Key concepts in Biology
1/41
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What is the meaning of prokaryotic?
single celled organism that has no nucleus
What is eukaryotic?
organism that has a nucleus
Example of eukaryotic cells
animal
plant cells
example of prokaryotic cells
bacteria
organelles
structures in a cell that have different functions
nucleus
contains DNA
Cytoplasm
jelly like substance that chemical reactions occur in
Cell membrane
controls what goes in and out of the cell
Mitochondria
where aerobic respiration takes place in to provide energy for the cell
Ribosomes
where protein synthesis occurs in
Found on a structure called the rough endoplasmic reticulum
Chloroplasts
where photosynthesis takes place providing food for the plant
contain chlorophyll pigment which makes plants green
what does a permanent vacuole
contain cell sap found in the cytoplasm
- provides strength for cell
what does the cell wall do
made from cellulose
provide strength for the cell
what does a flagella
Long thin tails that make bacteria cells move
how do cells specialise
by undergoing differentiation
what is differentiation
the cells gains ne sub- cellular structures for it to be suited to it’s role
what are the sub- cellular structures does sperm have
streamlined head and long tail
a lot of mitochondria
acrosome at the top of the head which has digestive enzymes to break down outer membrane of the egg cells
haploid nucleus- half the amount (23 chromosome)
What sub-cellular structures does the egg cell have
surrounded by a membrane that only allows one sperm during fertilisation
a lot of mitochondria to provide energy source for the embryo
large size and cytoplasm to allow quick division
What sub- cellular structures does a ciliated epithelial cell have
long hair-like processes called CILIA to waft bacteria trapped by sticky mucus own to the stomach where it is killed by the stomach acid
What sub- cellular structures does the root hair cell have
large surface area so more water can move in
large permanent vacuole affect speed of movement to cell
mitochondria to provide energy from respiration
What sub- cellular structures does a xylem cell have
when it is formed, a chemical called lignin is deposited to cause the cells to die.
they become hollow and a tube is formed
lignin is deposited in spirals to help the cell withstand the pressure of water movement
What sub- cellular structures does the phloem cell have?
cell walls form structures called sieve plates and break down to allow substances to move from cell to cell
the energy is supplied by the mitochondria of the companion cells
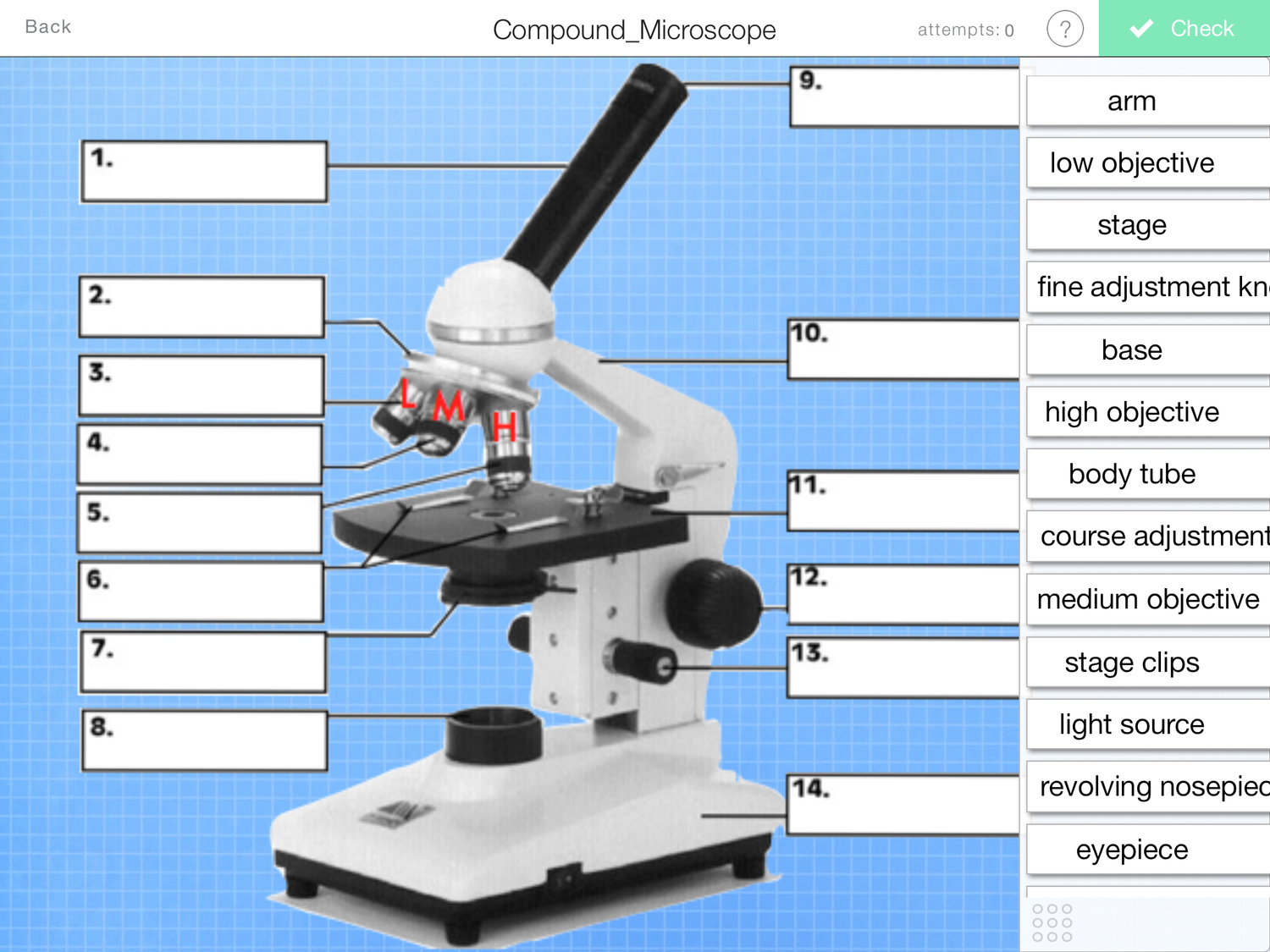
What is this number 11 of a microscope?
stage
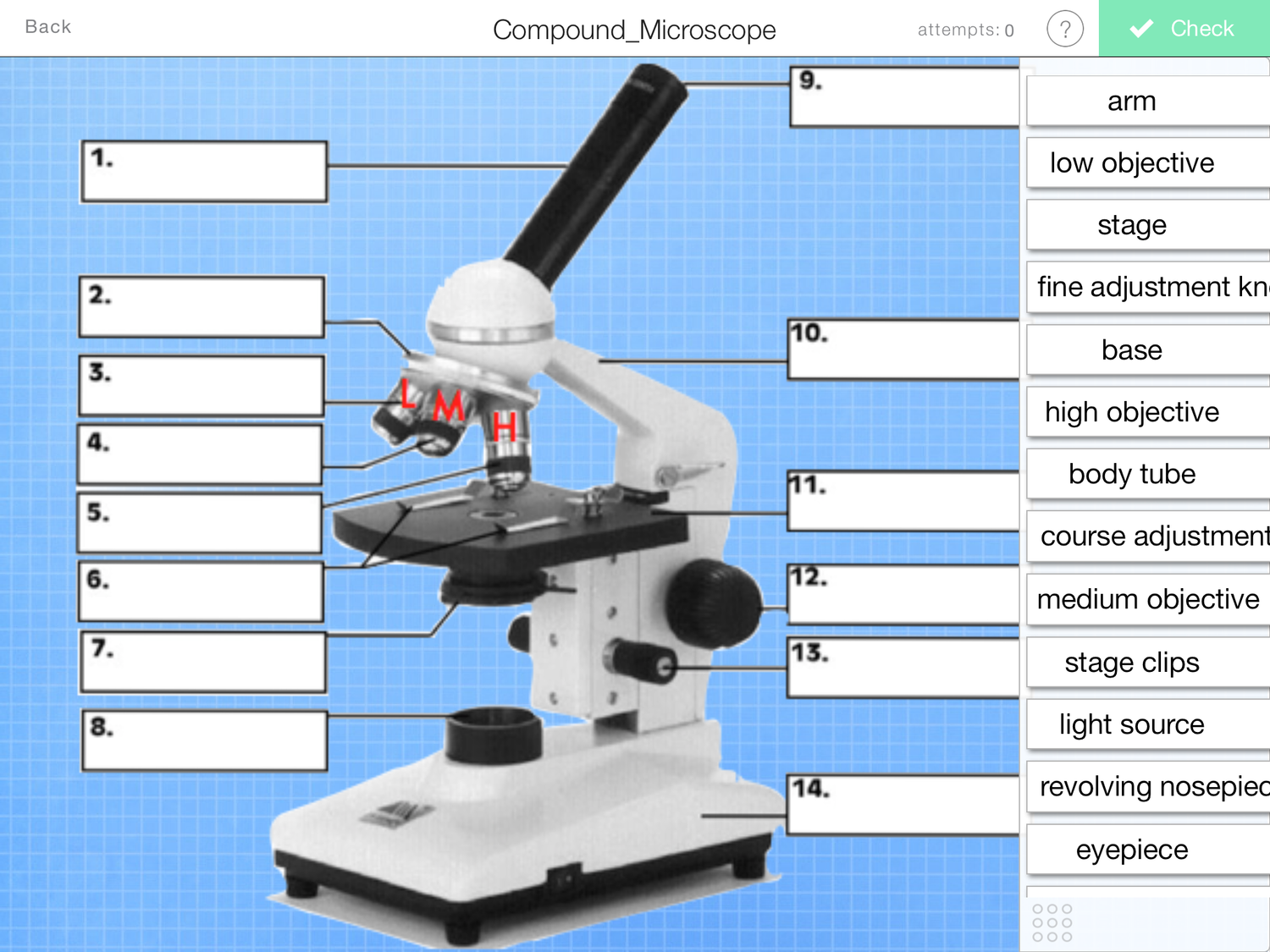
What is number 1?
