CW Doppler and Duplex Scanning
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
CW Doppler capabilities
evaluate for obstruction and venous incompetence
CW Doppler limitations
fixed sample volume, no anatomic image, no range resolution, difficult to differentiate deep venous obstruction vs extrinsic compression
CW Doppler physics principles
2 crystals, 5 Mhz, 45-60 degree angles
looking for CW Doppler signal
find the arterial signal and angle medially
reverse trendelenburg
position where pt legs are below the heart level
spontaneous flow should be present in the extremities without augmentation, except for
tibials, GSV, radial/ulnar
continuous flow patterns in extremities can be consistent with
proximal venous obstruction or shallow respirations
absence of augmentation with distal compression indicates _______, if venous reflux occurs, this indicates ______
obstruction, incompetent valves
venous reflux
a condition where blood flows backward in the veins, instead of upwards towards the heart
with prox compression or _____, venous flow should ____
valsalva, halt
if augmentation happens with valsalva/______, this indicates _____
prox compression, venous reflux
once prox compressions are______, signal should _____. If not, this indicates obstuction
released, augment
causes pulsatile flow in subclavian vein
proximity to heart
can cause pulsatile flow in the lower extremities
fluid overload, chronic venous insufficiency, or increased venous pressure
can result in increased venous pressure
a heart problem, like CHF
venous flow is related to _____ and can also be affected by _____
arterial peripheral resistance, venomotor tone
vasodilation of veins flow
continuous flow with less respiratory variations
vasocontriction of veins flow
decreased venous flow signals
false positive causes
extrinsic compression, peripheral arterial disease, improper doppler angle or probe pressure
peripheral arterial disease leads to
decreased venous filling
COPD leads to an elevated _____ which alters pressure gradients and reduces _____
central nervous venous pressure, venous flow patterns
CW Doppler false negative causes
partial thrombosis, collateral development, duplicate deep veins
Duplex false negative causes
technically limited, prox obstruction (iliacs)
Duplex scanning limitations
edema, recent surgery, obesity
duplex scanning abd/pelvic capabilities
portal hypertension, venous thrombus, extrinsic vs intrinsic, assess shunts, eval liver disease
automatic cuff inflator for FV eval
cuff at thigh, 80 mmHg
automatic cuff inflator for pop eval
cuff at calf, 100 mmHg
automatic cuff inflator for PTV eval
cuff at transmetatarsal, 120 mmHg
<0.5 s
normal flow reversal
0.5-1.0 s
abnormal flow reversal
color flow imaging reveals venous reflux as a _____ during ____
directional shift, valsalva
subclavian and innominate are difficult to ______, and along with IJV have _____ waveforms
compress, pulsatile
dilated IVC size
>2 cm
can cause dilated IVC and pulsatile MPV
cardiac failure, and fluid overload
acute thrombus
not fully compressible, low-level echoes, dilated vein, rouleau formation
if flow is not spontaneous at CFV, FV, or POP V
obstruction distal to or at site
continuous flow instead of phasic in CFV, FV, and POP V
prox obstruction
no augment with distal comp at CFV, FV, and POP V
obstruction between imaging and comp or slightly more prox
no augment with prox release in CFV, FV, POP V
prox obstruction
forms subclavian vein
cephalic and axillary
forms the innominate vein
subclavian and IJV
forms the axillary vein
basilic and brachial
forms brachial vein
radial and ulnar
thrombus _____ over time and leaves a ____ wall
retracts, thickened
miscellaneous findings
edema, lymph node, muscle tear, nerve, sarcoma, venous aneuryysm
budd chiari
results from hepatic vein occlusion and presents with hepatomegaly, abdominal pain, and ascites onset
perforator vein incompetence
more often associated with reflux in the superficial veins
perforator size >3.5 mm
reflux present 90% of the time
stasis changes at the ankle
most obviously affected area lies directly above an incompetent perforator
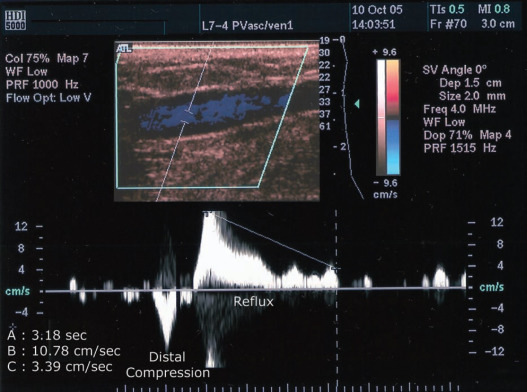
what is being shown in this image?
