BOT 14 - 7 - Angiosperm Classification Systems
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Artificial
Types of Classification Systems
classifies plants using one or few characters (Bauhin, Tournefort, John Ray, Carolus Linnaeus)
Natural
Types of Classification Systems
classifies plants using all information available at that time (de Candolle, Robert Brown, de Lamarck, Bentham and Hooker)
Phylogenetic
Types of Classification Systems
classify plants based on evolutionary relationships derived from morphology or DNA sequences (Eichler, Hutchinson, Bessey, Cronquist, APG)
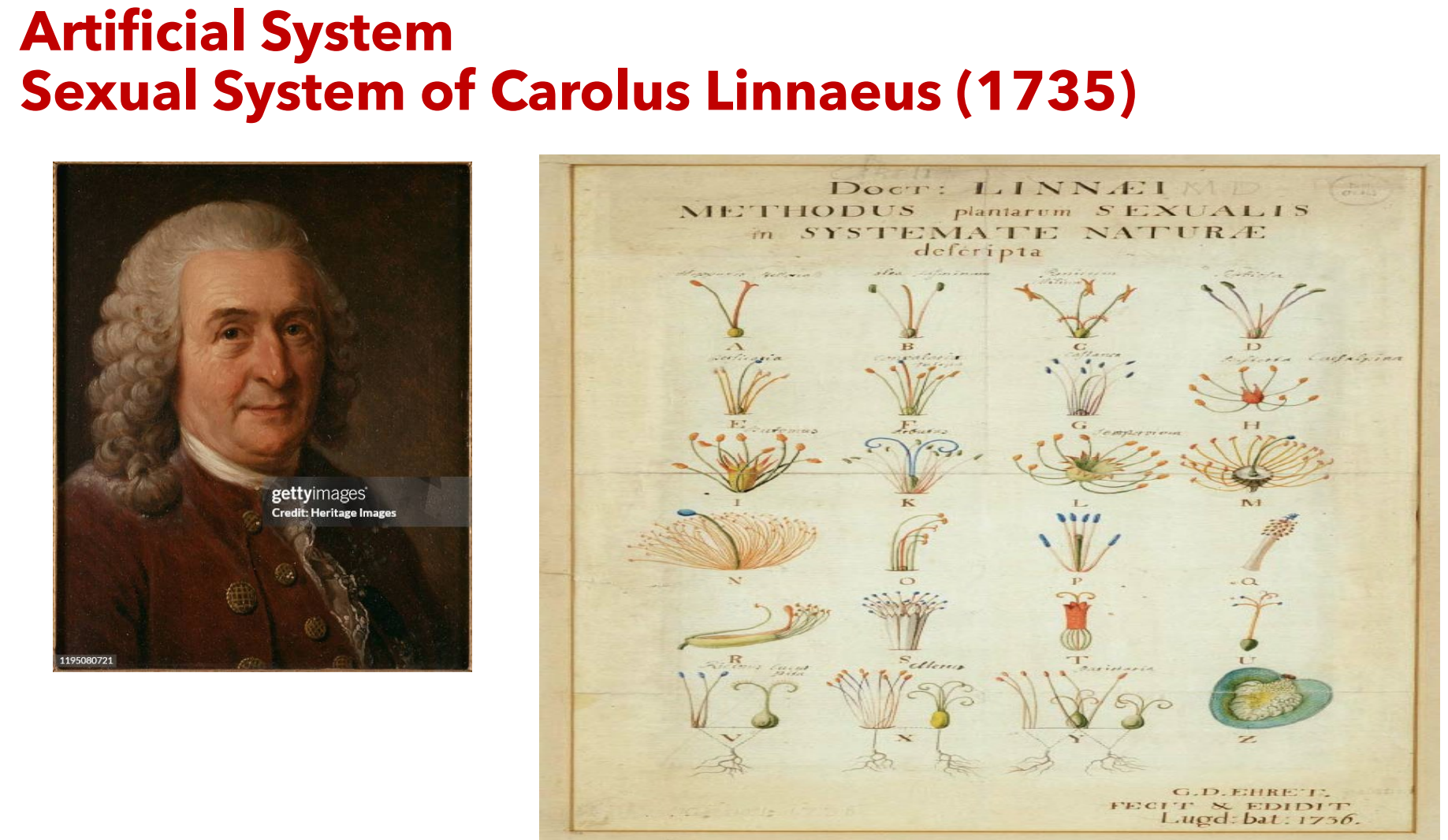
Whos system of classification was the Artificial System?
