Psychology Unit 3 Topic 2-4
1/192
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
193 Terms
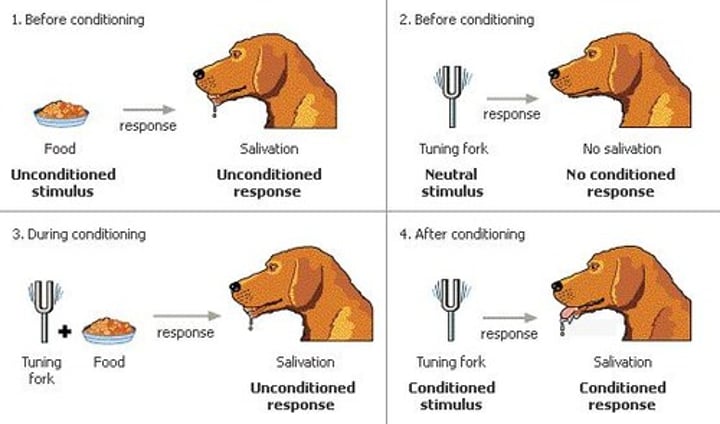
Classical Conditioning
Classical conditioning is the process where an organism can passively learn to show a naturally occurring reflex action, in response to any stimulus.
Ie. Learning by association.
Operant Conditioning
A type of learning where behaviour becomes controlled by its consequences.
Types of conditioning
Reinforcement - to increase behaviour
Punishment - to decrease behaviour
Positive - adding stimulus
Negative - removing stimulus
Negative reinforcement
Removing an unpleasant stimulus to promote behavior
Positive punishment
Providing an unpleasant stimulus to reduce behavior
Negative punishment (response cost)
Removing a positive outcome to reduce behavior
Applications of operant conditioning
Teaching appropriate behavior to kids/students and basis behind many behavioral therapies and approaches
Stimulus generalization - operant conditioning
Behavior is displayed because of an antecedent that is similar to the original
Spontaneous conditioning - operant conditioning
Conditioned behaviour reappears after a period of rest (indicates you can easily unlearn a behaviour).
Social learning theory
Describes the way in which people acquire certain behaviors by watching and learning from role models. When observer demonstrates the learnt behaviour by imitating it, this is referred to as modelling.
Observational learning process
Stage 1 - Attention: learner actively watches model.
Stage 2 - Retention: learner stores mental representation of behaviour
Stage 3 - Reproduction: learner has mental and physical ability to perform behaviour
Stage 4 - Motivation: environmental stimuli make learner wish to perform behaviour
Stage 5 - Reinforcement: positive outcomes means the learner will repeat the behaviour when again motivated to do so.
Unconditioned stimulus (UCS)
Stimulus that naturally causes an unconditioned response (UCR)
Conditioned stimulus (CS)
Previously neutral stimulus that now causes a conditioned response (CR)
Conditioned response (CR)
Developed automatic response to what was a neutral stimulus (NS)
Extinction - classical conditioning
When the conditioned response (CR) is extinguished after the conditioned stimulus (CS) is shown several times without reinforcement
Positive reinforcement
Providing a reward to promote behavior
Effects of frequent punishment on participants.
Can result in a person feeling frustrated, helpless, or even aggressive towards the person administering punishment
Observational learning
Happens when a person learns by watching behaviour demonstrated by another.
Vicarious conditioning/learning
When an individual witnesses another being rewarded or punished for a behavior and decides to act in the same or different way
Positive vicarious reinforcement
When an individual witnesses another being rewarded for a behavior and decides to act in the same way
Negative vicarious reinforcement
When an individual witnesses another being punished for a behavior and discontinues that behavior themselves
Unconditioned response (UCR)
Natural response to an unconditioned stimulus (UCS)
Neutral stimulus (NS)
Something that causes no natural response
Stimulus generalisation - classical conditioning
When an organism responds to any stimulus similar to the conditioned stimulus (CS)
Stimulus discrimination - classical conditioning
When an organism only responds to the conditioned stimulus (CS) and not to similar stimuli
Spontaneous recovery - classical conditioning
When the extinguished response reappears after a rest period
Stimulus discrimination - operant conditioning
Behaviour stops being applied to similar situations and only to the correct antecedent
extinction - operant conditioning
Conditioned behaviour disappears over time after reinforcement/punishment has ceased.
