EXAMINATION OF THE THORACOLUMBAR SPINE (P2; LUMBAR SPINE)
1/168
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ASASASASASASA
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
169 Terms
How many pairs of facet joints are there in the lumbar spine
5 pairs (10 joints total)
With a normal intact disc, the facet joints carry about how much percent of the axial load?
If the IV disc is degenerated how much percent of the axial load does the facet joints carry?
20% to 25%
70%
The facet joints also provide how many percent of the torsional and shear strength?
40%
The motion segment of the vertebrae include which components?
the facet joints and disc
A defect in the pars interarticularis or the arch of the vertebra is called?
Degeneration of the intervertebral disc is called?
A forward displacement of one vertebra over another is called?
A backward displacement of one vertebra on another is called?
Spondylolysis
Spondylosis
Spondylolisthesis
Retrolisthesis
True or False:
The superior facets, or articular processes, face medially and backward and in general are convex.
False:
The superior facets, or articular processes, face medially and backward and in general are concave.
Anomality/Abnormality in the facet (usually shape of the facet) are also called?
Tropisms
Tropisms commonly occur at what level?
L5–S1 level
True or False:
In the lumbar spine, the transverse processes are virtually at the same level as the spinous processes.
True
Due to the shape of the facet joints in the lumbar spine, what movements are limited and what are facilitated?
Limited: Rotation
Facilitated: Side flexion, extension, and flexion
In what movement of the lumbar spine does the facet joints experience an increase in weight bearing function?
Extension
Normally, the facet joints carry only a small amount of weight; however, with increased extension, they begin to have a greater weight-bearing function.
Lumbar Spine
Resting position:
Close packed position:
Capsular pattern:
Lumbar Spine
Resting position: Midway between flexion and extension
Close packed position: Full extension
Capsular pattern: Side flexion and rotation equally limited, extension
True or False:
Even if only one facet joint in the lumbar spine has a capsular restriction, the amount of observable restriction is significant since the vertebrae are connected.
FALSE:
if only one facet joint in the lumbar spine has a capsular restriction, the amount of observable restriction is minimal
In some cases the S1 segment may be mobile. This occurrence is called?
lumbarization of S1
results in a sixth “lumbar” vertebra
the fifth lumbar segment may be fused to the sacrum or ilium, resulting in?
sacralization
True or False
S1 and L5 are sometimes called transitional vertebra
True
Ligament which connects the transverse process of L5 to the posterior ilium and helps to stabilize L5 with the ilium and to prevent anterior displacement of L5
iliolumbar ligament
The intervertebral discs make up approximately how many percent of the total length of the vertebral column?
paulit ulit na to
20% to 25%
IVD + 2 adjacent vertebra forms a?
functional segmental unit
The annulus fibrosus, the outer laminated portion of the disc and has 3 zones:
an outer zone made up of fibrocartilage classified as what?
an intermediate zone made up of another layer of what?
an inner zone primarily made up of fibrocartilage and containing the (smallest/largest?) number of cartilage cells.
The annulus fibrosus, the outer laminated portion of the disc and has 3 zones:
an outer zone made up of fibrocartilage classified as Sharpey’s Fibers
an intermediate zone made up of another layer of Fibrocartilage
an inner zone primarily made up of fibrocartilage and containing the largest number of cartilage cells.
The annulus fibrosus contains how many concentric, collar-like rings of collagenous fibers?
20
these fibers crisscross each other to increase their strength and accommodate torsional movements
True or False
At birth, the nucleus pulposus is made up of a hydrophilic mucoid tissue, which is gradually replaced by hyaline cartilage.
FALSE:
At birth, it is made up of a hydrophilic mucoid tissue, which is gradually replaced by fibrocartilage.
True or False:
With increasing age, the nucleus pulposus increasingly resembles the annulus fibrosus
True
degenerative changes (spondylosis) begin to occur after the which decade of life?
Second decade
True or False:
Initially, the disc contains approximately 85% to 90% water, but the amount decreases to 65% with age.
True
What causes the disc to be able to act as an incompressible fluid?
mucopolysaccharides
mucopolysaccharides decrease with age and are replaced with what?
collagen
True or False:
The nucleus pulposus lies slightly anterior to the center of rotation of the disc in the lumbar spine.
False:
The nucleus pulposus lies slightly posterior to the center of rotation of the disc in the lumbar spine.
The cartilaginous end plates are approximately how many mm thick to allow fluid to move between the disc and the vertebral body?
1 mm
True or false:
The discs are primarily avascular, with only the center receiving a blood supply
False:
The discs are primarily avascular, with only the periphery receiving a blood supply
True or false:
Until the age of 10 years, the intervertebral discs have some vascularity; with age, however, this vascularity decreases.