Eyepiece
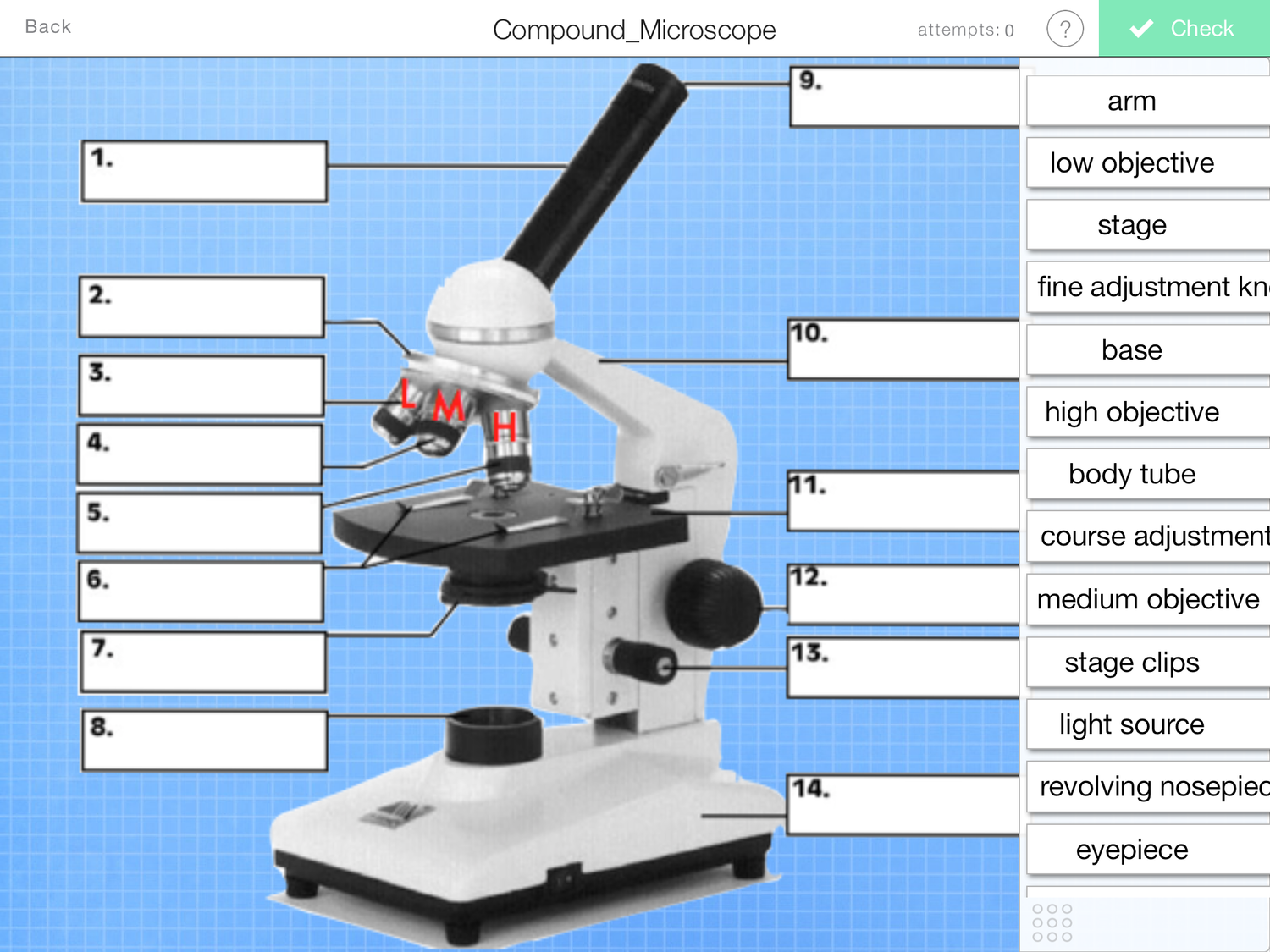
What is number 12?
