AP Language Terms (1st 9 Weeks)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Rhetorical triangle
The relationship between speaker, audience, and message (rhetorical pyramid-exigence, speaker, audience, context, message, purpose)

Alliteration
repetition of the same sound beginning several words or syllables in sequence

Allusion
Brief reference to a person, event, or place (real or fictional) or to a work of art
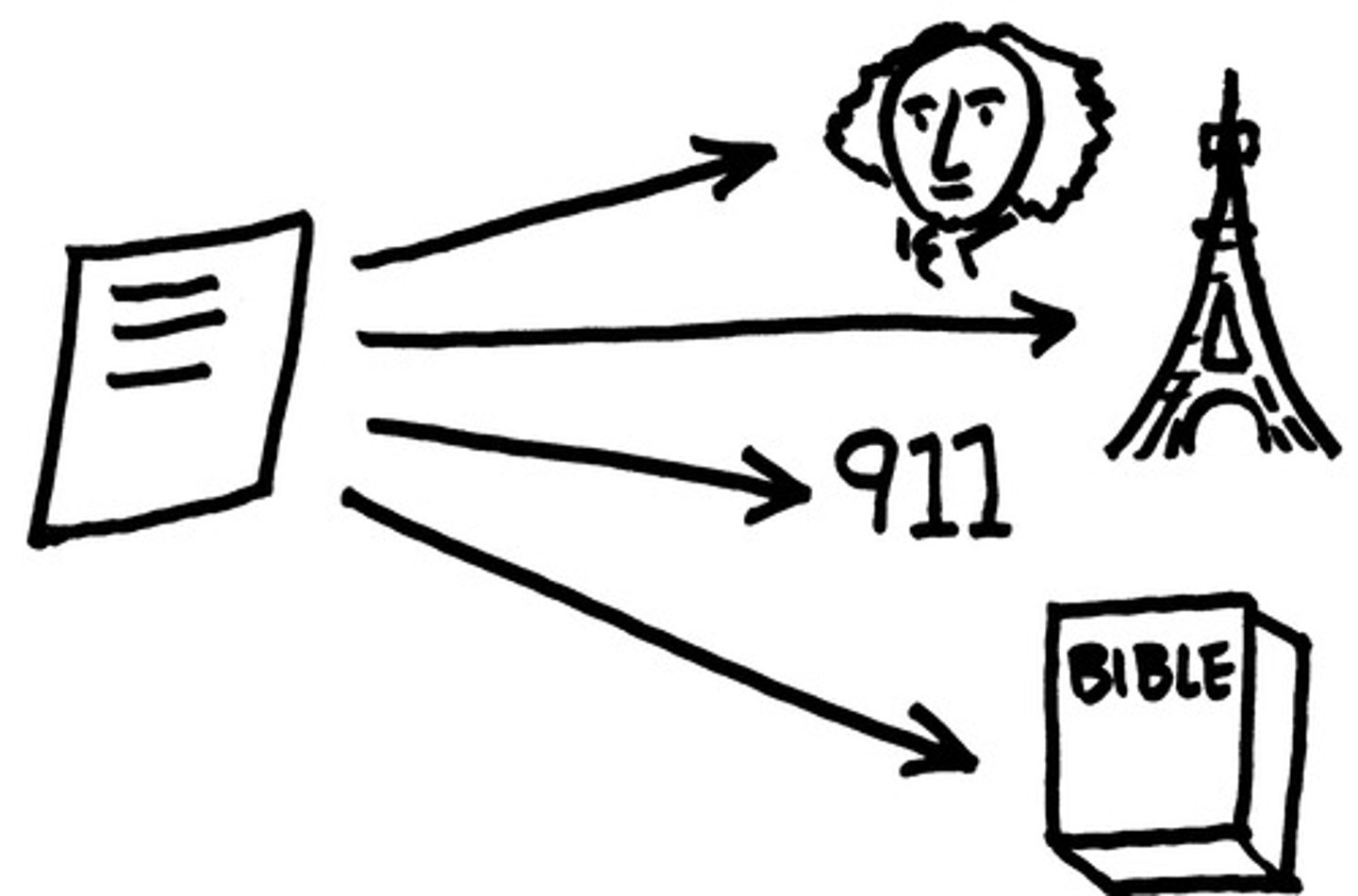
Anaphora
Repetition of words or phrases at the beginning of successive phrases, clauses, or lines.
Antithesis
Opposition, or contrast, of ideas or words in a parallel construction
Metaphor
Figure of speech that compares two things without using like or as
Oxymoron
A paradox made up of two seeming contradictory words

Parallelism/ Parallel Structure
Similarity of structure in a pair or series of related words, phrases, or clauses.
Exigence/Exigency
the urgency that led to the creation of a text
Rhetorical question
Figure of speech in the form of a question posed for the rhetorical effect rather than for the purpose of getting an answer.
Claim
States the author's argument, main idea, or position.
Style
the unique way an author presents his ideas. Diction, syntax, imagery, structure, and content all contribute to a particular style.
Diction
a speaker's choice of words.
Logical fallacy
potential vulnerabilities or weaknesses in an argument. They often arise from a failure to make a logical connection between the claim and the evidence used to support it.
Syntax
the grammatical structure of prose and poetry.
Understatement
opposite of an exaggeration. It is a technique for developing irony and/or humor where one writes or says less than intended.
Irony
A contrast between expectation and reality
Satire
the use of humor, irony, exaggeration, or ridicule to expose and criticize people's stupidity or vices, particularly in the context of contemporary politics and other topical issues.
Deduction
This is making a conclusion by going from whole to part
Induction
This is making a conclusion by going from part to whole
Analogy
A similarity or comparison between two different things or the relationship between them.
Anecdote
a short and amusing or interesting story about a real incident or person
Connotation
an idea or feeling that a word invokes in addition to its literal or primary meaning.
Colloquialism
A word or phrase (including slang) used in everyday conversation and informal writing but that is often inappropriate in formal writing (y'all, ain't)
Denotation
The dictionary definition of a word
Figurative language
Language that cannot be taken literally since it was written to create a special effect or feeling.
Hyperbole
exaggeration
Imagery
language that appeals to the senses
Inference
A conclusion reached on the basis of evidence and reasoning
Juxtaposition
Placement of two things closely together to emphasize comparisons or contrasts
Paradox
A statement or proposition that seems self-contradictory or absurd but in reality expresses a possible truth.
Rhetoric
the art of using language effectively and persuasively
Tone
Attitude a writer takes toward the audience, a subject, or a character
Idiom
A common, often used expression that doesn't make sense if you take it literally.
Verbal irony
A figure of speech in which what is said is the opposite of what is meant
Ethos
credibility of the author (and ethical appeal)
Pathos
Appeal to emotion
Logos
Appeal to logic