Genomics and inheritance
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
genotype
genetic material inherited from parent
How many copies of each gene does an individual have?
2 (one from each parent) - EXCEPT on x or y chromosome
What is the expressed phenotype of cells/organisms influenced by?
genotype
inherited epigenetic factors
non-inherited environmental factors
What do alterations to the genetic code have a potential to do to a specific protein?
increase
modify
stop production
Are consequences of alterations to coding or non-coding sequence easier to predict?
coding sequence
Does dominance indicate whether an allele is beneficial, detrimental or neutral?
NO
What does the dominant alleles usually produce?
functional protein
Dominant allele
only one copy required to affect phenotype
complete or partial (incomplete)
Recessive allele
2 recessive copies required to affect phenotype
What does it mean for alleles to be ‘co-dominant’?
both alleles manifest at the same time as eachother
What can cause DNA alterations?
physical or chemical damage
replication going wrong during mitosis & meiosis
somatic cell errors not being repaired leading to dysplasia or neoplasia
errors within gametes or embryonic cells lead to novel characteristic
What does chromosomal separation during mitosis and meiosis result in?
altered structures of chromosomes
movement of long sections of DNA or their inversion

What is munchkin deformity caused by?
dominant, lethal gene with variable penetration

What does bully whippet appearance occur due to?
2-bp deletion in myostatic gene located on canine chromosome 37
monozygous affected dogs look like this - too much muscle, end up with lots of muscle damage due to inability to get oxygen

What does this image show?
belgian blue cattle - excessive muscles
What causes hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in Maine Coon cats?
missense mutation in cardiac myosin binding protein C
What are the steps in genome mapping in animals?
identify gene(s) responsible for genetic trait of economic or clinical importance
marker-assisted selection
What can we use identifying gene(s) responsible for genetic trait of economic or clinical importance for?
model for human disease
map genes in animal pedigrees
eliminate affected individuals and carriers from gene pool
What is marker-assisted selection used in?
conventional breeding programmes to increase frequency of desirable traits
introgression of genetic material from one population to another
What technique is used for DNA sequencing?
Sanger technique
What are reactions containing individual ddNTPs run on in the sanger technique?
gel
labelled with different fluorophores
What are the methods used for DNA sequencing?
sanger sequencing
pyrosequencing
What are single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)?
any single position within the genome sequence where nucleotide differences may occur
What can the presence of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) be used as?
linkage markers for the presence of nearby genes controlling traits of interest (because these differences are passed down generations)
How are SNPs analysed?
hybridisation of SNP alleles and detection using fluorescence
What are the applications of SNP-array analysis?
genome-wide association studies (GWAS) enabled selection
identification of quantitative trait loci
evaluation of genetic merit of individuals
comparative genetic studies
What is an example of an applications of SNP-array analysis?
sensory neuropathy in border collie
What are the types of point mutations?
insertion
deletion
substitution of base pairs
What can alteration of the exonic sequence result in?
silent
missense
nonsense
frame shift
silent mutation
no change in aa sequence
missense mutations
a different aa is encoded
nonsense mutations
a premature stop codon is introduced
frame shift mutation
change in aa sequence from that point on
What can alteration of the intronic sequence result in?
no changes
altered splicing sites → change in aa sequence
altered gene expression (increased or decreased)
exonic sequence
coding
intronic sequence
non-coding
What are the characteristics of autosomal dominant defects
dominant
defect seen in every generation
every affected patient has at least one affected parent
normal offspring from affected parents will produce normal offspring
equal numbers of male and females will be affected
What are 2 examples of autosomal dominant defects?
feline polycystic kidney disease
Scottish fold osteodystrophy
What are the characteristics of autosomal recessive variance?
defect may skip a generation
all offspring of affected parents will be affected
‘normal’ parents of an affected individual must be a carrier
equal numbers of male and female affected
Name examples of autosomal recessive traits
hyperuricosuria in dalmatian dogs
Avermectin sensitivity in collie dogs
What are the characteristics of X-linked dominance variance?
every affected offspring has at least one affected parent
affected males mated to normal females will transmit the defect to all their daughters and none of their suns
unless defect common (affected female will be heterozygous and when mated to normal male the defect will be transmitted to half the offspring
Name an example of an x-linked dominant trait
X-linked dominant hereditary nephritis in Samoyed
What are the characteristics of x-linked recessive variance?
may ‘skip a generation’
incidence in male > female
when defect rare: affected individuals will be males and will have in inherited the gene from the dam
Name an example of X-linked recessive traits
Haemophilia A (factor VIII deficiency) in Havanese dogs
more likely to see this in cocker spaniels but cause unknown
genotype
organism’s full hereditary information
phenotype
actual observed properties
Heritability of the characteristic =
proportion of the phenotypic variation that is due to genotypic variation
What can heritability be predicted by?
analysis of population statistics
What are some examples of heritability?
reproduction (dairy cattle,pigs) LOW
305-day lactation yield (dairy cattle) MODERATE
milk composition % (dairy cattle) HIGH
carcass fat depth (pigs) MODERATE
Why is heritability important?
how easy able to select for characteristics
List methods of selection
performance test
pedigree analysis and ancestor evaluation
progeny testing
performance of siblings
marker assisted selection
calculations (e.g. estimated breeding value, true breeding value, selection intensity)
performance test
selection of basis of phenotype
Name an example of where performance testing occurs
black vs red aberdeen angus
What are the limitations of performance testing?
phenotype may not reflect genotype
only effective for high heritability characteristics
if autosomal recessive trait select against - recessive allele cannot be eliminated due to presence of carriers
Pedigree analysis/ancestor evaluation
based off records of ancestors
What is using pedigree analysis/ancestor evaluation useful for?
late manifesting traits, where parental records are the only indication of a young animal’s potential performance
Progeny testing
look at performance of offspring to determine valuability of that individual
How can you look at the performance of the offspring in progeny testing?
assessing non-additive gene effects
assessing low heritability characteristics
assessing sex-limited characteristics
assessing carriers of a recessive gene
What is progeny useful for?
where semen is banked, e.g. Holstein cattle
What characteristics is assessing the performance of siblings useful for?
characteristics that cannot be seen and assessed on the live individual
What is marker assisted selection (in cattle) used for?
bulls used in artificial insemination across several different herds
What is marker assisted selection/ best linear unbiased prediction (BLUP) in cattle?
a number of marker sites have been mapped in the bovine genome with loci (QTLs) linked to certain production rates
What was marker assisted selection/ best linear unbiased prediction (BLUP) in cattle originally developed for?
selection using phenotypic data
genetic gain is greater the _______ the selection intensity
greater
What impacts selection intensity?
males > female
larger population = greater possible selection intensity
What factors affect the rate of improvement?
heritability of trait
intensity of selection
generation interval
number of traits required for improvement
What methods are available for selection of more than one trait?
tandem selection
independent culling
selection index-marker assisted selection
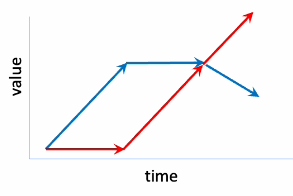
What method for selection for more than one trait does this graph show?
tandem culling
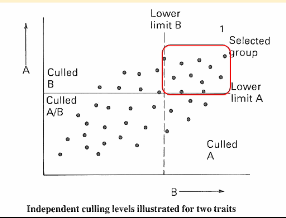
What method for selection for more than one trait does this graph show?
independent culling