coarse adjustment
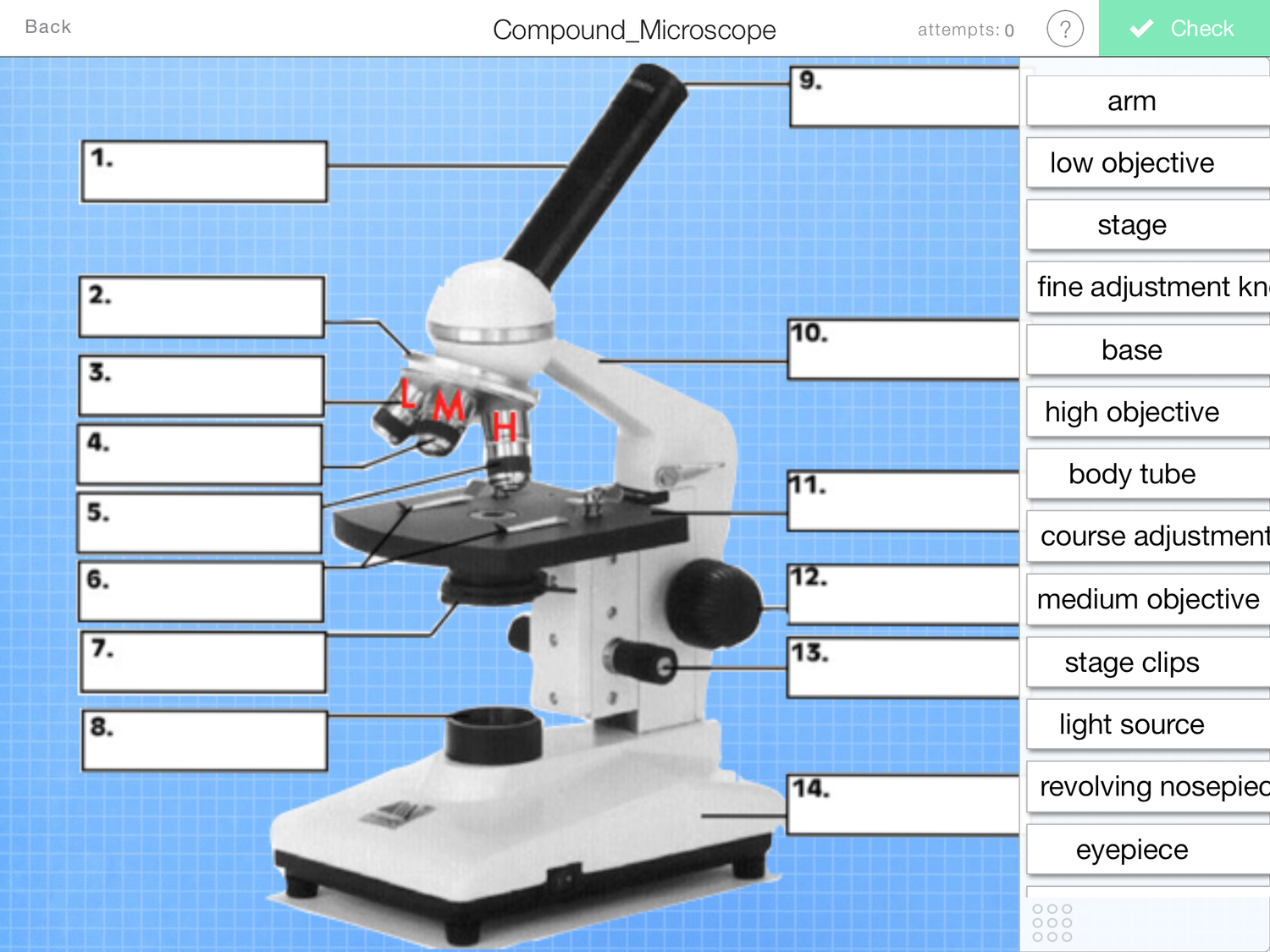
what is number 8?
