apbio unit 1.4 & 1.5
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is organic chemistry?
The study of compounds with covalently bonded carbon.
What are organic compounds?
Compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen.
How many valence electrons does carbon have?
Carbon has 4 valence electrons.
What types of covalent bonds can carbon form?
Carbon can form single, double, or triple covalent bonds.
What is the maximum number of covalent bonds a single carbon can form?
A single carbon can form up to four covalent bonds.
What are hydrocarbons?
Organic molecules consisting only of carbon and hydrogen.
What do carbon chains form in organic molecules?
Carbon chains form the skeletons of most organic molecules.
What are functional groups?
Chemical groups attached to the carbon skeleton that participate in chemical reactions.
What are the four classes of macromolecules?
Carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids.
What are polymers?
Chain-like macromolecules of similar or identical repeating units that are covalently bonded together.
What are monomers?
The repeating units that make up polymers.
What is a dehydration reaction?
A reaction that covalently bonds two monomers with the loss of H2O.
What is hydrolysis?
A reaction that breaks the covalent bonds in a polymer by adding H2O.
How many water molecules are needed to hydrolyze a polymer of 300 glucose monomers?
299 water molecules.
Why is carbon considered essential for life?
Carbon's ability to form diverse covalent bonds allows for the complexity of biological molecules.
What is polymerization?
The connection of many monomers to form a polymer.
What happens during a dehydration reaction?
The -OH of one monomer bonds to the -H of another, releasing H2O.