False:
Until the age of 8 years, the intervertebral discs have some vascularity; with age, however, this vascularity decreases.
The annulus fibrosus is innvervated by what nerve
sinuvertebral nerve.
The painsensitive structures around the intervertebral disc are?
anterior longitudinal ligament
posterior longitudinal ligament
vertebral body
nerve root
cartilage of the facet joint.
the pressure on the disc decreases as the patient assumes the natural _________ posture in the lumbar spine.
the pressure on the disc decreases as the patient assumes the natural lordotic posture in the lumbar spine.
These are herniations of the nucleus pulposus into the vertebral body:
Schmorl’s nodules
caused by too much direct vertical pressure
Schmorl’s nodules are found in how many percent of individuals?
20% to 30% of individuals.
True or False
Normally, an adult is 1 to 2 cm (0.4 to 0.8 inch) taller in the morning than in the evening. This change results from fluid movement in and out of the disc during the day through the cartilaginous end plate. This fluid shift acts as a pressure safety valve to protect the disc.
True
bwahahaha made u read allat
This happens when the disc bulges posteriorly without rupture of the annulus fibrosus.
Disc Protrusion
In the case of this condition, only the outermost fibers of the annulus fibrosus contain the nucleus
Disc Prolapse
With this condition, the annulus fibrosus is perforated, and discal material (part of the nucleus pulposus) moves into the epidural space.
Disc Extrusion
The condition where there is a formation of discal fragments from the annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus outside the disc proper
Sequestrated disc
These injuries can result in pressure on the spinal cord itself (upper lumbar spine), leading to a myelopathy; pressure on the cauda equina, leading to what type of syndrome?
Cauda equina syndrome
Activities that increase pressure at the IVD (remember the order i guess)
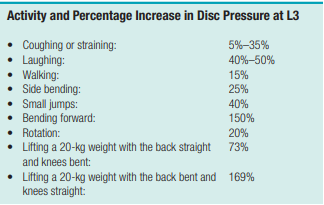
What is the disc between L4 and L5 called?
What nerve root does it compress when degenerated?
L4-5 disc
L5 nerve root
discs compress the nerve root below it, I think.
In general, which segment is the most common site of problems in the vertebral column?
L5-S1 segment
because this level bears more weight than any other vertebral level.
The center of gravity passes directly through this vertebra:
L5–S1
benefit because it may decrease the shearing stresses to this segment.
Which vertebrae is mobile in the L5-S1 segment?
Which is stable?
L5 mobile
S1 Stable
the transition from mobile to stable can increase the stress on this area
True or False:
Because the angle between L5 and S1 is lesser than the angles between the other vertebrae, this joint has a greater chance of having stress applied to it.
False:
Because the angle between L5 and S1 is greater than the angles between the other vertebrae, this joint has a greater chance of having stress applied to it.
Most mobile segments of the lumbar spine:
L5-S1
mobility is another factor that increases the amount of stress on this area
L4 and L5
True or False:
Problems of the lumbar spine are difficult to diagnose; in fact, diagnosing pain due to a disc is primarily a diagnosis of exclusion
True
True or False:
Individual red flags always means serious pathology.
False:
Individual red flags do not necessarily mean serious pathology but they should still be checked.
2 low back pain categories:
Back pain dominant
Leg pain dominant
Table for back pain dominant and leg pain dominant LBP: (seems important)
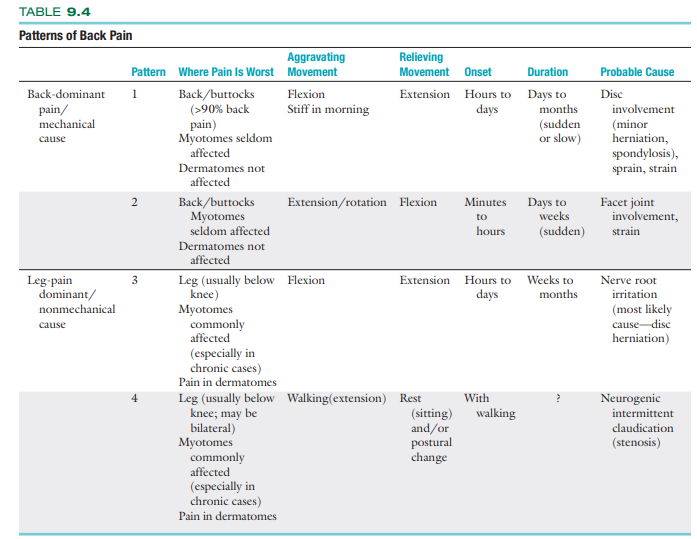
True or False:
If there are no radicular symptoms below the knee, it often becomes easier for the examiner to determine where in the spine the problem is
False:
If there are no radicular symptoms below the knee, it often becomes difficult for the examiner to determine where in the spine the problem is
disc problems usually occur between what years of age?
ankylosing spondylitis is evident between what years of age?
