Lecture 6 - Soft Tissue Mobilization 2
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Muscle Dysfunction and Injury
Loss of mobility (tone and/or length)
Muscle Tissue Properties
Composed of contractile and non-contractile elements!
Non-Contractile Components
1. Endomysium
2. Perimysium
3. Epimysium
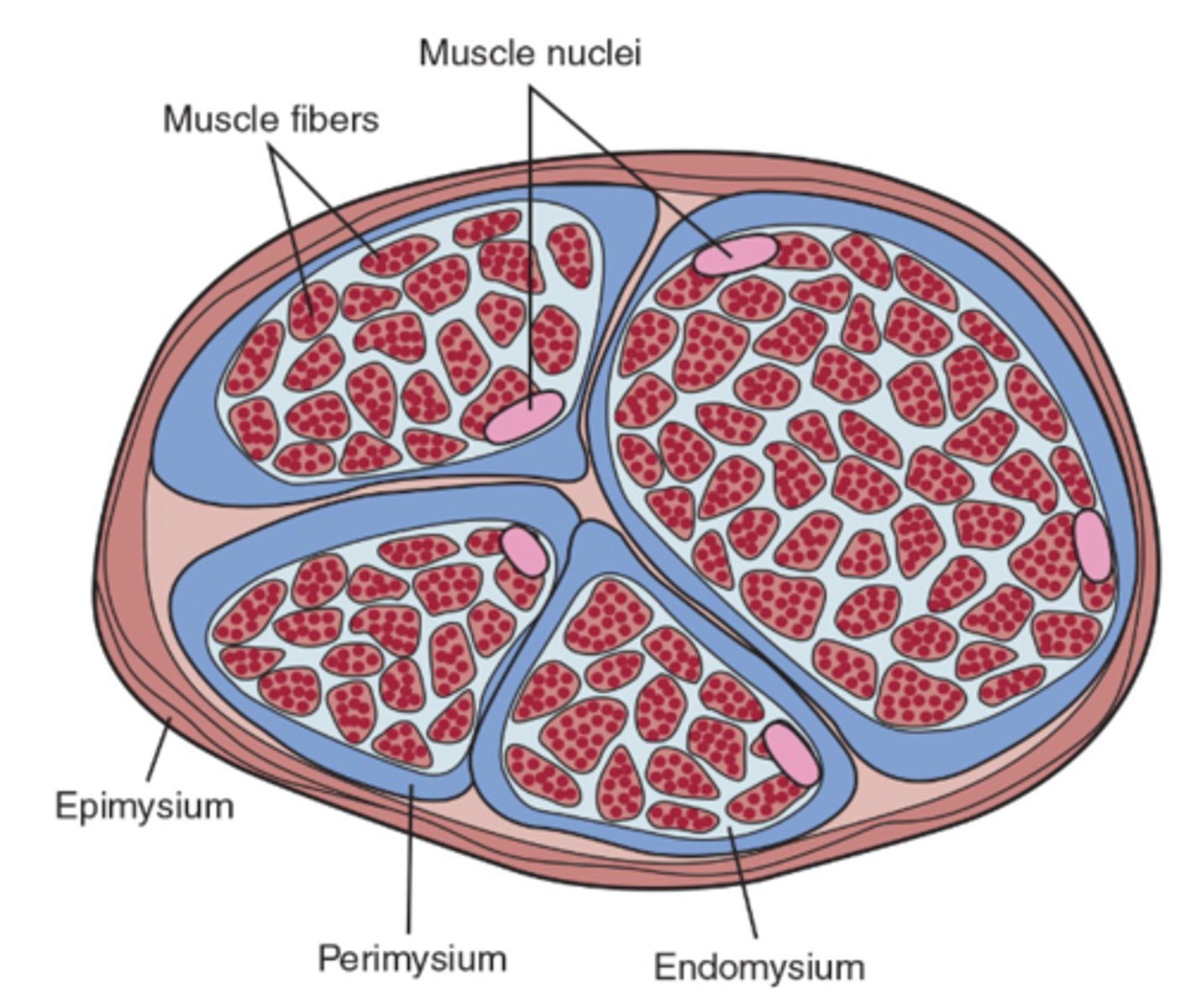
Endomysium
Innermost layer that separates individual muscle fibers
Perimysium
Middle layer that encases fiber bundles
Epimysium
Outermost layer that encases entire muscle
Contractile Components
Actin and Myosin
- Give muscle ability to contract/relax
Muscle Play
Muscle's ability to move independently from surrounding structures
- Ability to trace specific fibers
- How well specific fibers slide between one another
Muscle Tone
Amount of passive resistance to motion present in muscle
How is muscle tone evaluated?
