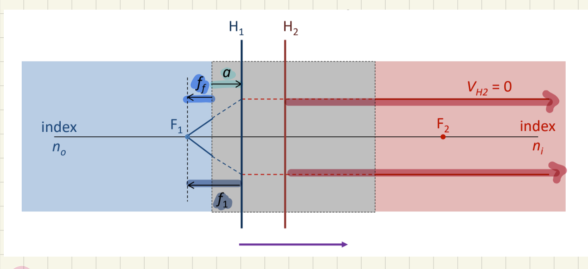
ff is the length from ____ to ____
the front of the system; F1
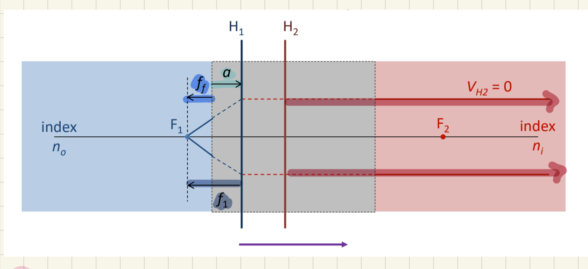
a is the length from ___ to ____
the front of the system; H1
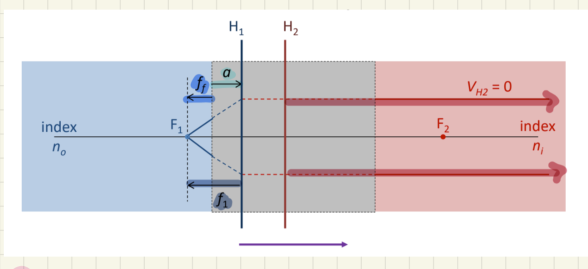
f2 is the length from ___ to ___
H2 to F2
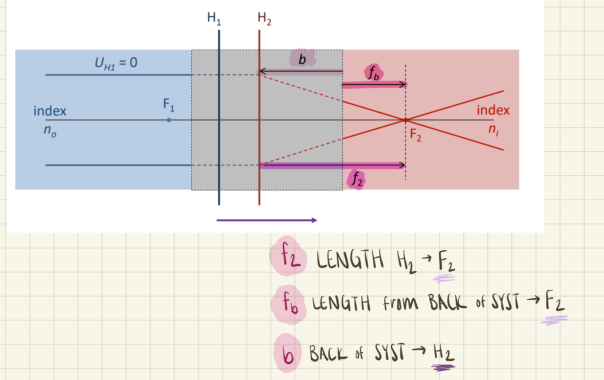
fb is the length from ____ to ____
the back of the system; F2
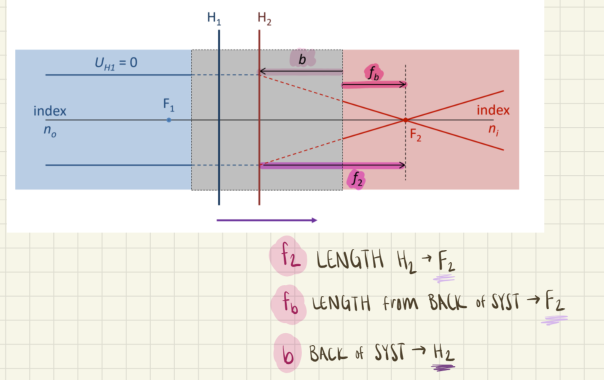
b is the length from ___ to ____
the back of the system; H2
When the unit magnification of a multicomponent system is m = +1, what does this tell you?