What is the multistore model of memory?
Sensory, short term, and long term stores. All 3 stores function simultaneously and interact with each other.
What is sensory memory?
Store for fleeting sensory info.
How long does iconic memory last?
0.3 seconds.
How long does echoic memory last?
3-4 seconds.
What is STM? (include duration + capacity + interference)
Short-term memory.
Duration: 12-30s
Capacity: 5-9 pieces of info
Interference: When new information enters and displaces older information.
What are the types of maintenance rehearsal?
Verbal (vocal - words out loud, subvocal - thinking words) and non-verbal (visualizing - keeping image in mind, muscular - imagining how it feels).
How is information encoded in LTM?
Info is encoded by its meaning and stored in semantic networks (ordered pattern of nodes linked to other related nodes)
What is a semantic network?
An ordered pattern of nodes linked to other related nodes in LTM.
What are the types of LTM?
Procedural memory and declarative memory.
What is procedural memory?
Memory for how to do things, acquired through practice.
What is explicit memory?
Conscious retrieval of memory. Declarative, episodic, semantic.
What is implicit memory?
Unconscious retrieval of memory. Procedural.
What is encoding?
Putting info into a form for storage.
What is storage?
Maintaining info in a memory store.
What is retrieval?
Process of getting info back from LTM.
What is iconic memory?
Fleeting storage of visual info.
What is echoic memory?
Fleeting storage of auditory info.
Why is sensory memory important?
Prevents overwhelm and filters incoming info.
What does sensory memory allow us to do?
Perceive the world as ongoing.
What is the purpose of rapid decay in sensory memory?
Allows for new incoming info.
What are the types of sensory memory?
Iconic and echoic memory.
What is maintenance rehearsal?
Repeating information to retain it in STM or move it to LTM.
What is LTM? (include duration + capacity)
Store for encoded info that can be retrieved as long as you know about it. Hard to know duration and capacity as the right retrieval cue (mental reminder or prompt used to assist recollection) can cause previously forgotten memories to suddenly return.
What is declarative memory?
Memory for facts and knowledge. Comprised of episodic (personalised memories of events) and semantic memory (memories of facts/knowledge).
What is Visual STM + function?
Visuospatial sketchpad - storage of what we see, allows us to see/keep an image in our minds as we process other things.
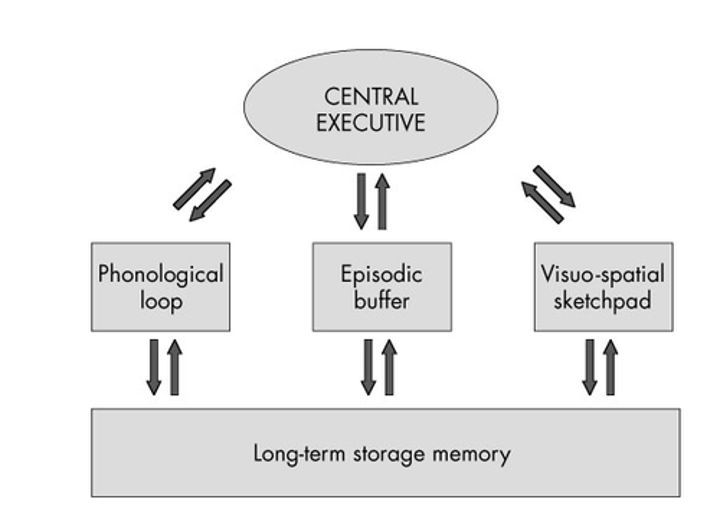
What is Auditory STM + function?
Phonological loop - storage of what we hear. Allows us to understand sentences if more than a few words.