What happens during hydrolysis?
One -H of H2O bonds to one monomer, and the remaining -OH attaches to the other monomer.
What does the position of silicon on the periodic table tell us in comparison to carbon?
Silicon is in the same group as carbon, suggesting it may have similar bonding properties, but carbon's versatility makes it more essential for life.
What are the four main types of biological macromolecules?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, Proteins
What are the basic building blocks of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides, which are simple sugars.
What is the molecular formula for most monosaccharides?
Multiples of the unit CH2O.
What is the most common monosaccharide?
Glucose.
What are disaccharides?
Two monosaccharides joined together by covalent bonds.
What is the most common disaccharide?
Sucrose, composed of glucose and fructose.
What are polysaccharides?
Polymers made of many sugars joined via dehydration reactions.
What is the function of starch in plants?
To store excess glucose.
What do animals store as a polysaccharide?
Glycogen, stored in liver and muscle cells.
What is cellulose?
A structural polysaccharide that forms plant cell walls.
What are lipids?
A class of molecules that do not include true polymers and are generally hydrophobic.
What are the major functions of fats?
Energy storage, support cell function, and provide insulation.
What are the components of fats?
Glycerol and fatty acids.
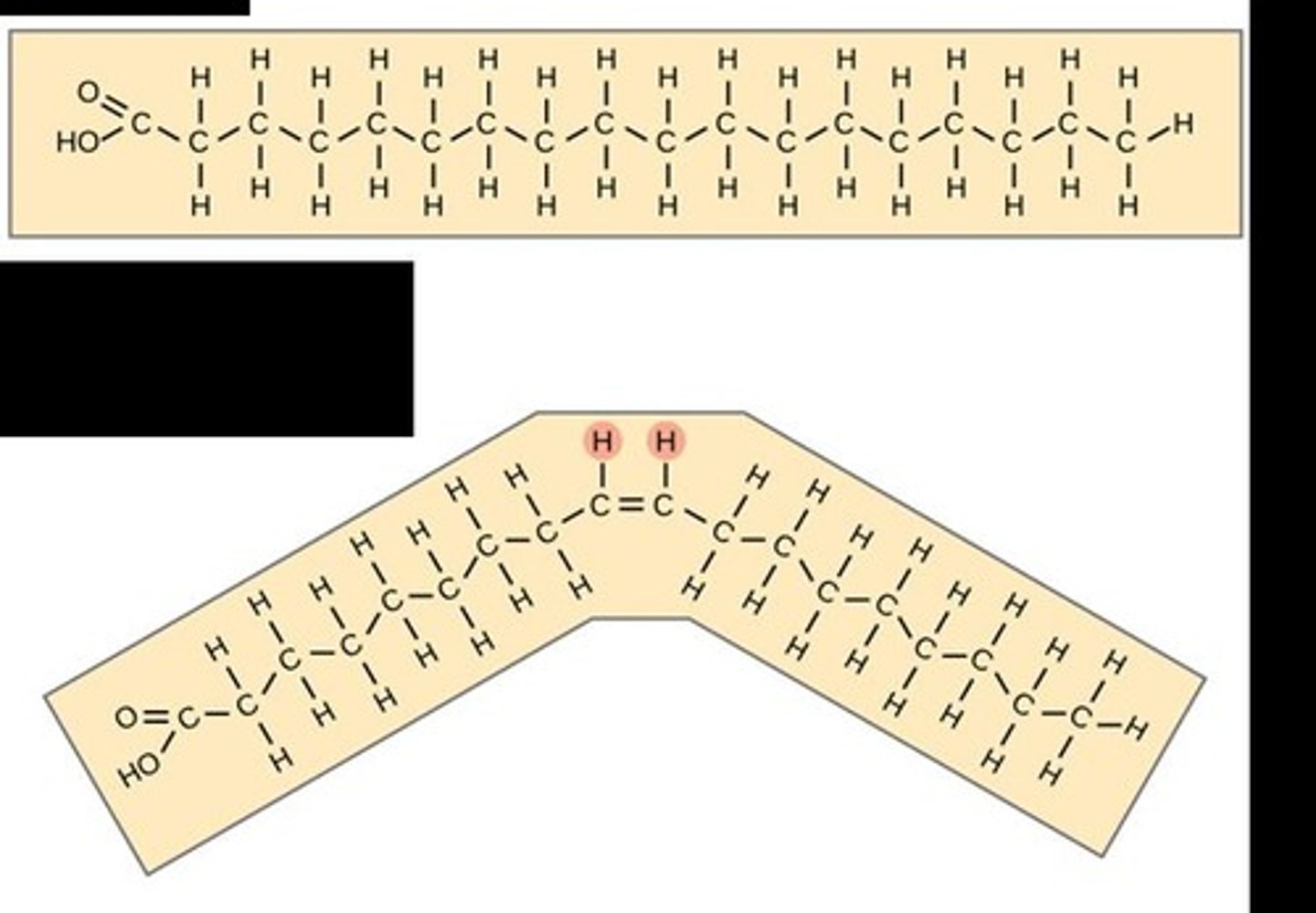
What distinguishes saturated fatty acids from unsaturated fatty acids?
Saturated fatty acids have single bonds between carbons, while unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds.
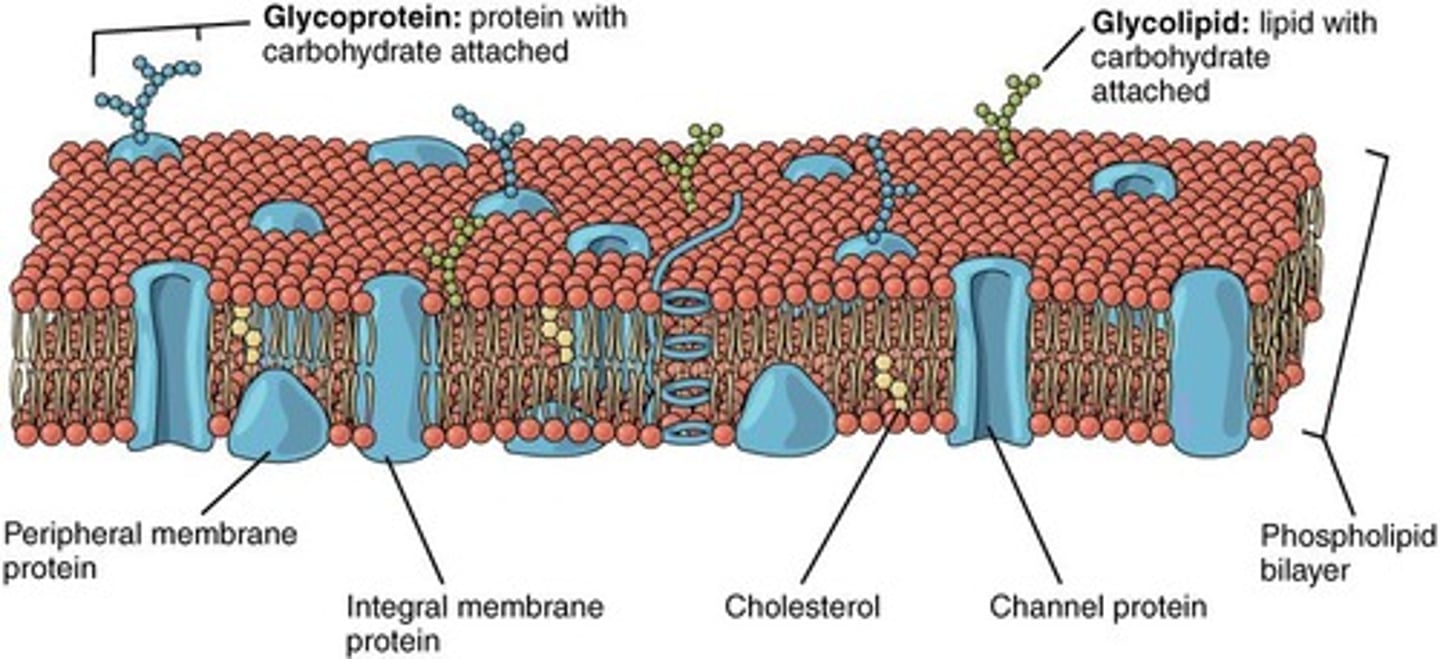
What are phospholipids?
