nucleic acids
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
what are the 2 main types of nucleic acids?
DNA and RNA
polymer and monomer of these molecules:
monomer: nucleotides
polymer: nucleic acids (such as dna and rna)
what is DNA?
deoxyribonucleic acid is an important information-carrying molecule
it is the genetic material in all living organisms ranging from single celled bacteria to multicellular organisms
what does the DNA code do?
it tells us what to do and what proteins to make
what is the genome?
the cell’s entire genetic content
the study of the genome is genomics
difference of DNA location in eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
eukaryotes- DNA is found mainly in the nucleus, but there is also some in the chloroplasts and mitochondria
prokaryotes- DNA is not enclosed in a membrane envelope
what is RNA?
ribonucleic acid is similar to DNA
it is mostly involved in synthesising proteins
what is formed from RNA?
ribosomes
and proteins are the protein builders of the cell
role of mRNA?
DNA never leaves the nucleus, so it uses messenger RNA (mRNA) to transfer genetic information to the rest of the cell
mRNA moves out of the nucleus to transfer information to the ribosomes.
the mRNA is then used to make proteins
components of nucleic acids?
DNA and RNA are made of monomers called nucleotides
nucleotides join together to form polynucleotides
polynucleotides make up nucleic acids such as DNA or RNA
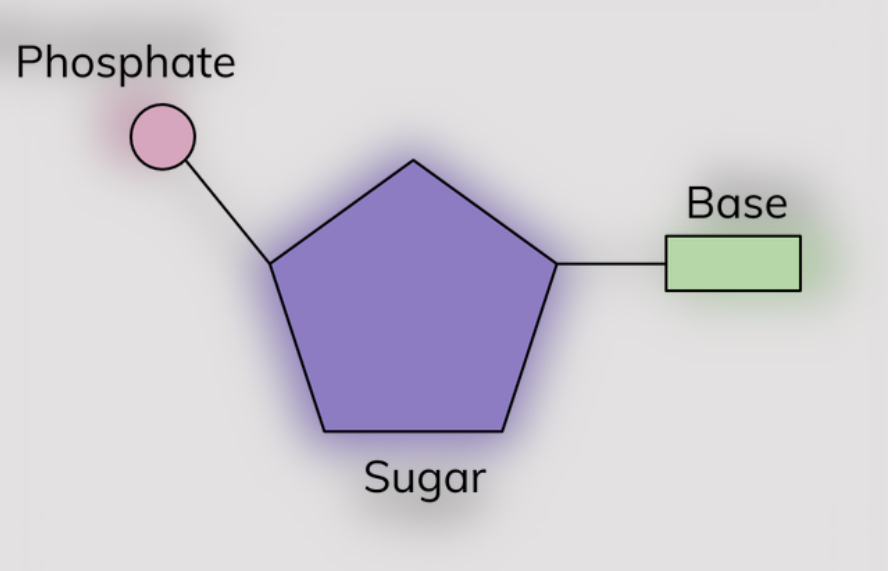
structure of nucleotides?
each nucleotide is formed from a pentose sugar, a nitrogen-containing organic base and a phosphate group
how is a phosphodiester bond formed between 2 nucleotides within a DNA molecule?
condensation reaction between phosphate and deoxyribose
resulting in the elimination of a water molecule
this is catalysed by DNA polymerase
what does a condensation reaction between 2 nucleotides form?
a phosphodiester bond
these condensation reactions happen between a sugar group on one nucleotide and a phosphate group on a different nucleotide

what 2 groups are involved in the phosphodiester linkage?
