iGCSE Edexcel Physics Forces & Motion
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is speed?
How fast an object travels a certain distance

What is a scalar quantity?
A quantity that has only magnitude/size and no direction
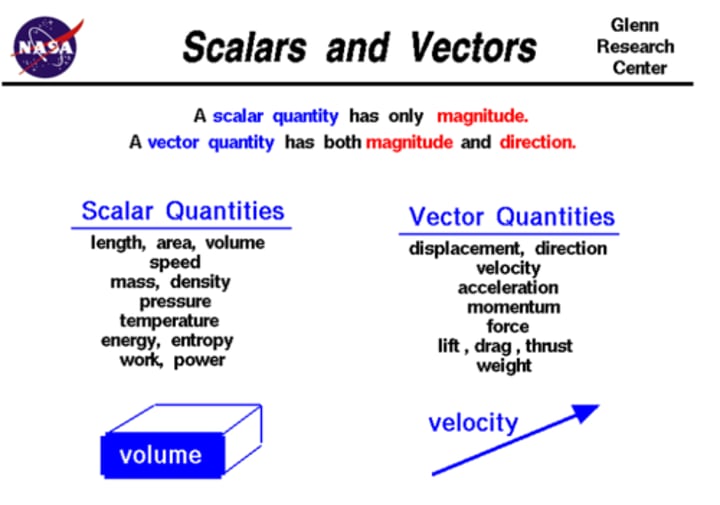
What is a vector quantity?
A quantity that has both magnitude/size and direction
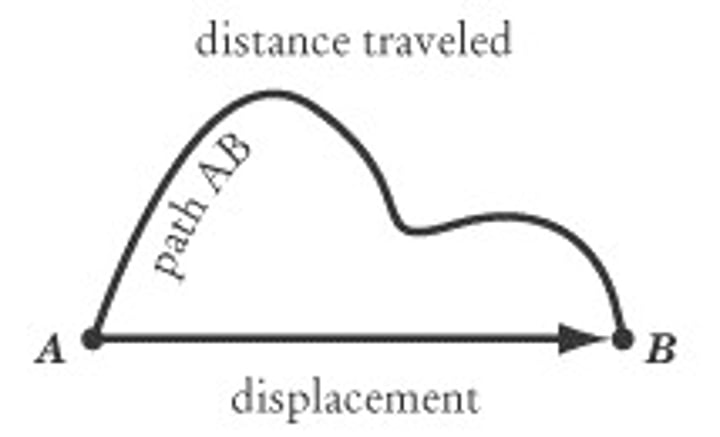
What is displacement?
Distance travelled in a particular direction
What is velocity?
Speed in a particular direction
What is acceleration?
The rate of change of velocity
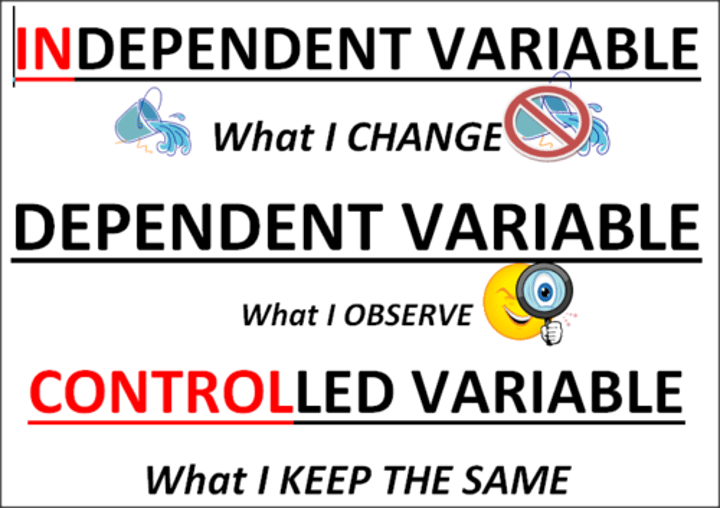
What is the independent variable?
The variable that is changed
What is a dependent variable?
The variable that is measured/observed/derived beacause it changes an outcome
What is a control variable?
The thing you keep the same
What is an anomaly?
A point significantly out of place compared to the other results

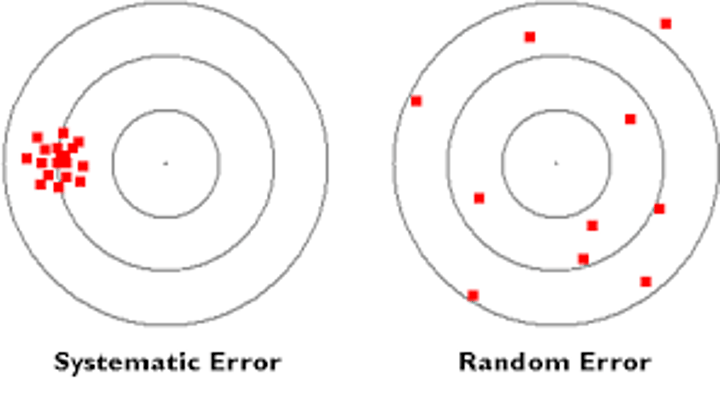
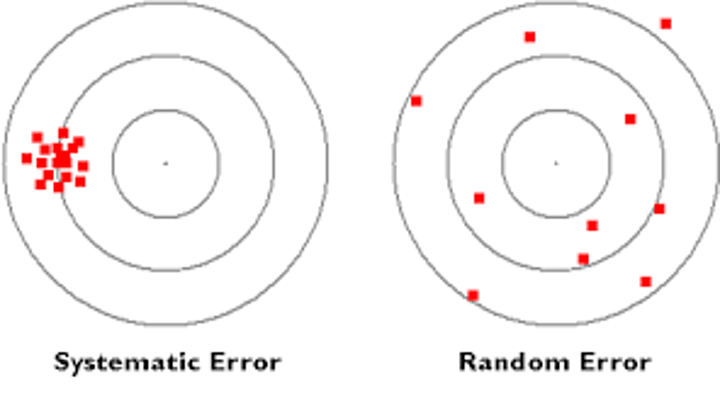
What is a random error?
An error that affects each measurement differently
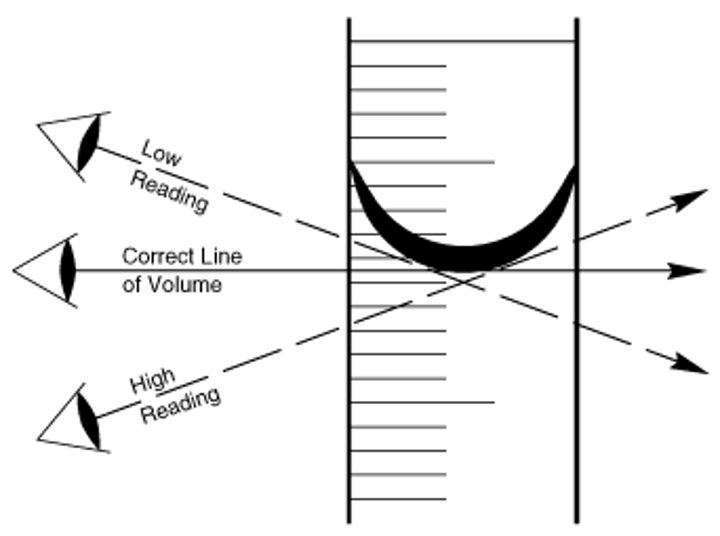
What is parallax error?
Caused when reading from a needle meter, when not looking straight at meter
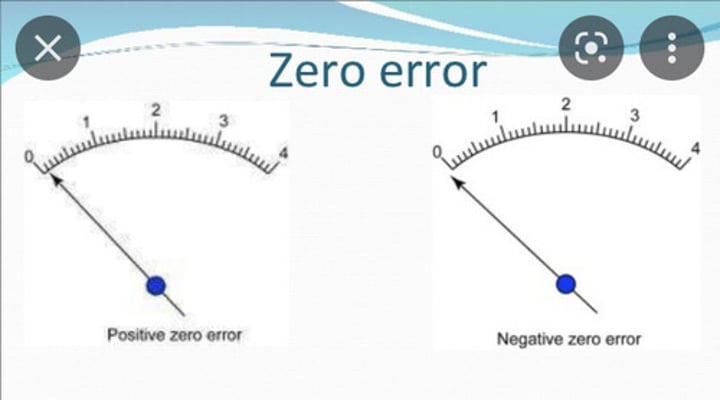
What is a zero error?
Caused by measuring instruments that have a false zero
What is a systematic error?
An error that occurs to the same amount every time you take a particular reading
What is a force?
Can change the shape of something, its speed or the direction that it is moving in
What are the types of forces?
Contact and non-contact forces
What is a contact force?
When two objects have to be touching for a force to act
What is a non-contact force?
When objects do not need to be touching for a force to act

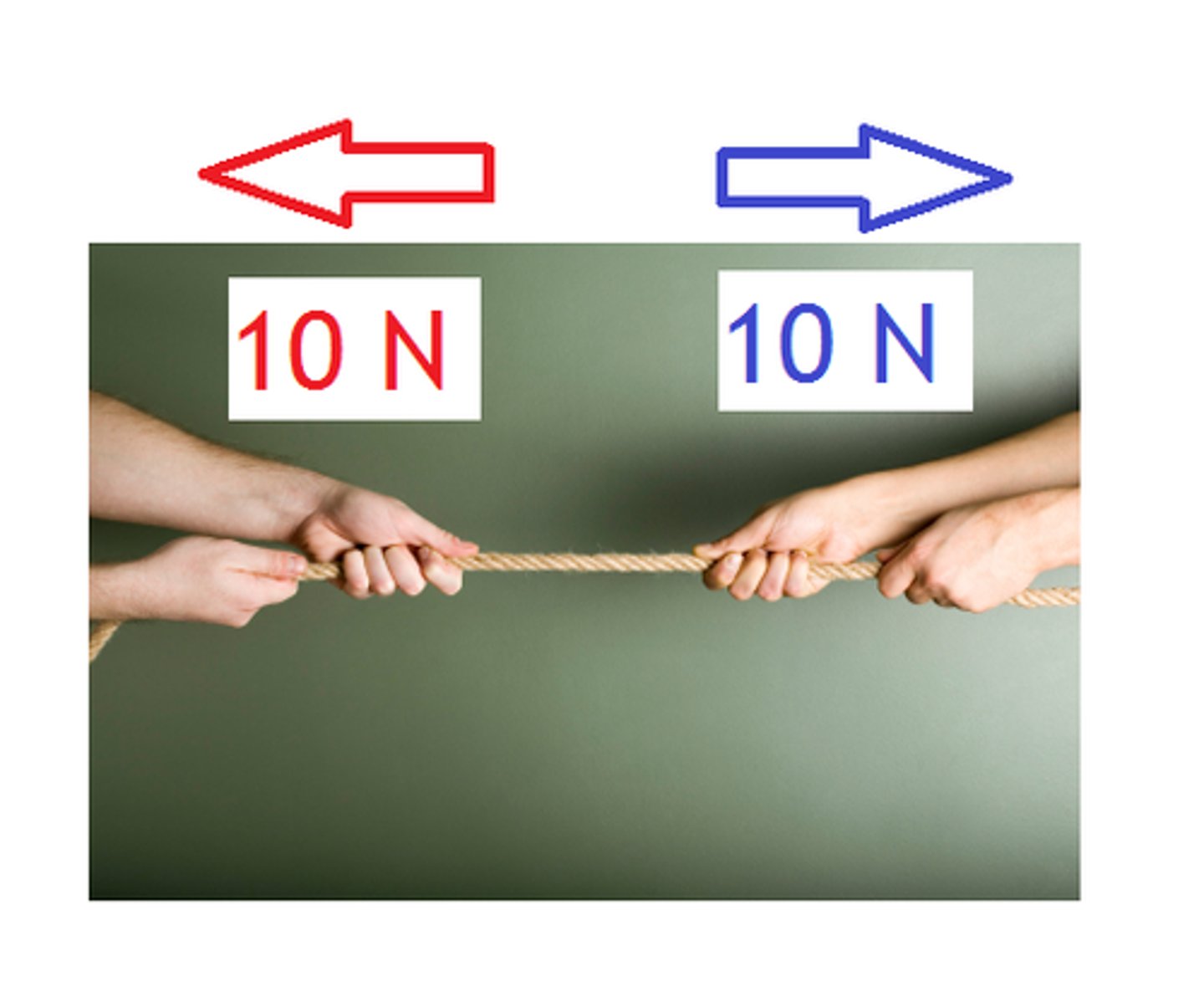
What happens when forces are balanced?
