MCB 2610 Exam 2
1/735
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
736 Terms
Why might people be interested in cultivating bacteria?
- model systems (stress response)
- people for health benefits
What do microorganisms generally need to grow?
- macronutrients
- micronutrients (trace elements)
Macronutrients Needed by Microorganisms
carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen
Macronutrients needed by enzymes as cofactors
potassium, sodium, magnesium, calcium, and iron
Micronutrients needed by microorganisms
Mn, Zn, Co, Mo, Ni, and Cu
are trace elements often added to media?
typically don't have to; sometimes they contaminate other parts of your media, they can also leach out of glassware
What are micronutrients often used for?
enzyme cofactors
Elements that make up proteins
C, H, O, N, S
elements that make up lipids
CHOP
elements that make up carbohydrates
C, H, O
elements that make up nucleic acids
C, H, O, N, P
only macromolecules that contain phosphorus
lipids and nucleic acids
all organisms require:
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and electrons
what is the backbone of all organic components present in cell?
carbon
electron role in macromolecules
energy production
ATP is
the biological currency of energy
redox reactions
chemical reactions that transfer electrons between reactants
autotrophs
assimilate carbon from inorganic sources
heterotrophs
assimilate carbon in preexisting organic form
phototroph
an organisms that captures light energy to produce ATP
chemotrophs
organisms that capture energy from oxidation of reduced organic or inorganic compounds
organotroph
microorganism that acquires electrons from organic molecules (glucose, sodium)
lithotroph
an organism that uses reduced inorganic compounds as its electron source (elemental sulfur, hydrogen gas, ferric iron) -- "rock eaters"
what does it mean to be organic?
CHO; CO2 is not organic
Why is carbon needed?
for nutrients
Acquisition of Energy Subtypes:
Phototrophs or Chemotrophs
Electron Acquisition Subtypes
organotrophs or lithotrophs
mixotrophs
some organisms have great metabolic flexibility and alter their metabolism in response to environmental changes
- can be advantageous
Why isn't everyone a mixotroph?
genome has to encode additional pathways so more genomic space taken up, more resources are needed and it may slow the growth
Where are mixotrophs typically found?
- unstable, dynamic environments
Where do we find nitrogen?
amino acids, amine groups, purines, pyrimidines, some carbohydrates, lipids, enzyme cofactors, etc
How is nitrogen supplied?
- Metabolism of amino acids, nitrates, ammonia from the atmosphere
- Nitrogen fixation
nitrogen fixation
Process of converting nitrogen gas into ammonia
nitrogenase
an enzyme of nitrogen-fixing microorganisms that catalyzes the conversion of nitrogen to ammonia to allow the ability to rip apart ammonia and turn into any macromolecule you need
enzyme needed to undergo nitrogen fixation
nitrogenase
how do the majority of microorganisms obtain nitrogen?
from the environment
where do we find phosphorus?
nucleic acids, phospholipids (membranes), coenzymes, some proteins (not a lot)
Common Phosphorus Sources
- inorganic phosphate
- organic molecules containing a phosphoryl group (pull apart and release phosphate)
sulfur sources
amino acids, coenzymes
where is sulfur obtained from?
1. amino acids cysteine and methionine
2. Sulfate
assimilatory sulfate reduction
sulfate to sulfite to hydrogen sulfide
growth factors
organic compounds that cannot be synthesized by an organism but are essential for growth
what are sterols important for?
membrane formation
microplasma
lack a cell wall
what is added to media for those with microplasmas
sterol like molecules to help growth
3 classes of growth factors
amino acids, purines and pyrimidines, vitamins
amino acid growth factors
protein synthesis
purines/pyrimidine growth factors
nucleic acid synthesis
vitamin growth factors
enzyme cofactors, needed in small amounts
hemen
important for cytochrome function -- needed for electron transport chains and generating ATP
hemofluous influenza
unable to make hemen (can't make ATP) so won't grow; needed hemen to be added to media
environmental factors that play a role on growth of microorganisms
nutrients, oxygen, reactive oxygen species, enzymes that protect against O2 toxicity, pH, temperature, solutes and water
nutrient concentration
-Growth rate will depend on the amounts of nutrients in the environment.