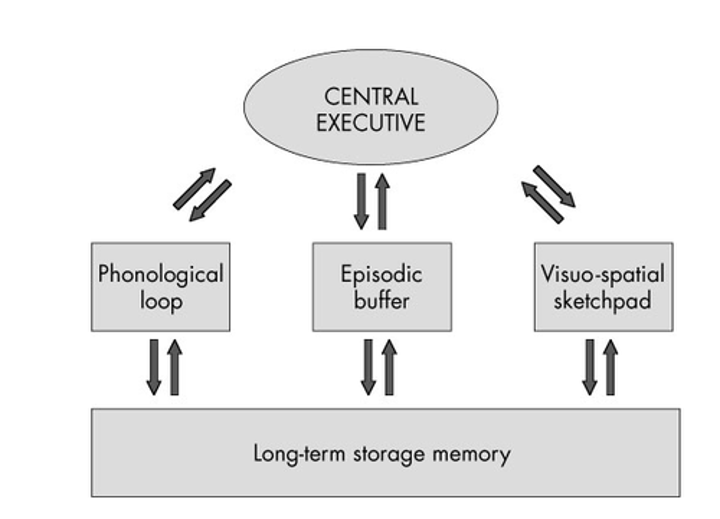
What is the Episodic buffer?
Bridge and filter between LTM and central executive and storage components in working memory.
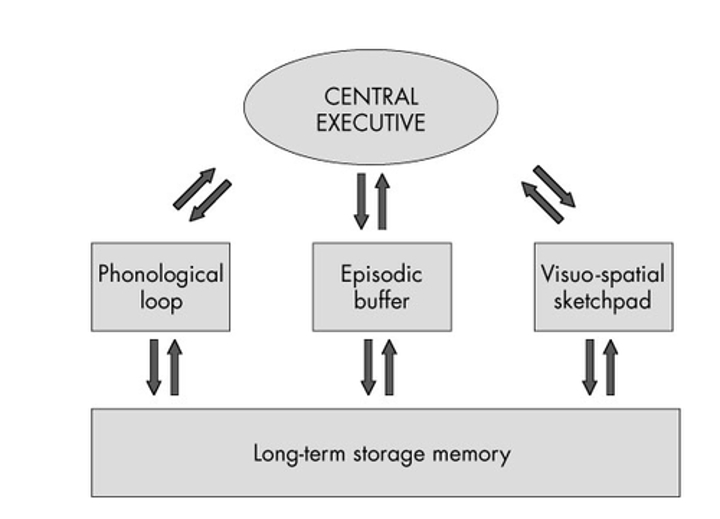
What is the Central Executive?
Responsible for switching attention from task to task and deciding what goes in or out of LTM.
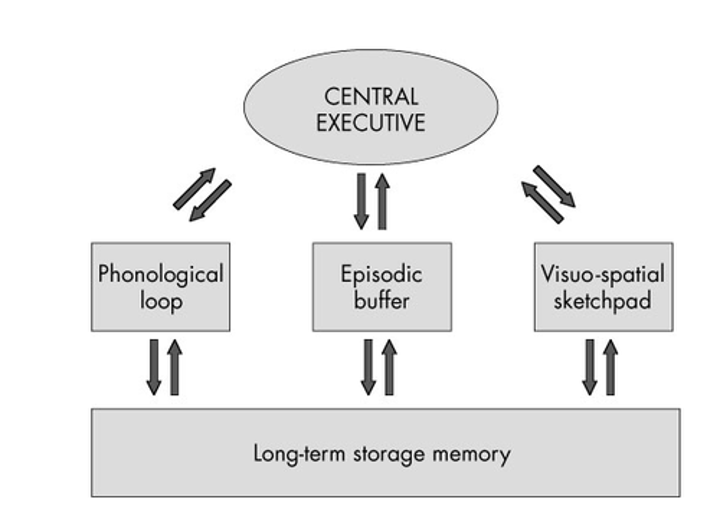
What are the functions of the Central Executive?
Inhibiting (screening out irrelevant material), switching (changing attention from one item to another), and updating (modifying items brought in from LTM before recommitting them to memory through episodic buffer).
What is the Levels of Processing (LOP) Model of Memory and what does it suggest?
Memory is encoded based on the depth of processing. Suggests memory is not about separate stores, but about the depth of processing.
What are the types of encoding in the LOP Model?