The object is either stationary or moves with constant velocity
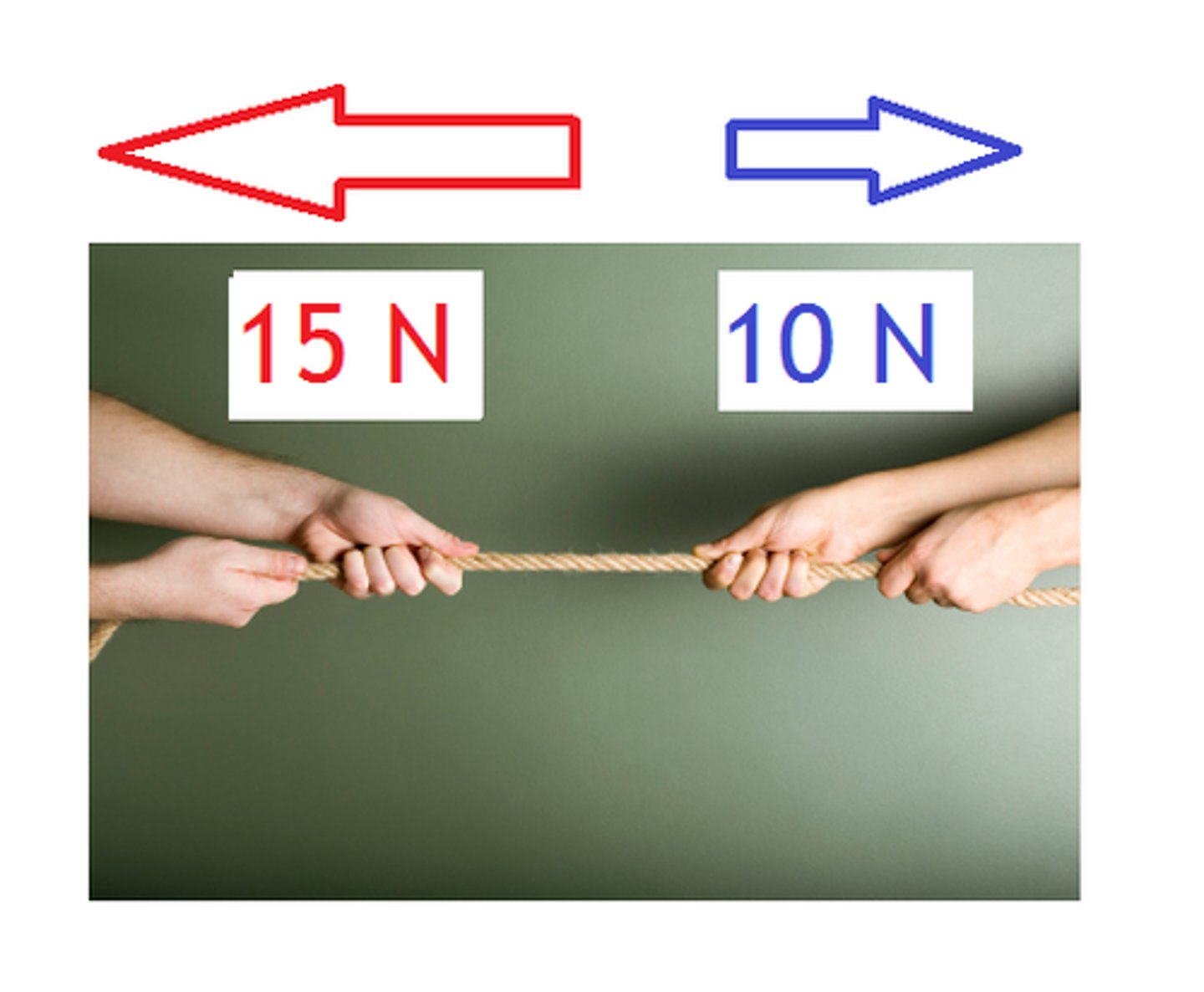
What happens when forces are unbalanced?
The object either accelerates or deccelerates
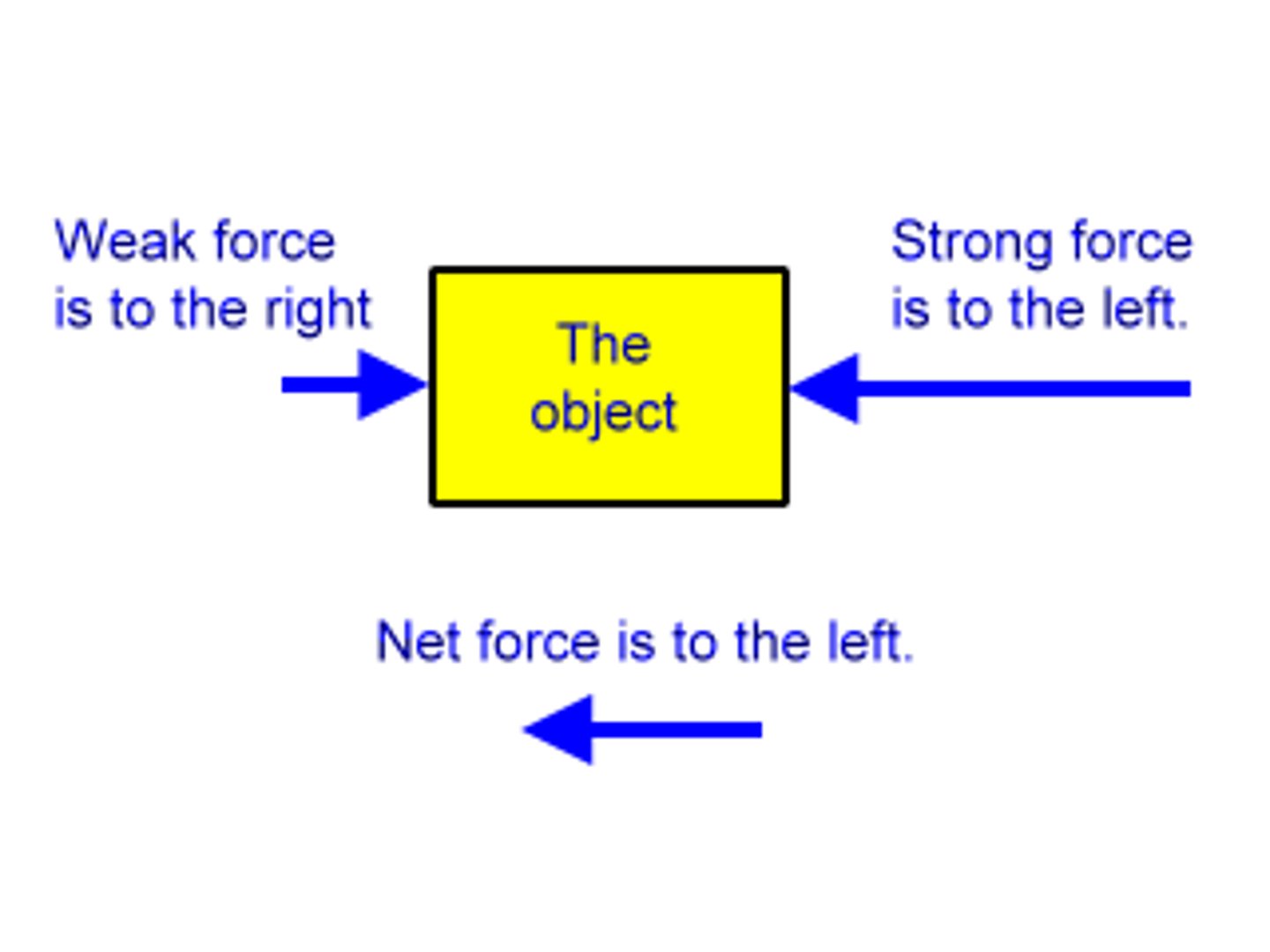
What is a resultant force?
The overall force on a point or object
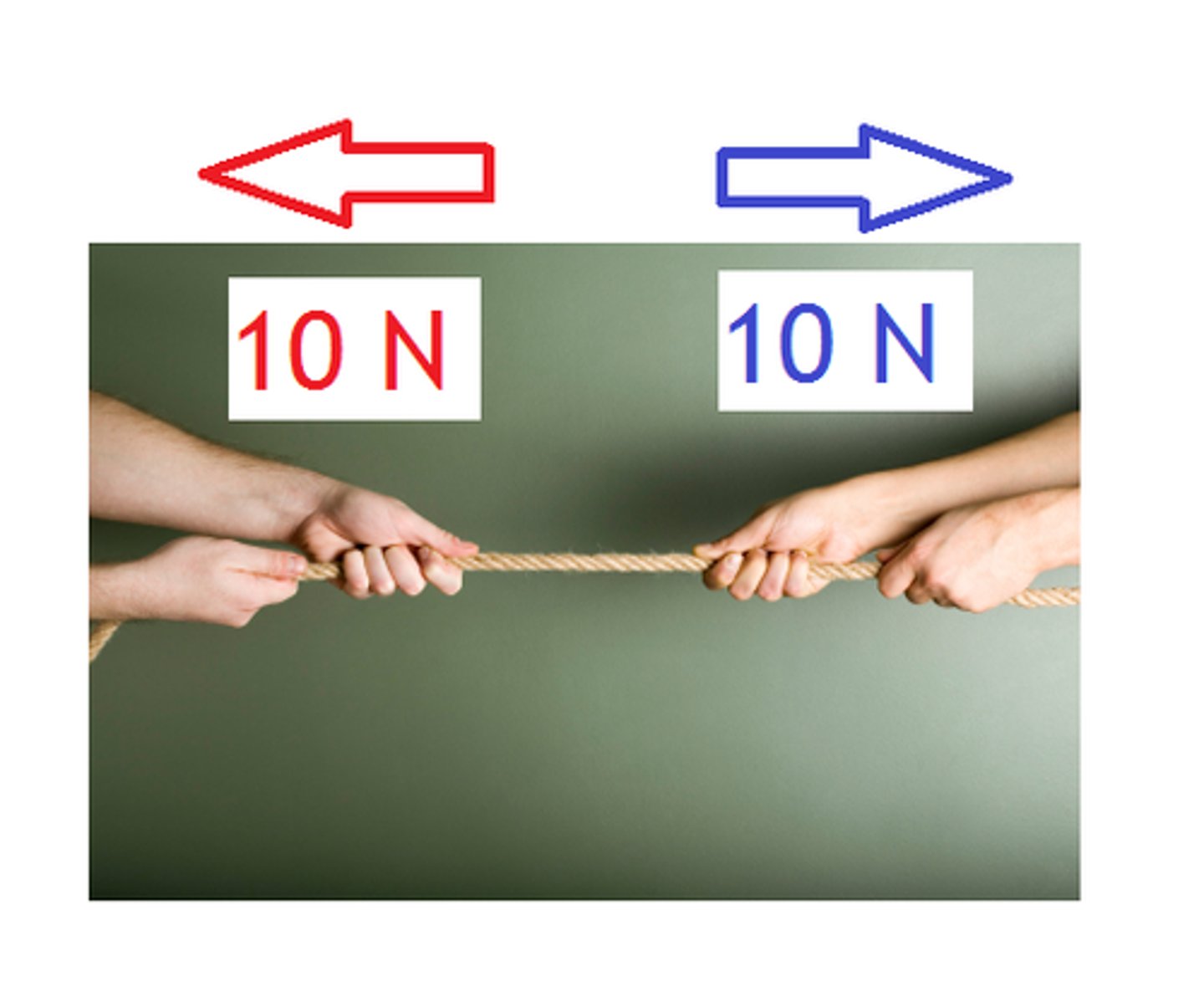
What happens if the resultant force is zero?