3’ hydroxyl and 5’ phosphate
components of a DNA nucleotide?
a deoxyribose sugar
a phosphate group
an organic base- adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine
components of an RNA nucleotide?
a ribose sugar
a phosphate group
an organic base- adenine, uracil, cytosine, guanine
structure of DNA?
a DNA molecule is a double helix with 2 polynucleotide chains held together by hydrogen bonds between specific complementary base pairs
the sugar and phosphate lie on the outside of the helix and form the DNA’s backbone
the nitrogenous bases are stacked on the inside of the helix, like a pair of staircase steps
hydrogen bonds hold the base pairs together
RNA is only made of one polynucleotide
explain how the structure of DNA is related to its function? (6 marker)
for storage of information
long/large molecules to store lots of information
helix/coiled making the molecule compact
for function in DNA replication:
double stranded to allow for semi-conservative replication
complementary base pairing to allow accurate replication
weak hydrogen bonds to allow replication/separation of strands
for strength and stability:
double-stranded helix to provide strength/stability
many hydrogen bonds making the molecule strong
how many bonds are there between adenine and thymine, compared to cytosine and guanine?
adenine and thymine- 2 hydrogen bonds
cytosine and guanine- 3 hydrogen bonds
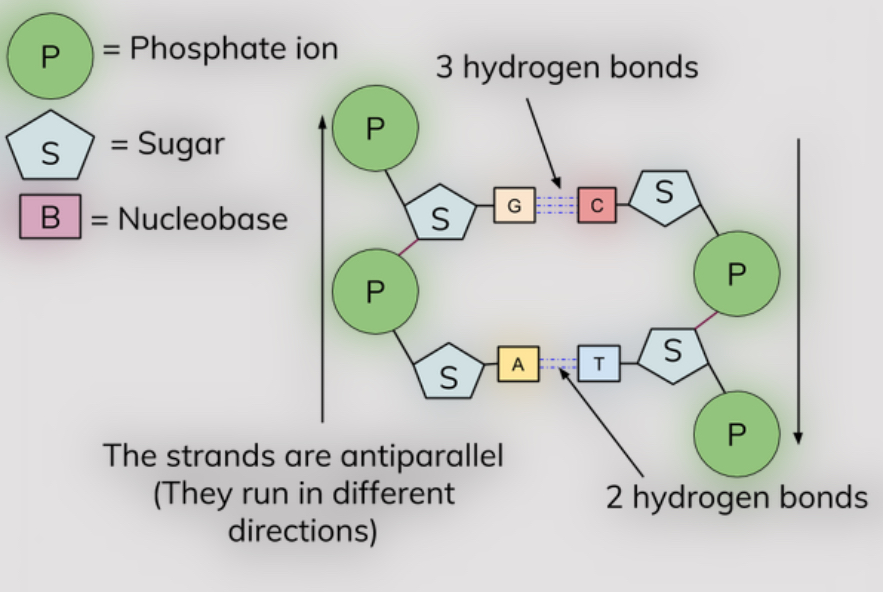
base pairing rules in DNA:?
adenine can pair with thymine
cytosine can pair with guanine
this means that there is always an identical number of adenine and thymine bases and of guanine and cytosine bases in DNA
strands are complementary to each other
types of bonding in RNA and DNA?
DNA: base pairing holds the 2 DNA polynucleotides together by hydrogen bonding
RNA: the single polynucleotide chain is held together by phosphodiester bonds between the nucleotides
why are the 2 polynucleotide strands antiparallel?
because they run in opposite directions
why do the arrows in which dna polymerase is added point in different ways?
dna has antiparallel strands
shape of the nucleotides are different
enzymes have active sites with specific shape
only substrates complementary shape can bind with the active site of the dna polymerase enzyme
name of the protein associated with DNA in a chromosomes?
histone
difference between prokaryotic DNA and eukaryotic DNA?
prokaryotic dna:
circular/ non-linear dna
not associated with proteins/histones
no non-coding DNA
exam question: humans and grasshoppers have similar percentages of each base in their DNA but they are very different organisms, how is this possible?
different genes
so bases are in a different sequence
so different amino acid coded for different protein/polypeptide
what happens when a cell divides?
it forms 2 daughter cells
this means that before cell division, the cell must duplicate its DNA so that each daughter cell can inherit the full set of DNA
DNA replication?
