2. Nerve tissue
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
neuron
A nerve cell
receive, analyze, conduct and transmit information
nerve tissue contains
neurons
glial cells
Characteristic cell and matrix components of the peripheral and central nervous systems
Neurons consists of
dendrite(s), a cell body (soma), and an axon that may or may not be myelinated
CNS
brain + spinal cord
Interneurons
connect and send information between sensory neurons and motor neurons.
located within the central nervous system
PNS has
nerves & ganglions
PNS Carry sensory
sensory (afferent) inputs to the CNS
Sensory or afferent neurons send information from sensory receptors in skin, eyes, nose, tongue, ears, etc. toward the central nervous system
PNS Carry motor
Carry motor (efferent) outputs from CNS to skeletal, cardiac, smooth muscles of blood vessels, organs and glands
Motor or efferent neurons send information away from the central nervous system to muscles or glands. In response to impulses, muscles contract and glands secrete
2 main functional subdivisions of nervous system
Somatic (voluntary/conscious) control
Autonomic (involuntary/unconscious) control
parasympathetic
sympathetic
enteric digestive
Parasympathetic
located between spinal cord and medulla
Rest and digest/Feed and breed
Sympathetic
located near thoracic and lumbar regions of spinal cord
Fight or flight response (HR, rate of respiration, pupillary response,etc
in PNS: clusters of neurons with associated nerve fibers and supporting cells are referred to as
ganglia
In CNS: clusters of neurons are referred to as
"nuclei”
Supporting Cells (names in CNS vs PNS)
non-conducting cells that are in intimate positions with neurons
CNS: Neuroglia aka Glia
PNS:
Schwann cells: surround processes of nerve cells separating them from ECM
Satellite cells: surround nerve cell bodies (analogous to Schwann)
Functional Components of neuron
Cell body (perikaryon)
Axon
Synapse
Dendrites
Axon
long process (usually one) extending from the cell transmitting impulses
Synapse
specialized terminal → another neuron or effector cell
Dendrites
shorter processes that transmit impulses from the periphery (other neurons) towards the cell body
cell processes that receive action potentials from other neurons
One neuron may have many dendrites each with numerous branches
Are never covered with myelin
Nissl substance (Nissl body)
Ribosomes and rER are seen in clumps
CYTOSKELETON IN NEURONS
Microfilaments (actin)
Microtubules
neurofilaments
Microtubules
move materials throughout the neuron, especially in the axon
neurofilaments
function to support the dendrites and axons
Intermediate filaments
silver stain
cell body (soma)
Contains a nucleus and cytoplasm called perikaryon (‘peri-kar-ee-in’)
No myelin associated with the soma
Nissl substance is present
Responsible for the maintenance of the neuron because most protein synthesis occurs here
receives information from other neurons via synapses
soma morphology
reflects its high metabolic activity
Little heterochromatin in the nucleus
A very prominent nucleolus
Nissl substance (Nissl bodies) are observed in the perikaryon
indications of a lot of protein synthesis
Axon
Each neuron has only ONE AXON
Action potentials travel along axons from the cell body → down axon → and toward synapses at the axon terminal
Axons make synaptic contacts with other neurons or with target organs such as muscle and glands
Depending on the diameter of the axon, it may be myelinated
do not have Nissl substance and must receive all proteins from the cell body
Myelin is made by
Schwann cells (supporting cell in PNS)
staining neurons in the CNS
The nucleus and perikaryon of the soma are basophilic with H/E
You can usually see both axons and dendrites and their connection to the soma of neurons in the central nervous system
staining neurons in the PNS
You don’t usually see the axons or dendrites or their connection to the
soma in neurons of the peripheral nervous system
NEURON CLASSIFICATION: PSEUDO-UNIPOLAR
do not have separate dendrites and an axonal process, but rather one
branched process that serves both functions
Dorsal root ganglia contain cell bodies of sensory neurons (located in DR ganglion near but outside spinal cord)
Types: Sensory neurons with cell bodies in spinal and cranial nerve ganglia
Examples: dorsal root ganglia and cranial nerve ganglia
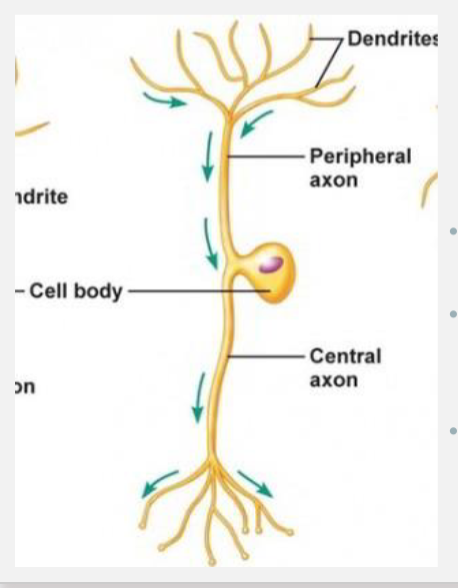
T-shaped process
A central process (axon) extends toward the spinal cord.