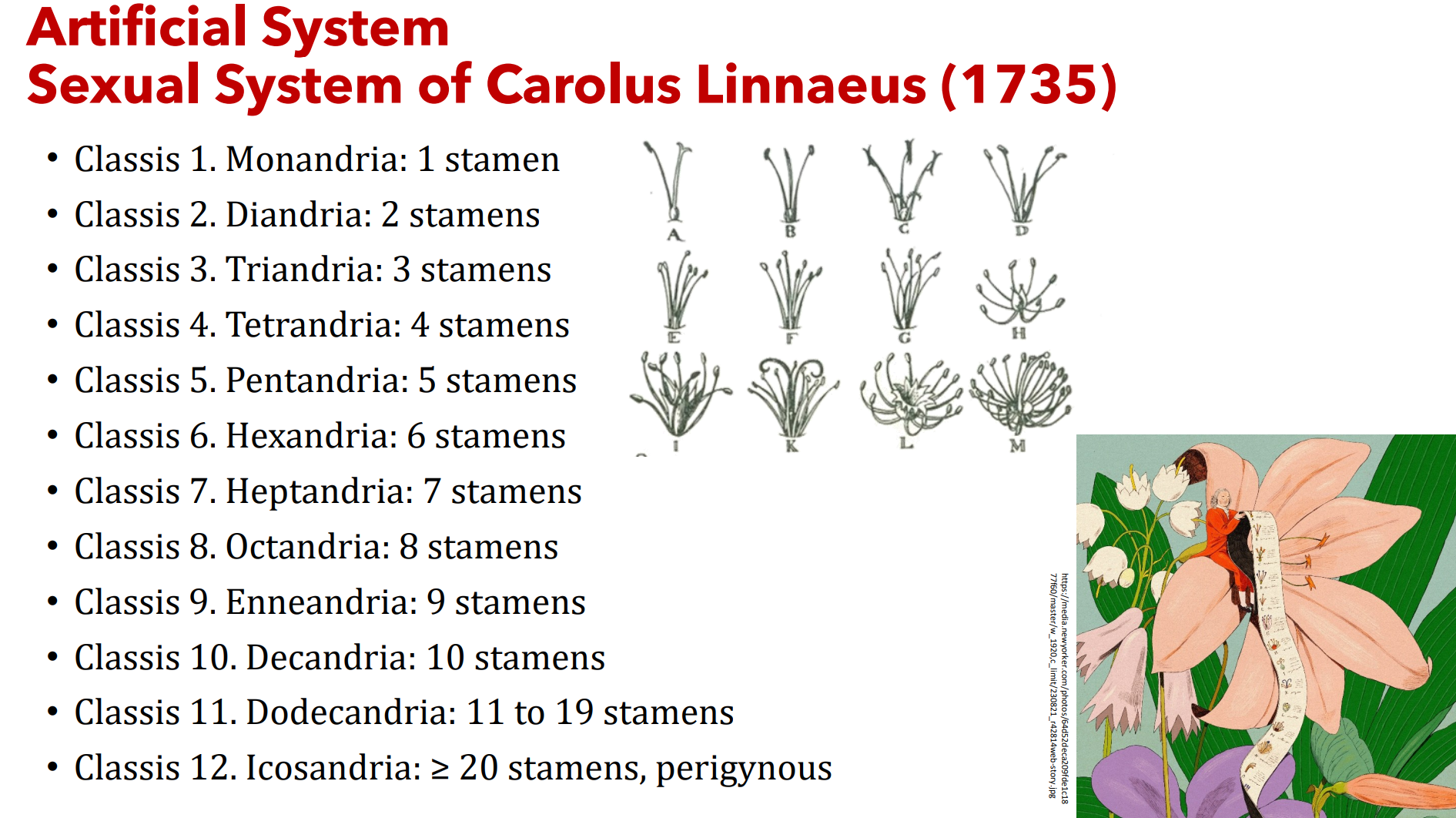
Classis 1. ____________: 1 stamen
Classis 2. ____________: 2 stamens
Classis 3. ____________: 3 stamens
Classis 4. ____________: 4 stamens
Classis 5. ____________: 5 stamens
Classis 6. ____________: 6 stamens
Classis 7. ____________: 7 stamens
Classis 8. ____________: 8 stamens
Classis 9. ____________: 9 stamens
Classis 10. ____________: 10 stamens
Classis 11. ____________: 11 to 19 stamens