Object is at H1 and Image will be at H2
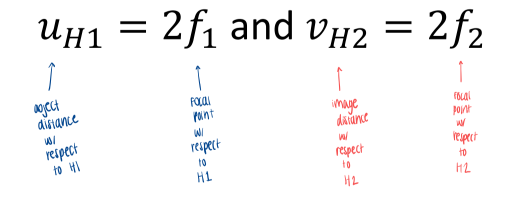
When the lateral magnification of a multicomponent system is m= -1, what does this tell you?
uH1 = 2f1
vH2 = 2f2
In a multicomponent system, the object location is defined as the distance from ___ to ___
H1; object
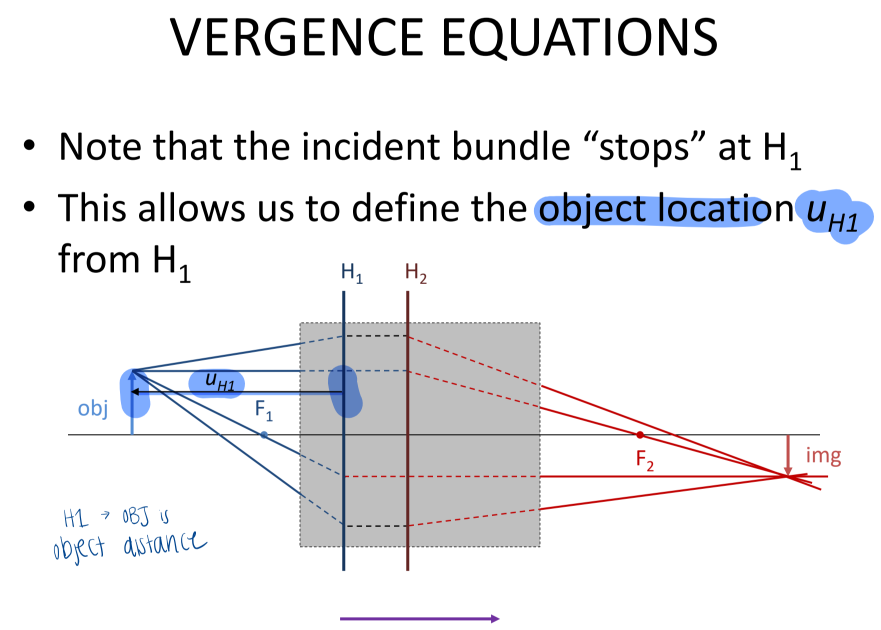
In a multicomponent system, the image location is defined as the distance from ___ to ___
H2; image
If the object and image are located at the nodal points of a multicomponent system, what does this tell you about its lateral magnification?
m = no/ni
What is significant with cardinal points?
When light is reversed through a system, the pair stays in the same place but exchanges roles

The principal planes of a spherical interface coincide at ____
the vertex
The nodal points of a spherical interface coincide at the ______
center of curvature