DNA is made of 2 polynucleotide chains that form a double helix
during DNA replication, each of the 2 strands are used as a template from which new strands are copied
semi conservative model?
after replication, the new DNA is made up of one original polynucleotide strand, and a new complementary strand
this explains why DNA replication is described as semi-conservative because one original strand is conserved
process of DNA replication: step 1?
DNA helicase binds to the DNA and breaks the hydrogen bonds between the two strands/ between the base pairs
the DNA helix unwinds and the 2 strands separate
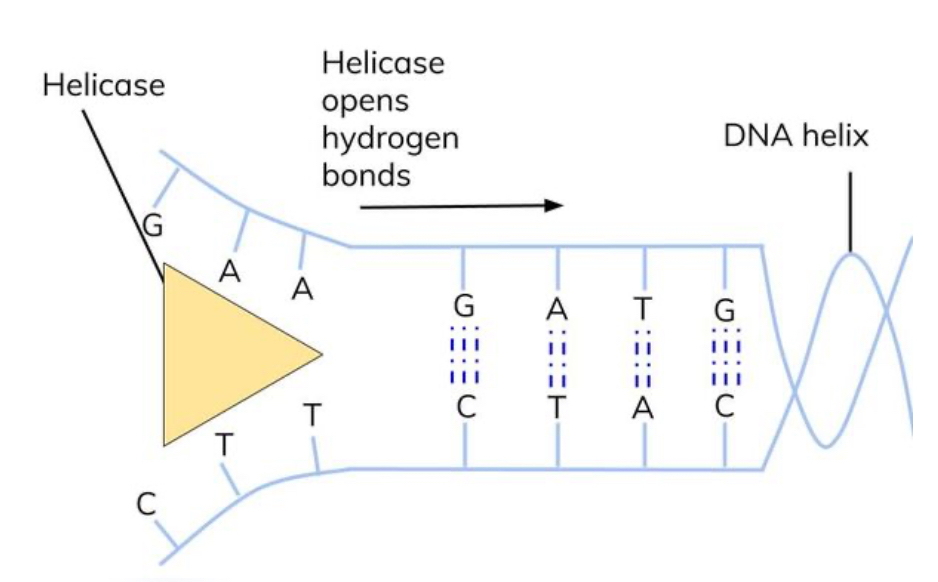
process of replication: step 2?
free floating nucleotides form hydrogen bonds with the complementary bases
each strand is used as a template to produce complementary strands
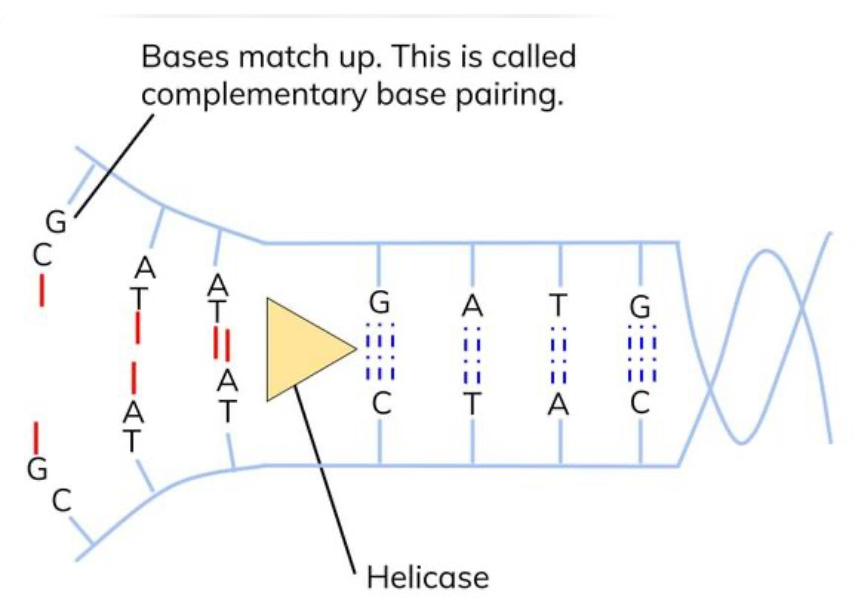
process of replication: step 3?
