Economics 102: Macroeconomics Ch 2. Comparative Advantage, Specialization and Exchange
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Comparative Advantage
when a person or a nation has a lower opportunity cost in the production of a good
everyone has something they can produce at a lower opportunity cost than others
The Law of Comparative Advantage
a person or nation should specialize in the good they can produce at the lowest opportunity cost
everyone has something they can produce at a lower opportunity cost than others, and by trading with others, everyone is better off
Absolute Advantage
being able to produce more of a good or service with the same amount of resources
able to produce it more cheaply than anyone else
Theory of Comparative Advantage
based on lower opportunity cost NOT absolute advantage
A person or nation that has a comparative advantage in the production of a good, should _____.
automatically has an absolute advantage
have the highest opportunity cost
decrease their production of that good
not specialize in the production of that good
specialize in the production of that good
specialize in the production of that good
If Sally can produce 1 term paper or 4 cookies in one hour, and Adam can produce 2 term papers or 1 cookie in the same amount of time, which of these statements is true?
Sally uses more resources to produce cookies than she does to produce term papers.
Sally has a comparative advantage in cookies, while Adam has a comparative advantage in term papers.
Both Sally and Adam have the same opportunity costs for these two goods.
Adam has a comparative advantage in cookies, while Sally has a comparative advantage in term papers.
Adam uses more resources to produce term papers than he does to produce cookies.
Sally has a comparative advantage in cookies, while Adam has a comparative advantage in term papers.
Country A can either produce 10 cars or 10 computers, while country B can produce either 4 cars or 8 computers.
Based on this information, which of the following comparisons is TRUE?
Country A has no advantage in computers.
Country B has a comparative advantage in computers.
Country A has no advantage in cars.
Country A has a comparative advantage in computers.
Country B has a comparative advantage in computers.
According to the Law of Comparative Advantage, where should a good be produced?
In the country with the highest absolute advantage
Where opportunity costs are the highest
Where prices are the highest
Where opportunity costs are the lowest
Where there are more consumers
Where opportunity costs are the lowest
Which of the following are problems that all economies face?
How to shrink the money supply, and how to increase opportunity costs for everyone equally.
How to decide what goods and services to produce, how much to produce, and for whom to produce, and how to increase opportunity costs for everyone equally.
How to use scarce resources to satisfy unlimited wants, and how to shrink the money supply.
How to use scarce resources to satisfy unlimited wants.
How to use scarce resources to satisfy unlimited wants, how to decide what goods and services to produce, how much to produce, and for whom to produce.
How to use scarce resources to satisfy unlimited wants, how to decide what goods and services to produce, how much to produce, and for whom to produce.
Theory of Comparative Advantage
nations should specialize in the production of the goods in which they have the lowest opportunity cost, and trade with other nations
Absolute Advantage
The United States can produce more strawberries with the same amount of resources than Canada can
Benefits of Specialization
a larger quantity of goods and services can be produced
improved productivity
a nation can produce beyond its production possibility curve
resources will be used more efficiently
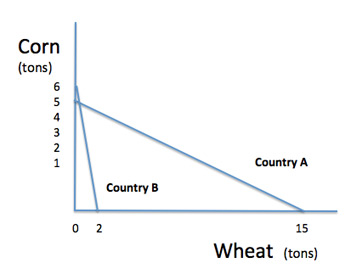
According to the two production possibility curves shown, Country A should specialize in the production of which of the following?
Both corn and wheat.
Wheat
Corn
Neither corn nor wheat.
Wheat
The United States can produce 20 strawberries or 80 apples, while Canada can produce 15 strawberries or 5 apples. Which of the following describes what will happen if these two countries trade with each other?
Canada will benefit, but the US will not.
The United States will benefit, but Canada will not.
Neither country will benefit from trading.
Both countries will benefit from trading.
Both countries will benefit from trading.
Country A's opportunity cost of producing 1 ton of corn is 5 tons of wheat, while Country B's opportunity cost of producing 1 ton of corn is 1/3 of a ton of wheat. Which of the following statements is true?
Country A should specialize in producing corn, while Country B should specialize in producing wheat.
There will be no gains from trade if these two countries exchange goods.
Country B should specialize in producing corn, while Country A should specialize in producing wheat.
Both countries should produce both goods.
Country B should specialize in producing corn, while Country A should specialize in producing wheat.
When countries specialize in the goods in which they have a comparative advantage, which of the following is true?
Both countries will experience gains from trade.
Production costs will increase for both countries.
One country is usually better off, and the other is worse off.
Both countries are worse off.
Both countries will experience gains from trade.
Which of the following is NOT a benefit of specialization and exchange?
Larger quantities of goods and services can be produced.
Resources can be used more efficiently.
A country can produce beyond its production possibility curve.
Taxes will be reduced.
Taxes will be reduced.
Adam Smith
countries should specialize and trade
Absolute Advantage
when you can produce a good more efficiently in the same amount of time
Opportunity Cost
what you have to give up in order to make a choice
Theory of Comparative Advantage
nations should specialize in producing the good in which they have the lowest opportunity cost
everyone has a comparative advantage in something, but may not have an absolute advantage
a nation can have an absolute advantage in the production of every good, but they won’t have a comparative advantage
Labor Productivity
how long it takes to produce one good
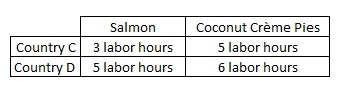
The table here shows the labor hours necessary to produce one unit of two goods, salmon and coconut creme pies, in two countries. If labor is the only input used, which of the following statements is true?
Country D has an absolute advantage in the production of one good, but not both.
Country C has an absolute advantage in the production of one good, but not both.
Neither country has an absolute advantage in the production of these two goods.
Country D has an absolute advantage in the production of both goods.
Country C has an absolute advantage in the production of both goods.
Country C has an absolute advantage in the production of both goods.
What happens if a nation doesn't have an absolute advantage in producing anything?
It will only sell raw materials to the rest of the world.
It will not have a comparative advantage either.
It will always have a comparative advantage in something.
It will not trade with anyone.
It will have a higher tax rate.
It will always have a comparative advantage in something.
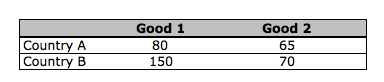
Assume that there are only two countries, Country A and Country B, producing only two goods, corn cereal and designer jeans. The table here shows the production possibilities for these two countries. Which of the following statements is correct?
Country A has an absolute advantage in one good, but not both.
Country A has an absolute advantage in the production of both goods.
Country B has an absolute advantage in both goods.
Country B has an absolute advantage in one good, but not both.
Neither country has an absolute advantage in the production of these two goods.
Country B has an absolute advantage in both goods.
What does it mean for a nation to have an absolute advantage in the production of a good?
It takes more raw materials than another nation to produce the good.
It can produce the good at a lower opportunity cost than another nation.
It can produce the good more efficiently than another nation.
It must automatically have a comparative advantage in the production of this good.
It cannot also have a comparative advantage.
It can produce the good more efficiently than another nation.
Which of the following statements is true?
A nation can have a comparative advantage in the production of every good, but not an absolute advantage.
A nation will not trade unless it has an absolute advantage in the production of a good.
A nation cannot have an absolute advantage in the production of every good.
A nation will have a comparative advantage only if it has an absolute advantage in the production of the same good.
A nation cannot have a comparative advantage in the production of every good.
A nation cannot have a comparative advantage in the production of every good.