Immunotherapy Q's
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/156
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:10 AM on 6/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
1
New cards
Humanized monoclonal antibodies are used as treatments for cancer. Which of the following explain how they can exert their therapeutic effects?
a. They deliver toxic agents or radioactive isotopes.
b. They bind to soluble growth factors or membrane-associated growth-factor receptors.
c. They inhibit complement fixation.
d. They target transcription factors.
e. They mediate ADCC.
a. They deliver toxic agents or radioactive isotopes.
b. They bind to soluble growth factors or membrane-associated growth-factor receptors.
c. They inhibit complement fixation.
d. They target transcription factors.
e. They mediate ADCC.
a, b, e
2
New cards
One approach to improving a T cell’s ability to recognize tumor cells is to engineer the tumor-specific **CD8** T cells to have which of the following characteristics?
a. to express high affinity T-cell receptors specific for the tumor
b. to express elevated levels of B7
c. to express larger amounts of CTLA4
d. to store a larger quantity of cytotoxins
a. to express high affinity T-cell receptors specific for the tumor
b. to express elevated levels of B7
c. to express larger amounts of CTLA4
d. to store a larger quantity of cytotoxins
a
3
New cards
What is the process of isolating and manipulating an individual’s T cells and giving them back to the same individual by reinfusion?
a. immunogenetics
b. graft-versus-leukemia effect
c. adoptive T-cell transfer
d. immunosurveillance
a. immunogenetics
b. graft-versus-leukemia effect
c. adoptive T-cell transfer
d. immunosurveillance
c
4
New cards
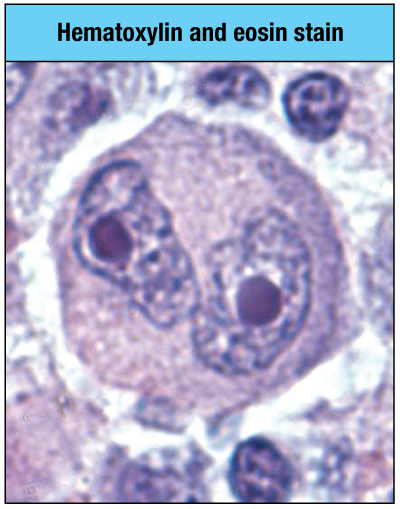
Which type of cancer is associated with the cell shown in the micrograph here? (owl eyes)
a. Hodgkin’s lymphoma
b. multiple myeloma
c. anaplastic large-cell lymphoma
d. Burkitt’s lymphoma
a. Hodgkin’s lymphoma
b. multiple myeloma
c. anaplastic large-cell lymphoma
d. Burkitt’s lymphoma
a
5
New cards
Which of the following are characteristics of anaplastic large-cell **lymphoma** (ALCL)?
a. horseshoe-shaped cells
b. expression of CD30
c. expression of NPM–ALK fusion protein
d. overexpression of the *MYC* oncogene
e. expression of CD15
a. horseshoe-shaped cells
b. expression of CD30
c. expression of NPM–ALK fusion protein
d. overexpression of the *MYC* oncogene
e. expression of CD15
a, b, c
6
New cards
In which lymphoid organ do sipuleucel-T-activated dendritic cells activate naive T cells?
a. lymph node
b. thymus
c. bone marrow
d. spleen
a. lymph node
b. thymus
c. bone marrow
d. spleen
d
7
New cards
Which of the following occur after the introduction of sipuleucel-T into cell culture containing monocytes from an individual with cancer?
\
a. The GM-CSF receptor of monocytes binds to GM-CSF, driving their differentiation into dendritic cells.
b. The fusion protein is internalized and prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP) is processed.
c. GM-CSF expands populations of PAP-specific T cells.
d. Prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP)-specific B cells are selected to proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells.
e. The fusion protein binds to B cells bearing prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP)-specific immunoglobulin.
\
a. The GM-CSF receptor of monocytes binds to GM-CSF, driving their differentiation into dendritic cells.
b. The fusion protein is internalized and prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP) is processed.
c. GM-CSF expands populations of PAP-specific T cells.
d. Prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP)-specific B cells are selected to proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells.
e. The fusion protein binds to B cells bearing prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP)-specific immunoglobulin.
a, b
8
New cards
Which of the following are associated with Burkitt’s **lymphoma**?