Classis 12. ____________: ≥ 20 stamens, perigynous
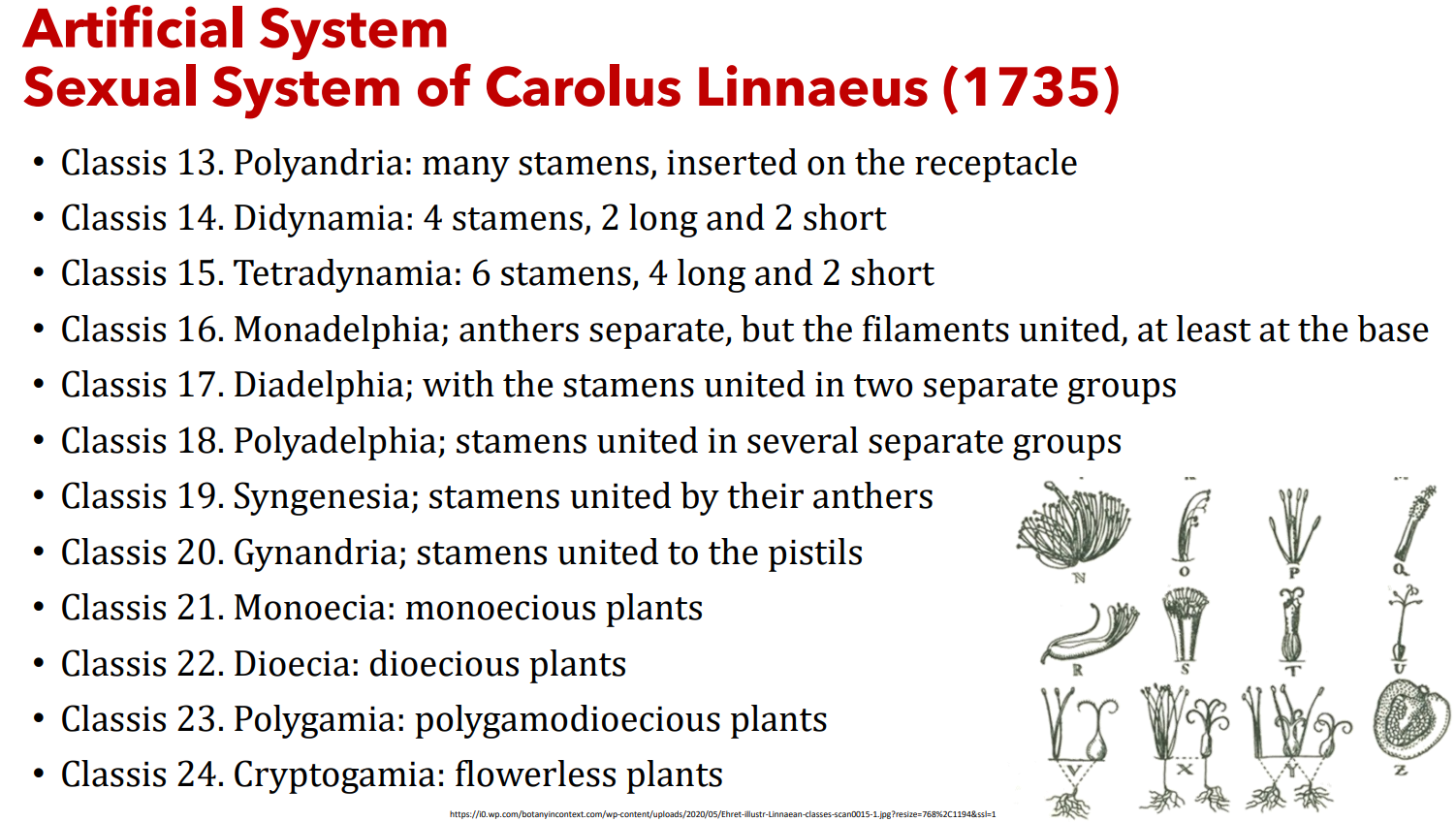
Classis 13. ____________: many stamens, inserted on the receptacle
Classis 14. ____________: 4 stamens, 2 long and 2 short
Classis 15. ____________: 6 stamens, 4 long and 2 short
Classis 16. ____________; anthers separate, but the filaments united, at least at the base
Classis 17. ____________; with the stamens united in two separate groups
