Physics A-Level
1/60
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Accuracy
A measure of how close the measurement is to the true value.
Precision
A measure of how close a measurement is to the mean value.
This only gives an indication of the magnitude of random errors, not how close data is to the true value.
Random Error
Unpredictable variation between measurements that leads to a spread of values about the true value.
Reducing Random Error
Take at least 3 repeats, calculate a mean and identify anomalies, use computers/data loggers/cameras to reduce human error, use appropriate equipment.
Cannot fully get rid.
Systematic Error
Causes all readings to differ from true value by a fixed amount.
Reducing Systematic Error
Calibration. Read background radiation and read meniscus at eye level if relevant. Use fiducial markers.
Repeatable
The same experimenter can repeat a measurement using the same method and equipment and obtain the same value.
Reproducible
An experiment can br repeated by a different experimenter using a different method and different apparatus and still obtain the same results.
Resolution
The smallest change in a quantity that causes a visible change in the reading that a measuring instrument records.
Uncertainty
The interval that a value is said to lie within, with a given level of uncertainty.
Uncertainty in a Reading
± half the smallest division
Uncertainty in a Measurement
At least ± the smallest division
Uncertainty in Digital Readings
± the last significant digit
Uncertainty in Repeated Data
Half the range
Uncertainty when Adding/Subtracting
Add absolute certainties
Uncertainty when Multiplying/Dividing
Add percentage uncertainties
Electron Relative Mass
1/2000
Proton Radius
10^15
Atom Radius
10^-10
Beta Minus Exchange Particle
W-
Beta Plus Exchange Particle
W+ Boson
Electron Capture Exchange Particle
W+
Electron-Proton Collision Particle
W-
Electron-volt (eV)
The work done to accelerate an electron through a potential of 1V.
1eV corresponds to 1 V
Hadron
A class of subatomic particle that experience the strong nuclear force.
Lepton
A group of elementary subatomic particles. Does not experience SNF.
Meson
A class of hadron that is made up of a quark and antiquark pair.
Pair Production
When a photon of sufficiently high energy converts into a particle-antiparticle pair. Usually occurs near a nucleus to conserve momentum.
Stopping Potential
The minimum PD required to stop the highest KE electrons from leaving the metal plate in the photo electric effect.
Threshold Frequency
Minimum frequency of photons required for photoelectrons to be emitted from the surface of a metal plate through the photoeletric effect.
Work Function
The minimum energy required to remove an electron from a metal’s surface.
What factors affect the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted?
Frequency of incident photons,
Work function of the metal.
Intensity has NO effect.
What effect does decreasing the intensity of incident photons have on the photoelectric effect?
Fewer photons are incident on the plate,
So number of photoelectrons emitted from the plate (photoelectric current) decreases.
Has NO effect on KE of photoelectrons nor stopping potential.
What affect does voltage have on electron diffraction rings?
Larger accelerating voltages reduces the diameter of a given ring.
Lower accelerating voltages increases the diameter of the rings.
What effect does speed have on electron diffraction?
Increasing electron speed increases momentum.
This decreases the wavelength and makes the diffraction ring diameters decrease/closer.
What effects the radius of electron diffraction patterns?
The larger the wavelength, the more light spreads out causing a larger radius (and vice versa).
What are superconductors?
Materials with no resistance below a critical temperature, useful for producing strong magnetic fields and reducing energy loss.
Superconductor Pros and Cons
Pro: Zero resistance, so reduces power loss.
Con: Difficult to keep below the critical temperature.
What is cladding?
A lower optically dense layer surrounding the core.
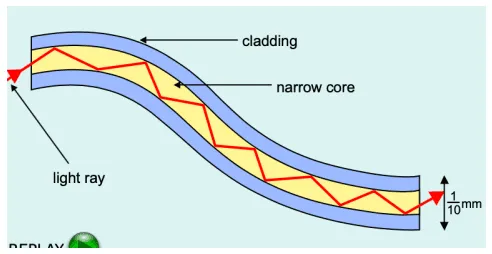
What is the cladding’s role?