- Actual muscle length assessment
- Palpable resting activation of the muscle (STM)
Central Hypertonicity
Abnormal increased tone due to neurological reasons
- Common post-stroke
- Spasticity + Rigidity
Spasticity
Impaired ability of damaged motor neurons to regulate descending pathways
- Velocity dependent
- Increased speed = Increased tone
What happens if you try to move a spastic patient thru their ROM?
They move back quickly, as the muscle spindle contracts
Rigidity
Increased resistance throughout entire ROM
- Not affected by speed of movement
General Hypertonicity
Muscle Guarding; Protective mechanism
- Tight but flexible muscle
General Hypertonicity Causes
- Injury
- Excessive hypermobility (protective)
- Pain
- Fatigue (muscle spasm)
General Hypertonicity: Therapeutic Goal
Improve STRENGTH
- NOT flexibility
Trigger Points
Localized, painful, or sensitive areas in skeletal muscle
- Associated w/ palpable nodules
- In taut bands of muscle fibers
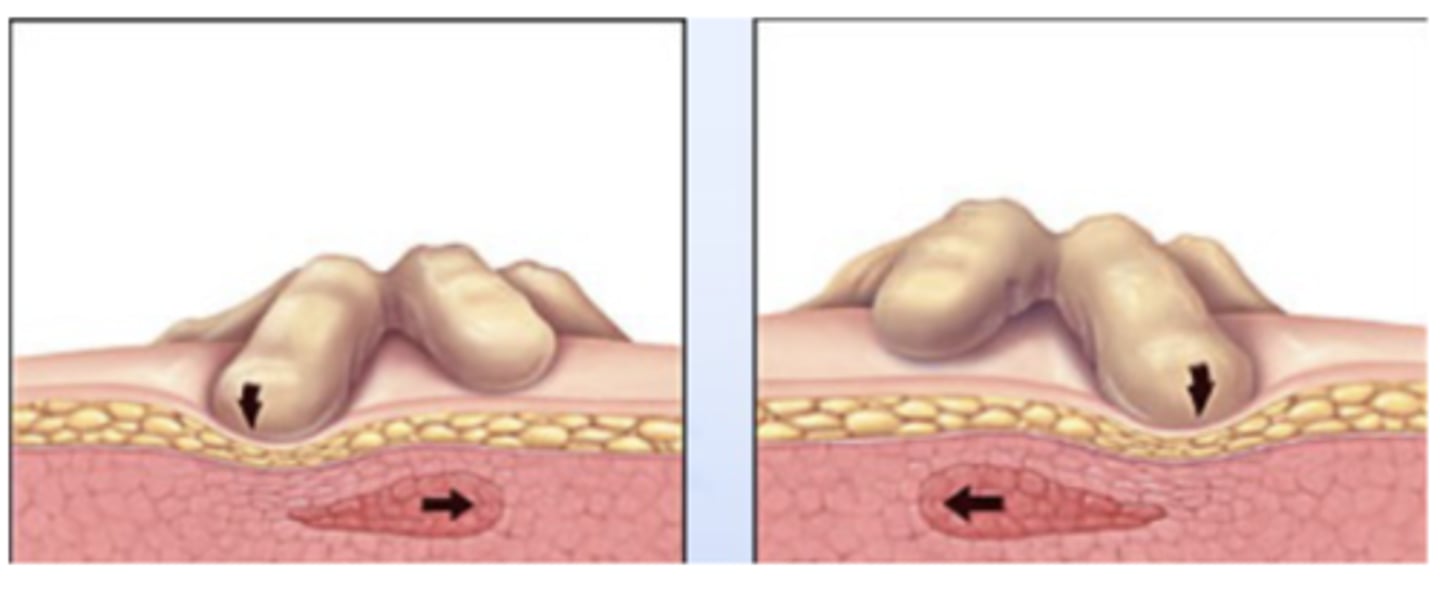
Trigger Points: EMG
Spontaneous electrical activity at sites
