Geography IGCSE - Settlements
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Site
the land on which a settlement is built
Situation
position of settlement in relation to the surrounding area
Function
a settlement’s main activity or purpose
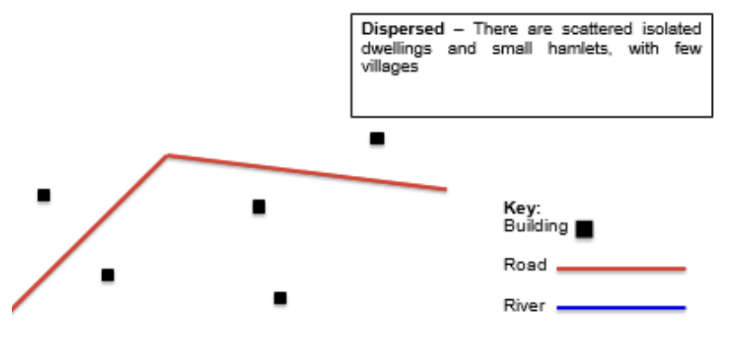
Dispersed
houses/buildings are far apart, following a random arrangement that doesn’t follow a specific pattern.
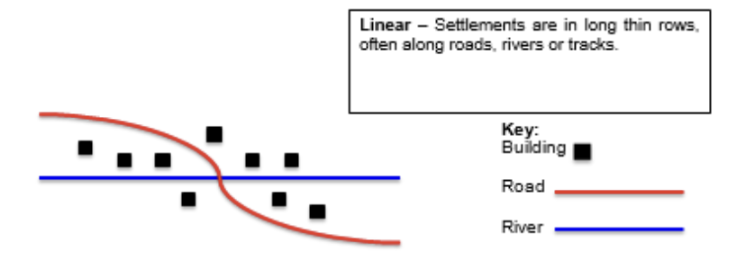
Linear
houses/buildings follow a specific pattern, are usually built following a river or a road.
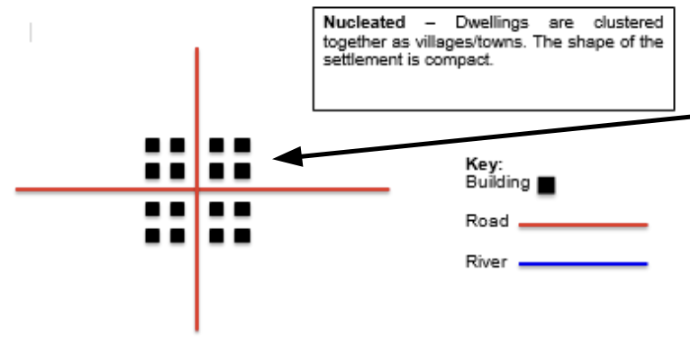
Nuclear
houses/buildings are all built in a specific area, usually very close together. An example could be a CBD area. There are usually high population densities in this area.
Factors influencing sites, growth and function of settlement:
Soil → fertile soil → agriculture
water and food supply → steady supply of food
situation features → resources and defensive features
accessibility to other settlements → grow faster if well connected to other towns → trade and movement
transportation methods availability → growth with trade and accessibility
climate → extreme climates limit growth
Urban sprawl
unplanned growth of urban areas into surrounding countryside
effects and changes of urban sprawl
Effects | Impacts |
more businesses | more accessibility for long distance travelling |
Overcrowding | housing shortages → urban sprawl to fix it |
overcrowding | more pollution |
Privately owned cars | more traffic congestion |
Sphere of influence
area around a settlement that people will travel from to use a service
Low order goods
(or convenience goods) are goods people buy on a daily basis
High order goods
(or comparison goods) are goods you buy less often, tend to be more expensive and people are prepared to travel further to compare prices before buying
Threshold population
minimum population needed for a service to be offered
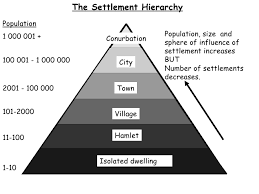
Hierarchy of settlements
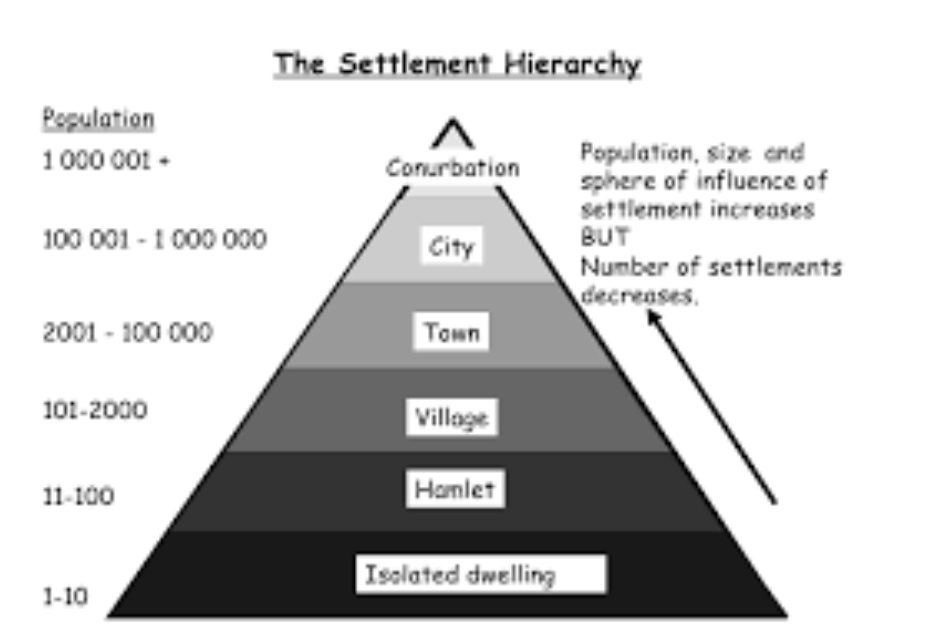
Reasons for the hierarchy of settlements and services
The bigger the settlement, the more services are provided. For example cities have a lot more services that can provide the citizens than towns and villages, while they only have really basic and essential services. Also rural areas have a lot less services compared to urban areas, because urban areas are more developed and offer more services in general.