Protects the thin core from damage/scratching,
Prevents light escaping the core which would cause signal degradation/ information to be lost.
Keeps the signals secure/maintains the original signal quality.
Keeps the core separate from other fibres prevent cross talk.
What is the core tube?
Optically dense layer made of plastic or glass which guides the wave by TIR.
Modal Dispersion
Pulse broadens due to path differences due to light rays having different angles of incidence and so undergoing TIR a different amount of times. Prevented by very narrow cores.
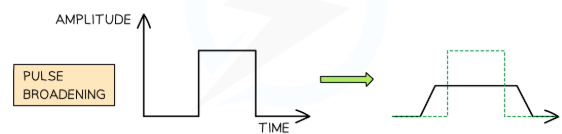
Pulse Broadening
Caused by modal and material dispersion. Can result in merging pulses distorting information and decreasing signal amplitude. Reduced by using single-mode fibre (only a single wavelength passes through core) and fibre repeaters.
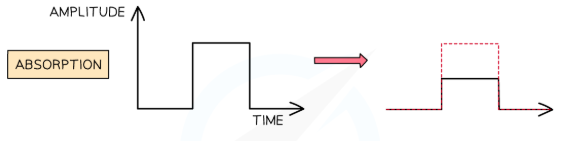
Absorption
When fibre absorbs part of the signal’s energy, reducing amplitude causing information to be lost. Reduce by using transparent core or fibre repeaters (regenerates signal).
Material Dispersion
When light consists of different wavelengths travelling different speeds along the fibre. Can avoid with monochromatic (single frequency/energy) light.