**Associated with Burkitt's Lymphoma**
a. overexpression of the MYC oncoprotein
b. chromosomal translocation involving chromosome 8
c. Reed-Sternberg cells
d. ‘starry-sky’ appearance arising from two types of cells
e. absence of Pax-5 expression
**Associated with Burkitt's Lymphoma**
a. overexpression of the MYC oncoprotein
b. chromosomal translocation involving chromosome 8
c. Reed-Sternberg cells
d. ‘starry-sky’ appearance arising from two types of cells
e. absence of Pax-5 expression
a, b
9
New cards
How do metalloproteinase inhibitors enhance **ADCC** of NK cells?
a. by increasing the rate of uptake of inhibitory NK-cell receptors
b. by permitting more effective cross-linking of NKG2D activating receptors
c. by blocking the degradation of their Fc ligands on the target cell
d. By retaining FcγRIII on the NK-cell surface
a. by increasing the rate of uptake of inhibitory NK-cell receptors
b. by permitting more effective cross-linking of NKG2D activating receptors
c. by blocking the degradation of their Fc ligands on the target cell
d. By retaining FcγRIII on the NK-cell surface
d
10
New cards
The causative chromosomal **translocation** in Burkitt’s **lymphoma** involves the *MYC* **proto-oncogene** and what other gene locus?
a. one of the heavy- or light-chain immunoglobulin loci
b. the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) locus
c. the *ABL* proto-oncogene locus
d. the nucleophosmin locus
a. one of the heavy- or light-chain immunoglobulin loci
b. the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) locus
c. the *ABL* proto-oncogene locus
d. the nucleophosmin locus
a
11
New cards
Cancer immunotherapy sometimes uses a **chimeric antigen receptor** (**CAR**). Which of the following is true of a **CAR**?
a. It contains antigen-specific antibody domains and is expressed on the surface of NK cells.
b. It contains antigen-specific antibody domains and is expressed on the surface of T cells.
c. It contains antigen-specific T-cell receptor domains and is expressed on the surface of T cells.
d. It contains antigen-specific T-cell receptor domains and is expressed on the surface of NK cells.
a. It contains antigen-specific antibody domains and is expressed on the surface of NK cells.
b. It contains antigen-specific antibody domains and is expressed on the surface of T cells.
c. It contains antigen-specific T-cell receptor domains and is expressed on the surface of T cells.
d. It contains antigen-specific T-cell receptor domains and is expressed on the surface of NK cells.
b
12
New cards
Which of the following are drawbacks to the strategy involving the use of engineered T-cell receptors that have high-affinity for tumor:MHC complexes?
a. Engineering T-cell receptors is a laborious process, and the recombinant DNA is usable only in individuals with cancer who express the HLA class I allotype to which the engineered T-cell receptor is restricted.
b. Engineered T-cell receptors have a broad specificity for multiple antigens and may cause autoimmunity.
c. If a subpopulation of tumor cells downmodulates the expression of the HLA class I allotype required for antigen presentation, then the engineered T-cell receptor cannot interact with the HLA:peptide complex needed to stimulate the CD8 T cell.
*d. In vitro* manipulation of CD8 T cells stimulates induction of apoptosis
a. Engineering T-cell receptors is a laborious process, and the recombinant DNA is usable only in individuals with cancer who express the HLA class I allotype to which the engineered T-cell receptor is restricted.
b. Engineered T-cell receptors have a broad specificity for multiple antigens and may cause autoimmunity.
c. If a subpopulation of tumor cells downmodulates the expression of the HLA class I allotype required for antigen presentation, then the engineered T-cell receptor cannot interact with the HLA:peptide complex needed to stimulate the CD8 T cell.
*d. In vitro* manipulation of CD8 T cells stimulates induction of apoptosis
a, c
13
New cards
Hodgkin’s **lymphoma** is characterized by the absence of what?
a. CD30
b. PAX-5
c. Reed-Sternberg cells
d. CD15
a. CD30
b. PAX-5
c. Reed-Sternberg cells
d. CD15
b
14
New cards
What is the best description of sipuleucel-T?
a. a vaccine made by combining an adjuvant with prostate biopsy tissue from an individual with prostate cancer
b. a fusion protein of GM-CSF and prostatic acid phosphatase
c. a chimeric protein containing immunoglobulin-variable regions specific for prostatic acid phosphatase and signal-activation domains
a. a vaccine made by combining an adjuvant with prostate biopsy tissue from an individual with prostate cancer
b. a fusion protein of GM-CSF and prostatic acid phosphatase
c. a chimeric protein containing immunoglobulin-variable regions specific for prostatic acid phosphatase and signal-activation domains
b
15
New cards
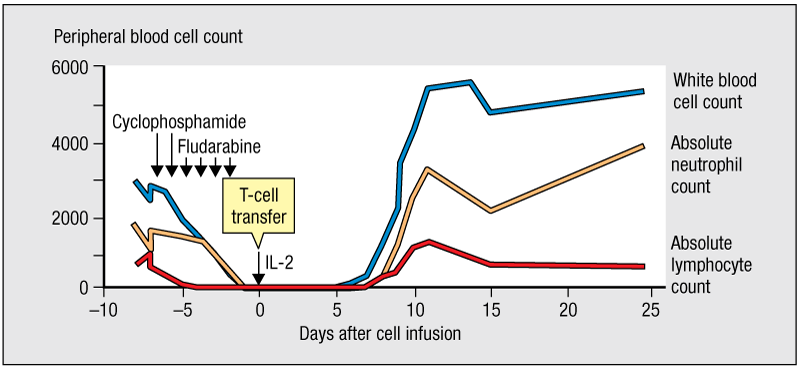
Adoptive cell transfer (ACT) has shown promise as an immune therapy against melanoma. The figure shown outlines the treatment regimen for ACT. What is the therapeutic effect of treatment with cyclophosphamide and fludarabine?
