Bio of Fishes Simplified/Basic Flashcards (NO pics)
1/251
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
252 Terms
Taxon
A taxonomic group of any rank, such as a species, family, or class.
Taxonomic category
A rank in the hierarchical classification of organisms, e.g., kingdom, phylum, class.
Systematics
The study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time.
Taxonomy
The science of defining and naming groups of biological organisms on the basis of shared characteristics.
Phylogeny
The evolutionary history of a species or group of species, often represented as a branching diagram.
Phylogenetic tree
A branching diagram showing the inferred evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities.
Synapomorphy
A shared derived character or trait that distinguishes a clade from other groups.
Node (phylogeny)
A branching point on a phylogenetic tree representing a common ancestor for the taxa stemming from that point.
Monophyletic group
A group of organisms that consists of a common ancestor and all of its descendants.
Convergent evolution
The independent evolution of similar features in species from different lineages.
Placoid scales
Shark scales, tooth-like structures made of dentin and enamel.
Ganoid scales
Thick, hard, rhomboid scales found in primitive bony fishes like gars, often covered with ganoine.
Cycloid scales
Smooth-edged, disc-shaped scales common in more advanced bony fishes like salmon.
Ctenoid scales
Scales with comb-like edges, found in many teleost fishes like perch, providing a rough texture.
Pelvic fin
Paired fins located ventrally on a fish, used for stability, braking, and steering.
Anal fin
A single fin located on the ventral side of a fish behind the anus, used for stability.
Spine (fin)
A hard, sharp, often unsegmented and unbranched fin ray, typically found in dorsal, anal, and pectoral fins.
Soft ray (fin)
A flexible, segmented, and often branched fin ray, supporting fins in most bony fishes.
Heterocercal fin
A caudal fin where the vertebral column extends into the upper lobe, making it asymmetrical, characteristic of sharks.
Diphycercal fin
A caudal fin that is symmetrical externally and internally, with the vertebral column extending straight to the tip, characteristic of lungfishes.
Terminal mouth
A mouth located at the anterior-most tip of the head, allowing for direct forward feeding.
Superior mouth
A mouth opening upwards, adapted for feeding on prey above the fish.
Inferior mouth
A mouth opening downwards, adapted for feeding on bottom-dwelling prey.
Rover predator (body form)
A streamlined, fusiform body shape adapted for continuous swimming in open water, e.g., tuna.
Lie-in-wait predator (body form)
An elongated body form with fins positioned posteriorly, adapted for sudden bursts of speed from a stationary position, e.g., pike.
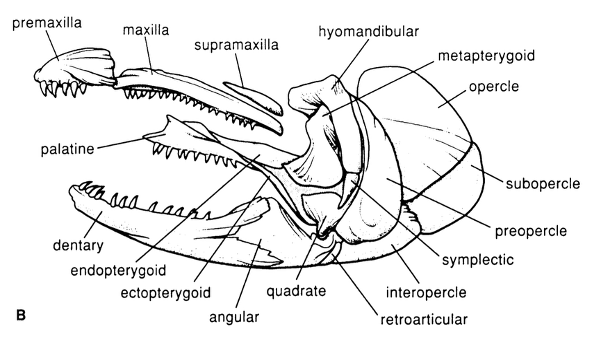
Premaxilla
The anterior-most bone of the upper jaw in most fishes, often bearing teeth.
Dentary
The main bone of the lower jaw, typically bearing teeth.
Suspensoriumn
A series of bones connecting the jaws to the neurocranium, crucial for jaw protrusion and mobility.
Preoperculum
The crescent-shaped bone anterior to the operculum, part of the opercular series.
Suboperculum
A bone in the opercular series, located ventral to the operculum.
Interopercum
A bone in the opercular series, located anteroventral to the operculum, connecting to the lower jaw.
Branchial arches
Cartilaginous or bony arches supporting the gills, also involved in feeding in some fishes.
Pharyngeal jaws
Secondary jaws located in the pharynx (throat) of many fishes, used for processing food after it's been caught.