Progressive Wave
A wave that transfers energy from one point to another without transferring material.
Compression
A region of increased pressure in longitudinal waves causing nearby particles to vibrate with more energy.
Rarefaction
A region of decreased pressure in a longitudinal wave.
Polarisation
Wave propagation (of transverse waves ONLY) are limited to a singular plane. Only unpolarized waves can be polarised.
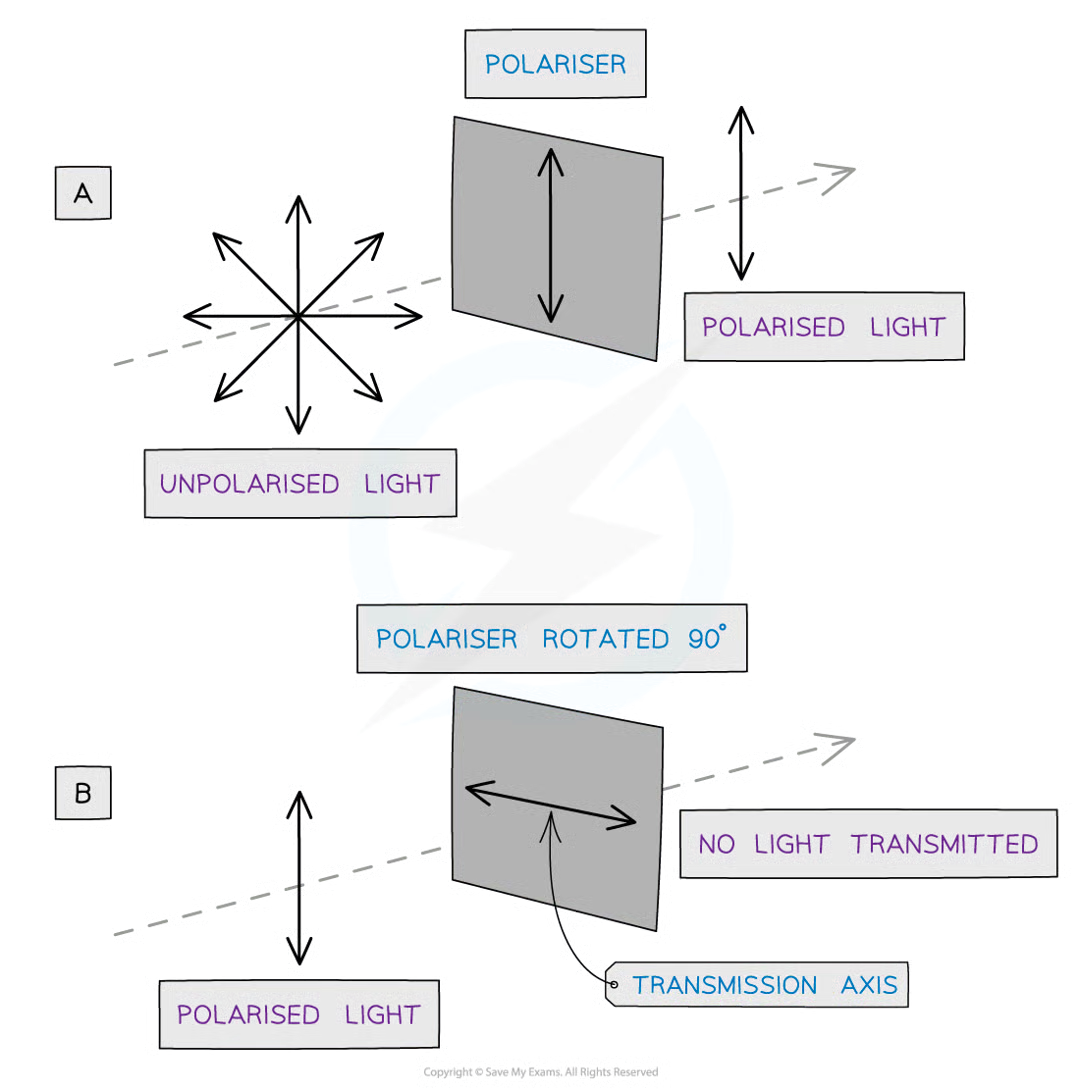
How does reflection affect the plane waves oscillate in?
When light is reflected it undergoes partial plane polarisation,
Therefore if the surface is horizontal, a proportion of the reflected light oscillates more in the horizontal plane than vertical.
How do polaroid sunglasses work?
Sunglasses have a vertical polarising filter.
When light is reflected and partially horizontally polarised, upon passing through the glasses the light’s intensity will be greatly reduced (since horizontally polarised light cannot be transmitted).
This allows object below the water to be viewed clearer.
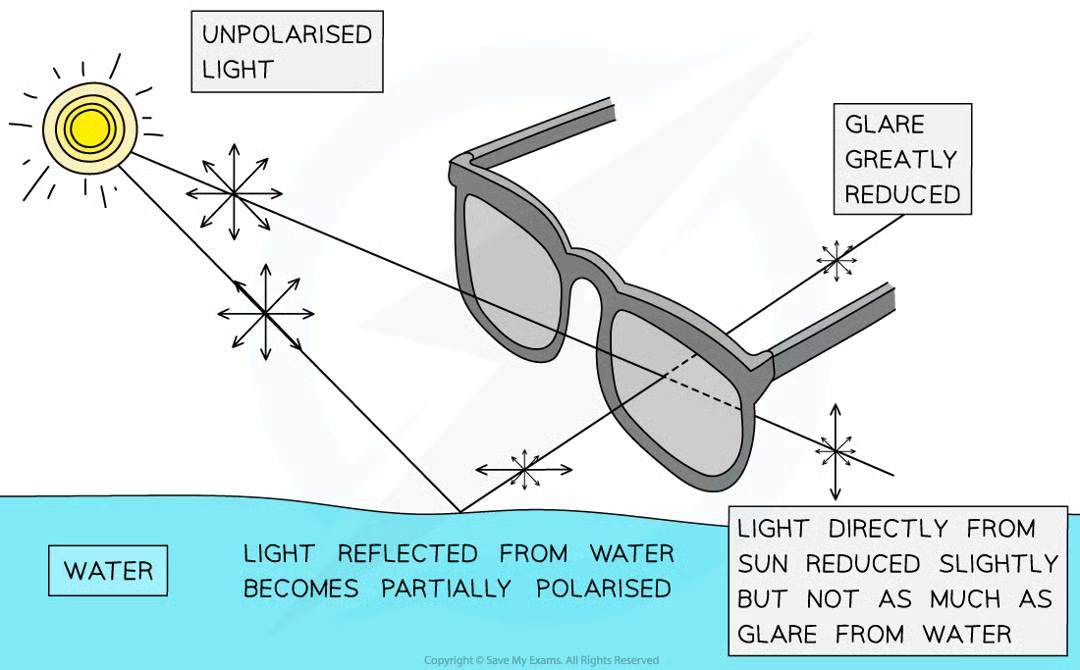
Why is light from underwater objects not partially plane polarised?