a. It activates cells of the innate immune system.
b. It decreases tumor mass.
c. It triggers proliferation of circulating T cells.
d. It depletes leukocytes in circulation of the individual.
a. It activates cells of the innate immune system.
b. It decreases tumor mass.
c. It triggers proliferation of circulating T cells.
d. It depletes leukocytes in circulation of the individual.
d
16
New cards
What is the process by which therapeutic monoclonal antibodies induce killing of tumor cells by NK cells?
a. antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC)
b. complement fixation
c. opsonization
d. agglutination
a. antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC)
b. complement fixation
c. opsonization
d. agglutination
a
17
New cards
What is anaplastic large-cell **lymphoma** (ALCL) an example of?
a. B-cell lymphoma
b. granuloma
c. T-cell lymphoma
d. myeloma
a. B-cell lymphoma
b. granuloma
c. T-cell lymphoma
d. myeloma
c
18
New cards
What is the term for a conjugate composed of a **monoclonal antibody** coupled to a toxic protein derived from a plant or microbe?
a. inflammasome
b. immunosuppressive drug
c. immunotoxin
d. immune complex
a. inflammasome
b. immunosuppressive drug
c. immunotoxin
d. immune complex
c
19
New cards
In addition to transmembrane, VL and VH domains, CARs also contain which additional structural feature?
a. domains derived from Igα/Igβ molecules
b. domains derived from CD3ε molecules
c. TIR regions of Toll-like receptors
d. domains derived from different cytoplasmic signaling molecules
a. domains derived from Igα/Igβ molecules
b. domains derived from CD3ε molecules
c. TIR regions of Toll-like receptors
d. domains derived from different cytoplasmic signaling molecules
d
20
New cards
Sipuleucel-T is a **cancer vaccine** used to treat which of the following?
a. melanoma
b. multiple myeloma
c. late-stage metastatic prostate cancer
d. cervical cancer
a. melanoma
b. multiple myeloma
c. late-stage metastatic prostate cancer
d. cervical cancer
c
21
New cards
How does ADCC work in Mab therapy?
NK-cell-mediated mechanism that destroys **target cells** bound to the therapeutic **monoclonal antibody**
22
New cards
What do NK cells express?
**FcγRIII** (CD16)
23
New cards
What do CD16 do?
Signals from CD16 are augmented by additional NK-cell-activating signals, stimulating the unleashing of the cytotoxic machinery on the cancer cell.
24
New cards
What is associated with *MYC* oncogene expression?
Burkitt’s lymphoma
25
New cards
What do Hodgkin’s lymphoma express?
CD15
26
New cards
How does NPM-ALK fusion protein in ALCL arise?
from a chromosomal **translocation** between the anaplastic **lymphoma** kinase gene on chromosome 2 and the nucleophosmin gene on chromosome 5
27
New cards
In ALCL what is easily detected by IHC?
The NPM-ALK fusion protein made from the chimeric gene is oncogenic
28
New cards
What tumours express CD30?
Marker of APC, ALCL and Hodgkin’s lymphoma
29
New cards
How is ALCL distinguished in H&E?
large horseshoe-shaped cells
30
New cards
IMMUNOTHERAPY
by harnessing the body’s immune system to recognize and eradicate debilitating diseases, specifically cancer and chronic viral infections
31
New cards
Immunotherapies
are directed at a specific antigen or cluster of antigens that compose the __unique__ signature of a virus or cancer cell that is dissimilar to its host, thus recognizing self from non-self
32
New cards
Why is immunotherapy dependent on reduction of tumour load?
\
Immune system cannot cope with large tumours
If had lots of antigen shedding would stimulate the regulatory T-cells
Immune system cannot cope with large tumours
If had lots of antigen shedding would stimulate the regulatory T-cells
33
New cards
A last-resort treatment for Hodgkin’s lymphoma and ALCL
conjugate of an anti-CD30 monoclonal antibody (brentuximab) and the cytotoxin auristatin (vedotin).
34
New cards
An advantage of immunotoxins over conventional chemotherapy
toxin’s destructive power is specifically targeted at the tumor and away from healthy proliferating tissues
35
New cards
Why must Auristatin be administered with an antibody?
Alone it is very toxic
36
New cards
When brentuximab–vedotin binds CD30 on the lymphoma-cell surface
* the conjugate is endocytosed.
* On reaching the lysosomes the drug is cleaved from the antibody by cellular cathepsin.
* Thus released, the drug enters the nucleus where it prevents further division and proliferation of the lymphoma cells by impeding the polymerization of tubulin to form the mitotic spindle
* On reaching the lysosomes the drug is cleaved from the antibody by cellular cathepsin.