light source
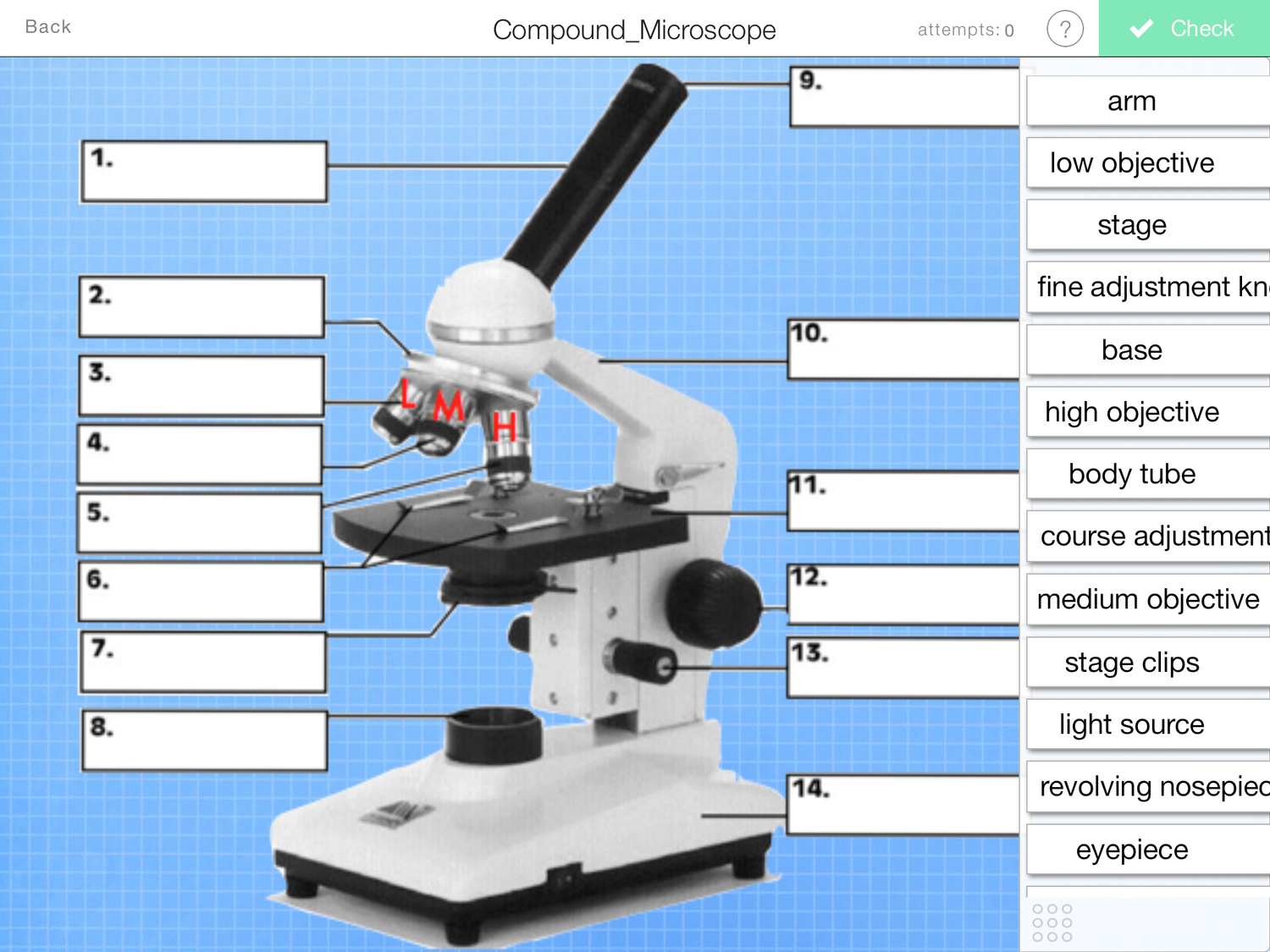
What is number 2?