Hyoid apparatus
A complex of bones and cartilages supporting the tongue and floor of the mouth, involved in respiration and feeding.
Vomer
A median bone on the ventral surface of the neurocranium, often bearing teeth.
Parasphenoid
A large, median bone forming the floor of the neurocranium.
Centrum (vertebrae)
The main body of a vertebra, which typically consists of a cylindrical central part and processes extending from it.
Neural arch
The dorsal arch of a vertebra that encloses and protects the spinal cord.
Haemal arch
The ventral arch of a vertebra in the caudal region that encloses and protects blood vessels.
Pleural ribs
Ventral ribs attached to the vertebral column in the trunk region, protecting internal organs.
Hypurals
Flattened bones in the caudal skeleton that support the caudal fin rays.
Epurals
Elongated bones located dorsally in the caudal skeleton, contributing to tail fin support.
Urostyle
A posteriormost fusion of caudal vertebrae, part of the caudal skeleton supporting the tail fin in teleosts.
Uroneurals
Paired bones overlying the urostyle in the caudal skeleton, providing additional support.
Coelacanthiformes
An order of lobe-finned fishes, including coelacanths, known for their ancient lineage.
Dipnoi
A subclass of lobe-finned fishes commonly known as lungfishes, characterized by the ability to breathe air.
Lungfishes
Fish belonging to the subclass Dipnoi, capable of breathing air using a modified swim bladder (lung).
Ceratodontiformes
An order of lungfishes, including the Australian lungfish.
Lepidosireniformes
An order of lungfishes, including the African and South American lungfishes.
Tetrapoda
A superclass of vertebrates with four limbs, including amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, evolved from lobe-finned fish ancestors.
Polypteriformes
An order of basal ray-finned fishes, including bichirs and ropefish, known for ganoid scales and multiple dorsal finlets.
Bichirs
Fish belonging to the order Polypteriformes, characterized by their elongated bodies and multiple dorsal finlets.
Ropefish
An elongated fish species within the Polypteriformes, often kept in aquariums, similar to bichirs.
Acipenseriformes
An order of basal ray-finned fishes, including sturgeons and paddlefishes, known for cartilaginous skeletons and bony scutes.
Paddlefishes
Large, cartilaginous fish within the Acipenseriformes, characterized by an elongated, paddle-like snout.
Lepisosteiformes
An order of ray-finned fishes, including gars, known for their elongated bodies and ganoid scales.
Gars
Fish belonging to the order Lepisosteiformes, characterized by long, narrow jaws with sharp teeth and ganoid scales.
Amiiformes
An order of ray-finned fishes, containing only the bowfin, known for its large dorsal fin and ability to gulp air.
Bowfin
A freshwater fish (Amia calva) from the order Amiiformes, characterized by a long, undulating dorsal fin and a bony gular plate.
Protrusible jaw (Teleostei)
A key synapomorphy of Teleostei where the upper jaw can be extended forward, increasing feeding efficiency.
Teleost caudal skeleton synapomorphy
Characterized by a highly flexible and symmetrical homocercal caudal fin supported by fused vertebral elements (urostyle, hypurals, epurals) allowing for diverse swimming modes.
Osteoglossomorpha
An ancient order of teleost fishes, including 'bony-tongues' like arowanas and elephantfishes.
Elopomorpha
An infraclass of teleost fishes, including eels, tarpons, and ladyfishes, characterized by a leptocephalus larval stage.
Otocephala
A large clade of teleost fishes characterized by a specialized connection between the ear and swim bladder.
Clupeomorpha
A superorder of teleost fishes, including herrings and anchovies, known for their schooling behavior and filter feeding.
Ostariophysi
A superorder of freshwater teleosts, including carp, piranhas, and catfishes, characterized by a Weberian apparatus.
Characiformes
An order within Ostariophysi, including piranhas and tetras, mostly South American freshwater species.
Cypriniformes
An order within Ostariophysi, including carps, minnows, and loaches, a diverse group found in Eurasia and North America.
