First week - Valvular Regurgitation
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Murmur characteristics PI
Low pitched
Diastolic
Increased with inspiration
PI w/ Pulm HTN murmur is called a
Graham Steel Murmur (Board question)
systolic murmurs are heard when there’s regurgitation with
Atrioventricular valves
diastolic murmurs are heard when there’s regurgitation with
Semilunar valves
Acute regurgitation always results in
pressure overload
Etiology (causes) PI (6)
Pathologic PI is not frequent
MOST COMMONLY caused by pulmonary HTN
Leads to Annular dilation
Endocarditis
Rheumatic Heart Disease
Tetralogy of Fallot
Carcinoid
% of people with normal PI
40-87%
Pathologic PI
NOT FREQUENT
This valve usually doesn’t have a lot of problems
Why is it difficult to see the valve cusps on a 2D echo
Pulmonic valve leaflets are very thin
Pulmonic insufficiency directed towards the Tricuspid leaflet causes:
Diastolic fluttering on M-Mode
RV Volume overload on M-Mode causes (2)
RV Enlargement and paradoxical septal motion
Evaluate _______ & ________ of the PI Color doppler jet
EXTENT & AREA
Assess CW Spectral doppler jet _______ for _______
assess CW spectral doppler jet DENSITY for SEVERITY
Severe PI causes
Rapid equalization of RV and Pulmonary artery pressures
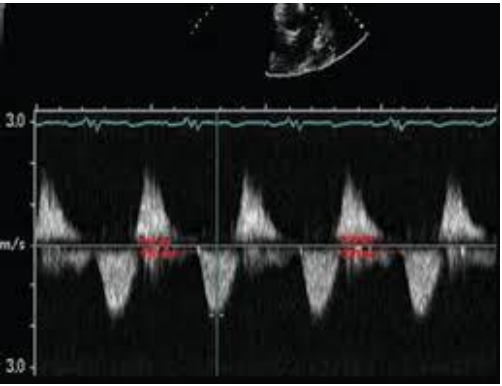
(2)
Regurgitation for PI is above the baseline and SEVERE PI IS DAGGER SHAPED
Rapid reversal
rapid desceleration
BAD BAD BAD!
Murmur - TV (2)
holosystolic
increase with respiration
Etiology (causes) TR (10)
Pulmonary HTN
Due to RV enlargement and Annular Dilation
can be caused by MV Disease or Pulmonary HTN
Rheumatic Heart Disease
Triscupid valve prolapse
Often associated with Mitral valve prolapse
RV Failure
RV MI
Carcinouid
TV is most affected by radiation
CHD
Marfans sydrome - poor connective tissue
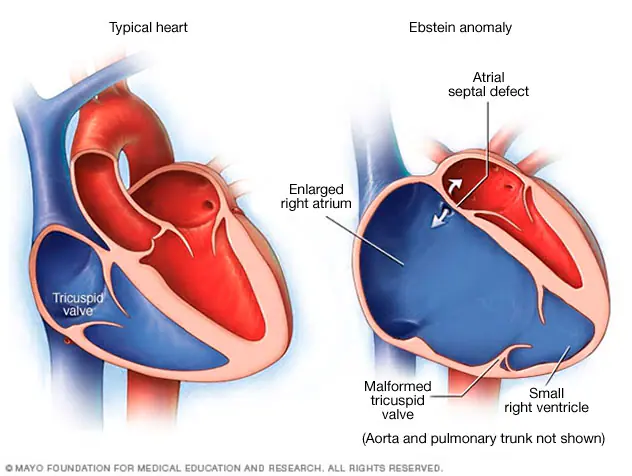
Ebstein Anomoly
CHD
Trauma
Endocarditis
Pacerwire
Goes through the TV
Ebstein anomoly
Assessment of TR
CW (3)
PW
Extent, area, direction of TR Jet
PW of hepatic vein in SUBC
Views for assessing TR (6)
RVIT
PSAX
A4C
SUBC
RT FOCUSED A4C
A3C RT HEART VIEWS
Is PISA used often for TR
Nah bruh (rarely)