The principal planes and nodal points of a thin lens will coincide at ____
the vertex
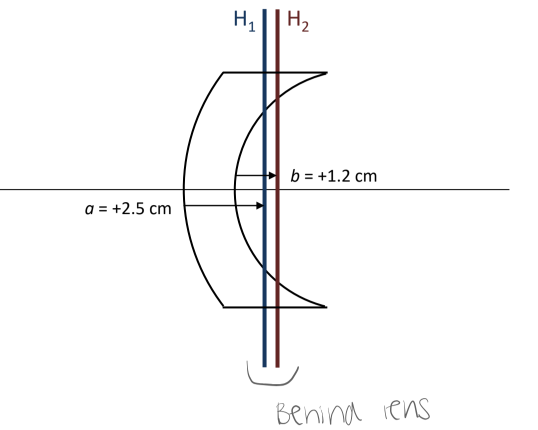
For a biconvex thick lens, H1 and H2 are _____
inside the lens
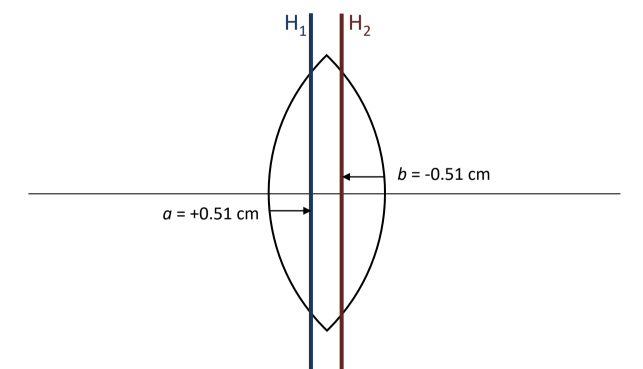
For a plano-convex thick lens, H1 and H2 are ____
coincident with the front and inside the lens respectively
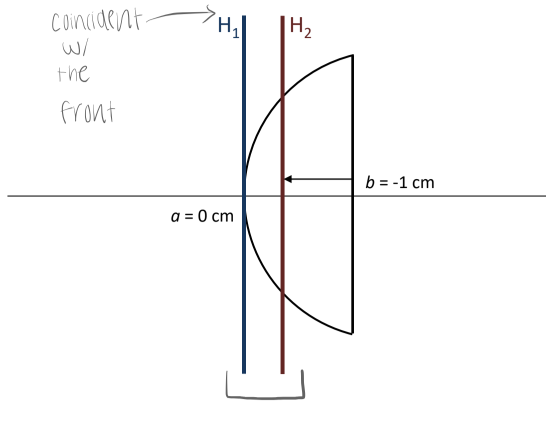
For a convex meniscus thick lens, H1 and H2 are _____
in front of the lens
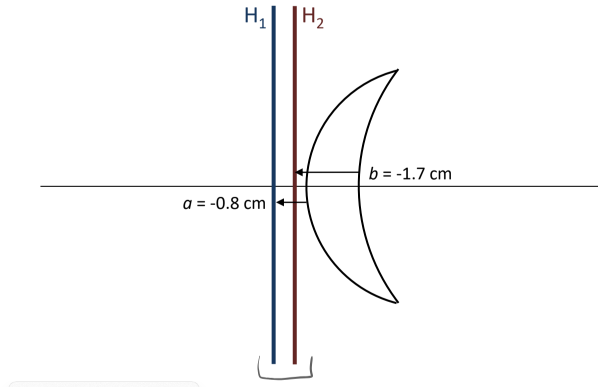
For a concave meniscus lens, H1 and H2 are ____
behind the lens
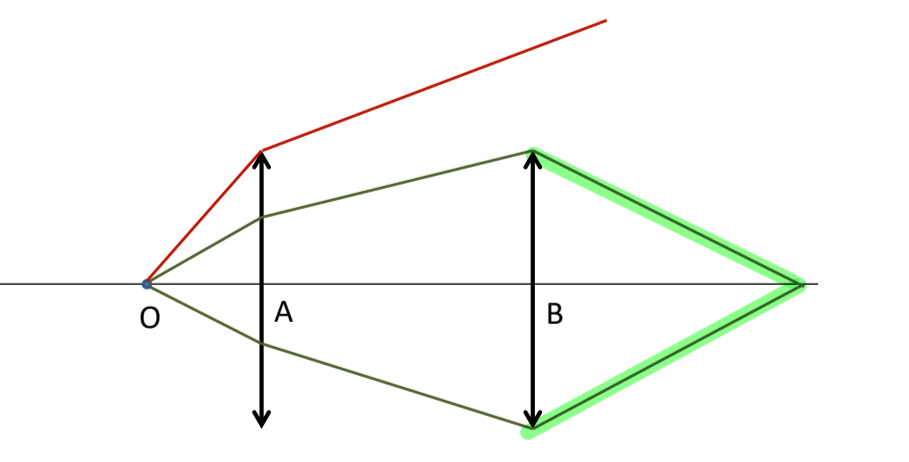
a(n) ____ is any device that limits the amount of light passing through a system
aperture
From the point of view of the object, the device that does the best job at limiting the amount of light passing through the system is called the _______
aperture stop
What are 5 examples of apertures?