Classis 18. ____________; stamens united in several separate groups
Classis 19. ____________; stamens united by their anthers
Classis 20. ____________; stamens united to the pistils
Classis 21. ____________: monoecious plants
Classis 22. ____________: dioecious plants
Classis 23. ____________: polygamodioecious plants
Classis 24. ____________: flowerless plants

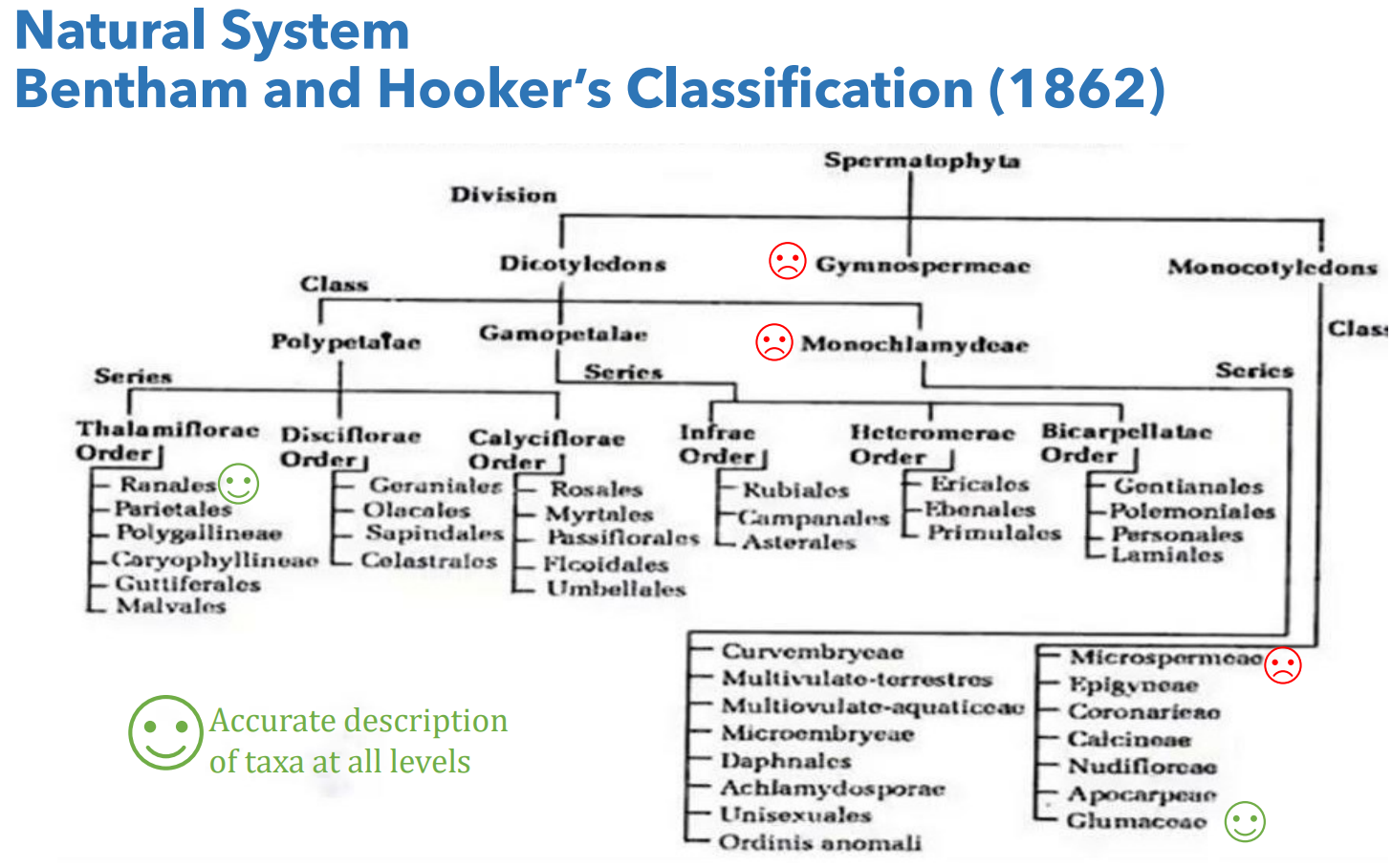
Whos system of classification was the Natural System?