Osteoarthritis and spondylosis are more evident in people older than how many years of age?
malignancy of the spine is most common in people older than how many years of age?
15-40 y/o
18-45 y/o
>45 y/o
>50 y/o
True or False:
Back pain tends to be more prevalent in people with strenuous occupations
True
Patients who have chronic low back pain develop a type of syndrome which leads to decreased muscle strength, impaired motor control, and decreased coordination and postural control.
What is this syndrome called?
Deconditioning syndrome
Is low back pain more common in males or females?
Females
Is ankylosing spondylitis more common in males or females?
Males
When one is standing, the disc pressure is approximately how many percent of the pressure that occurs in the relaxed sitting position.
35%
True or False
Stress on the lower back tends to be 15% to 20% higher in women than in men.
False:
the lower back tends to be 15% to 20% higher in men than in women
because men are taller and their weight is distributed higher in the body
Acute back pain lasts for how many weeks?
3 to 4 weeks
Subacute back pain lasts for how many weeks?
12 weeks
Chronic pain is any pain lasting longer than how many months?
3 months
Predictors of Chronicity Within the First 6 to 8 Weeks (Yellow Flags)
Nerve root pain or specific spinal pathology
Reported severity of pain at the acute stage
Beliefs about pain being work related
Psychological distress
Psychosocial aspects of work
Compensation
Time off work
The longer someone is off work with back pain, the lower the probability that he or she will return to work
Unilateral pain with no referral below the knee may be caused by what?
injury to muscles (strain) or ligaments (sprain)
the facet joint
sacroiliac joints
If the pain is unilateral with no referral below the knee, what is the low back pain called?
mechanical low back pain (Lumbago in old books)
Here there is seldom if ever peripheralization of the symptoms. The symptoms tend to stay centralized in the back.
True or False:
With facet joint problems, the range of motion (ROM) decreases.
False:
With facet joint problems, the range of motion (ROM) remains the same (it may be restricted from the beginning).
Pain on standing that improves with walking and pain on forward flexion with no substantial muscle tenderness suggests what?
Disc Involvement
True or False:
The sacroiliac joints will show pain when pain-provoking (stress) tests are used
True
Table for patterns of back pain (skim and pray)
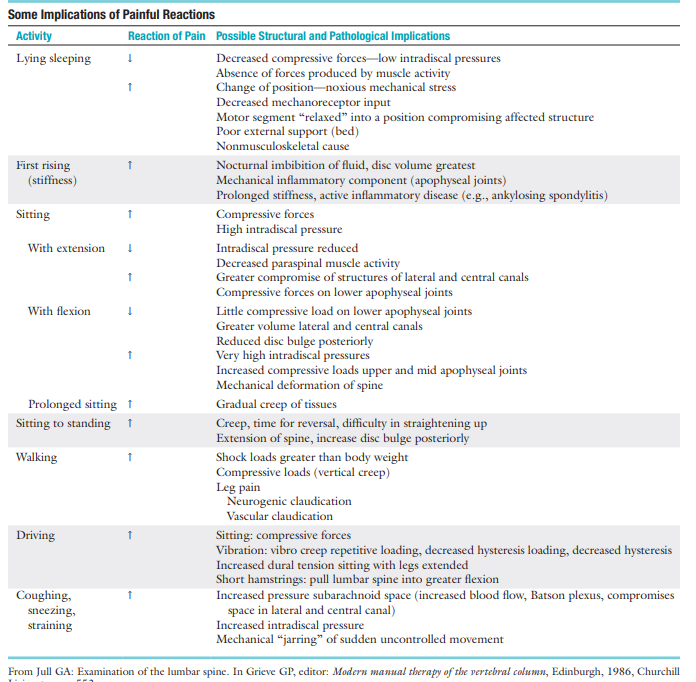
True or False:
A minor disc injury (prolapse) may show the same symptoms, but the pain is more likely to be bilateral if it is a central protrusion, spondylolisthesis, spinal stenosis, or metastases
FALSE:
A minor disc injury (protrusion) may show the same symptoms, but the pain is more likely to be bilateral if it is a central protrusion, spondylolisthesis, spinal stenosis, or metastases
_______ pain is extra segmental and felt over a larger area whereas ________ pain is usually restricted to one dermatome.
Dural pain is extra segmental and felt over a larger area whereas radicular pain is usually restricted to one dermatome.
Pressure on a nerve root sheath by a disc lesion will usually result in pain followed by _____________.
Pressure on a nerve root sheath by a disc lesion will usually result in pain followed by paresthesia.
