Abdominal Vascular System
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
tunica intima
innermost layer of vessel wall
tunica media
middle layer of vessel wall
tunica adventitia (externa)
outer layer of vessel wall
arteries
thicker walls are a characteristic of _____________
arteries
________________ have internal & external elastic membranes
arteries
the tunica media is thicker in _______________
arteries
the lumen is smaller in _________________
arteries
________________ are pulsatile and not collapsible
arteries
______________ have no valves
veins
thinner walls are a characteristic of ______________
veins
_____________ have no internal or external elastic membranes
veins
the tunica media is very thin in _________________
veins
the lumen is larger in ______________
veins
_____________ are collapsible and not usually pulsatile
veins
_____________ have valves
aorta
largest artery in the body
arises from LVOT
aortic ectasia
absence of aorta tapering
celiac axis/trunk
first anterior aortic branch
common hepatic artery, splenic artery, and left gastric artery
the 3 branches of the celiac axis are:
common hepatic artery
right branch of celiac trunk
splenic artery
largest branch of celiac axis
runs left
left gastric artery
smallest branch of celiac axis
runs left & superiorly
superior mesenteric artery (SMA)
second anterior aortic branch
superior mesenteric artery (SMA)
the ______________ feeds the colon and the small intestine
renal arteries
arise from the aorta inferiorly to SMA at about level of 1st lumbar vertebrae
right renal artery
longer than left renal artery
usually runs post. to IVC and ant. to vertebral column into hilum of right kidney
left renal artery
runs from aorta directly into hilum of left kidney
inferior mesenteric artery (IMA)
one of the main branches of the aorta inferior to the aorta and the renal artery branches
tributaries
branches that empty into IVC
hepatic veins, Rt adrenal vein, Rt and Lt renal veins, Rt gonadal vein, inf phrenic vein, lumbar veins, Rt & Lt common iliac veins, median sacral veins
hepatic veins
largest visceral tributary
originate in liver & drain into IVC
3 branches: right, left, and middle
renal veins
5-6 branches join to form main renal vein on each side
right renal vein
flows directly from right kidney to posterolateral IVC
usually no tributaries into it outside kidney
left renal vein
exits hilum of left kidney on medial side
flows from left kidney to IVC
longer than the right one and accepts tributaries from left adrenal, left gonadal, & lumbar veins
splenic vein, superior mesenteric vein, and inferior mesenteric vein
the 3 tributaries of the portal venous system are:
Doppler shift
the amount of the perceived frequency change
time
on a spectral Doppler display, the x axis is:
Doppler shift frequency (velocity)
on a spectral Doppler display, the y axis is:
quantity of blood flowing at a given velocity
on a spectral Doppler display, the z axis is:
laminar flow (parabolic flow)
flow travels in layers
normal arterial flow down a straight vessel
fastest flow in center of vessel, slowest near vessel wall due to friction
place cursor in center of vessel to get accurate peak velocity
see in vessels with lower resistance/slower velocities
plug flow
most of blood is traveling at the same velocity
seen in vessels with higher resistance & higher velocities
resistance
opposition to blood flow
mainly due to friction between blood & vessel wall
blood viscosity, blood vessel radius, and blood vessel length
the three factors of resistance are:
blood viscosity
thickness of blood
blood vessel radius
how big the radius is around the lumen
increases
when blood viscosity increases, resistance _____________
decreases
when blood vessel radius increases, resistance __________
increases
when blood vessel length increases, resistance ______________
high resistance
describes flow that has little or no diastolic flow
low resistance
describes flow that has forward flow throughout diastole
spectral window
the area within a laminar or plug flow spectral profile when there are no echoes
spectral broadening
filling in of the spectral window because blood cells are flowing at many velocities
perpendicular
when the receiver is absolutely _______________ to the transmitter, there is no Doppler shift, and therefore no Doppler information is generated