Whos system of classification was the Phylogenetic System?
Morphological
Phylogenetic System
Cronquist’s Classification (1968)
___________ features: structure and appearance of plants
Anatomical
Phylogenetic System
Cronquist’s Classification (1968)
_____________ features: internal structure of plants
Embryological
Phylogenetic System
Cronquist’s Classification (1968)
_____________ features: development of plant embryos
Cytological
Phylogenetic System
Cronquist’s Classification (1968)
______________ features: chromosomes and their number, structure, and behavior
Palynological
Phylogenetic System
Cronquist’s Classification (1968)
_____________ features: pollen grains, including their shape, size, and surface ornamentation
Phytochemical
Phylogenetic System
Cronquist’s Classification (1968)
_____________ features: chemical composition of plant proteins and other substances.
Ultrastructural
Phylogenetic System
Cronquist’s Classification (1968)
_______________ features: fine structure of plant cells as revealed by electron microscopy
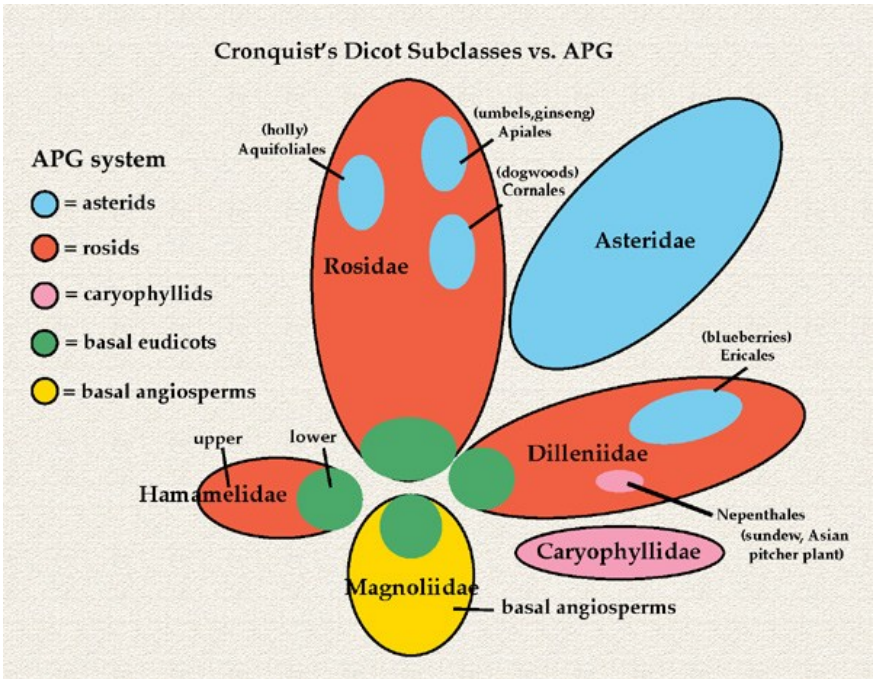
Magnoliopsida
Class ______________: This class consists of 6 subclasses with 64 orders and 321 families.
Magnoliidae (8 orders and 39 families)
Hamamelididae (11 orders and 25 families)
Caryophyllidae (3 orders and 14 families)
Dilleniidae (13 orders and 78 families)
Rosidae (18 orders and 118 families)
Asteridae (11 orders and 50 families)

What are the six subclasses of Class Magnoliopsida?
______________ (8 orders and 39 families)
______________ (11 orders and 25 families)
______________ (3 orders and 14 families)
______________ (13 orders and 78 families)
______________ (18 orders and 118 families)
______________ (11 orders and 50 families)
Liliopsida
Class ______________: This class consists of 5 subclasses with 19 orders and 65 families.