True or False:
If any paresthesia is painless, a disc problem is likely and conditions such as cord compression, diabetes, pernicious anemia, or multiple sclerosis should be considered.
False:
If any paresthesia is painless, a disc problem is unlikely and conditions such as cord compression, diabetes, pernicious anemia, or multiple sclerosis should be considered.
True or false:
pain in the upper lumbar/ lower thoracic spin are commonly caused by disc lesions and serious disorders unrelated to activity are rare in this area.
FALSE
pain in the upper lumbar/ lower thoracic spin are rarely caused by disc lesions and serious disorders unrelated to activity are common in this area.
“Mechanical” Low Back Pain (Lumbago) Characteristics:
Pain is usually cyclic
Low back pain is often referred to the buttocks and thighs
Morning stiffness or pain is common
Start pain (i.e., when starting movement) is common • There is pain on forward flexion and often also on returning to the erect position
Pain is often produced or aggravated by extension, side flexion, rotation, standing, walking, sitting, and exercise in general
Pain usually becomes worse over the course of the day
Pain is relieved by a change of position
Pain is relieved by lying down, especially in the fetal position
This implies that the pain is moving toward or is centered in the lumbar spine:
Centralization
This implies the pain is being referred or is moving into the limb.
Peripheralization
disc problems account for only about how many percent of patients with low back pain
5%
True or False:
All disc injuries cause radiating pain to the leg because of nerve affectation.
False:
Minor injuries, such as protrusion of the disc, may result only in back or buttock pain.
This pain tends to be referred to the buttock and posterior leg (and sometimes to the lateral aspect of the leg).
Lumbar and Sacroillac pain
This pain tends to be in the groin and anterior thigh although it may be referred to the knee (usually medial side).
Hip pain
coughing, sneezing, deep breathing, straining, laughing increase the pressure inside the covering of the spinal cord.
What is this pressure called?
intrathecal pressure
True or False
disc pathology causes increased pain on sitting, lifting, twisting, and bending
True
tumors of the __________ refer pain to the low back.
Pancreas
Stiffness or pain after rest may indicate what?
Ankylosing spondylitis or Scheuermann disease.
This type of pain increases if the patient maintains a single posture (especially flexion) for a long period.
Discogenic pain
True or false:
In neutral pelvic position, the anterosuperior iliac spines (ASISs) are one to two finger widths higher than the posterosuperior iliac spines (PSISs).
FALSE:
In neutral, the anterosuperior iliac spines (ASISs) are one to two finger widths lower than the posterosuperior iliac spines (PSISs).
___________ of the facet joints leads to morning stiffness, which in turn is relieved by activity.
osteoarthritis of the facet joints leads to morning stiffness, which in turn is relieved by activity.
Diff Dx of Lumbago
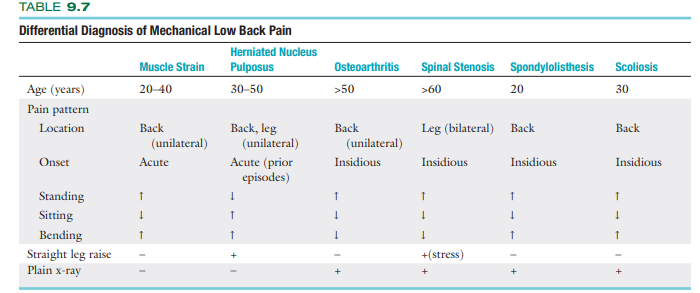
What muscles tend to respond to pathology with tightness in the form of spasm or adaptive shortening
Postural / Static Muscles
What muscles tend to respond with atrophy
Phasic / Dynamic Muscles
True or False:
Patients with disc herniation have trouble moving to the seated position
False:
Patients with lumbar instability or lumbar muscle spasm have trouble moving to the seated position
True or False:
pts w/ discogenic pain usually have pain in flexion (e.g., sitting) and the pain stays the same while sitting for prolonged periods.
False
pts w/ discogenic pain usually have pain in flexion (e.g., sitting) and the pain may increase the longer they are seated
True or False:
Bilateral pain in the upper sacroiliac region or in the groin on extension may indicate injury to the iliolumbar ligaments.
False:
Unilateral pain in the upper sacroiliac region or in the groin on extension may indicate injury to the iliolumbar ligaments
Abnormal sensations in the perineal area are often associated with what problems?
Micturition (urination) problems.
True or False
The nerve root is often compressed by the disc at the same level except when the protrusion is more lateral.
False:
The nerve root is seldom compressed by the disc at the same level except when the protrusion is more lateral.
There can be how many degrees of difference in straight leg raise while lying and sitting because of the change in lordosis and position of the pelvis?
10° to 20°