parallel
the largest Doppler shift, and therefore the best Doppler information occurs when the flow is ____________ to the sound beam (Doppler angle 0)
Nyquist limit
aliasing occurs when the ____________ is exceeded
Nyquist limit
maximum frequency shift that can be displayed in PW Doppler without aliasing
PRF
aliasing can be corrected by increasing the ____________ or adjusting to a window where vessel is closer to the transducer
pulsed wave Doppler
aliasing only occurs with ______________
presence/absence, direction, and disturbance
Doppler is commonly used to detect the ________________ of flow
does not change
the flow in the celiac axis _______________ after meals
hepatic artery
always check the _____________ in heart and liver transplant patients
splenic artery
most turbulent celiac branch
prone to aneurysm
pancreatic pseudocysts
always do a Doppler exam (color and PW) of ______________ as they could be an aneurysm instead
non-resistive
after a meal, the SMA becomes _____________
renal arteries
have a low resistance pattern
renal veins and hepatic veins
variable flow like IVC
IVC
variable 2-step forward/1 step back waveform
always look for tumor or clot
athersclerosis
form of arteriosclerosis in which intimal lining of arteries is altered by the accumulation of lipids, carbs, blood, fibrous tissue, and calcium deposits
abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)
risk factors include over age of 60, hypertension, smoking, vascular disease, and being male
infrarenal
most common location of aneurysm
below the origin of the renal arteries
perirenal
location of aneurysm that involves the level or origin of the renal arteries
hard to repair
suprarenal
location of aneurysm that is located above renal artery origins
may extend above diaphragm
3
normal aortic lumen diameter is less than __________ cm
pseudoaneurysm
a collection of blood in tissue caused by a leaking hole in an artery
most commonly seen after catheterization via femoral artery puncture
aortic dissection
separation of aortic wall layers with blood coursing through false lumen
frequently fatal
Stanford and DeBakey
the two main classifications of aortic dissection are:
vascular stenosis
vessel lumen narrowed by plaque or arteriosclerotic changes
mesenteric artery stenosis/ischemia
results from lack of adequate blood supply (ischemia) to the GI tract either due to occlusion (embolic event) or atherosclerosis
aka mesenteric (intestinal) insufficiency
origin/proximal
majority of stenotic lesions are found in the ___________ segment of vessels
plaque
renal artery stenosis is most commonly caused by _______________
renovascular hypertension (RVHT)
the term used to describe elevated blood pressure that is primarily caused by renal artery stenosis
good perfusion
RI of .7 or less
possible rejection
RI of .7 to .9
probable rejection
RI >.9
azygous & hemiazygous veins
if the IVC is obstructed, the ______________ takes over
venous thrombosis of the lower extremities
the most common origin of pulmonary embolus (PE) is:
renal cell carcinoma
the most common malignancy to invade the IVC
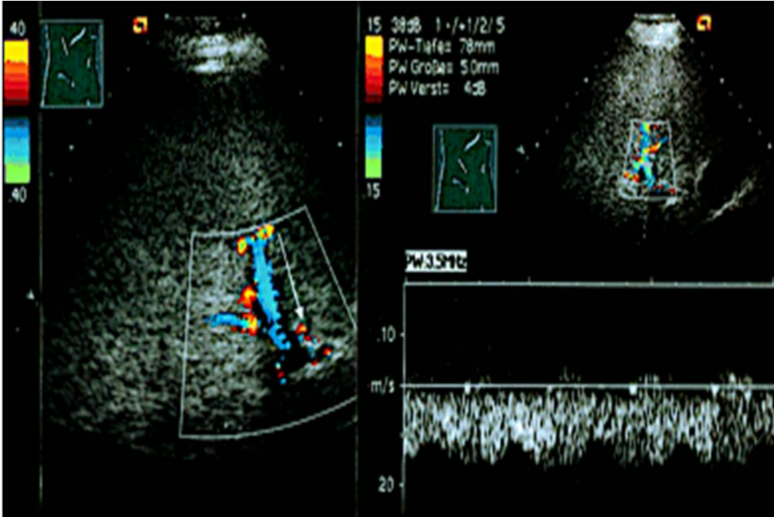
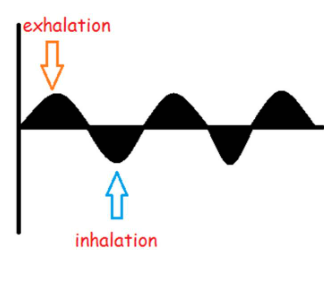
normal portal vein flow
hepatopetal flow
decreased forward flow on inhalation
increased forward flow on exhalation
forward flow continuous
mild portal hypertension
respiratory phasicity seen in normal PV flow is lost
continuous forward flow still seen
increased pressure in liver stops effects of respiration but does not reverse it
moderate portal hypertension
hepatopetal PV flow only seen upon exhalation
no flow seen on inhalation
pressure in liver high enough to eliminate forward flow into liver with inhalation
early severe portal hypertension
PV flow becomes back and forth with hepatopetal flow upon exhalation and hepatofugal flow on inhalation
pressure in liver & with inhalation so high that flow reversed in PV
severe portal hypertension
flow becomes completely hepatofugal
pressure in the liver becomes so high that blood cannot enter it
normal portal vein flow
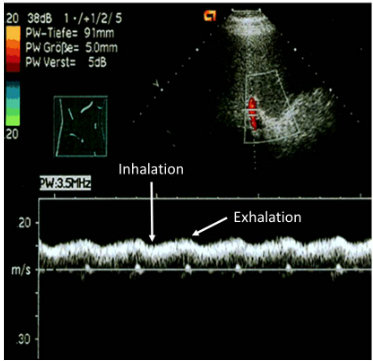
mild portal hypertension
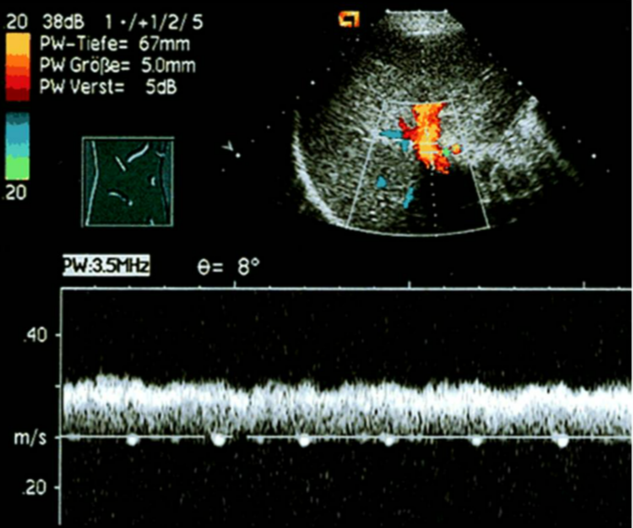
moderate portal hypertension
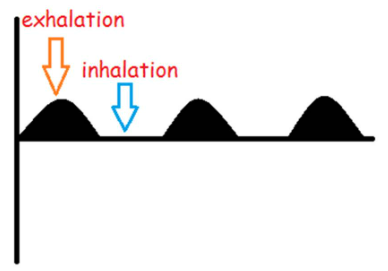
early severe portal hypertension
severe portal hypertension