The object is stationary or travels at constant velocity
What happens if the resultant force is NOT zero?
The object accelerates or deccelerates

When does friction occur?
When two surfaces rub together
What is drag?
The frictional force experienced by an object travelling through a liquid
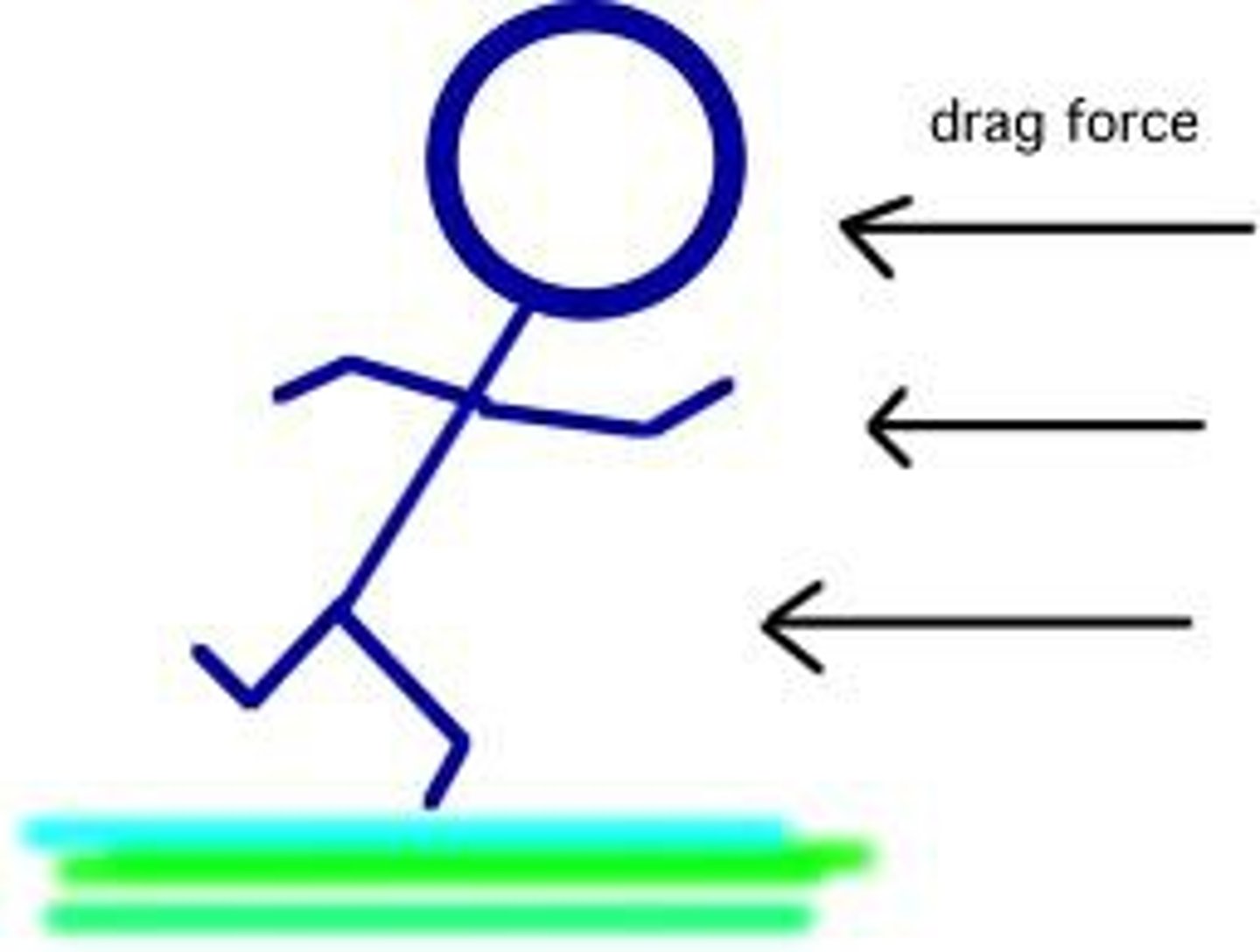
What is air resistance?
Friction caused by an object moving through air

What is the gravitational field strength on earth?
10N/kg
What is the formula for average speed?
total distance travelled/time taken
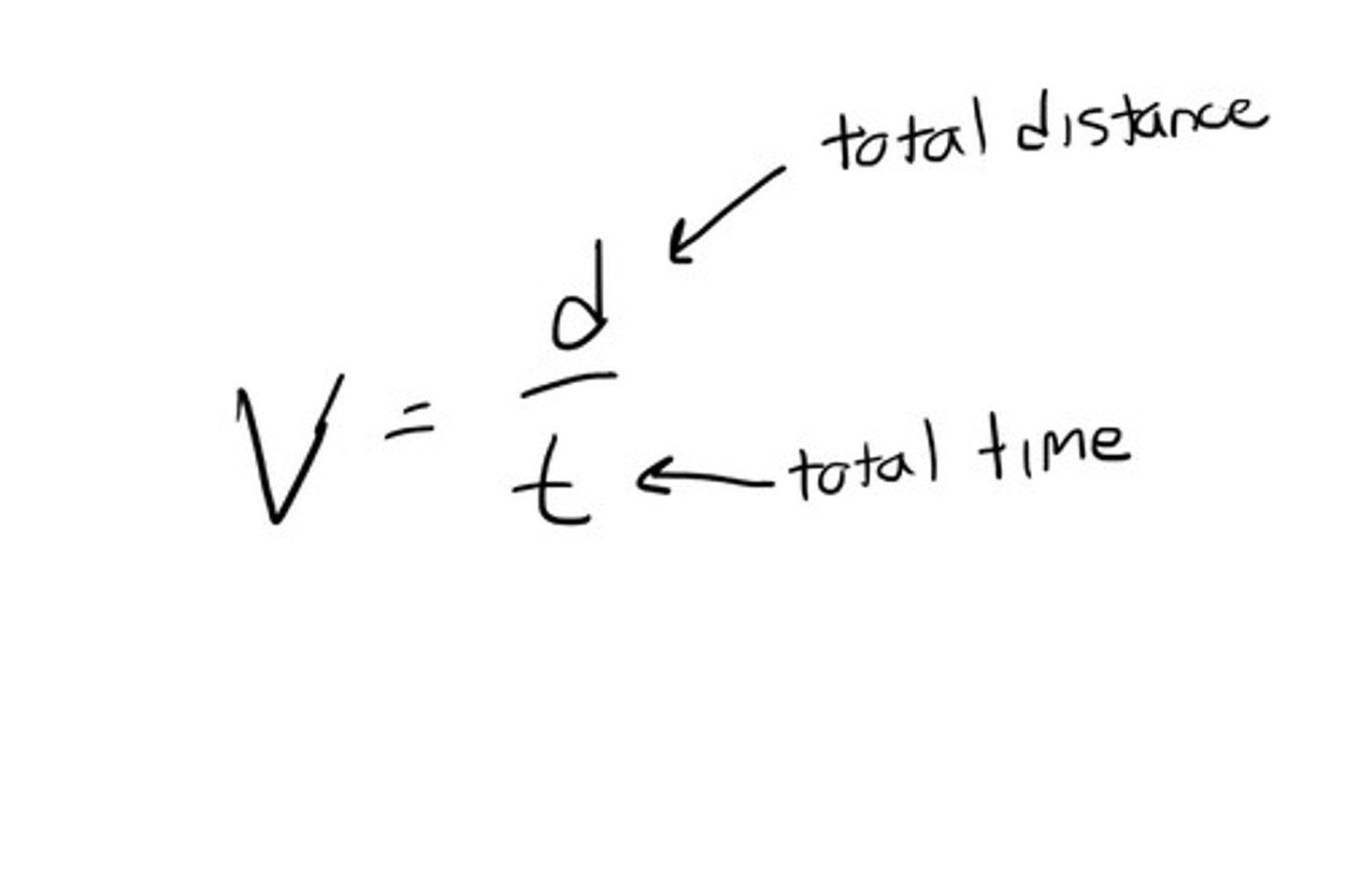
What is the formula for gradient?
rise/run
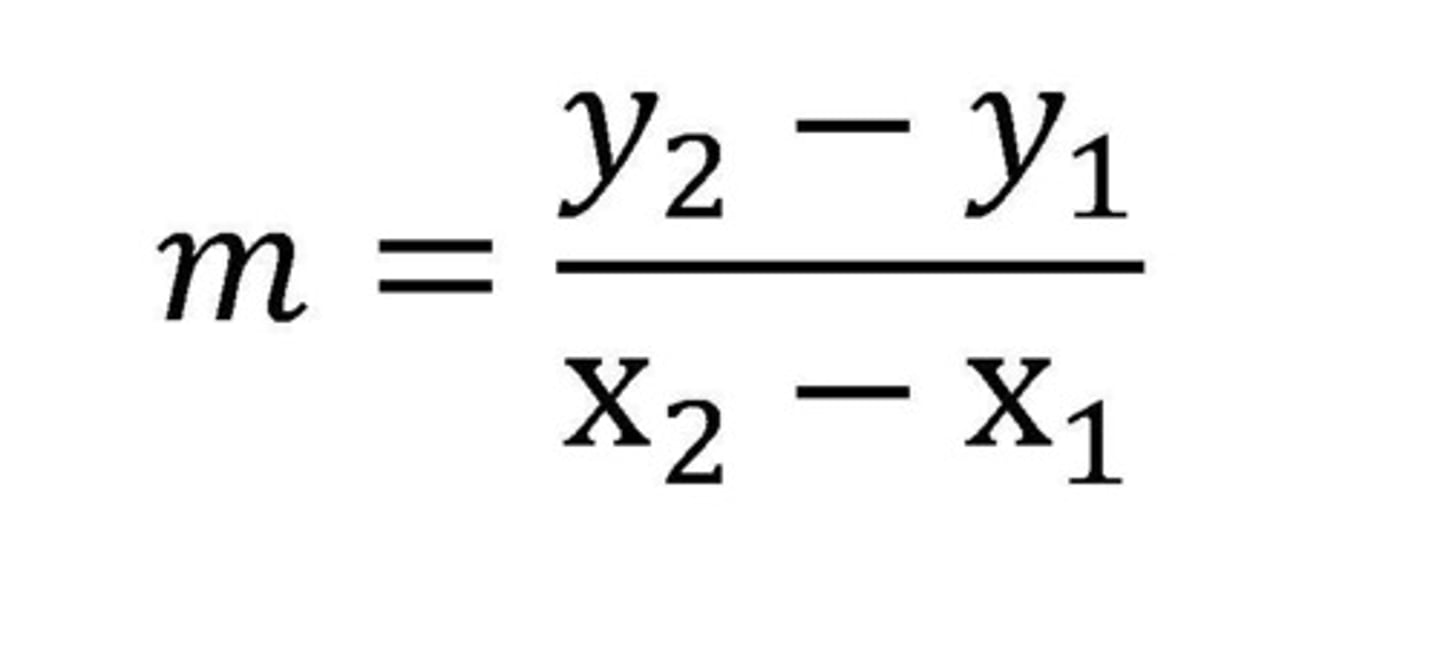
What is the formula for average velocity?