-One key nutrient, available in the lowest amount, will dictate how much growth can occur over time (i.e., it will be a limiting factor).
nutrients added in excess except for one
the one that is limited will limit the overall growth potential of the culture
High Nutrient Content results in:
a faster growth rate until it plateaus
type of oxygen that refers to what a macromolecule needs
atmospheric
aerobes
grow in presence of oxygen
obligate aerobes
require oxygen; will not grow if no oxygen
microaerophiles
grow best when there is less oxygen than normal
Where are microaerophiles typically found?
high altitudes, underground (not too low), in water
Anaerobic growth
occurs without oxygen
aerotolerant anaerobes
do not utilize oxygen but can survive and grow in its presence
obligate anaerobes
organisms that cannot live where molecular oxygen is present; oxygen will kill
facultative anaerobes
CAN use oxygen but can also grow in the absence of oxygen (prefers oxygen but don't have to have it)
obligate aerobe
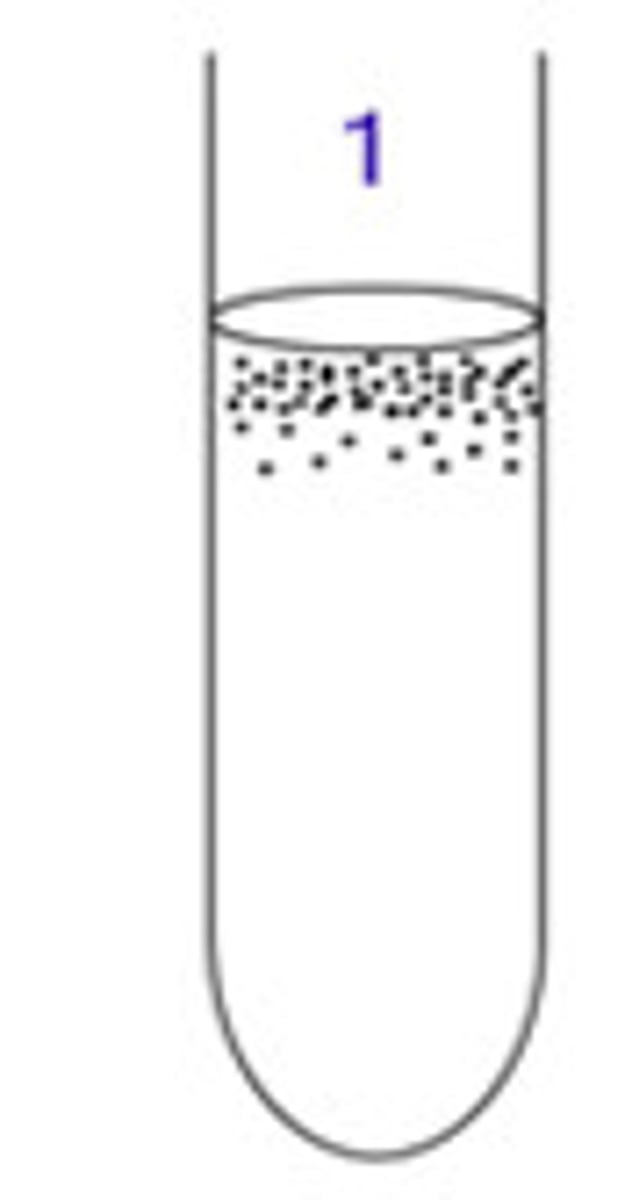
facultative anaerobe
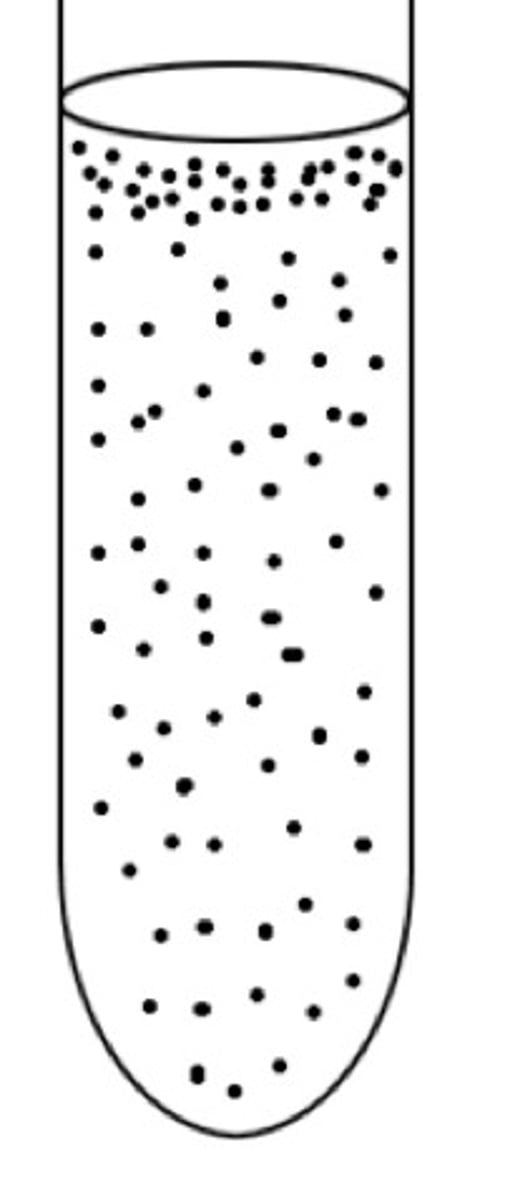
aerotolerant anaerobe
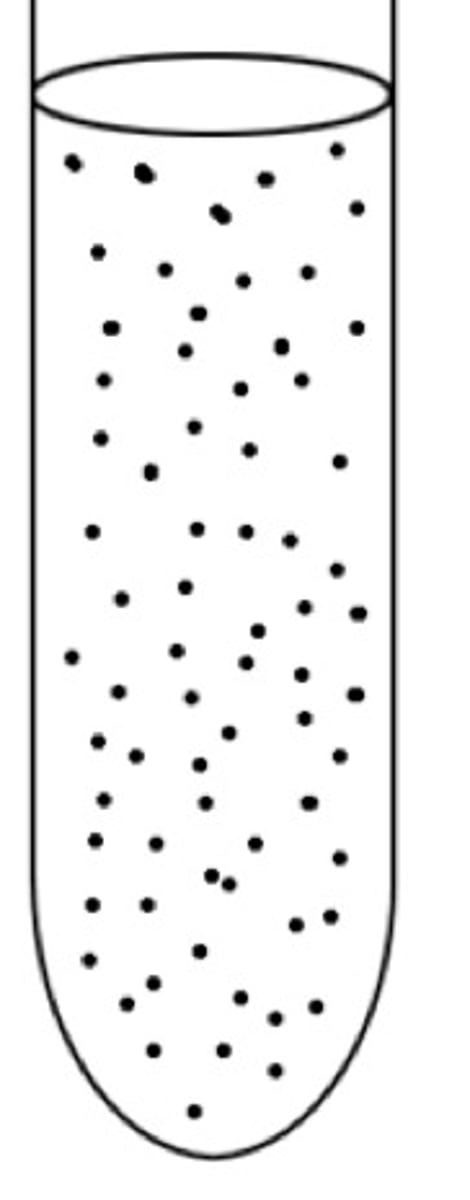
strict anaerobe
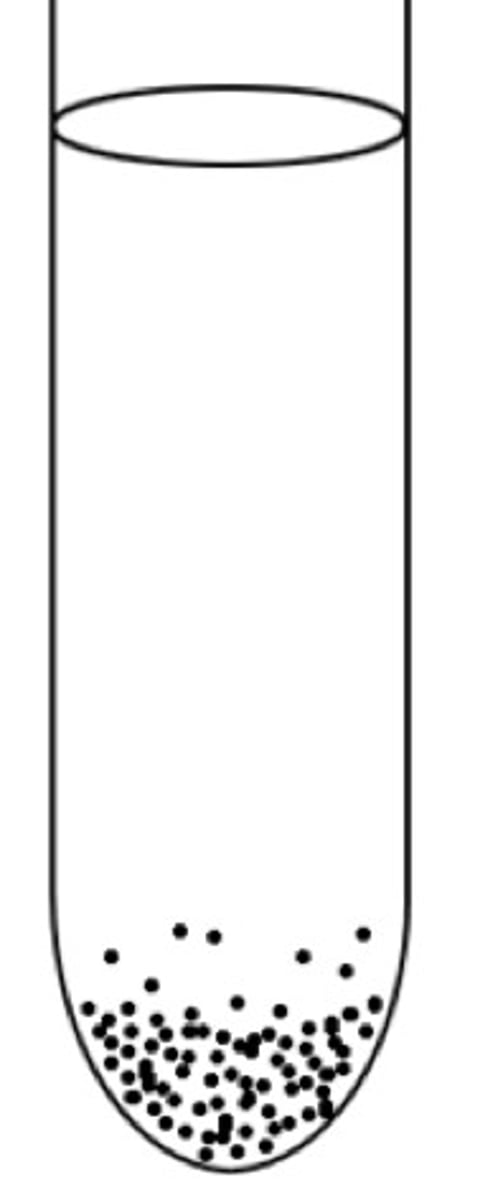
Microaerophiles
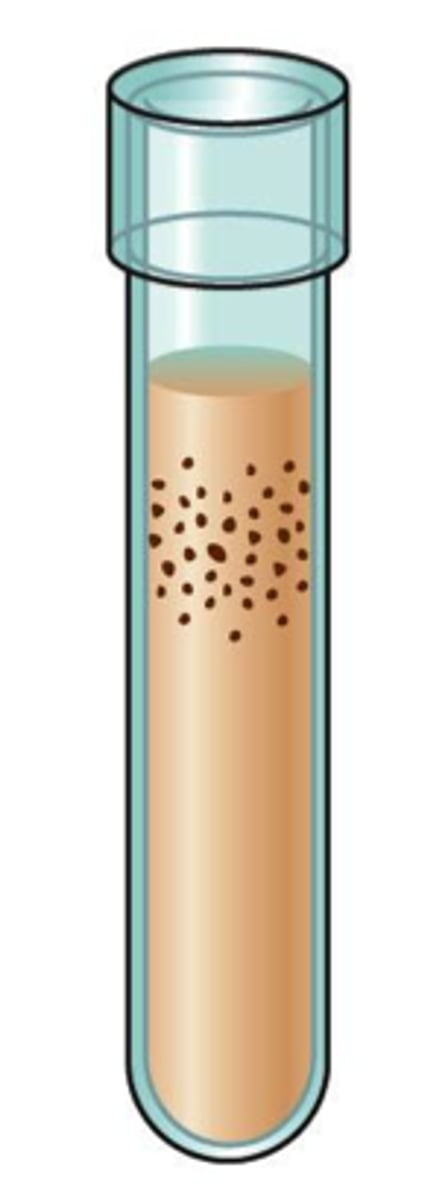
enzyme content of obligate aerobes
+SOD
+Catalase
enzyme content of facultative anaerobe
+SOD
+Catalase
aerotolerant enzyme content