- While adjacent muscle tissues are silent
Latent trigger point
Asymptomatic unless palpated
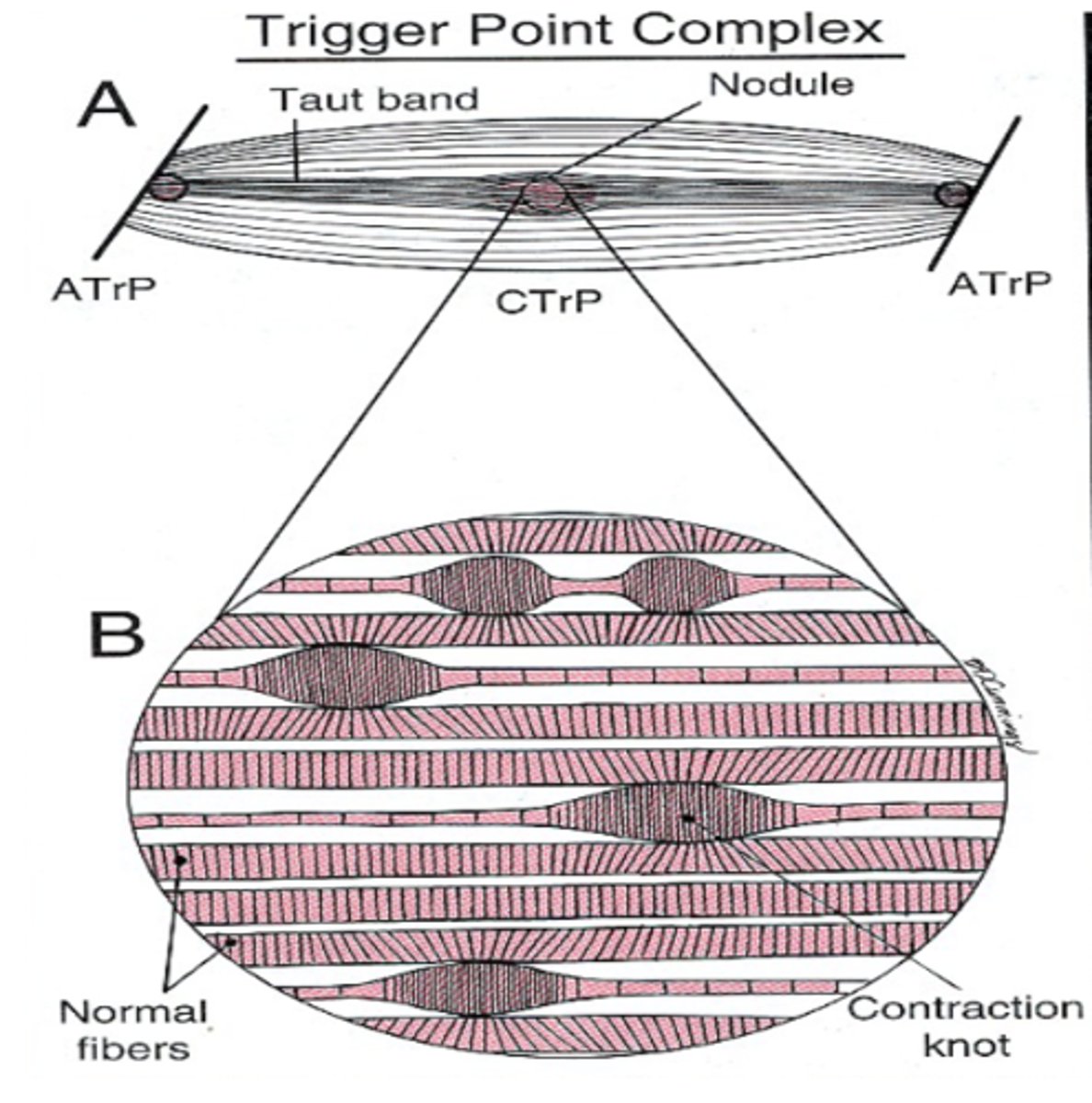
Active trigger point
Tender point in muscle can:
- Restrict muscle lengthening
- Restrict contraction
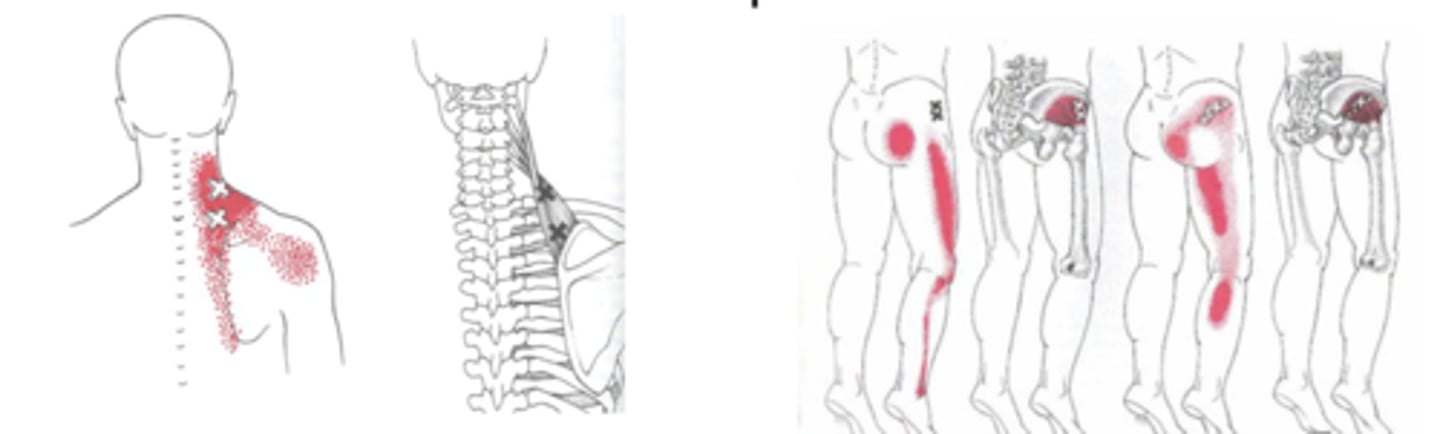
- Refer pain in muscle/limb/nerve pattern
Active trigger point characteristics
Symptomatic without palpation
- DIRECTLY related to problem at hand
Trigger Points: Causes
1. Direct Trauma
- Injury to muscle
2. Acute overload