* Thus released, the drug enters the nucleus where it prevents further division and proliferation of the lymphoma cells by impeding the polymerization of tubulin to form the mitotic spindle
37
New cards
How can humanised MAb be administered?
alone as ‘naked’, conjugated with a toxin or radioactive isotope
38
New cards
How do naked antibodies reduce tumour growth?
by inhibiting the functions of signaling receptors and promoting the opsonization of tumor cells and their phagocytosis or killing by NK cells
39
New cards
What target of monoclonal antibodies are not directed at a cell-surface component?
Bevacizumab IgG1 an antibody specific for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
40
New cards
What do VEGF targets do?
by neutralizing VEGF it prevents the angiogenesis that is necessary for tumors to grow
41
New cards
In the treatment of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody ibritumomab serves two purposes.
* When conjugated to indium-111, its purpose is to image the tumor by detection of the indium-111 γ-radiation.
* For immunotherapy, the antibody is conjugated to yttrium-90, which emits β-radiation and kills the lymphoma cells. An initial dose of nonradioactive anti-CD20 combined with indium-111 conjugated to anti-CD20 is followed a week later by therapeutic conjugate of yttrium-90 anti-CD20.
* For immunotherapy, the antibody is conjugated to yttrium-90, which emits β-radiation and kills the lymphoma cells. An initial dose of nonradioactive anti-CD20 combined with indium-111 conjugated to anti-CD20 is followed a week later by therapeutic conjugate of yttrium-90 anti-CD20.
42
New cards
The advantage of a radioactive antibody conjugate over conventional radiation therapy
is that much less radiation is needed, because it is specifically delivered to the tumor target by the antibody. Thus much less damage is done to healthy cells and tissue than with conventional therapy
43
New cards
What is the mechanism that many theraputic monoclonal antibodies kill tumour cells?
NK cell–mediated antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
44
New cards
NK cell–mediated antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
* The monoclonal antibody binds to the tumor-cell antigen with its two Fab arms and to FcγRIII on the NK cell with its Fc region, thus creating a strong adhesion between the two cells
* The activating signals generated by FcγRIII are augmented by signals coming from NKG2D and other NK-cell receptors to activate the cytotoxic machinery of the NK cell.
* The activating signals generated by FcγRIII are augmented by signals coming from NKG2D and other NK-cell receptors to activate the cytotoxic machinery of the NK cell.
45
New cards
An unwanted feature of ADCC, however, is that activation of the NK cell is followed by shedding of FcγRIII from the NK-cell surface through the action of the ADAM33 metalloproteinase. How would you combat this?
Adding an inhibitor of the metalloproteinase to the patient’s treatment regimen increases tumor-cell killing by ADCC.
46
New cards
Why do most melanoma patients cannot eliminate tumours?
Although most melanoma patients make an adaptive immune response against their tumor, the response is too weak to either control or eliminate the tumor
47
New cards
immunotoxin
conjugate composed of a specific antibody chemically coupled to a toxic protein usually derived from a plant or microbe. The antibody is designed to bind specifically to target cells, such as cancer cells, and deliver the toxin to kill them.
48
New cards
Checkpoint inhibitor
a drug that inhibits the physiological process that controls and limits the strength of the T-cell response. An example is the anti-CTLA4 antibody used to treat melanoma.
49
New cards
Adoptive cell transfer ACT
any procedure in which (usually) T cells are transfused into a patient for therapeutic purposes. In cancer immunotherapy, they are usually the patient’s own T cells that have been isolated, manipulated in culture (for example, to make them more responsive to the patient’s tumor), and then reinfused
50
New cards
Chimeric antigen receptor CAR
chimeric cell-surface protein composed of a single antigen-binding site spliced to a series of intracellular signaling domains. It has potential applications in cancer immunotherapy.
51
New cards
CART cell
T cell that has been engineered to express a chimeric antigen receptor, one part of which is specific for a tumor antigen. CAR T cells are being developed for cancer treatment.
52
New cards
Cancer vaccine
preparation of the patient’s own white blood cells that have been engineered to enhance the immune response against cancer antigens
53
New cards
treatment for patients with late-stage metastatic prostate cancer.
isolate a patient’s dendritic cells, culture them in vitro with a tumor antigen, and then infuse the antigen-primed dendritic cells back into the patient
54
New cards
Adoptive transfer of antigen-activated dendritic cells
* Monocytes isolated from the patient’s blood are cultured with a recombinant fusion protein called sipuleucel-T a fusion protein of a prostate cancer antigen (prostatic acid phosphatase; PAP) and GM-CSF, a monocyte growth factor.
* When GM-CSF binds to its receptor on the monocytes, it activates the cells and drives the monocytes differentiate into dendritic cells that present peptides derived from PAP on MHC class II.
* When the receptor and the bound GM-CSF are internalized and taken to the endosomes and lysosomes for degradation, the prostatic acid phosphatase is carried with them.
* This facilitates the processing of the antigen into peptides and their presentation on the monocyte surface by MHC class II.