displacement/time

What is the formula for acceleration?
final velocity-initial velocity/time
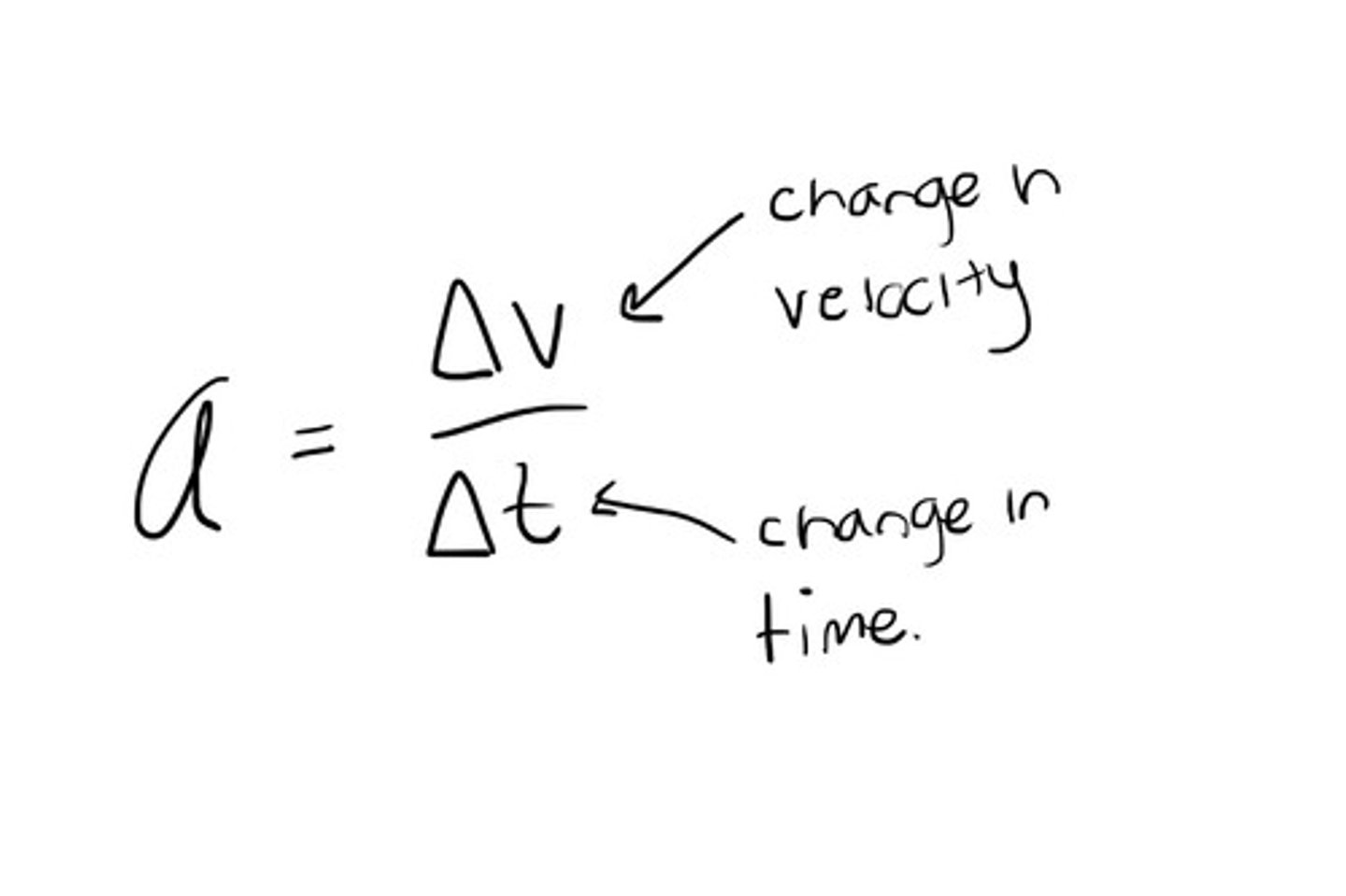
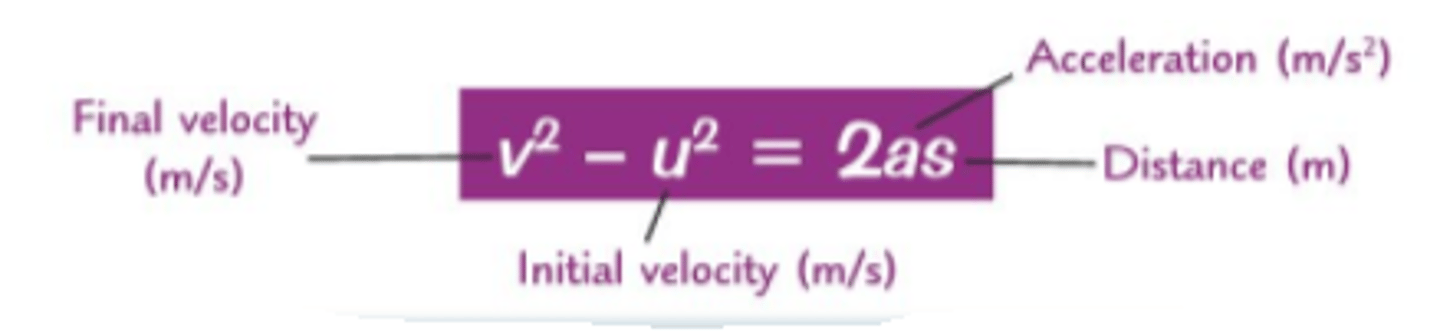
What is the formula for uniformly accelerated motion?
v^2=u^2 + 2as
When speeding up, velocity increases and there is?
Acceleration
When slowing down, velocity decreases and there is?
Deceleration or negative acceleration
What kind of quantity is acceleration?
Vector
What kind of quantity is distance?
Scalar
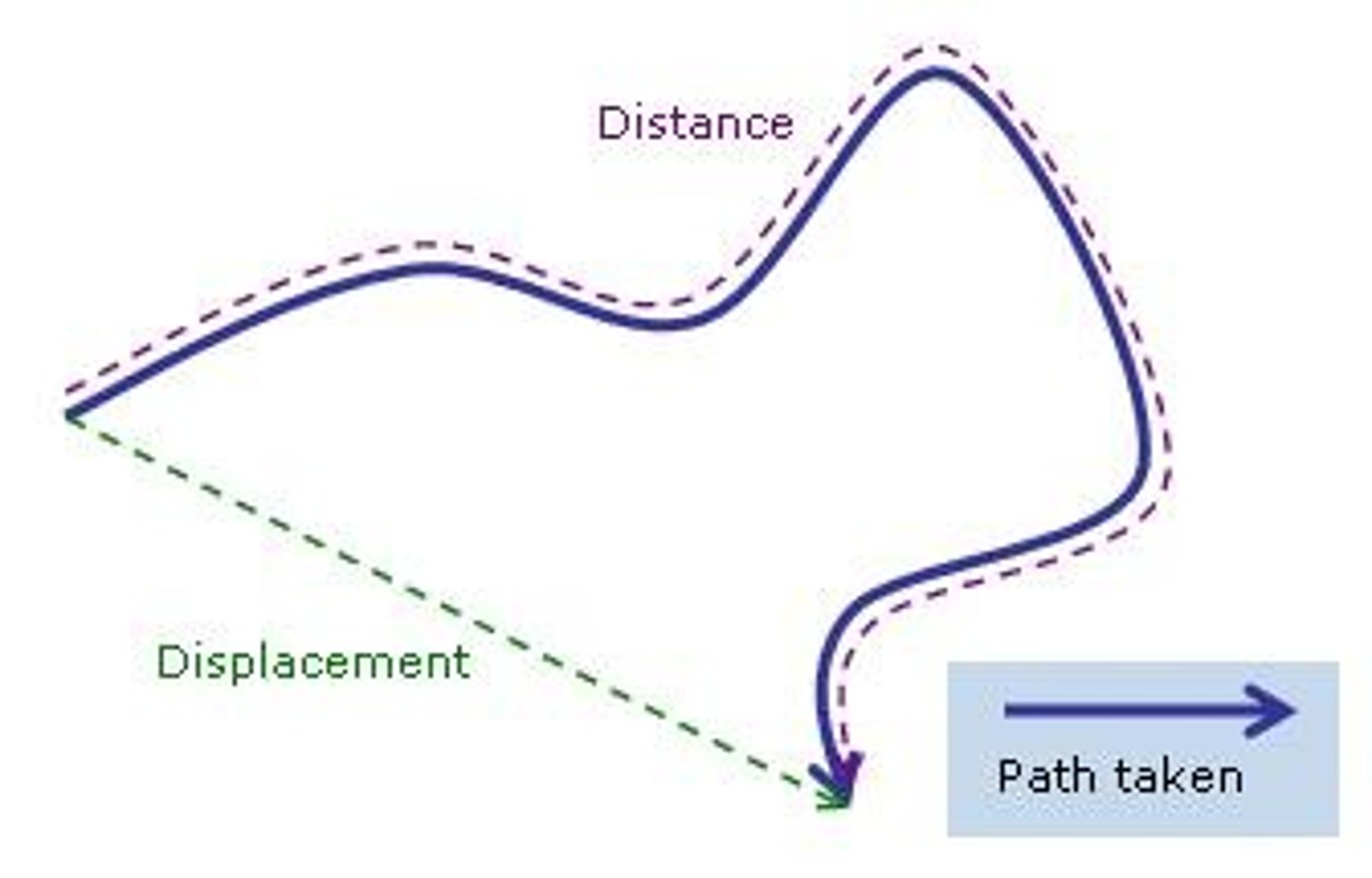
What kind of quantity is displacement?
Vector
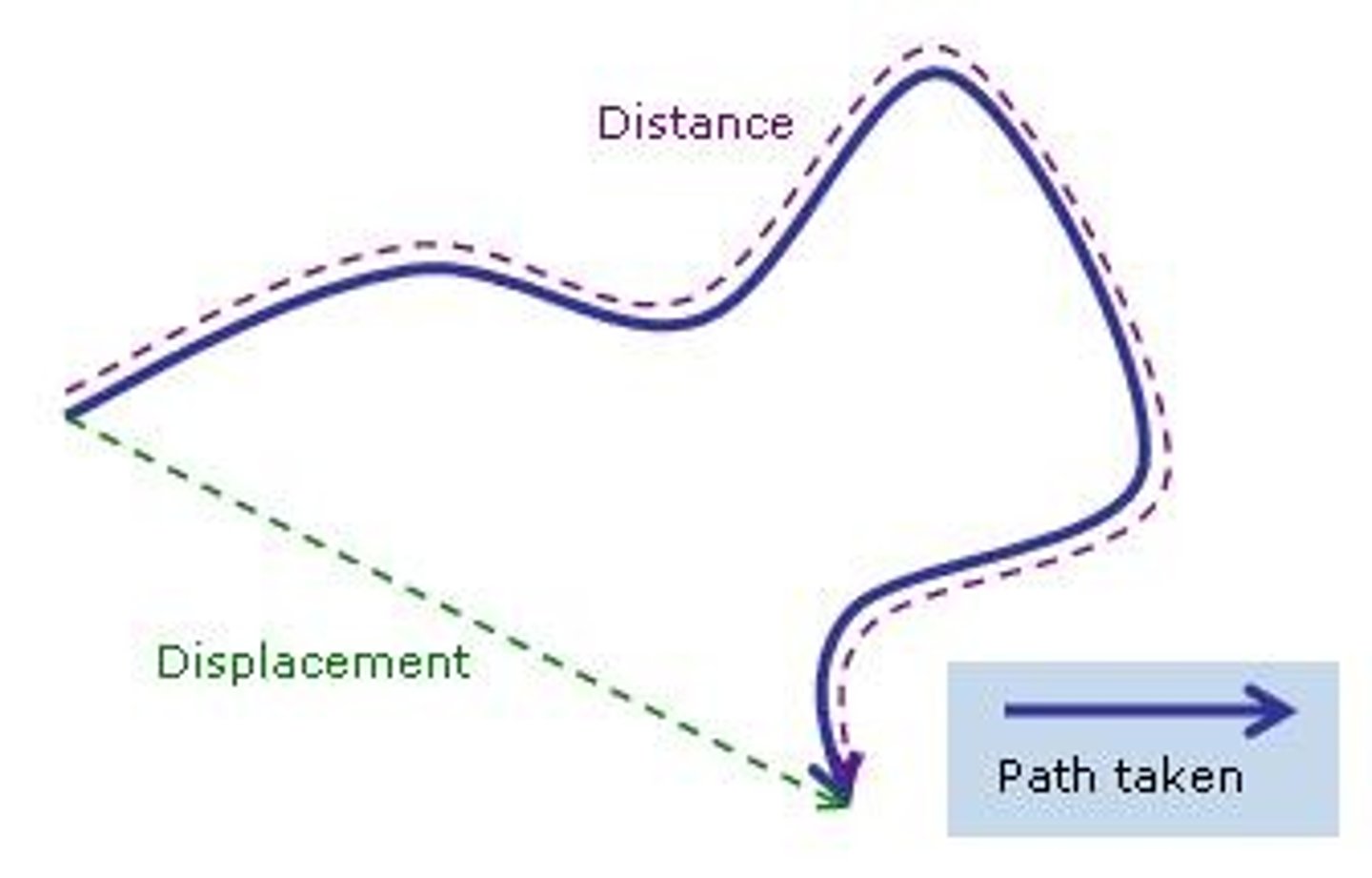
What kind of quantity is speed?