- Too much too soon, inefficient movement patterns
3. Chronic Overload
- Prolonged, static postures
- Muscular fatigue and failure
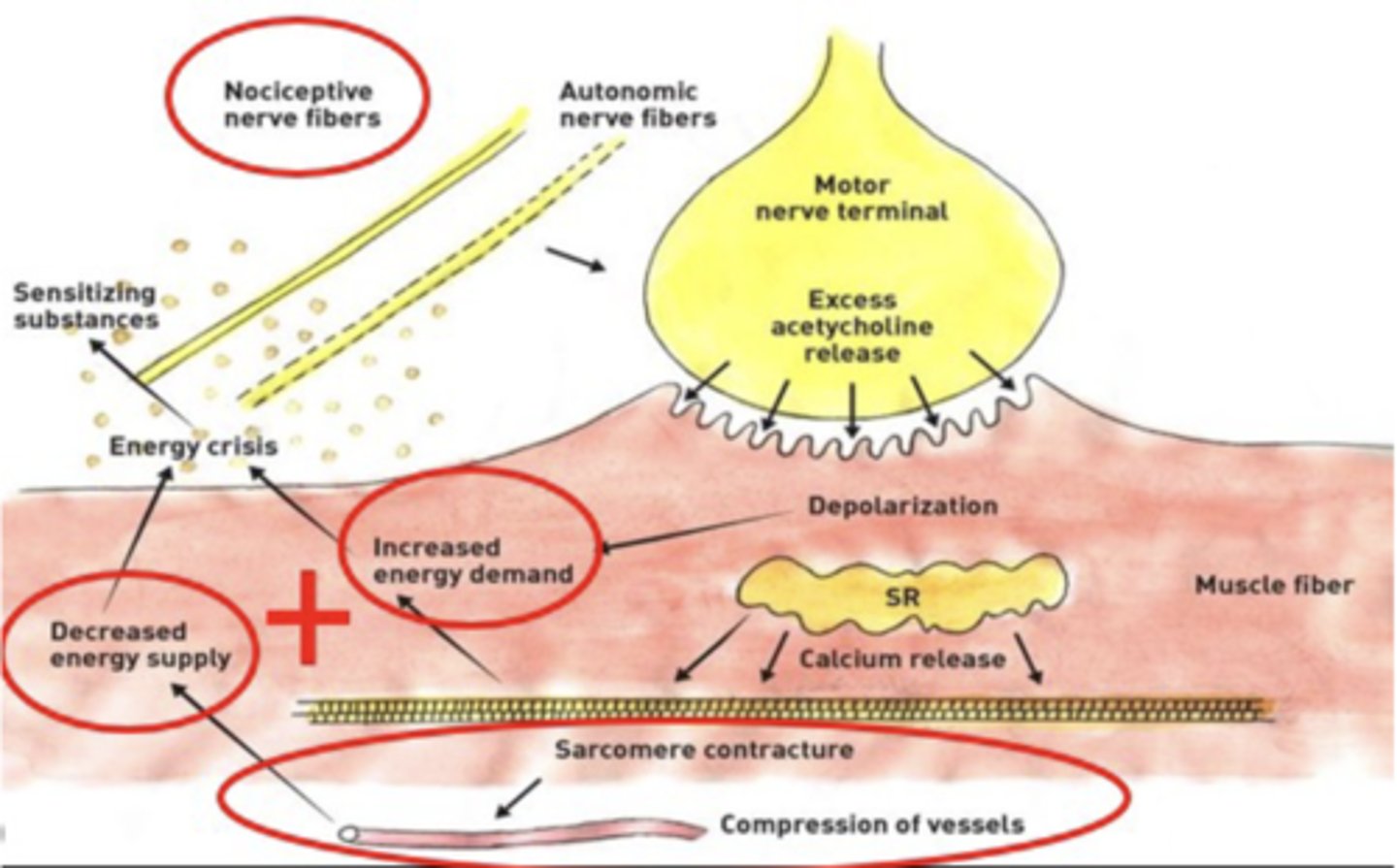
Trigger Points: Energy Crisis
Supply/Demand issue!
- Increased muscle work = Increased demand
- Reduces oxygen in and around muscle
- Activation of nociceptors
Dry-needling
Microtrauma to trigger point space increases blood flow to that area
Trigger Points: Subjective Pain
Sensitized nociceptors described as DEEP ACHING PAIN
- Present w/ common referral factors