small opening, pinhole, diaphragm, lens, mirror
Which component plays the role of the aperture stop depends on _______
the location of the object
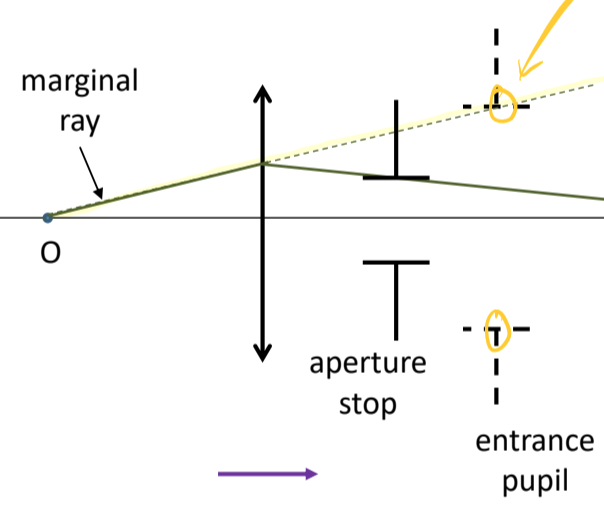
The image of the aperture stop formed by any lenses in front of it is the _____
entrance pupil
What are the steps to determine which component is the entrance pupil?
1) Find the image of each component with respect to the component in front of it
2) Determine which component subtends the smallest angle using tanθ = o/a (where o is the radius of the image of the component formed by the lens in front of it and a is the distance from the obj to the img of the component)

The ___ ___ is the image of the aperture stop formed by any lenses behind it
exit pupil
what is the relationship between the entrance and exit pupils?
both are images conjugate to the aperture stop of the system
a ray that just passes through the aperture stop, and therefore goes through the edge of the entrance pupil is the ______
marginal ray
The ray that is aimed at the center of the entrance pupil and therefore passes through the center of the aperture stop is the ___ ray
chief ray
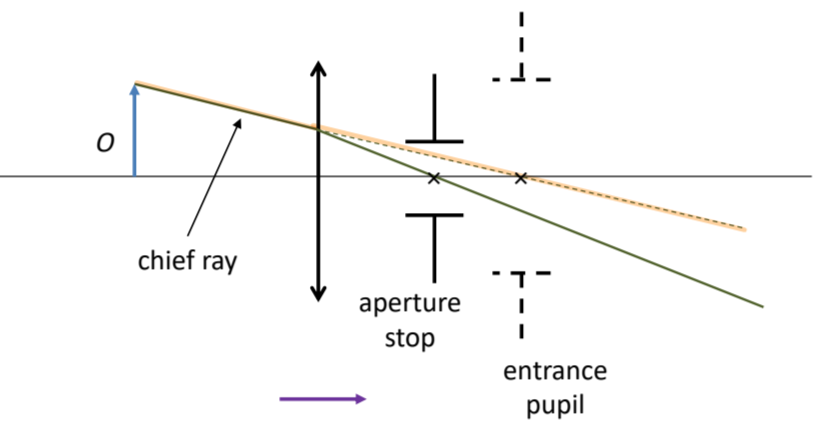
It is the ___ ray that determines the size of a blurred image when the screen is closer than the point image location
chief
Of the eye system, the entrance pupil is ____
the image of the eye’s pupil as seen through the cornea
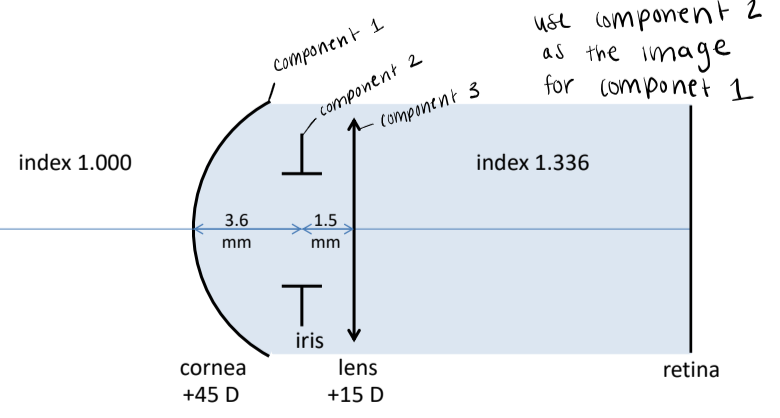
Of the eye system, the aperture stop is ____
the anatomical pupil
When you look at someone’s eye, you are seeing the ______
entrance pupil
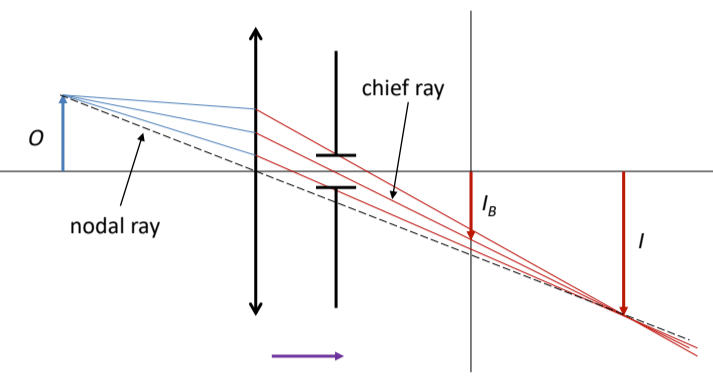
lateral magnification is based on ____ while angular magnification is based on _______
object and image distance; angle the nodal ray makes with the optical axis
when an object is far its retinal image will be _____ (smaller than/ bigger than/ the same size as) the retinal image of an object that is closer
