lecture 12 Groundwater
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Groundwater
______ is the water found underground in the cracks and spaces in soil, sand, and rocks. It is stored in and moves slowly through geologic formations of soil, sand, and rocks called aquifers
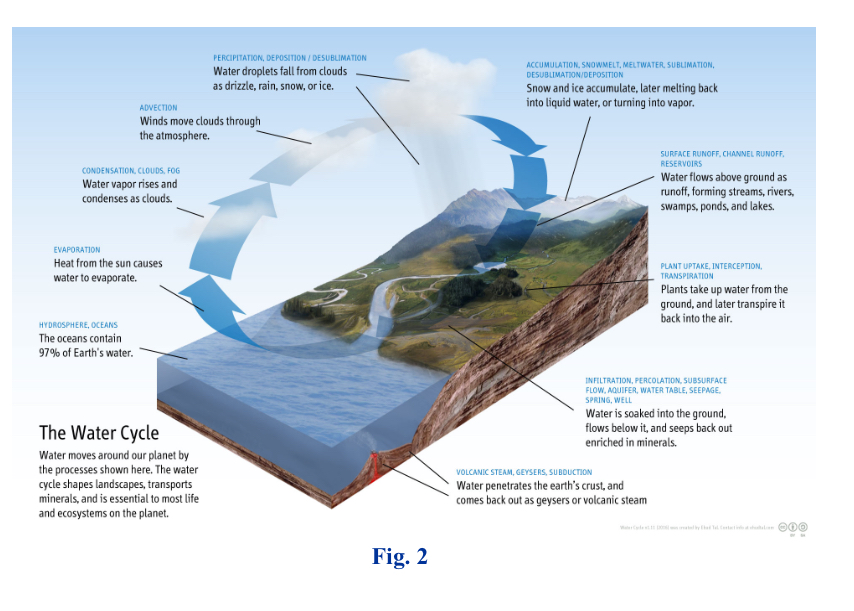
Hydrological cycle
Groundwater
_______ interacts with surface water systems (rivers & lakes) and the ocean
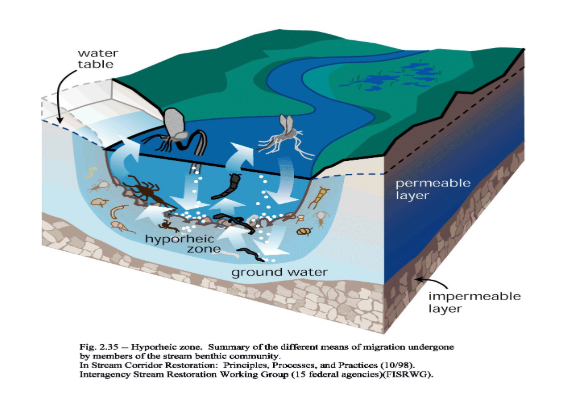
Hyporheic zone
Water is exchanged between surface and ground water in the _______
Primary porosity
_______ is the original porosity system formed during deposition of sediments
Secondary porosity
______ forms subsequently or results from a separate porosity that enhances the overall rock porosity
Folds and faults
______ & ______ are secondary porosity
Total porosity
_______ is the ratio of the volume of voids the total bulk volume of rock
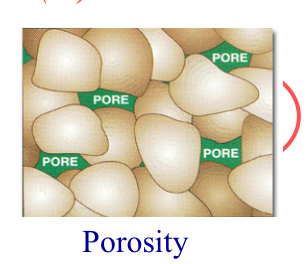
Porosity
The volume percentage of voids or openings in a rock and rock’s ability to hold water.
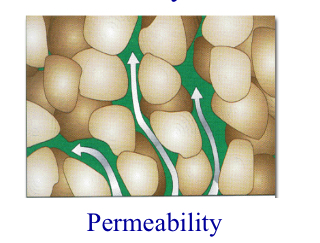
Permiablility
The capacity of a rock to transmit fluid through pore space and fractures.