Called the central axon in the diagram
peripheral process
A afferent axon that carries sensory information from periphery
respond to touch, temperature, pain, stretch)
Called the peripheral axon in the diagram
NEURON CLASSIFICATION: BIPOLAR
One true dendrite with variable branching
One axon
Types: Sensory neurons of taste, smell, hearing, and sight
NEURON CLASSIFIC ATION: MULTIPOLAR
Many dendrites
The extent of branching and the shape of the dendritic tree is characteristic of different neuron types
One axon
Example: Spinal motor neurons
Functionally, these neurons either conduct impulses that will cause activity
such as the contraction of muscles or conduct impulses that permit
communication between neurons within the central nervous system
Myelin + cells that make it (PNS + CNS)
surrounds axons only
an extension of a cell membrane
In PNS, the cells that form myelin are called Schwann cells
In CNS, the cells that form myelin are called oligodendrocytes
internode/internodal segment
Schwann cells or oligodendrocytes form myelin around 1 or 2 mm of the length of an axon.
node of Ranvier or a node
The region between myelin
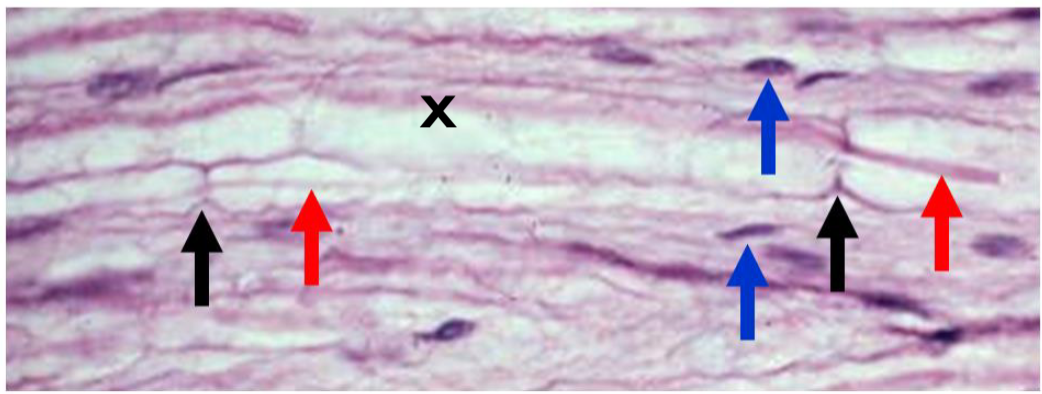
histology of myelin (light microscope)
Axons are eosinophilic (red arrows)
Schwann cell nuclei are basophilic (blue arrows)
Myelin is unstained (X)
Nodes of Ranvier (black arrows) are “pinches” along the axons
histology of myelin (TEM)
Myelin is osmiophilic (binds to osmium tetroxide)
used in the preparation of tissues for TEM
Myelin appears very electron dense using TEM
MYELIN ASSOCIATION WITH AXONS
In PNS: One Schwann cell forms myelin around only one axon
Schwann cells can surround many axons with cytoplasm but do not form any myelin
In CNS: One oligodendrocyte myelinates many axons
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (PNS) ORGANIZATION FOR HISTOLOGY PURPOSES
Neuron cell bodies (soma)\
Groups of soma in the PNS are called ganglia
Soma sometimes called ganglion cells
Satellite cells surround ganglion cells as glia
Axons
Groups of axons in the PNS are called nerves
Schwann cells form myelin around axons or surround axons without forming myelin
Blood vessels
Connective tissue investments
ganglion (s), ganglia (pl)
any group of neuron cell bodies in PNS
Histology of ganglia
Histology: Soma are round, have a large nucleus with prominent nucleolus, Nissl substance in cytoplasm (basophilic) and possibly lipofuscin (brown, represents waste pigment from breakdown of blood cells)
Satellite cells surround the soma as a protective covering
Loose connective tissue surrounds the soma
PNS NERVE
a bundle of axons held together by three types of connective tissue investments
The axons are also called nerve fibers
Peripheral nerves are mixtures of sensory and motor axons, and unmyelinated and myelinated axons
HISTOLOGY OF PERIPHERAL NERVES: LM
In longitudinal section peripheral nerve appears wavy
The paler staining regions represent areas of myelin. The basophilic dashes are the nuclei of Schwann cells
In cross section peripheral nerve appears like a group of small circles
HISTOLOGY OF PERIPHERAL NERVES: TEM
Myelinated axons have an electron dense band around them (M)
Unmyelinated axons are groups of axons surrounded by Schwann cell cytoplasm (NM)
endoneurium
a layer of collagen type I and reticular fibers (collagen type III) that surrounds individual axons
peripheral nerves
fascicles + perineurium