+SOD
- Catalase
enzyme content of strict anaerobe
-SOD
-Catalase
does NOT have protective enzymes
Enzyme content of a microaerophile
+SOD
+/- Catalase (low levels)
effects of oxygen on microbial growth are often determined by:
what defenses are available against oxygen's negative effects in the cell
toxic oxygen species
- singlet oxygen
- superoxide anion (O2-)
- Hydroxyl radical (OH)
- Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
what does H2O2 tend to react with?
iron -- will produce hydroxyl ions
what do toxic oxygen species do to cells?
damage DNA (or any of the 4 macromolecules; amino acids)
ROS
reactive oxygen species
enzymes that help to neutralize H2O2
catalase and peroxidase, superoxide dismutase
________________ produce protective enzymes
aerobes; encode neutralizing enzymes in genome
superoxide dismutase
neutralizes superoxide
catalase
an enzyme that catalyzes the reduction of hydrogen peroxide.
peroxidase
an enzyme that destroys hydrogen peroxide
things that help to neutralize singlet oxygen species
antioxidants, pigments, enzymes
strict anaerobic microorganisms lack
superoxide dismutase and catalase
how are anaerobes grown in a lab?
- work station with an incubator
- gaspak anaerobic system
should we shake a test tube when growing anaerobes?
NO
Labs that Contain a work station with an incubator
labs that work with anaerobic organisms all time time (permanent device)