smaller than
For an object inside the eyes primary focal point, a plus lens in front of the eye will produce a (small/large) (real/virtual) image
large; virtual
For a collimating magnifier to work, the object will be placed at ____ and ___ (converging/diverging/ plane) waves will exit the lens
F1; plane
For the collimating magnifier formula (M = |ue|P), ue is _____ and the units must be ___
the object distance for the unaided eye (for when the magnifier is not present); meters
Does Mcoll depend on lens-eye separation?
no - rays are parallel between the eye and lens (no vergence change)
angular magnification M compares ____ ____ _____
retinal image sizes
Maximum Mcoll is when d = ___, which would be the _____ ____
0; mythical maximum
Maximum accommodation with a magnifier occurs when the plus lens forms its image at ____
ue/ viewers near point
The lens closer to the object is called the ____ ___ (___)
objective lens (Po)
The lens closer to the object is called the ____ ___ (___)
eyepiece/ocular lens (Pe)
In a simple compound microscope, the ____ lens acts as a collimating magnifier
eyepiece
For a compound microscope to have the eyepiece lens acting as a collimating magnifier, the objective lens must place it image at _____
The primary focal point of the eyepiece lens (F1 of Pe)
The formula for magnification of a collimating magnifier is
M= mo|ue|Pe
where mo is the lateral magnification of the objective lens
The optical tube length of a compound microscope is
x’ (the distance between f2 of Po and f1 of Pe)
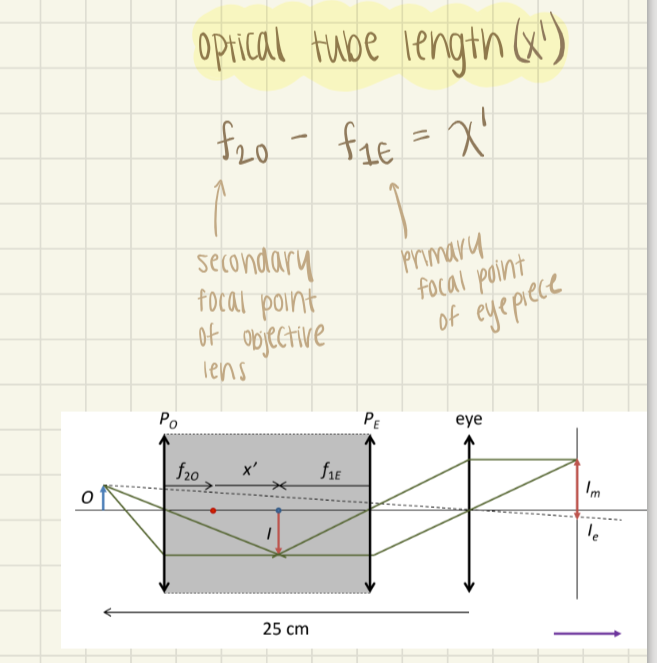
The 3 formulas to calculate the standard magnification of a compound microscope are
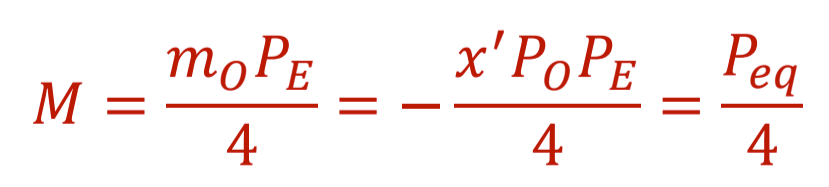
The retinal image of a compound microscope will be (smaller/larger), (upright/inverted) compared to the object
larger, inverted