Structural, Phonemic, and Semantic.
What is structural encoding?
Remembering physical features of words. Shallow level of encoding (20% recall).
What is phonemic encoding?
Learning words by their sounds. Moderate level of encoding (50% recall)
What is semantic encoding?
Encoding words based on their meaning. Deep level of encoding (80%+ recall).
What is the relationship between effort and recall in the LOP Model?
The more effort needed to encode, the stronger the recall.
How does personal connection affect memory?
It improves memory.
Memory in the limbic system
Basal ganglia - Long term procedural memory, movement.
Amygdala - Forms long term implicit memory (emotional memories, recognising emotion in faces).
Procedural memories - (skill learning, classical conditioning).
Hippocampus - Forming explicit memories, consolidating and retrieving long term declarative memories.
Memory in the cortex and brain stem
Frontal Lobe - Storage, processing, encoding of procedural memories, memory for motor skills tasks and languages.
Temporal Lobes - Memory for sounds and names of colours.
Parietal lobes - Spatial memory (awareness of oneself in space).
Occipital lobe - Memories for pictures.
Cerebellum - Storage, processing, encoding of procedural memories, memory for motor skills tasks, classically conditioned responses. Important for remembering procedural things. Patients with damage to hippocampus but not cerebellum show anterograde amnesia (unable to remember anything after injury, still able to learn new skills).
What is the role of the hippocampus?
Formation and retrieval of declarative memories.
What is the role of the amygdala?
Acquisition of implicit memories.
Where is the hippocampus located and what is it attached to?
Interior to the temporal lobes. Attached to frontal lobe, thalamus, and amygdala.
What is the hippocampus a part of?
The limbic system.
What is the hippocampus important for?
Formation of explicit (declarative) memories.
What type of memories does the hippocampus consolidate?
Declarative memories.
Does the hippocampus store memories?
No, it consolidates them.
Where are explicit memories transferred for permanent storage?
Relevant lobes of the brain.
When are explicit memories usually transferred for permanent storage?
During sleep (slow wave).
What factors can affect the function of the hippocampus?
Psychological factors, brain trauma, health-related conditions.
What type of memories are acquired by the amygdala?
Implicit memories.
What is recall?
Retrieval of info using minimal cues.
What is free recall?
Recalling as much info as possible in any order, without cues.
What is serial recall?
Recalling info in the order in which it was presented.
What is cued recall?
Recalling assisted by cues, not involving the original items to be retrieved.
What is recognition?
Process of retrieval that requires identification of a correct response from a set of alternatives.
How is recognition different from cued recall?
Recognition involves identifying correct responses from given alternatives, while cued recall involves using cues to assist retrieval.
What is relearning?
Learning again something that has already been committed to memory.
What is the encoding specificity principle?
The associations formed at the time of encoding new memories will be the most effective recall cues.
What are context-dependent cues?
External cues that assist retrieval from LTM. Eg. Sound, smell, temp, etc.
What are state-dependent cues?
Internal cues that assist retrieval from LTM. Eg. mood, level of anxiety, physiological or psychological state, etc.
What are some encoding problems that can cause you to forgot?
Inattention, lack of processing, lack of consolidation.
What does the retrieval failure theory suggest?
Inability to recall memories due to absence of cues or failure to use them.
What are retrieval cues?
Mental reminders or prompts to assist recollection.
What is the tip of the tongue phenomenon?
Feeling of knowing something but unable to recall it.
What are possible causes of the tip of the tongue phenomenon?
Retrieval failure or interference.
What is proactive interference?
Previously learned material inhibits encoding of new material.
What is retroactive interference?
Newly acquired material inhibits retrieval of previously learned material.
What is chunking?
Grouping items together to improve memory capacity.
How does chunking help with memory?
Improves memory capacity, especially in STM.
What is the purpose of rehearsal?
To keep information in STM or move it to LTM.
What is the benefit of giving numbers their own meaning during chunking?
Improves memory capacity even more.
What is the main condition that assists retrieval?
Context-dependent cues and state-dependent cues.
What is elaborative rehearsal?
Process of giving meaning to info and linking it to other memories.