venous reflux
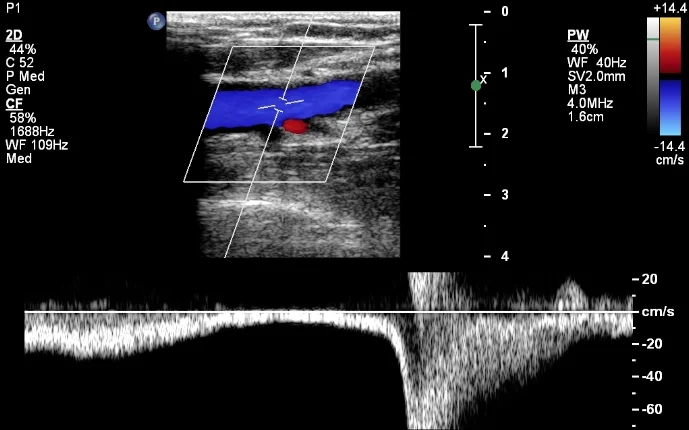
what is being shown in this image?
normal finding
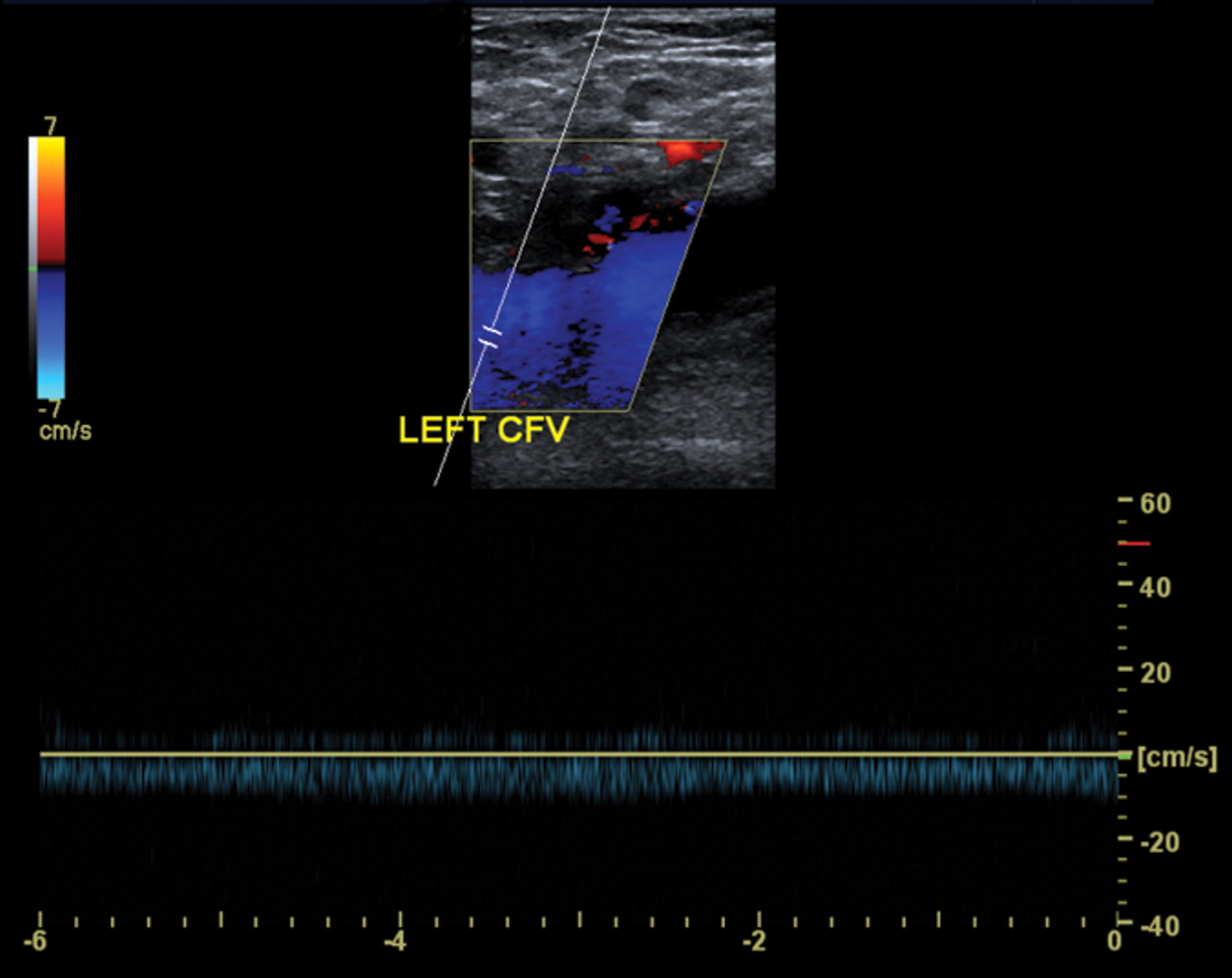
what is being shown in this image?
proximal obstruction