* At this point the antigen-primed monocytes are infused intravenously into the patient, where they home to the spleen and can present the peptide antigens to naive antigen-specific CD4 T cells
* When GM-CSF binds to its receptor on the monocytes, it activates the cells and drives the monocytes differentiate into dendritic cells that present peptides derived from PAP on MHC class II.
* When the receptor and the bound GM-CSF are internalized and taken to the endosomes and lysosomes for degradation, the prostatic acid phosphatase is carried with them.
* This facilitates the processing of the antigen into peptides and their presentation on the monocyte surface by MHC class II.
* At this point the antigen-primed monocytes are infused intravenously into the patient, where they home to the spleen and can present the peptide antigens to naive antigen-specific CD4 T cells
55
New cards
Adoptive cell transfer is a personalized immunotherapy in which
inherent weakness of the patient’s T-cell response to the tumor is overcome by a massive expansion and activation of the T cells in vitro. The improved T-cell receptor can then be expressed in T cells isolated from the patient, which are then returned to the patient’s circulation
56
New cards
CD19
a part of the B-cell co-receptor, which is expressed only by B-lineage cells and follicular dendritic cells.
57
New cards
In contrast to natural T-cell receptors, for which antigen recognition and signaling are performed by different polypeptides, CARs comprise a single polypeptide that combines both functions. Binding to the CD19 antigen is mediated by
* the amino-terminal part of the polypeptide, whereas signal transduction is mediated by the carboxy-terminal part
* The antigen-binding site consists of the VH and VL domains of a high-affinity anti-CD19 monoclonal antibody—a structure called an Fv fragment.
* The carboxy-terminal part of a CAR consists of the transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic tail with signaling domains derived from the ζ chain of the T-cell receptor complex the CD28 co-stimulatory receptor, and CD137, a member of the TNF-α receptor family
* This wealth of signaling domains gives CAR T cells a greater capacity than normal T cells for killing tumor cells. It also protects CAR T cells from becoming anergic.
* The antigen-binding site consists of the VH and VL domains of a high-affinity anti-CD19 monoclonal antibody—a structure called an Fv fragment.
* The carboxy-terminal part of a CAR consists of the transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic tail with signaling domains derived from the ζ chain of the T-cell receptor complex the CD28 co-stimulatory receptor, and CD137, a member of the TNF-α receptor family
* This wealth of signaling domains gives CAR T cells a greater capacity than normal T cells for killing tumor cells. It also protects CAR T cells from becoming anergic.
58
New cards
To make a population of CAR T cells for immunotherapy
circulating T cells are isolated from the patient’s blood and activated in culture with anti-CD3. At this stage, the CAR-encoding DNA construct is transfected into the activated T cells using a retroviral vector. The patient is conditioned with cyclophosphamide and fludarabine for 3 days before receiving the infusion of CAR T cells.
59
New cards
First CAR T cell therapy
tisagenlecleucel for treatment of children and young adults with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
60
New cards
anti-CD19 CAR-T therapy, axicabtagene ciloleucel, was approved for patients with
transformed follicular lymphoma, primary mediastinal lymphoma, and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma that resisted conventional therapy. In 2018, tisagenlecleucel was further approved for adults with certain types of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
61
New cards
Main adverse affect of CAR T
is a strong and systemic inflammatory reaction called cytokine release syndrome, which creates a cytokine storm and has led to the death of some patients.
62
New cards
Adoptive cell transfer improves the natural T-cell response to a tumor: melanoma
surgically remove the melanoma tissue and culture it in vitro so that the resident tumor-specific T cells are activated to proliferate and differentiate into effector T cells that then kill all the tumor cells in the culture.
63
New cards
How are the effector T cells used in tumours?
One aliquot of cells is infused back into the circulation of the patient, where the T cells home to any residual melanoma tissue and destroy it. The other T-cell aliquots are frozen and stored, for use if the melanoma relapses
64
New cards
How was ACT remission improved?
* by conditioning patients with the immunosuppressive drugs cyclophosphamide and fludarabine during the week before the T-cell infusion. causes a massive depletion of leukocytes from the circulation.
* Such depletion improves the effectiveness of ACT by a factor of 10. Removal of the patient’s leukocytes creates space and a more welcoming environment that extends the lives of the transplanted effector T cells.
* Such depletion improves the effectiveness of ACT by a factor of 10. Removal of the patient’s leukocytes creates space and a more welcoming environment that extends the lives of the transplanted effector T cells.
65
New cards
What advance improved T cell response to melanoma?
interfering with CTLA4, the co-inhibitory receptor that competes with CD28 for access to B7
66
New cards
ipilimumab, a fully human monoclonal anti-CTLA4 antibody
* By binding tightly to CTLA4, ipilimumab prevents CTLA4 from engaging B7 and generating inhibitory signals that attenuate the T-cell response
* Thus, ipilimumab raises T-cell effector functions to a higher level than would be physiologically permitted. The effect is a more effective killing and elimination of melanoma cells.
* Thus, ipilimumab raises T-cell effector functions to a higher level than would be physiologically permitted. The effect is a more effective killing and elimination of melanoma cells.