DNA polymerase forms phosphodiester bonds between the nucleotides
2 new DNA strands are synthesised
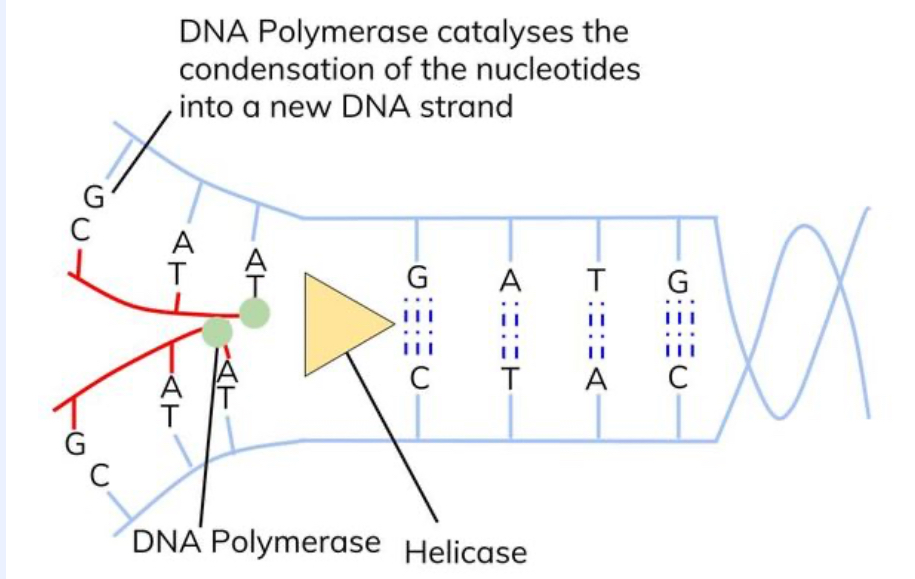
why are there single-stranded dna?
to act as template strand
to determine order of nucleotides/bases
how are the carbon atoms of the pentose sugar in DNA numbered?
the carbon atoms of the sugar molecule are number as 1’, 2’, 3’, 4’, 5’
how is each DNA strand different in its structure?
one end is called the 3’ and the other end is called the 5’
in a DNA helix, the strands run in opposite directions- they are antiparallel
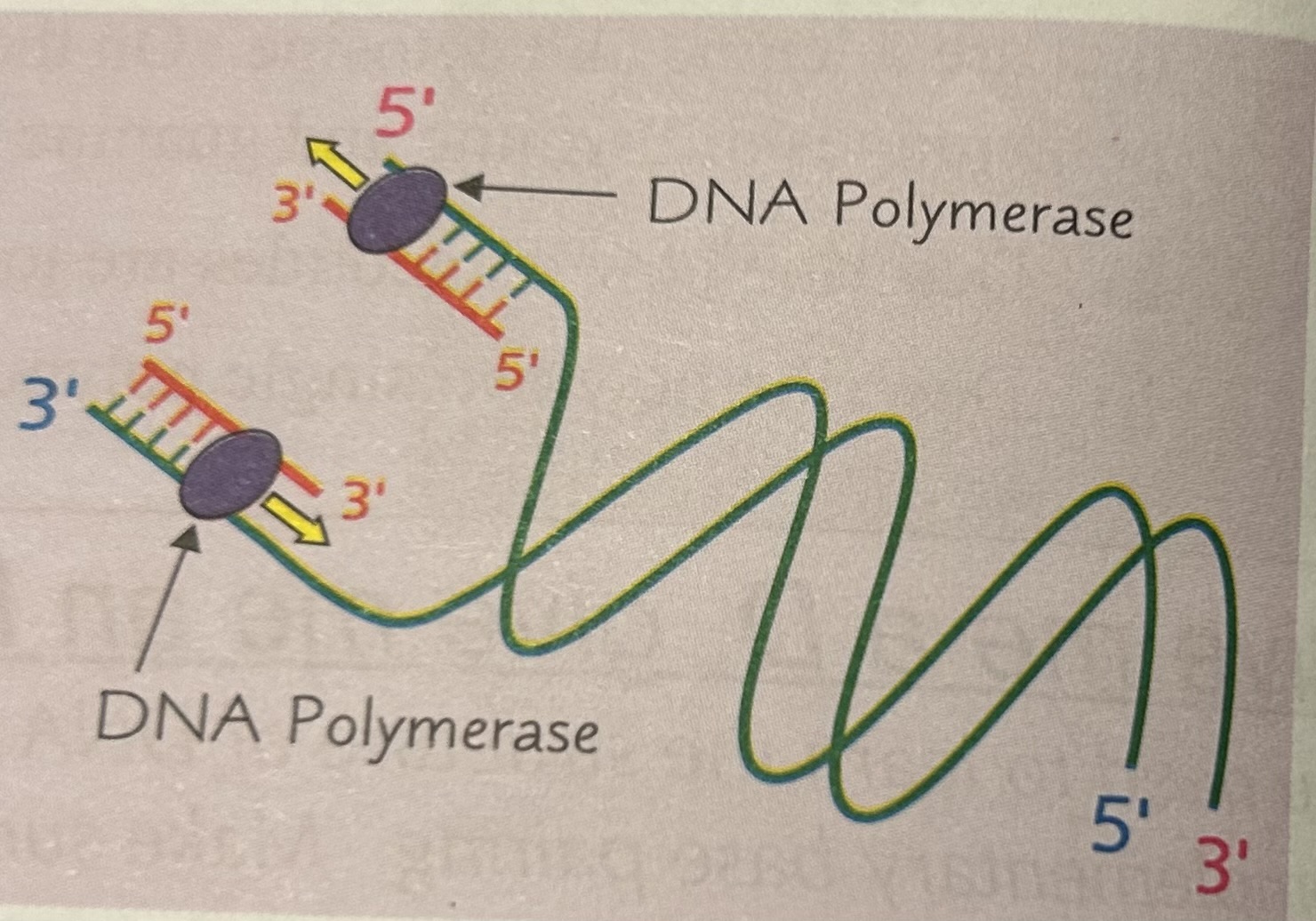
what is the active site of the DNA polymerase complementary to (in terms of the ‘prime’ ends?
it is only complementary to the 3’ end of the newly forming DNA strand, so the enzyme can only add nucleotides to the new strand at the 3’ end
how is the new strand made (in terms of primes)?
it is made in a 5’ to 3’ direction and that DNA polymerase moves down the template strand in a 3’ to 5’ direction
because the strands in DNA are antiparallel, the DNA polymerase working on one of the template strands moves in the opposite direction to the DNA polymerase working on the other template strand.
who were the 2 scientists that provided evidence for the semi-conservative model?
in 1953, watson and crick thought that each strand acts as a template from which the new complementary strand was copied
however, it was meselson and stahl who figured out that DNA replicates by the semi-conservation model
how did meselson and stahl conduct the experiment?
they grew e.coli for several generations in one medium containing a ‘heavy’ isotope of nitrogen (15N), and another medium containing ‘light’ isotope of nitrogen (14N)
during replication, the nitrogen gets included into the nitrogenous bases, and eventually into the DNA
meselson and stahl: isolating the DNA?
after each of the first few generations, the cells were harvested and the DNA was isolated, then centrifuged
the DNA from the heavy nitrogen settled lower down the centrifuge tube than the lighter nitrogen
meselson and stahl- conclusive evidence?
the DNA harvested from cells grown for 2 generations in 14N formed 2 bands
one DNA band was between 15N and 14N
the other DNA band corresponded to the band of 14N DNA
these results could only be explained if DNA replicates in a semi-conservative manner