Scalar
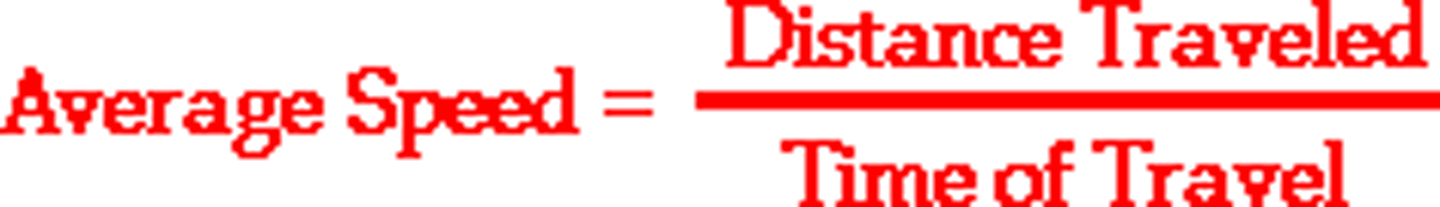
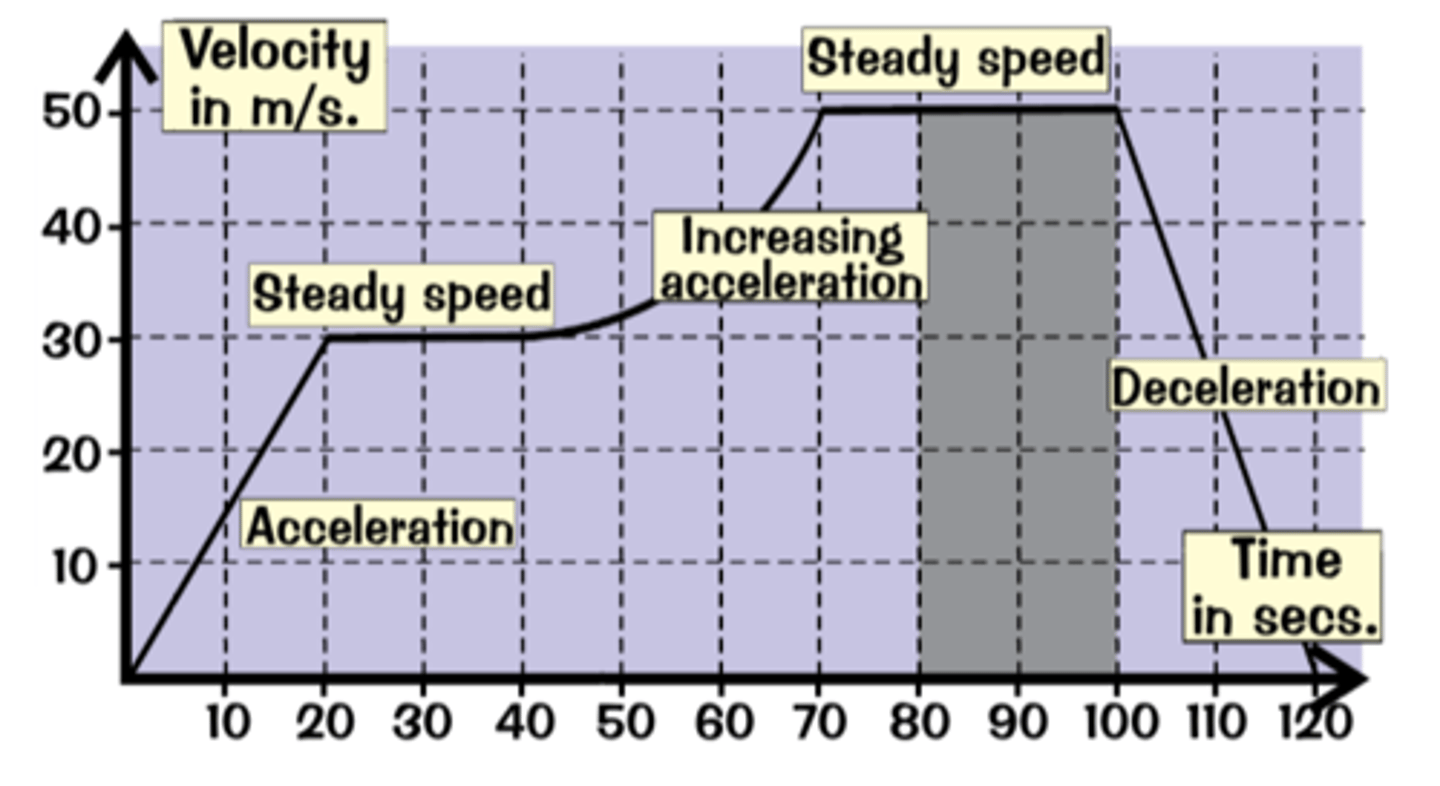
What does the gradient of a velocity-time graph represent?
Acceleration
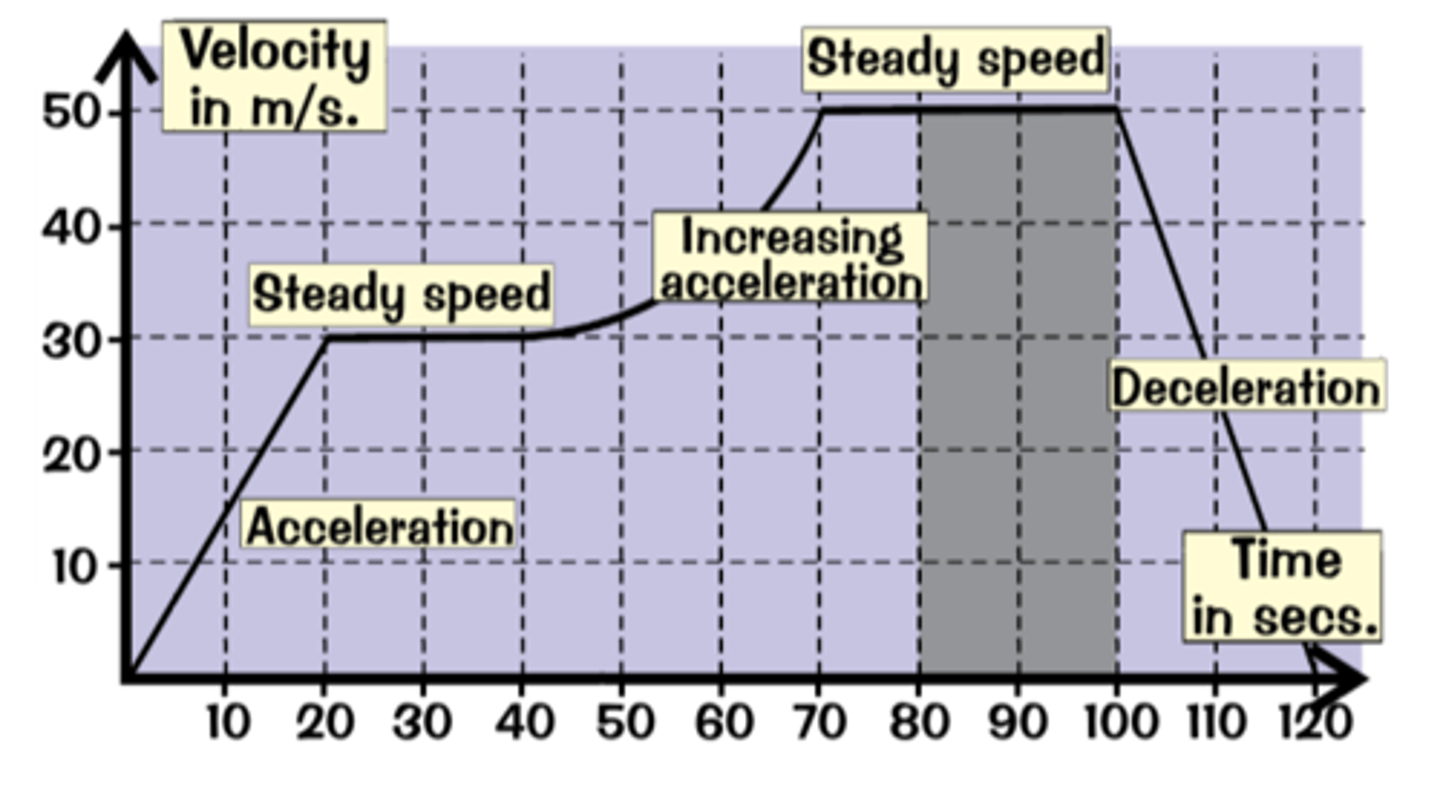
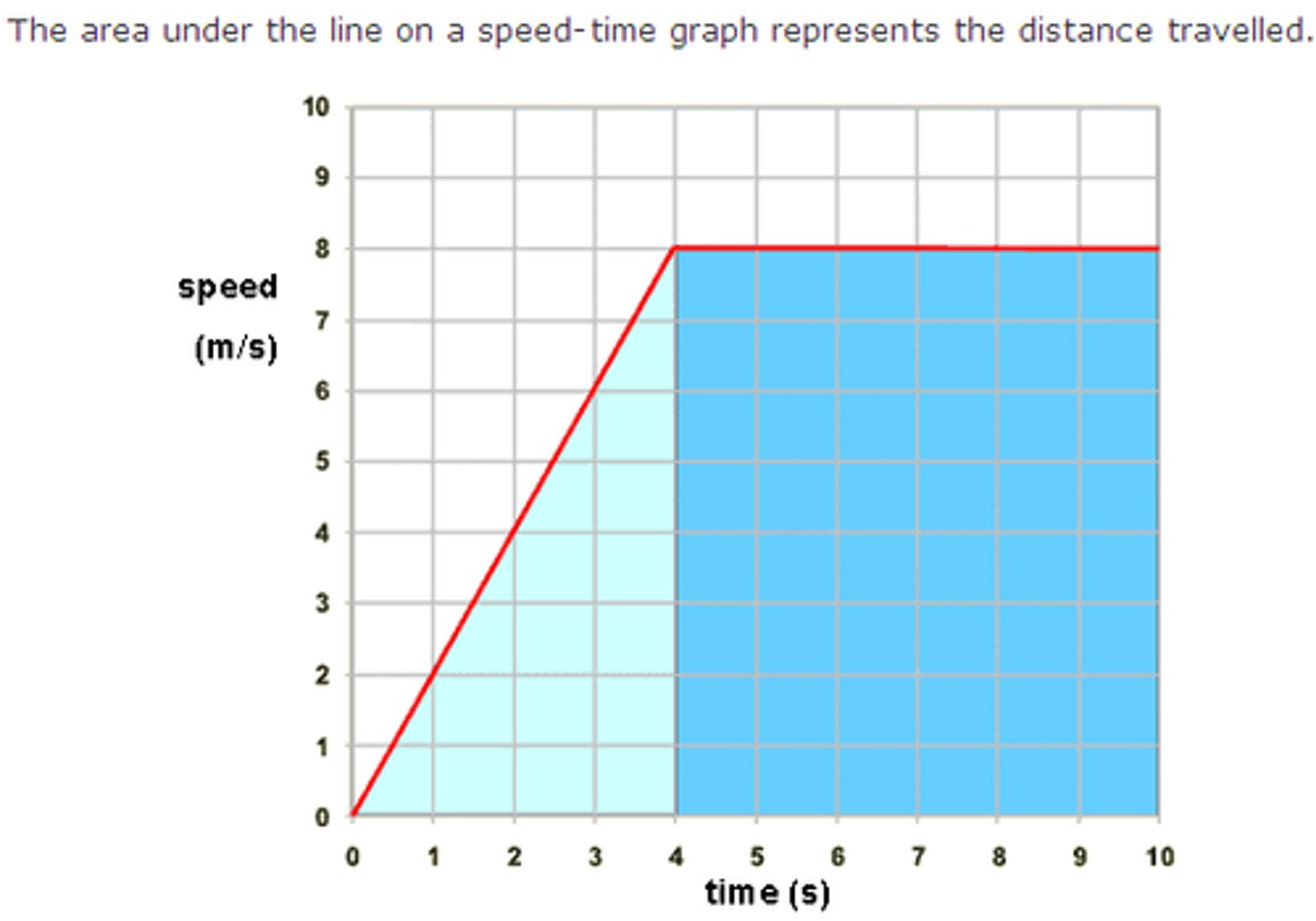
What does the area under a velocity-time graph represent?