67
New cards
How does Nivolumab, a human IgG4 monoclonal antibody, a checkpoint inhibitor work?
binds to the programmed death 1 protein (PD-1; CD279)
68
New cards
PD-1 is expressed by T cells and binds the PD-L1 ligand, which is expressed by a wide variety of somatic cells and tumors in the presence of inflammation. In the tumor environment, specific effector T cells encounter their tumor antigens. Continuing engagement of T-cell PD-1 by tumor PD-L1 induces
T cell exhaustion
69
New cards
What does nivolumab do to contribute to anti-tumour response?
PD-1 cannot engage PD-L1, which prevents T-cell exhaustion
70
New cards
An unwanted side-effect of checkpoint inhibitors is
autoimmunity
71
New cards
Why are checkpoint inhibitors is that they are highly effective in some patients, but not in others having the same type of cancer?
Microbiota
72
New cards
Microbiota and CPI
* Patients whose melanoma is diminished by the checkpoint inhibitor have a diverse microbiota containing several key species of bacteria.
* By contrast, patients whose melanomas do not respond to the therapy have a limited microbiota and lack key bacterial species, possibly due to past treatments with antibiotics.
* By contrast, patients whose melanomas do not respond to the therapy have a limited microbiota and lack key bacterial species, possibly due to past treatments with antibiotics.
73
New cards
Nivolumab is an effective treatment for
melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, renal cell carcinoma, and bladder cancer.
74
New cards
T-cell exhaustion _____. (Select all that apply.)
a. occurs during chronic viral infections, such as hepatitis C
b. results from the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1
c. helps promote the removal of cancer cells by CD8 T cells
d. cannot be addressed by current immunotherapies for cancer
e. may occur when CD8 T cells target tumor-specific antigens
f. results from the interaction between CD28 and B7
a. occurs during chronic viral infections, such as hepatitis C
b. results from the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1
c. helps promote the removal of cancer cells by CD8 T cells
d. cannot be addressed by current immunotherapies for cancer
e. may occur when CD8 T cells target tumor-specific antigens
f. results from the interaction between CD28 and B7
a, b, e
75
New cards
ADAM33 metalloproteinase inhibitors are sometimes co-administered with antitumor monoclonal antibodies in order to _____.
a. block angiogenesis
b. inhibit proteasome function in tumor cells
c. enhance NK-cell killing by ADCC
d. promote differentiation of dendritic cells
e. reduce the surface expression of MHC class I on tumor cells
a. block angiogenesis
b. inhibit proteasome function in tumor cells
c. enhance NK-cell killing by ADCC
d. promote differentiation of dendritic cells
e. reduce the surface expression of MHC class I on tumor cells
c
76
New cards
Explain the mechanism by which ipilimumab exerts its inhibitory function in the context of cancer treatment.
When blocked by ipilimumab, CTLA4 (a negative regulator of T-cell co-stimulation) is unable to bind to its ligand, CD28. Consequently, the T cell is not inhibited and is able to exert its effector function for longer periods in helping to strengthen the immune response against tumor cells.
77
New cards
Which type of cancer has been treated with ipilimumab? (ii) With what success?
Melanoma
Around 75% of untreated patients survive less than 1 year, but treatment has extended this to a 2-year survival rate in 24% of patients.
Around 75% of untreated patients survive less than 1 year, but treatment has extended this to a 2-year survival rate in 24% of patients.
78
New cards
Describe two different strategies for introducing tumor-specific high-affinity receptors into T cells for adoptive T-cell transfer.
1. engineer a tumor-specific T-cell receptor to improve its affinity for the complex of tumor peptide and HLA class I molecule it recognizes. The patient’s T cells are then treated ex vivo to achieve expression of the engineered T-cell receptor, before they are returned to the patient.
2. The other strategy uses a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) that is encoded by a single gene that encodes: (1) a tumor antigen–binding site made from antibody variable fragments (the variable domains of the heavy and light chains that are part of the same polypeptide and held together by a linker peptide); (2) a transmembrane anchor; and (3) a cytoplasmic tail containing multiple signaling domains from CD28, CD137, and the ζ chain of the T-cell receptor complex. After ex vivo manipulation of the patient’s T cells, those cells expressing the CAR are reintroduced to the patient.
79
New cards
What feature is associated with one of these strategies that restricts its application to a small cohort of patients?
The T-cell receptor strategy can only be administered to patients who have an HLA class I allotype that is compatible with the MHC restriction profile of the T cell from which the original T-cell receptor genes were isolated.
80
New cards
Describe a specific clinical application associated with the other strategy.