A compound microscope is used to view (large/small), (distant/ nearby) objects
small, nearby
A telescope is used to view (large/small), (distant/ nearby) objects
large, distant
A telescope is an afocal system because
it does not change the vergence of light
The length of a telescope is found by ____
secondary focal length of objective lens + primary focal length of eyepiece lens
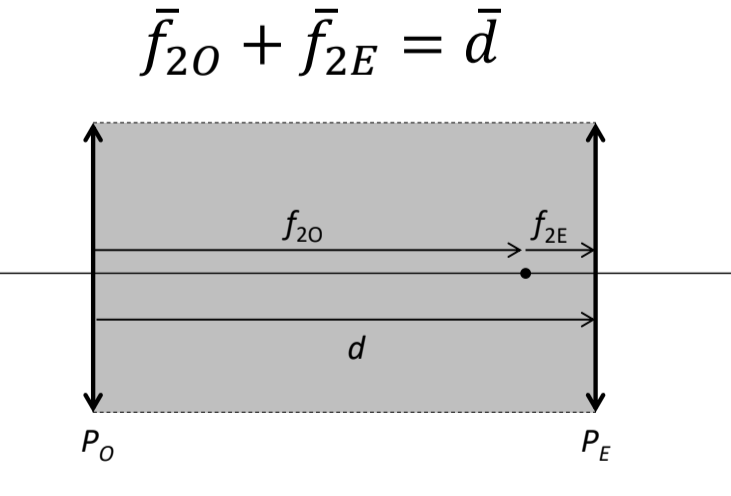
An afocal lens with two plus powered lenses is a _____ telescope
Keplerian
For a Keplerian telescope, the retinal image will be (upright/inverted) with respect to the unaided eye
inverted
For a telescope to work, ____ must be incident
plane waves
An afocal telescope with a minus powered ocular lens is a ____ telescope
Galilean
For a Galilean telescope, the retinal image will be (upright/inverted) with respect to the unaided eye
upright
M for a Keplerian telescope is always (pos/neg) and for a Galilean telescope is always (pos/neg)
negative; positive
To produce an erect image with an erecting lens without changing the angular magnification, the telescope length must be increased a distance ___
4fer (4x the focal length of the erecting lens)
If light exiting a telescope is diverging ____
the eye wont be able to accommodate enough to clearly view it
If the exiting light from a telescope is converging ___
the eye will be fogged
the goal of a reading cap is to _______
neutralize a nearby objects vergence so that plane waves are incident on the telescope
The formula for standard magnification of a telemicroscope is
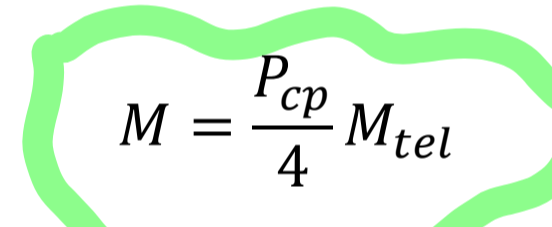
A highly detailed object has a (high/low) spatial frequency
high
A low detailed object has a (high/low) spatial frequency
low
Spatial frequency tells us ____ per ____
oscillations; unit space
The image quality transferred by an optical system is ____, which compares ____ and _______ ____ ____
modulation; minimum and maximum detectable luminance