STM effect on trigger points
1. Helps regulate tone
2. Localized increase in blood flow
3. Inhibits sympathetic NS
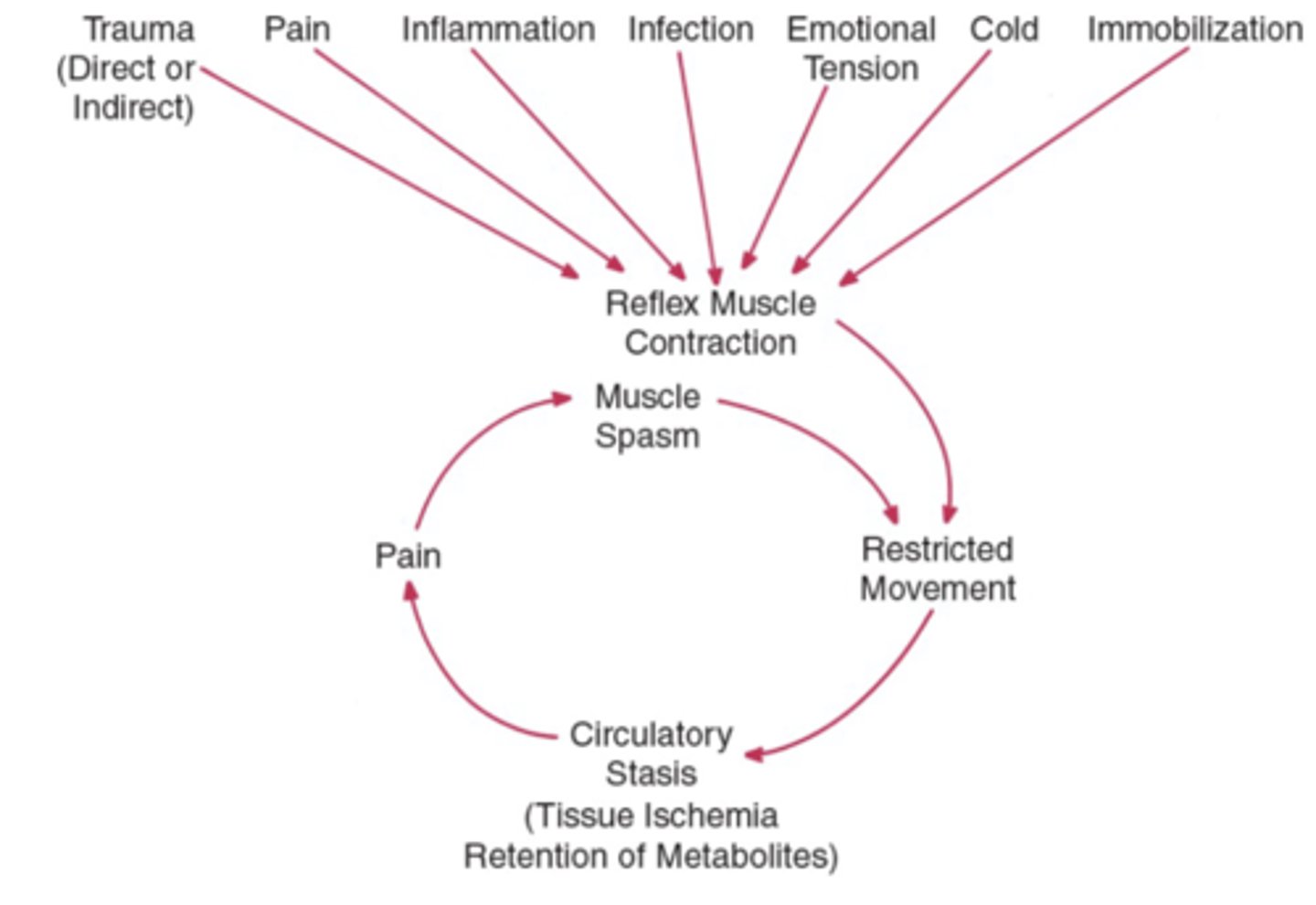
Muscle spasm cycle
Reflex muscle contraction --> More restricted movement
- THEN circulatory stasis, pain, and overall spasm!
Musculotendinous Junction
Where muscle belly becomes tendon
- Common site for injury/inflammation
- Common site for muscle tears
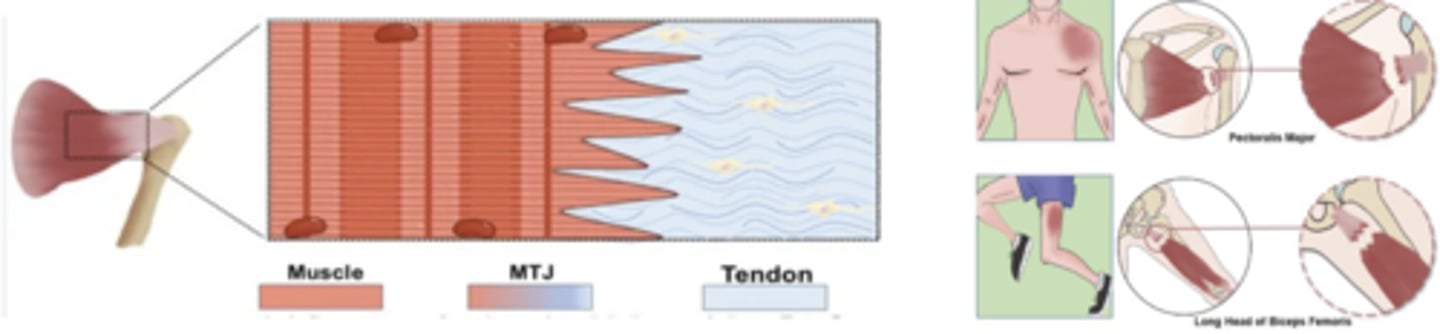
Musculotendinous Junction: Primary Function
Transmit force between muscle + tendon!