CAR
81
New cards
All of the following are characteristics of sipuleucel-T except _____.
a. it contains GM-CSF
b. it inhibits nurturing interactions between tumor cells and bone marrow cells
c. it drives monocytes to differentiate into dendritic cells
d. it was the first approved therapeutic cancer vaccine
e. it contains prostatic acid phosphatase
f. it gives rise to peptides that are presented by MHC class II molecules
a. it contains GM-CSF
b. it inhibits nurturing interactions between tumor cells and bone marrow cells
c. it drives monocytes to differentiate into dendritic cells
d. it was the first approved therapeutic cancer vaccine
e. it contains prostatic acid phosphatase
f. it gives rise to peptides that are presented by MHC class II molecules
b
82
New cards
Describe the difference between (A) ‘naked antibodies’ and (B) conjugated antibodies in the context of using humanized monoclonal antibodies for tumor killing.
* ‘Naked antibodies’ function in the same way as antibodies do during response to virally infected cells. They are not conjugated to toxins or radioactive isotopes. Upon binding to their target, they mediate a variety of effects including modulation of signaling by cell-surface receptors, opsonization of tumor cells (leading to complement fixation and phagocytosis), or NK-cell killing by antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). Some ‘naked antibodies,’ such as the anti-CD52 antibody, also induce apoptosis.
* Conjugated antibodies are chemically linked to either a toxin or a radioactive isotope. Toxins, such as auristatin, are internalized by tumor cells by endocytosis, where they selectively mediate their cytotoxic effect. Radioactive isotopes, such as yttrium-90, are similarly delivered with precision to the target cell, where DNA damage and cell death occur via radioactive decay (β-radiation). \[Parham, Peter. The Immune System\]
* Conjugated antibodies are chemically linked to either a toxin or a radioactive isotope. Toxins, such as auristatin, are internalized by tumor cells by endocytosis, where they selectively mediate their cytotoxic effect. Radioactive isotopes, such as yttrium-90, are similarly delivered with precision to the target cell, where DNA damage and cell death occur via radioactive decay (β-radiation). \[Parham, Peter. The Immune System\]
83
New cards
Monoclonal antibodies are used in cancer treatment because of their ability to _____. (Select all that apply.) a. target tumor cells for immune responses such as ADCC or opsonization
b. suppress regulatory cells
c. deliver radioactive molecules to track the status of metastasis
d. enhance the expression of tumor-specific antigens
e. be conjugated to cytotoxic drugs to kill tumor cells
b. suppress regulatory cells
c. deliver radioactive molecules to track the status of metastasis
d. enhance the expression of tumor-specific antigens
e. be conjugated to cytotoxic drugs to kill tumor cells
a, c, e
84
New cards
At 63 years old, Lauren Brooks was successfully treated with chemotherapy and radiation for cancer of the urinary bladder epithelium. At a later follow-up appointment with her oncologist, however, tests revealed that the cancer had returned. Her physician opted to try a different strategy aimed at inducing an in situ state of chronic inflammation intended to stimulate an antitumor immune response. Which of the following is the most likely course of action?
a. intramuscular vaccination with the BCG vaccine
b. intradermal vaccination with tumor antigens derived from the patient’s tumor cells from a bladder biopsy
c. intravenous infusion of a monoclonal antibody specific for IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine
d. intravenous infusion of the patient’s tumor cells transfected ex vivo with a gene encoding IL-13, an anti-inflammatory cytokine
e. intravesical adjuvant therapy with BCG vaccine via bladder instillation
a. intramuscular vaccination with the BCG vaccine
b. intradermal vaccination with tumor antigens derived from the patient’s tumor cells from a bladder biopsy
c. intravenous infusion of a monoclonal antibody specific for IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine
d. intravenous infusion of the patient’s tumor cells transfected ex vivo with a gene encoding IL-13, an anti-inflammatory cytokine
e. intravesical adjuvant therapy with BCG vaccine via bladder instillation
e
85
New cards
Humanised monoclonal antibodies (naked)
¡inhibit functions of signalling receptors so stop tumour growth (like neutralisation during infection)
¡Promote opsonisation of tumour cells and their phagocytosis (complement mediated lysis recruitment of macrophage)
¡Opsonisation of tumour cells also causes their destruction by NK ADCC, apoptosis and sensitization (chemo and radio)
86
New cards
Immunoconjugates
antibodies conjugated to a second molecule, usually a toxin, radioisotope or label.
87
New cards
Monoclonal antibodies against cell-surface antigens are destroyed by NK cells (ADCC)
Process:
1. The monoclonal antibody binds to the tumor cell antigen with its two Fab arms and to FcγRIII on the NK cell with its Fc region, thus creating a strong adhesion between the two cells.
2. The activating signals generated by FcγRIII are augmented by signals coming from NKG2D and other NK-cell receptors to activate the cytotoxic machinery of the NK cell
88
New cards
Chimeric (-xi-)
molecules made up of domains from different species. For example, the Fc region or all the constant regions of a mouse mAb may be replaced with those of a human or (any other species) antibody
89
New cards
Humanised (-zu-)
A type of antibody made in the laboratory by combining a human antibody with a small part of a mouse or rat monoclonal antibody.
90
New cards
HAMA response
human anti mouse antibody, which quickly clears the mouse monoclonal antibodies from the bloodstream and lowers the therapeutic efficiency of subsequent administration.