gaspak anaerobic system labs
- labs that don't work with anaerobes a lot
- much less expensive
anaerobic workstation
Contains incubator, work glove hole, and airlock
Seals area and pumps in N and H to purge oxygen from system
Need palladium crystal for reducing agent
Catalize left over oxygen
what does the vacuum pump do in an anaerobic workstation?
pumps nitrogen and hydrogen in
GasPak Anaerobic System
Lid, lockscrew, clamp, catalyst chamber, gas generator envelope, rubber gasket seal, anaerobic indicator strip
oxygen removed from chamber by combining with hydrogen to form water -- catalyzed by the palladium pellets
catalyst chamber of the GasPak anaerobic system
contains palladium pellets -- reducing agents that bind to any oxygen in the system
how to determine the GasPak is cleared of oxygen?
anaerobic indicator strip
anaerobic indicator strip of The GasPak
methylene blue becomes colorless in absence of O2
gas generator envelope
Water is added to chemicals in envelope to generate H2 and CO2. Carbon dioxide promotes more rapid growth of microorganisms
why does carbon dioxide promote more growth in the GasPak?
a lot of anaerobic systems use inorganic sources of carbon
dessicant of GasPak
soaks up the H2O so ensure oxygen is removed
effects of pH on microbial growth
pH affects macromolecule structures and transmembrane electrochemical gradients
- microbes have an optimal pH range for growth