Siluriformes
An order within Ostariophysi, commonly known as catfishes, characterized by barbels and the lack of scales.
Protacanthopterygii
A superorder of ray-finned fishes, including salmon and pikes, considered relatively primitive teleosts.
Neoteleostei
A major clade of teleost fishes, characterized by significant muscle and skeletal modifications, including the retractor dorsalis muscle.
Retractor dorsalis muscle
A muscle unique to Neoteleostei that connects the vertebral column to the upper pharyngeal jaws, aiding in jaw protrusion.
Stomiiformes
An order of deep-sea teleost fishes, including viperfishes and hatchetfishes, often bioluminescent.
Viperfishes
Deep-sea fish from the order Stomiiformes, known for long, sharp teeth and bioluminescent organs.
Deep-sea hatchetfishes
Small, deep-sea fish from the order Stomiiformes, with highly compressed bodies and upward-facing eyes.
Aulopiformes
An order of marine teleost fishes, mostly deep-sea, including lizardfishes and tripodfishes.
Myctophiformes
An order of deep-sea teleost fishes, including lanternfishes, known for their prominent photophores.
Lanternfishes
Small, mesopelagic fish from the order Myctophiformes, characterized by rows of photophores for bioluminescence.
Acanthomorpha
A large superorder of teleost fishes (spiny-rayed fish), highly diverse and often characterized by true spines in their fins.
Paracanthopterygii
A superorder of teleost fishes within Acanthomorpha, including cods, anglerfishes, and toadfish.
Percopsiformes
An order of small, freshwater teleost fishes within Paracanthopterygii, known as trout-perches.
Ophidiiformes
An order of elongated, often deep-sea teleost fishes within Paracanthopterygii, including cusk-eels and viviparous brotulas.
Gadiformes
An order of marine teleost fishes within Paracanthopterygii, including cod, haddock, and pollock.
Batrachoidiformes
An order of benthic marine teleost fishes within Paracanthopterygii, commonly known as toadfish.
Lophiiformes
An order of teleost fishes within Paracanthopterygii, including anglerfishes and frogfishes, known for their modified dorsal fin ray (illicium) as a lure.
Community (ecology)
A group of different species living and interacting together in a particular habitat or area.
Filter/screen concept (ecology)
A conceptual framework explaining how environmental and biotic factors 'filter' species from a regional pool to local assemblages.
Parasitism
A symbiotic relationship where one organism (the parasite) benefits at the expense of another (the host), e.g., lampreys feeding on other fish.
True Estuarine fishes
Fish species that spend their entire lives within estuaries, adapted to fluctuating salinity and conditions.
Dependent Marine fishes
Marine fish species that regularly enter estuaries, often as juveniles for refuge and feeding, but return to the ocean as adults.
Fish
Aquatic vertebrate with characteristic scales, fins, and gills throughout life.
Clade
A monophyletic group including one common ancestor and all its descendants.
Dentary Bone
The lower mandible of a fish.
Vertebral Column
A serial arrangement of vertebrae that runs from the head to the tail.
provides structural support and protects the spinal cord.
The Backbone
Centrum: The main, often hourglass-shaped, body of each vertebra.
Neural Arch (Dorsal Arch): Arches dorsally over the spinal cord, ending in a neural spine.
Haemal Arch (Ventral Arch): Arches ventrally over the caudal artery and vein in the tail region, ending in a haemal spine.
Pleural Ribs: Attach to vertebral centra in the abdominal region, protecting internal organs
Heterocercal Tail
A type of tail where the upper lobe is longer than the lower lobe, common in sharks.
Agnathans
Jawless fishes, such as hagfish and lampreys.
Cartilaginous skeleton, no paired fins, single nostril, and no jaws.
Chondrichthyans
Class of cartilaginous fishes including sharks and rays.
Possess placoid scales and a cartilaginous skeleton. Have multiple gill slits
Sarcopterygians
Lobe-finned fishes and tetrapods.
Actinopterygians
Ray-finned fishes.
Inferior Mouths
Mouths that open downward, common in bottom-feeders.