Vena contracta width severe for TR when its over
0.7 cm (7mm) SEVERE
Use TR peak velocity to assess
PAP
Severe TR
vena contracta
spectral waveform
hep vein
PISA
Vena contracta >0.7 cm wide
Dense spectral doppler waveform
early peaking
triangular shaped
Hepatic vein
Blunted systolic wave, systolic flow reversal
PISA Radius > 0.9 cm
RV Volume overload
Right ventricular englargement
Pardoxical septal motion
PISA Radius width TR
mild
moderate
severe
Mild: <or= 0.5 cm
Moderate: 0.6-0.9 cm
Severe: >0.9 cm
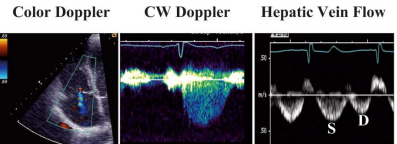
what does this show and why
MILD TR
Small color jet
round CW doppler
Systolic dominance in Hep vein
because LV is pushing blood through it
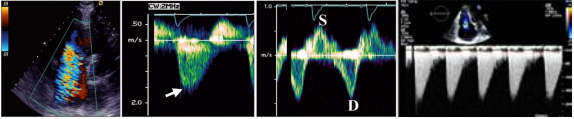
What is this and why
SEVERE TR
Big color jet
Steep and sharp reguritant CW Wwaveform
systolic flow reverasal in PW Hep vein
Dagger shaped high pressure that drops off quick
TR Due to RV enlargement and annular dilation common in what patient
IV Drug users because the dirty drugs hit the TV first
Severe TR is when there is more __________ flow than __________ flow
Severe TR is when there is more retrograde flow than antegrade flow
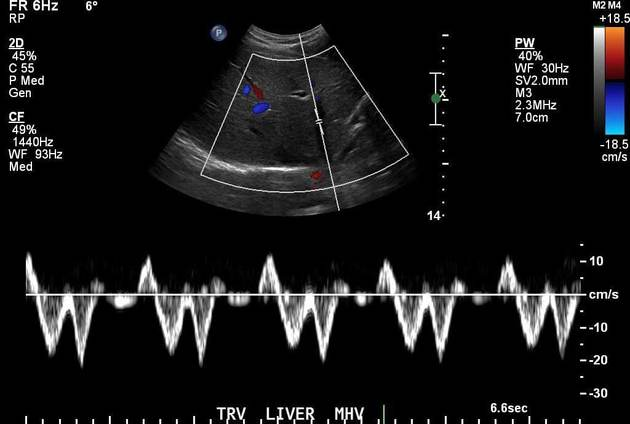
MODERATE TR
Systole and Diastole velocities are similiar
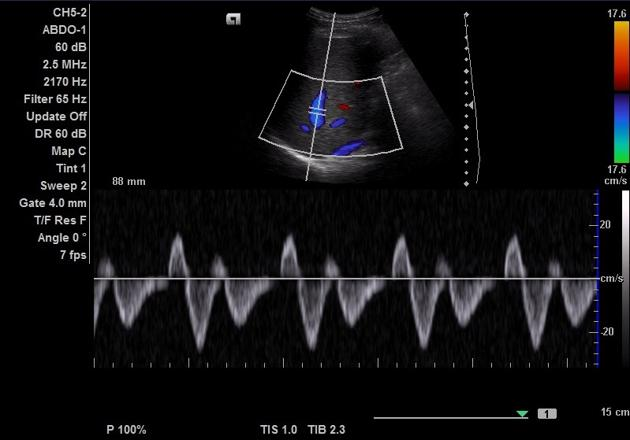
normal hepatic vein PW
Systolic is larger than diastolic
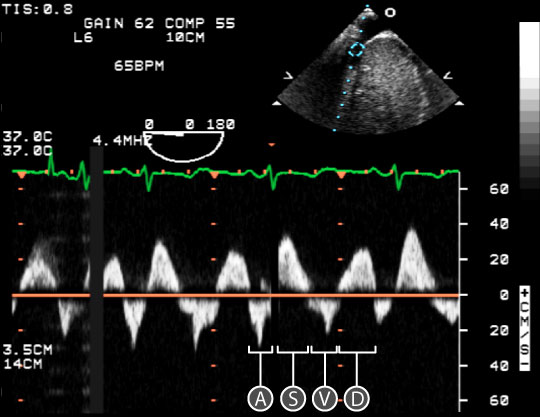
Hepatic vein FLOW REVERSAL
Look at systole! ITS GOING BACKWARDS BC PULMONARY PRESSURES ARE SO HIGH!!!
TR will causes a greater velocity in what part of diastole
TR = INCREASED E VELOCITY
Obtain peak CW TR for (2)
PAP
PISA Measurement
See what leaflets in these views
RVIT:
A4C
PSAX
TV
RVIT: Posterior & anterior
PSAX: Anterior & septal
A4C: Anterior & septal
primary regurgiation
Problem with the leaflets
secondary regurgitation
problem with the valve appartatus
examples of secondary regurtation TR (4)
cor pulmonal
RT HF (W/ Embolos usually)
RV MI
Pacemaker wires going through TV
Pulmonary HTN
RV Enlargement
annular dilation
leaflets fail to coapt
right sided failure will lead to
left sided failure
which dysfuction usually leads to the other
systolic = diastolic?
diastolic = systolic?
Systolic = diastolic