The distance the object has travelled
What does a steeper gradient show on a velocity-time graph?
Greater acceleration
What does the gradient of a distance-time graph represent?
Speed
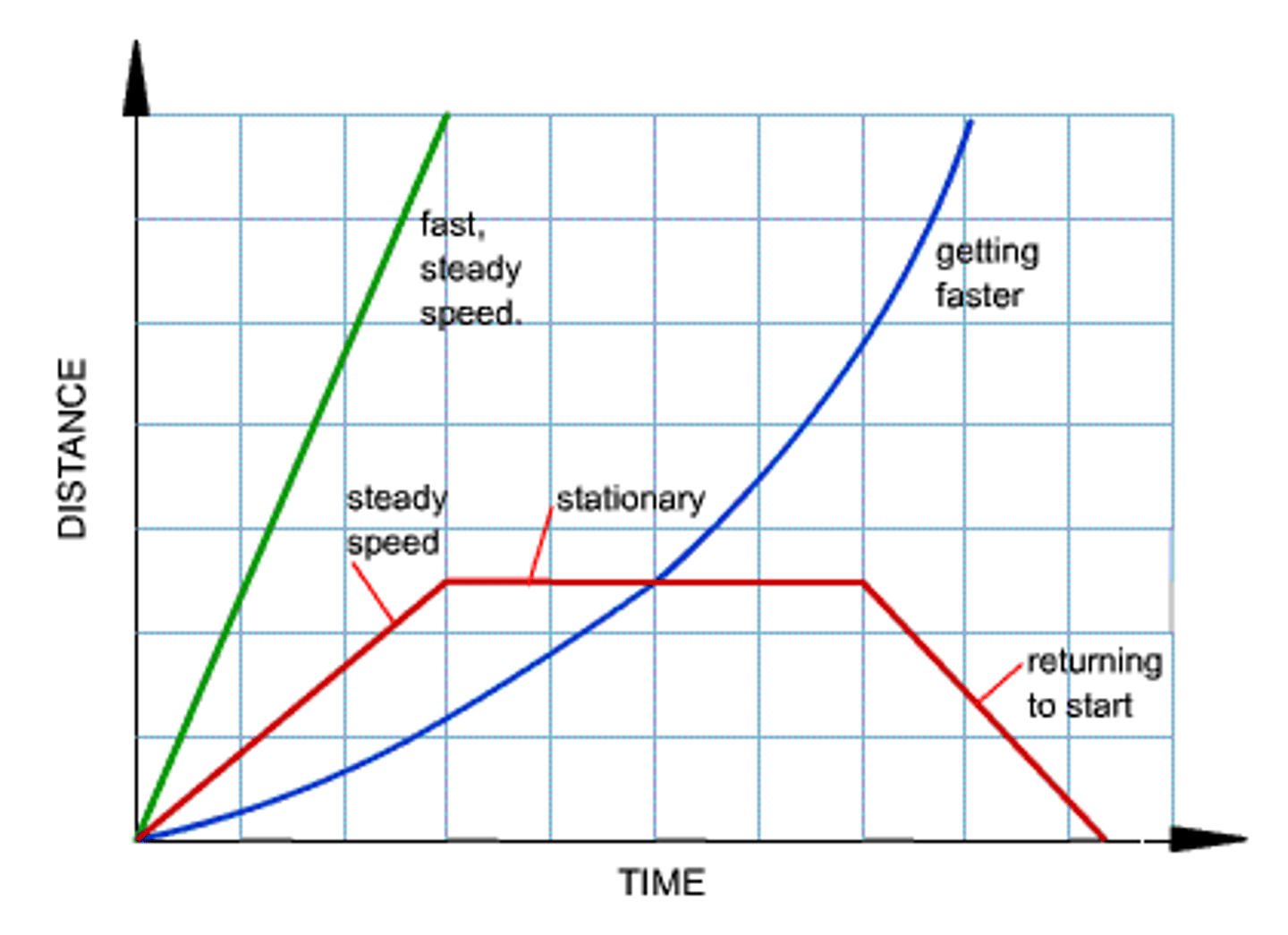
If the gradient is not changing, in a distance-time graph, how would you describe the speed?
The speed is constant
What is the unit of acceleration?
m/s^2

What is the formula for force?
Force = mass x acceleration
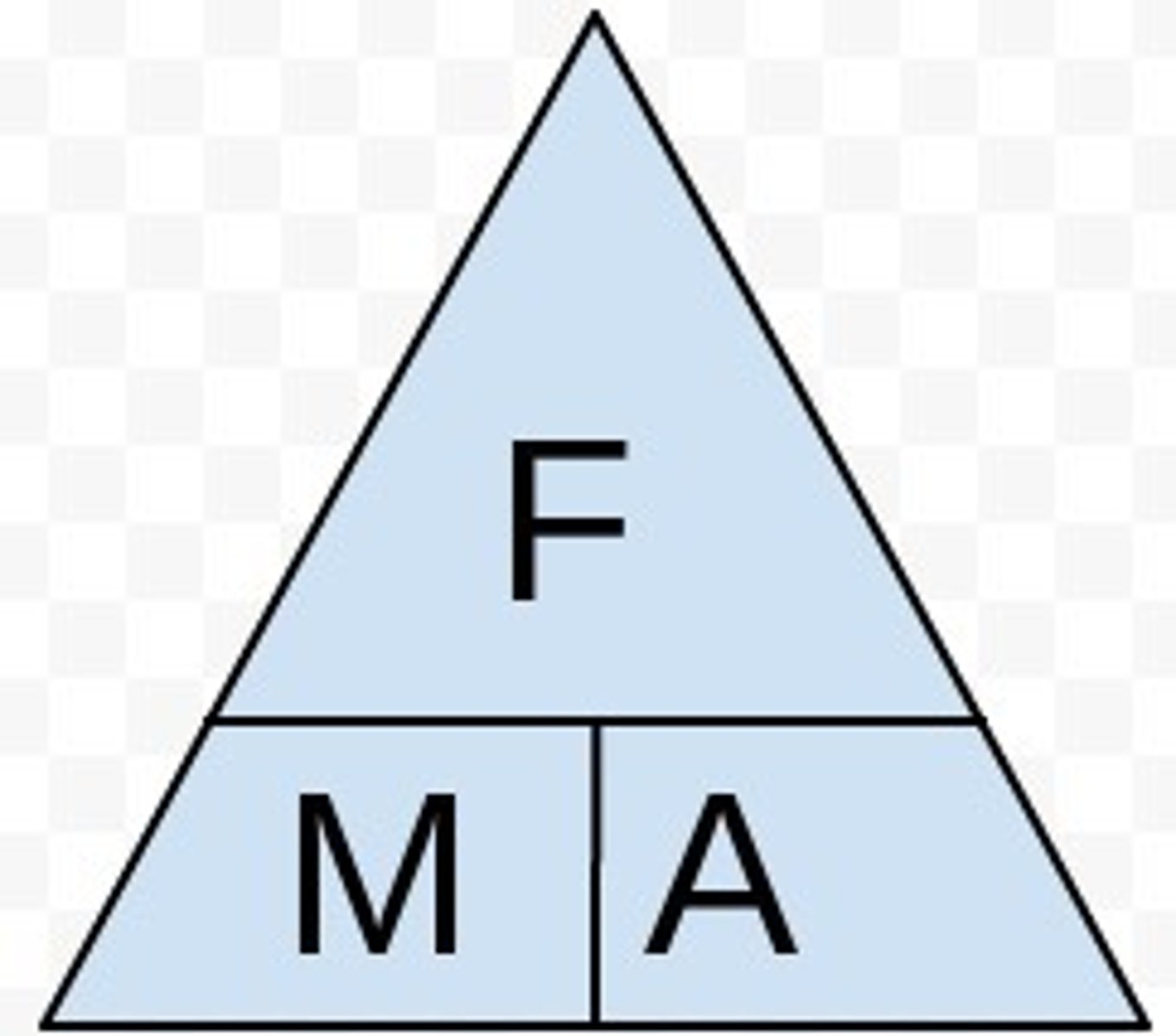
What kind of quantity is mass?
Scalar

What kind of quantity is weight?