Bundles of axons = fascicles
Connective tissue that surrounds fascicles = perineurium
peripheral nerves
epineurium
surrounds the entire nerve
Blood vessels that supply the nerve are located here.
peripheral nerves
Receptors
terminals of sensory nerves that receive and respond to stimuli
transducers that convert energy in the environment into impulses that are conducted along axons
classified based on the type of stimulus that they detect
mechanoreceptor
a sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion
thermoreceptor
responds to heat and cold
nociceptor
responds to pain
nerves in dental pulp are only nociceptors
ORGANIZATION OF NERVE TISSUE IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM IN ITS SIMPLEST FORM FOR HISTOLOGY PURPOSES: CNS
cerebrum, cerebellum, and spinal cord
• Neurons
• Supporting cells called glial cells, glia, or neuroglia
• Blood vessels
• Neuropil
• Connective tissue investments called the meninges
Gray matter
• Neuron cell bodies
• Beginning segments of axons and dendrites
• Ends of axons
• Glial cells
White matter
• Glial cells
• Dendrites
• Unmyelinated axons
• Myelinated axons
Neuropil
dense network of fine glial processes, neuronal processes (axons and dendrites), and fibrils in gray matter of CNS
Groups of neuron cell bodies that have similar morphology, connections,
and function in the CNS
nuclei
Tracts
groups of axons that have a common origin and destination
also called fascicles, lemniscus, columns
White matter
organized into dorsal columns, lateral columns, and ventral columns
Gray matter
organized into dorsal and ventral horns
glial cells of CNS
no loose connective tissue between neurons in CNS
Neuropil
the space between neuronal and glial cell bodies that is comprised of dendrites, axons, synapses, glial cell processes, and microvasculature
Oligodendrocytes
myelinate axons in the CNS
Cell processes end in a sheet of myelin that wraps around an axon
One oligodendrocyte can myelinate several axons
Microglia
macrophages of the CNS
can migrate and are found throughout the CNS tissue
Play a role in repair and inflammatory processes by removing dead or degenerating neurons and other glial cells
Ependymal Cells
neuroepithelial multiciliated cells lining the spinal cord and cerebral ventricles
Simple cuboidal ciliated epithelial cells
Line the fluid-filled ventricles within the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord
function in the secretion of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
astrocytes
subtype of glial cells that make up the majority of cells in the human CNS
perform metabolic, structural, homeostatic, and neuroprotective tasks such
as clearing excess neurotransmitters, stabilizing and regulating the blood-
brain barrier, and promoting synapse formation
Extend branching cytoplasmic processes (foot processes) in all directions
Foot processes contact blood vessels in the brain and spinal cord
A part of the blood-brain barrier
Meninges
three membranes layers that cover and protect your brain and spinal cord
protect and anchor your brain and provide a support system for blood vessels, nerves, lymphatics and the cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds your central nervous system.
Dura mater
dense irregular connective tissue
vascularized
Arachnoid
contains collagen and elastic fibers
non-vascularized
Pia mater
a delicate layer of collagen and elastic fibers
highly vascularized