Alismatidae (4 orders and 16 families)
Arecidae (4 orders and 6 families)
Commelinidae (7 orders and 16 families)
Zingiberidae (2 orders and 9 families)
Liliidae (2 orders and 19 families)
What are the five subclasses of Class Liliopsida?
______________ (4 orders and 16 families)
______________ (4 orders and 6 families)
______________ (7 orders and 16 families)
______________ (2 orders and 9 families)
______________ (2 orders and 19 families)

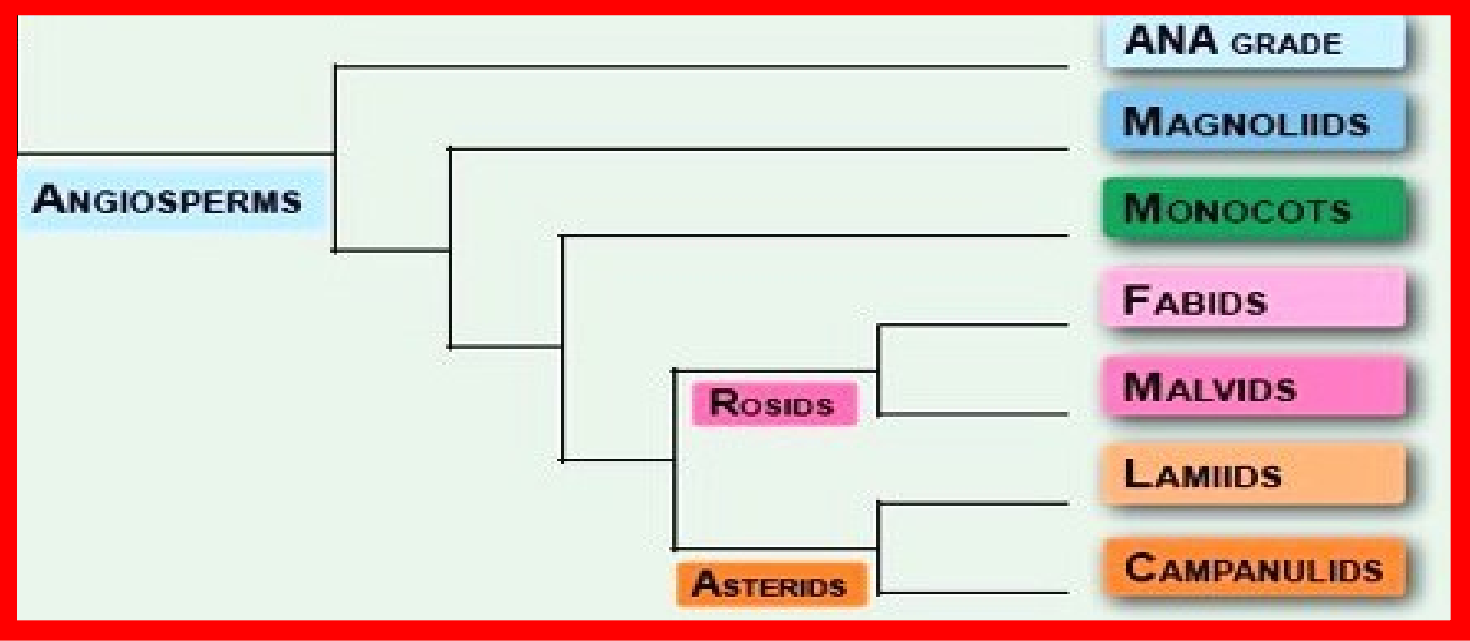
Molecular data
Phylogenetic System
Angiosperm Phylogeny Group
______________: uses DNA sequence data from various parts of the plant to infer relationships.
Phylogenetic analysis
Phylogenetic System
Angiosperm Phylogeny Group
______________: data analysis using phylogenetic methods to construct evolutionary trees
Monophyletic groups
Phylogenetic System
Angiosperm Phylogeny Group
______________: aims to classify angiosperms into _________________, which are groups that include all the descendants of a common ancestor
Higher-level relationships
Phylogenetic System
Angiosperm Phylogeny Group
______________: focuses on the classification of angiosperms at the family, order, and higher-level clade levels