nose piece
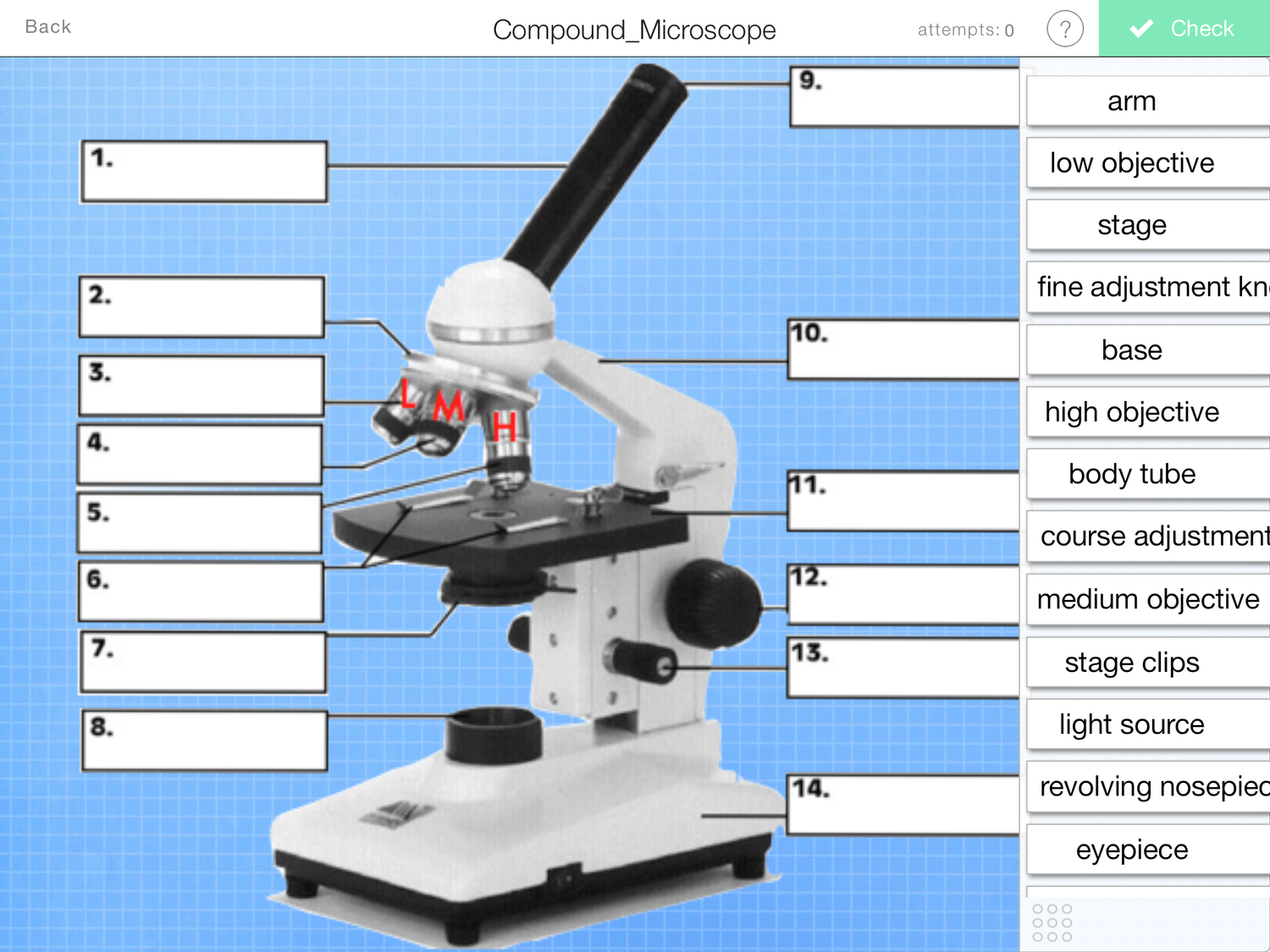
What is number 4?
Objective lens
When was the electron microscope discovered?
1930s
What is the approximate magnification of an electron microscope?
2,000,000
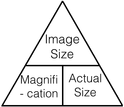
How do you calculate magnification of a light microscope?
magnification of eyepiece X magnification
How do you calculate size of an object?
size of image/ magnification
What are enzymes?
biological catalysts that increase the rate of reaction without being used up
what happens when the active site and enzyme combine?
it make an enzyme- substrate complex
What does an enzyme need to work well?
optimum temperature and pH
What happens if the temperature is too hot?
The bonds that hold the enzyme break down
What happens to the active site if the temperature is too high?
active site changes shape
What does protease break down?
proteins
What does amylase break down starch into?
sugars
If protease breaks down proteins what do they break down into…?
amino acids
what does lipase break down lipids into?
fatty acids and glycerol
How do you calculate percentage change?
change in mass/start mass