Hierarchy of settlements
Describe and give reasons for the characteristics of, and changes in, land use in urban areas
CBD → located in city centre → commercial and business center with high property values
Residential areas → vary from dense urban houses to suburban houses → wealthier countries see gentrification → developing countries rapid expansion into informal settlements
Industrial areas → on outskirts → declining in developed countries due to change in economies → expanding in developing
Rural - urban fringe → transition zone between the 2 → new developments → leads to land conflict
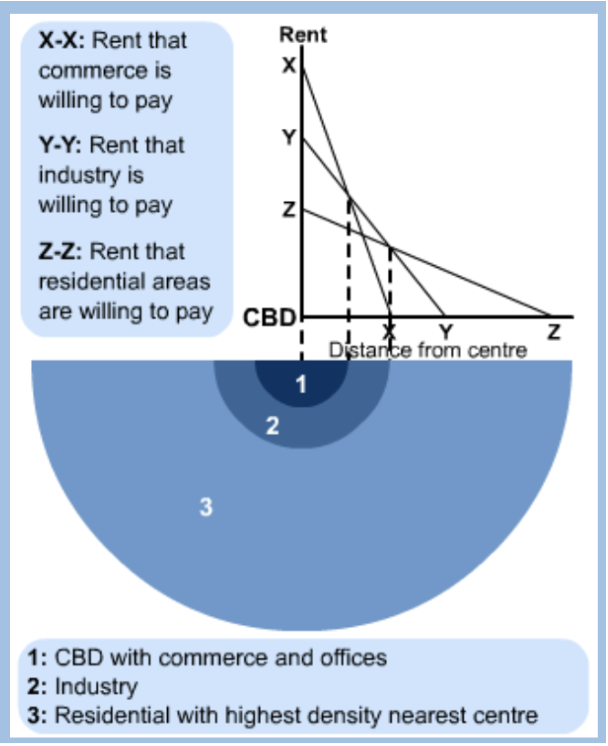
Bid-rent theory
Bid - rent shows that rent or value of land increases the closer it is to the centre
Land nearest to the CBD → most expensive (centrally located, very accessible and limited availability)
Rent or value decreases with distance from the CBD
This value determines how land is used (commercial, industry or residential)
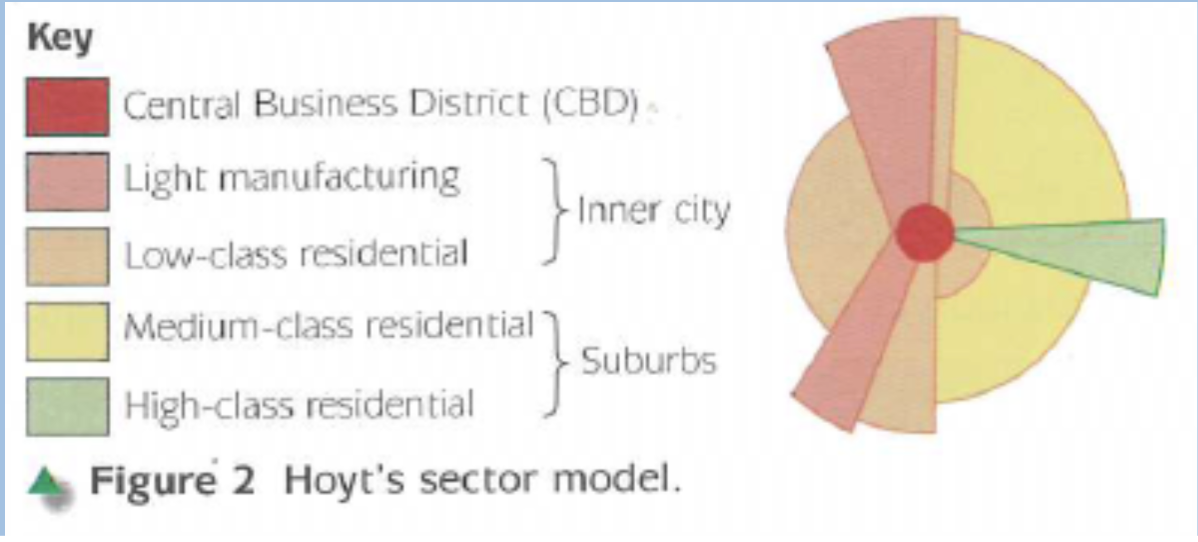
Hoyt’s Sector Model:
After the development of public transport systems and an increase in the use of cars
CBD remained central
Transport routes became more important when locating industry
Industry sectors (or wedges) extended along major transport routes
Low-class housing followed this pattern as workers needed to be closer to their workplaces
Main difference between low and high class residential
Location and Infrastructure:
LC → less desirable areas with basic infrastructure.