91
New cards
Why are chimeric less immunogenic?
constant regions are encoded by human dna, the abs have fewer mouse antigenic determinants, and are far less immunogenic when administered to humans than mouse monoclonal antibodies.
92
New cards
rituximab
targets CD20 of the B cells in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
93
New cards
HACA
Human anti-chimeric antibody response: can cause the patient to develop antibodies to the medicine itself
94
New cards
Production of fully human Ig in mice by antibody engineering: Panitumab (colorectal Ca) and Zanolimumab (lymphoma)
\
1. Mice Ig H and L loci removed (Knockout)
2. Embryonic stem cells from KO
3. HAC (human artificial chromosome) containing human Ig H and L loci
4. Transgenic mice that produced human Ig
Can make hybridomas that produce human Ig from mice
1. Mice Ig H and L loci removed (Knockout)
2. Embryonic stem cells from KO
3. HAC (human artificial chromosome) containing human Ig H and L loci
4. Transgenic mice that produced human Ig
Can make hybridomas that produce human Ig from mice
95
New cards
Antibodies as Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
¡Designed to overcome blockages to T cell activity mediated by immune checkpoints
¡Work by reactivating TILs (tumour infiltrating lymphocytes), particularly CD8+ cytotoxic T cells
¡CTLA-4 Checkpoint Inhibitors: Anti-CTLA-4 mAbs are designed to augment T cell activation by blocking inhibitor receptors such as CTLA-45
¡Checkpoint inhibitors against PD-1 and its ligand PD-L1 release PD-1 pathway-mediated inhibition of T cell activation
96
New cards
Checkpoint-inhibitor blockade with a monoclonal antibody enhances T-cell responses to tumors by countering the inhibitory effects of CTLA4
1. activation of T cells by recognition of tumor antigens depends on co-stimulatory signals sent by CD28 when it engages B7 on the tumor cell.
2. CTLA4 inhibits T-cell activation by competing with CD28 for binding to B7.
1. the therapeutic anti-CTLA4 monoclonal antibody ipilimumab prevents CTLA4 from competing with CD28, thereby promoting a degree of T-cell activation and effector function in excess of what is physiologically possible.
\
97
New cards
keytruda
¡blocks PD-1/PD-L1 pathway resulted in 3 year survival of metastatic melanoma patients 40%, whereas previously survival was measured in months
¡KEYTRUDA approved as first line treatment for advanced non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumours express PD-L1 at __>__50%, and other cancers
¡PD-LI is useful biomarker for effectiveness of PD-1 inhibitors such as KEYTRUDA or nivolumab as 1st line treatment in advanced NSCLC
¡approved in May 2017 as the first cancer treatment for **any** solid tumour\* with a specific genetic feature (**biomarker****)
¡First time the FDA approved a cancer treatment based on a common biomarker rather than tumour location
¡FDA approval of Keytruda (pembrolizumab) for the treatment of *adult and pediatric patients with unresectable or metastatic solid tumours** with a biomarker referred to as *microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or mismatch repair deficient (dMMR)***.
98
New cards
Monoclonal antibodies as Immune Agonists
¡These mainly antibody based drugs target specific cell surface proteins on T cells, causing stimulation of T cell activity
¡CD27 (on T cell) interacts with CD70 on antigen presenting cell to deliver “second signal”
¡Varlilumab can substitute CD70 by delivering costimulatory signal to CD27 positive T cells with engaged TCRs
¡Preclinical studies have demonstrated costimulatory activity of Varlilumab and decreased Treg in tumours
¡Varlilumab may also have direct benefits in CD27 positive tumours (some B and T cell lymphomas)
99
New cards
Bispecific T cell engager (BiTE®) Antibodies are designed
bridge cancer cells to CTLs
* One domain is designed to target an antigen on the surface of a cancer cell whereas the other is designed to engage CD3 on the surface of a T cell. With these two different domains, BiTE® antibodies aim to engage the endogenous cytotoxic potential of CTLs, bypassing MHC/antigen-dependent activation of T cells
* One domain is designed to target an antigen on the surface of a cancer cell whereas the other is designed to engage CD3 on the surface of a T cell. With these two different domains, BiTE® antibodies aim to engage the endogenous cytotoxic potential of CTLs, bypassing MHC/antigen-dependent activation of T cells
100
New cards
Adoptive T cell transfer
¡Involves generating large numbers of T cells, outside the body (*ex vivo*).
¡These isolated T cells can be genetically engineered so that they produce cytokines such as IL-2, which will boost their activity.
¡The T cells are expanded by in vitro stimulation with antigen presenting cells and are then put back into the patient.
¡By growing these cells *in vitro*, responses can be generated which are not found in vivo due to tumour derived inhibitory factors or the presence of T regulatory cells.
l1011 cells
lIL-2 *in vivo* or Th cells improves CTL survival & function
l75% of circulating T cells with anti-tumour activity
lResponse rates 40-50% in melanoma
lTransferred cells remain for up to 4 months
lCareful selection of T cell for tumour antigen to prevent autoimmunity