Vector
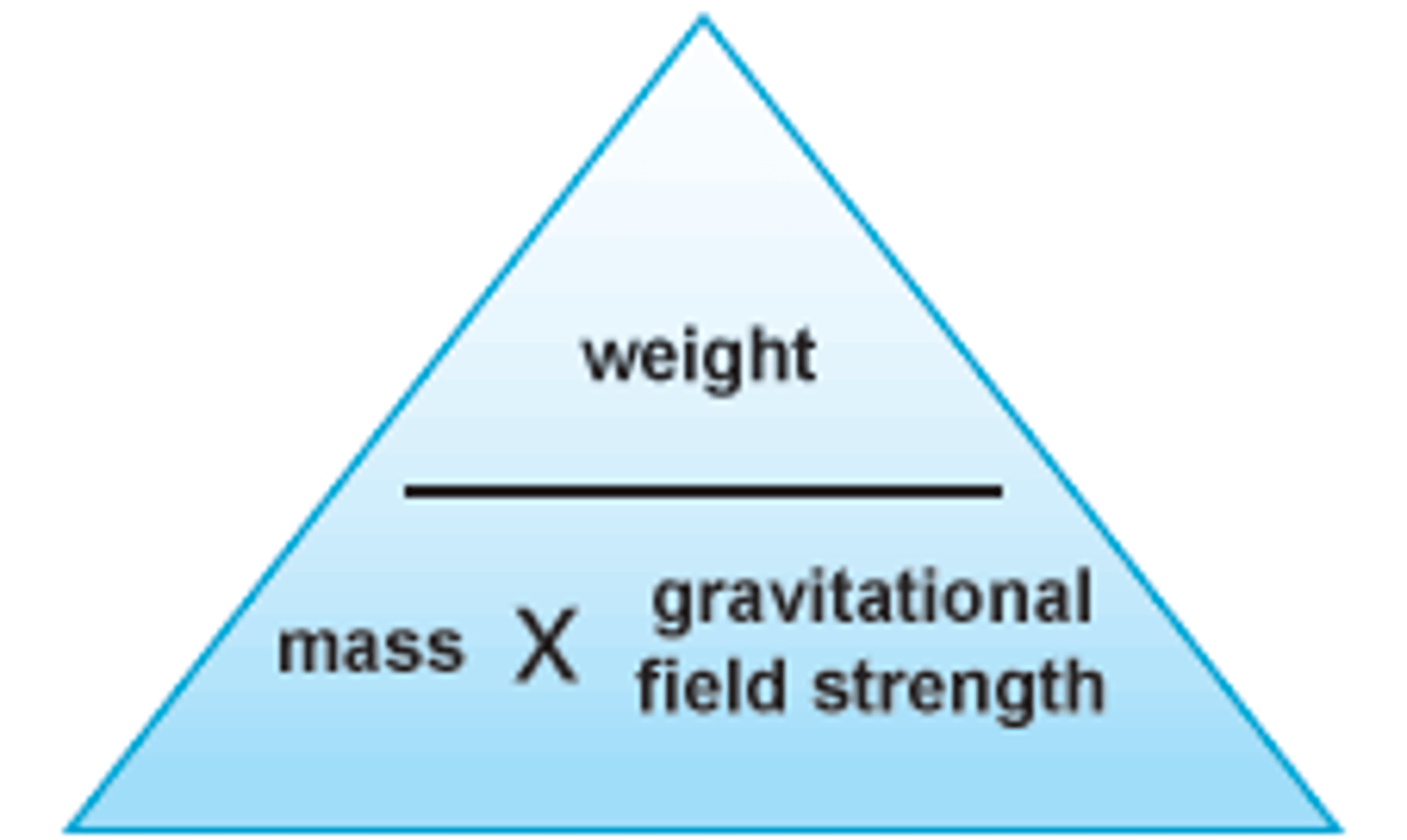
What is the formula for weight?
Mass x gravitational field strength
What is the formula for extension?
New length - old length
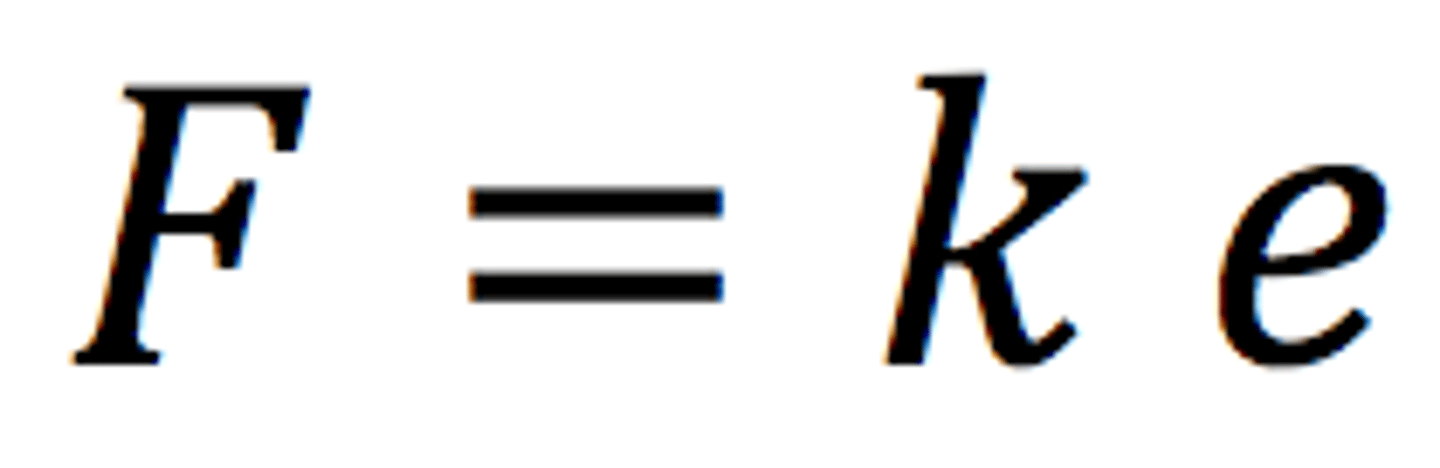
State the equation linking force, extension and spring constant
Force = spring constant x extension
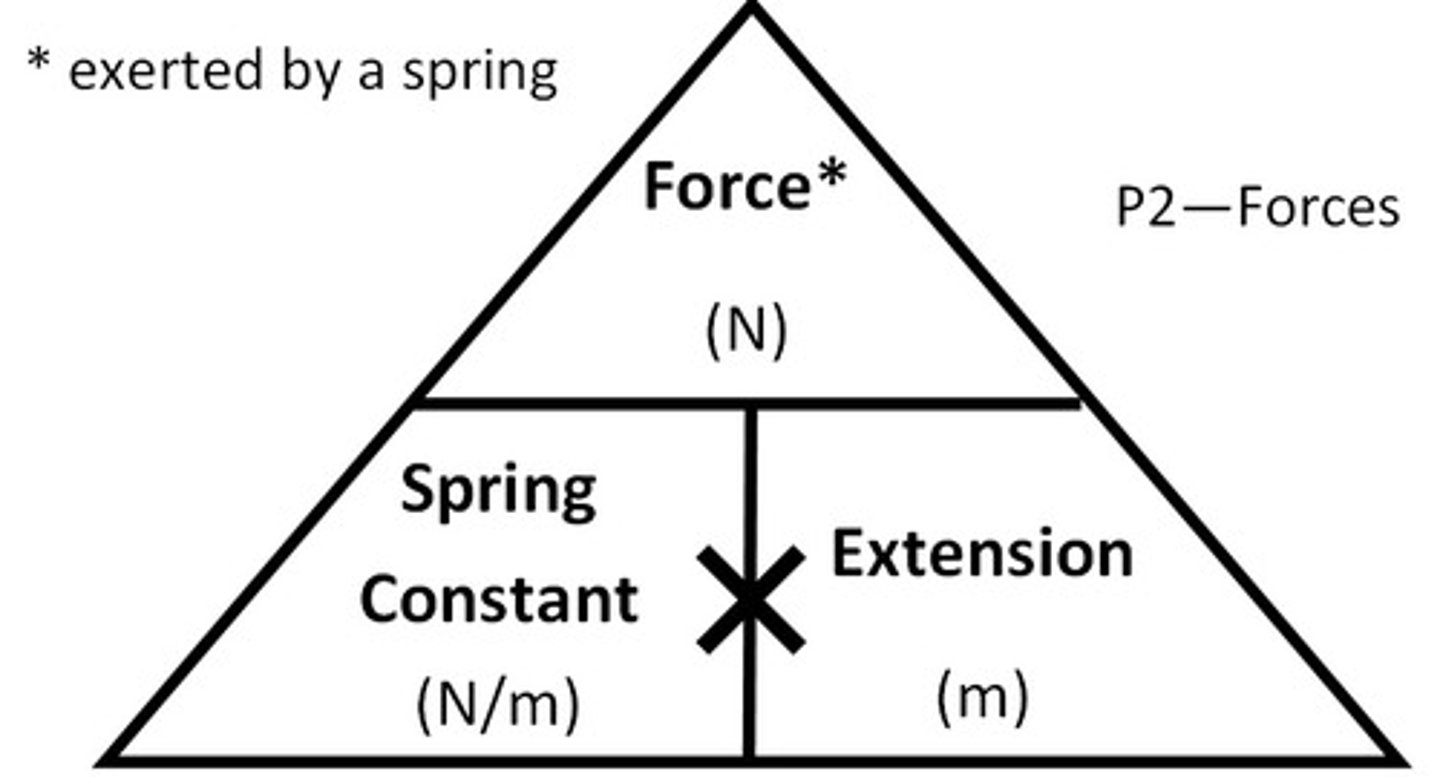
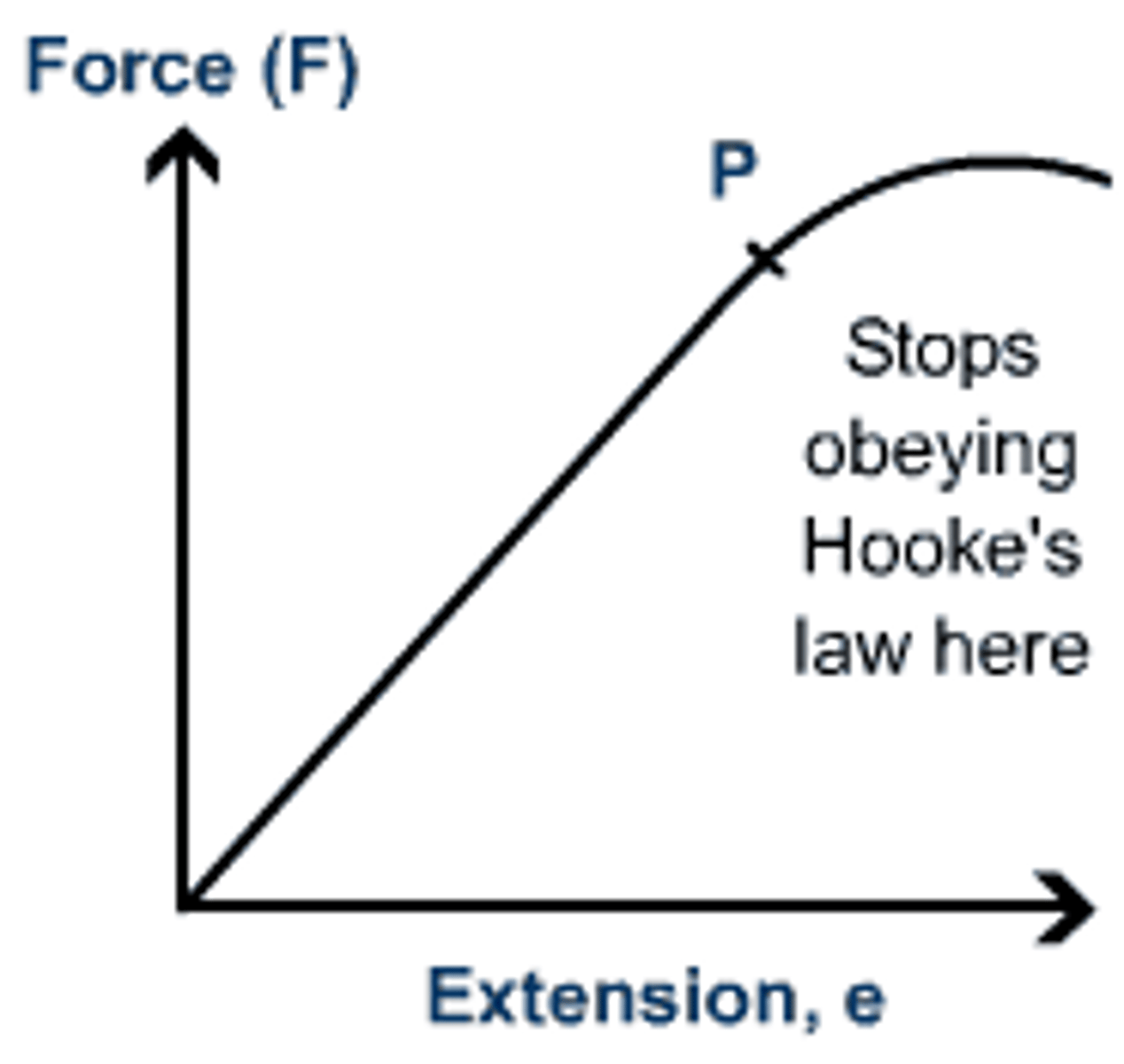
What is Hooke's Law?