The light is refracted not reflected.
Stationary Waves
Waves which store energy caused by the superposition of two waves of same frequency and amplitude in opposite directions (usually due to reflection). Each point has different amplitude and speed depending on amount of superposition.
Principle of Superposition
When two or more waves with the same frequency arrive at a point, the resultant displacement is the sum of the displacements of each wave.
Resonant Frequencies
When a whole number of half wavelengths (node to node) fit on the stretch string (with a stationary wave).
How do you produce a stationary wave in an air column?
There must be a node at one end and an antinode at the end with the loud speaker.
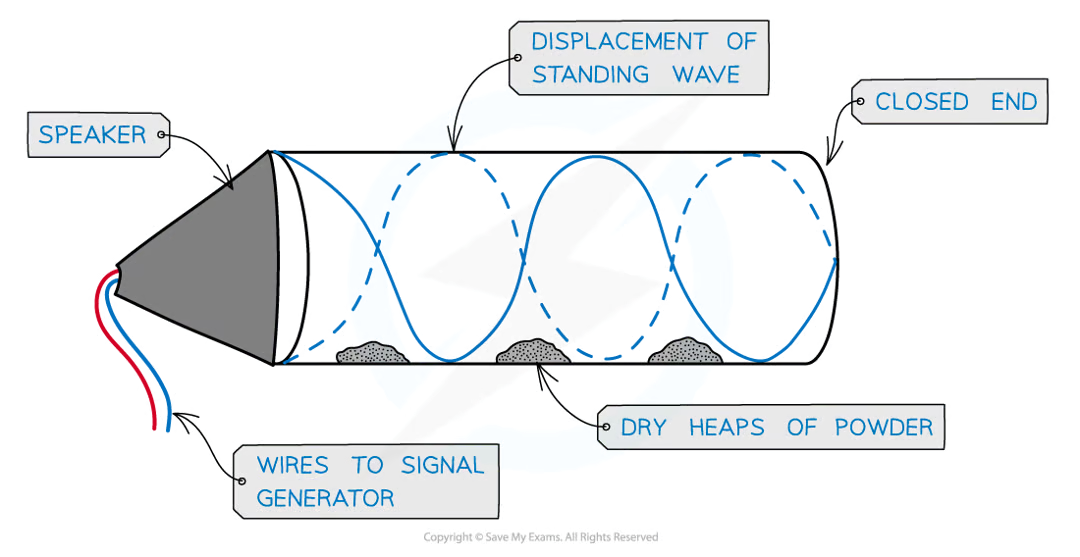
First Harmonic
The lowest frequency at which a stationary wave forms, causing two nodes and one antinode.
Interference
When waves superpose (are positioned over each other) and as a result their amplitudes combine.
Variation of Wave Intensity with Amplitude
The intensity of a wave at a point is related to the amplitude of the wave at that point.
Intensity is directly proportional to amplitude squared.
Diffraction
The spreading out of waves after they pass through a narrow gap or around an obstruction. Most noticeable when wavelength and width of the gap are similar size.
Diffraction Pattern