Major components of cell membranes, consisting of two fatty acids attached to a glycerol and a phosphate.
What are nucleic acids?
Polymers made of nucleotide monomers that store, transmit, and express hereditary information.
What are the two forms of nucleic acids?
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
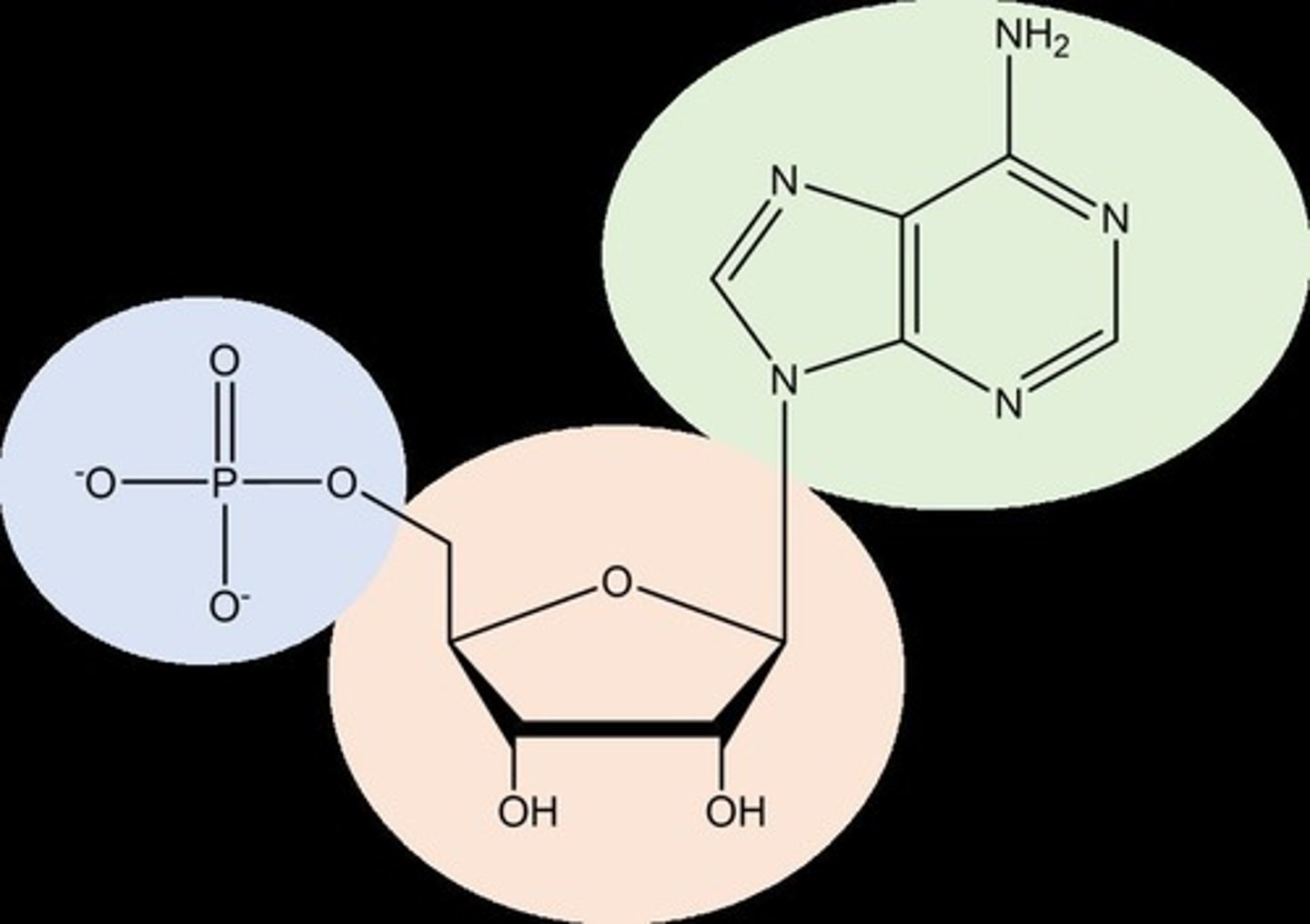
What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
A nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (pentose), and a phosphate group.
What are the two types of nitrogenous bases?
Pyrimidines (e.g., cytosine, thymine, uracil) and purines (e.g., adenine, guanine).
What is the structure of DNA?
Consists of two polynucleotides forming a double helix, with strands that are antiparallel.
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The unique sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide.
What determines the tertiary structure of a protein?
Interactions between the side chains of amino acids.
What is the quaternary structure of a protein?
The association of two or more polypeptides.
What are the main functions of proteins?
Antibody, enzyme, messenger, structural, and transport/storage roles.
What is a peptide bond?
A bond formed between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another, through a dehydration reaction.
What is the sugar-phosphate backbone in nucleic acids?
The alternating chain of sugar and phosphate groups that forms the structural framework of DNA and RNA.