Extension is directly proportional to the force, until it reaches its limit of proportionality
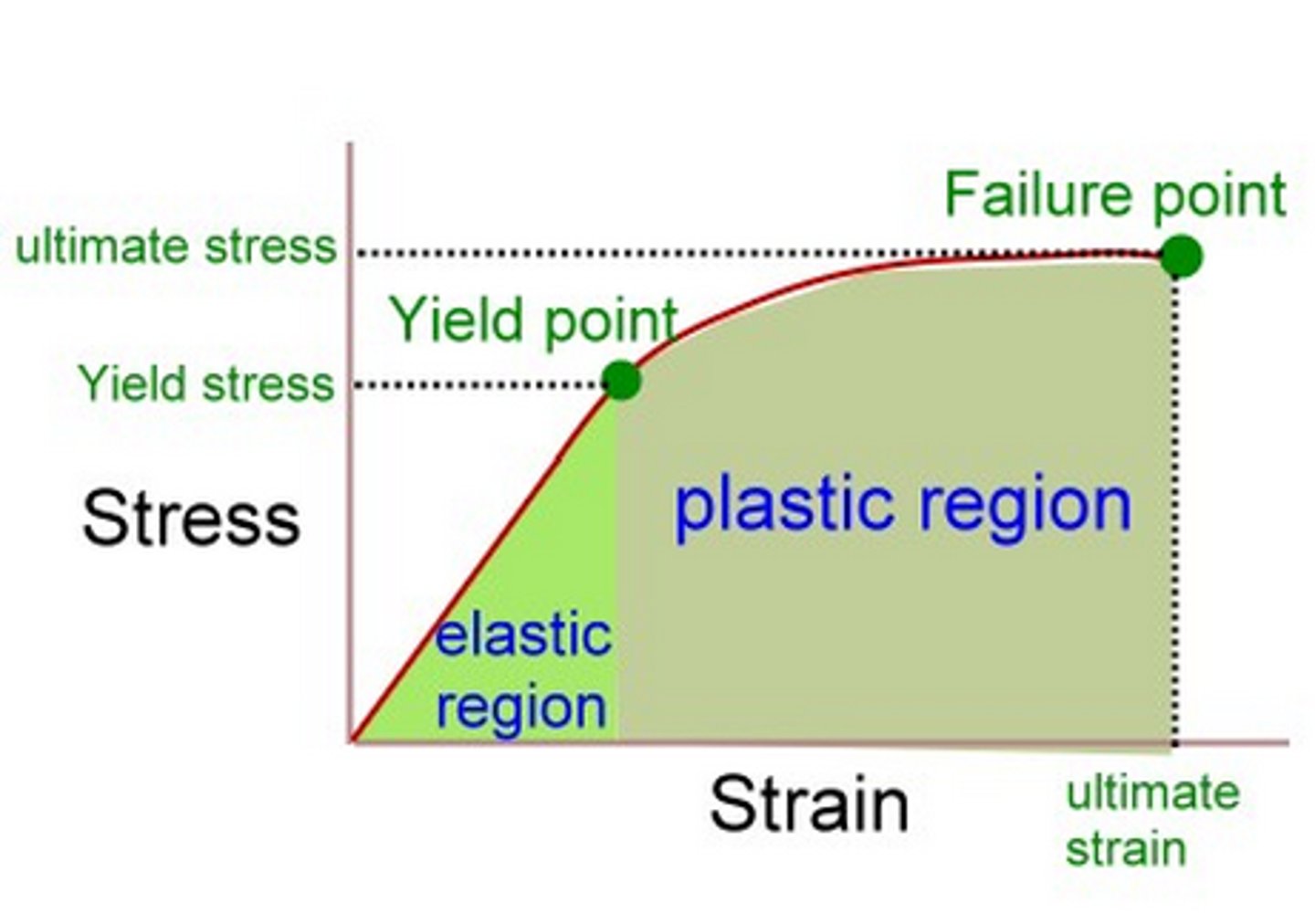
What is plastic deformation?
Permanent change in shape that remains once the load is removed
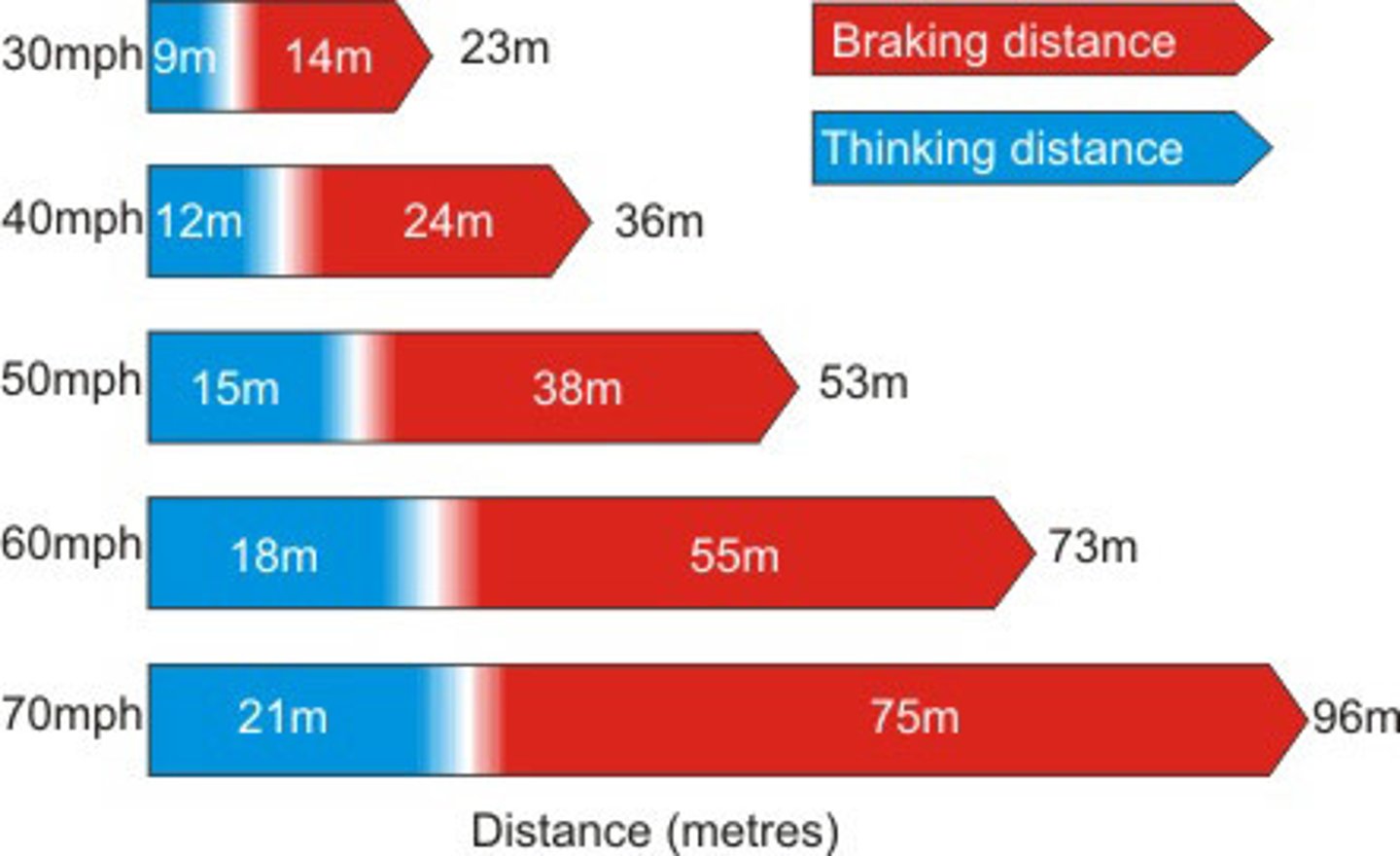
Formula for stopping distance
Thinking distance + braking distance
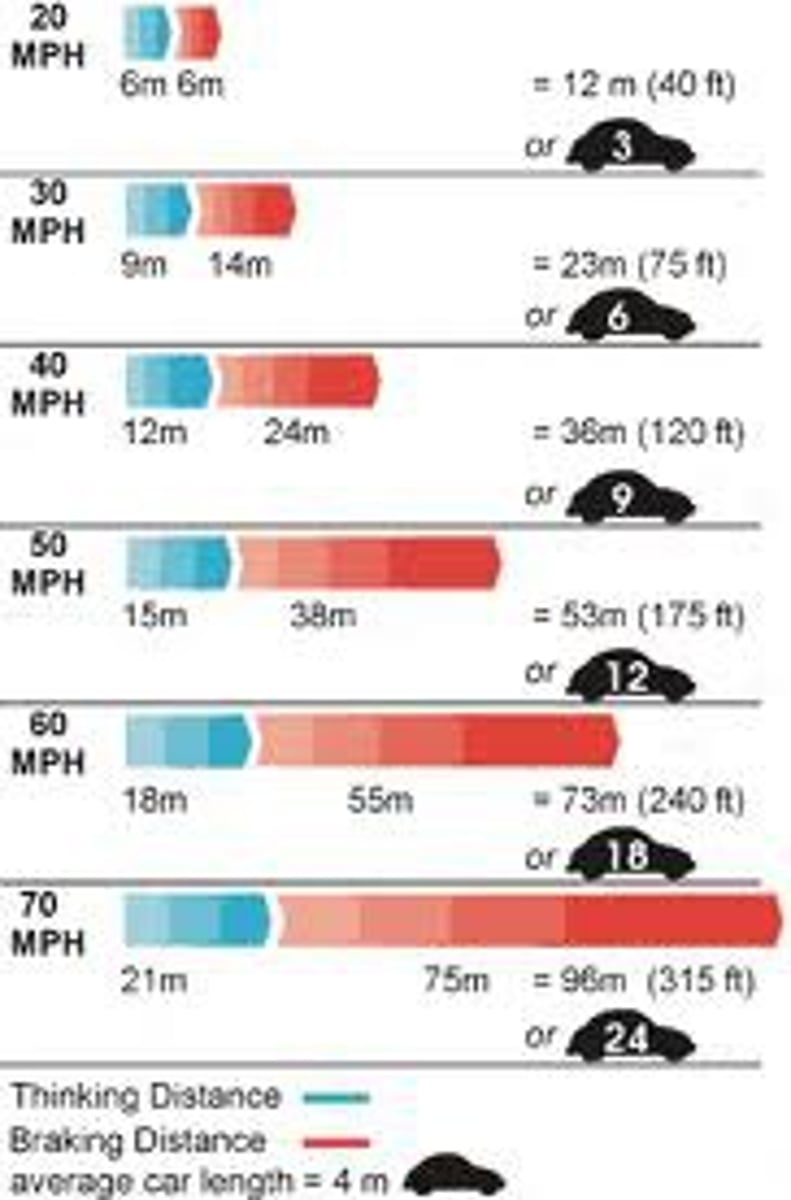
What factors affect the thinking distance?
-Alcohol
-Age and health of the driver
-Distractions
-Tiredness
-Effects of drugs and stimulants

What factors affect the stopping distance?
-Speed of travel
-Conditions of tyres
-Conditions of brakes
-Road conditions
-Mass of the car
-Aerodynamics