Permiable
_______ rocks allow water to flow easily
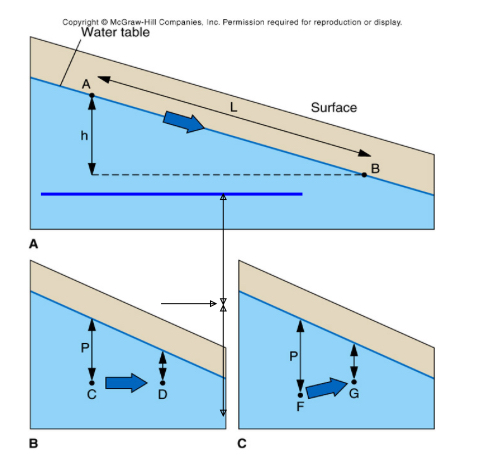
High, low
Ground water flows from ____ to _____
Perpendicular
Flow is always _____ to the lines of equal potential
Recharge
I after located in deep aquifers takes thousands of years to ______
Water table
The __________ mimics surface topography within a uniformly permeable rock
József Tóth (1963)
Discovered groundwater discharges not only in the deep valleys built in the sides of higher topographic elevations
Unconfined aquifer
Pumping in an __________ well lowers the groundwater surface (water table) and the area affected by the pumping is called the cone of depression.
Well drawdown
The total amount the water level drops in the well as it takes time for water to seep between grains
Subsidence
Excessive well extraction causes _______
Darce’s Velocity
And apparent velocity representing the velocity of water move through an aquifer were and open conduit
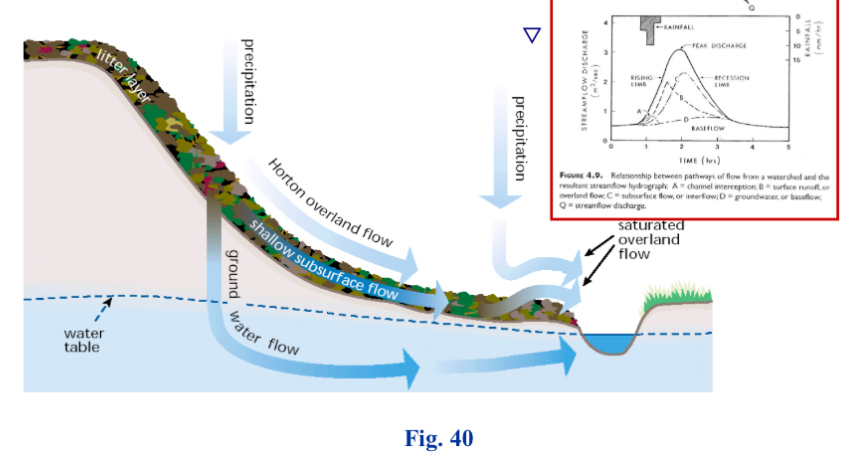
Base flow
Portion of the stream that is delayed shallow surface flow is sustained between precipitation events and fed to streams by delayed pathways
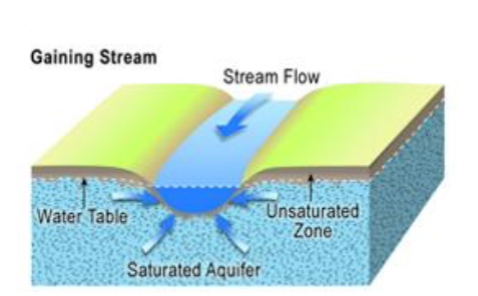
Effluent (gaining stream)
Ground water flows into a stream
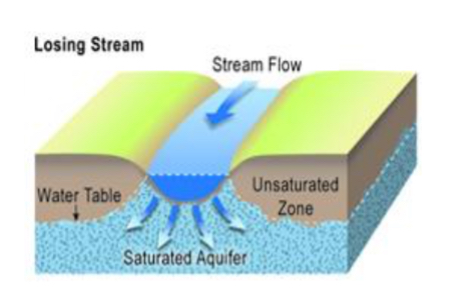
Influent (losing stream)
Water flows into saturated zone
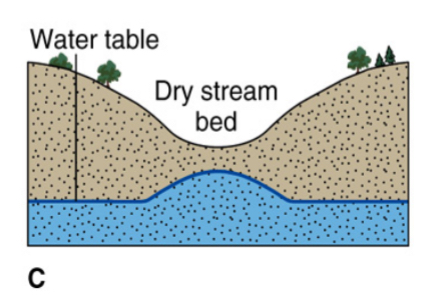
Dry stream bed
Changes in water table can result in a __________
Septic tanks
_______ are a big cause of ground water pollution
Salt water intrusion
Occurs where too much fresh water is pumped out of the ground and replaced by brackish and eventually salty water