HC → prime, well-connected modern areas
Amenities and Security:
LC → Limited amenities, minimal security.
HC → Lots of amenities, enhanced security with gated access and surveillance.
Property Value and Community Services:
LC → More affordable, lower property values + fewer community services.
HC → Higher property prices + rents, well-maintained with community services.
Explain the problems of urban areas + their causes
air, noise, water, visual pollution → globalisation + rapid urban growth
inequality →
housing issues → rapid urban growth
traffic congestion → rapid urban growth
conflicts over land use change → rapid urban growth → limited amount of land
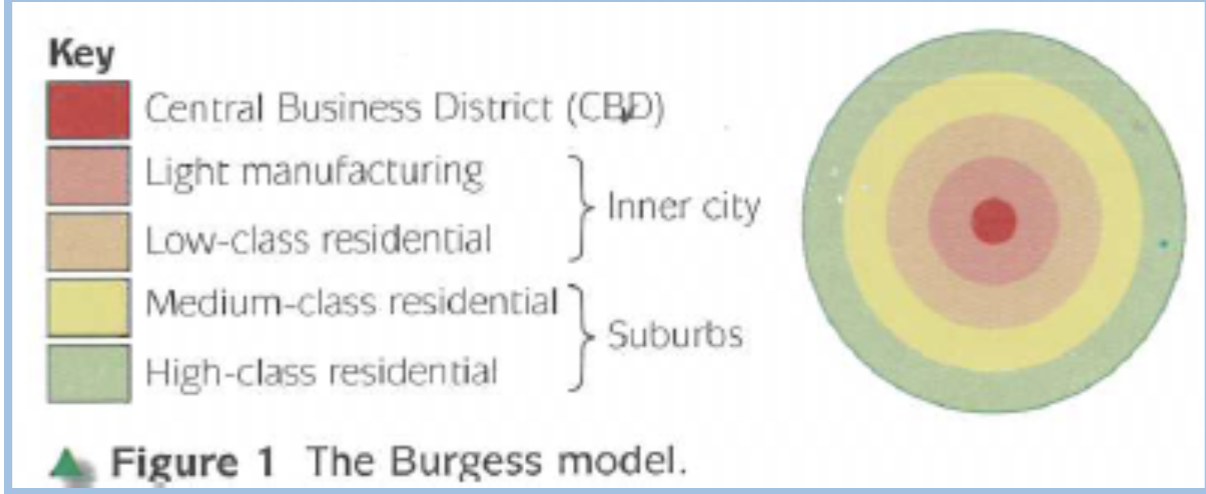
Burgess’s Concentric Zone Model:
Five concentric circles arranged around the CBD in a circular pattern
Each circle has has a different land use
Land costs are higher in the CBD
Land costs are lower with increasing distance from the city centre
CBD: MBS shopping mall, orchard
Light manufacturing: Sawmill, paper making
Low class residential: HDB
Medium class residential: apartments
High class residential: Landed housing
Explain the problems of urban areas + possible solutions
air, noise pollution → public transport, energy efficiency, noise policies
water pollution → globalisation + rapid urban growth
inequality → green infrastructure techniques
housing issues → public housing, affordable
traffic congestion → road pricing, public transport
conflicts over land use change → land use policies, urban sprawl
reasons for rapid urban growth physical, economic and social factors which result in rural depopulation and the movement of people to major cities
urban pull factors → higher wages, better job opportunities, accessible public utilities
Rural push factors → limited healthcare + education, mechanisation of farming, harsh + monotonous lifestyle
positive impacts of urban growth on both rural and urban areas
creation of employment opportunities
Quality education and medical facilities
Improved transportation
Technological and infrastructure improvements
negative impacts of urban growth on both rural and urban areas + solutions
Slums → relocating the people + improving the infrastructure so it’s a proper living space
Visual pollution → laws for graffiti, strict planning
characteristics of squatter settlements
houses built from dried mud as the walls and corrugated iron for the roof.
no proper toilets
no electricity between phone lines
no running water, sewage or electricity in homes
no paved roads or sewers
little space between houses
weak infrastructure
extremely high density