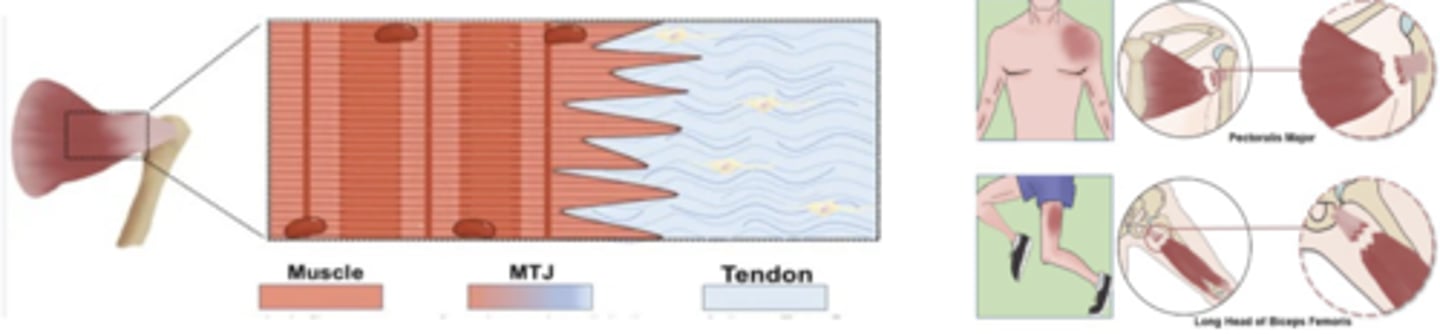
Musculotendinous Junction: Blood Flow
Muscle needs blood flow, whereas tendon needs LESS
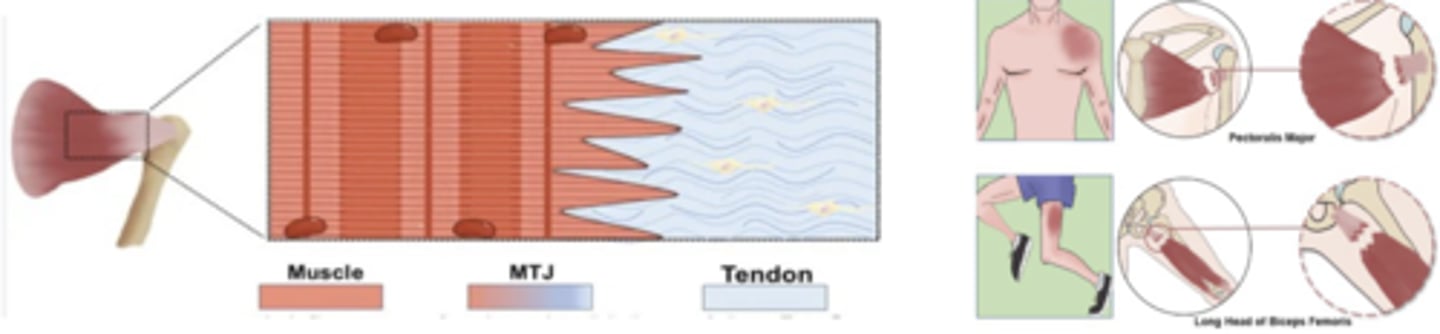
Tenoperiostial Junction
Where tendon attaches to bone
- Common site of avulsion fracture
STM and Muscle Intervention
- Increase blood flow
- Maintain soft tissue mobility
- Affect fiber orientation (when complimentary)
Adhesions
Can lead to muscle limitations/damage
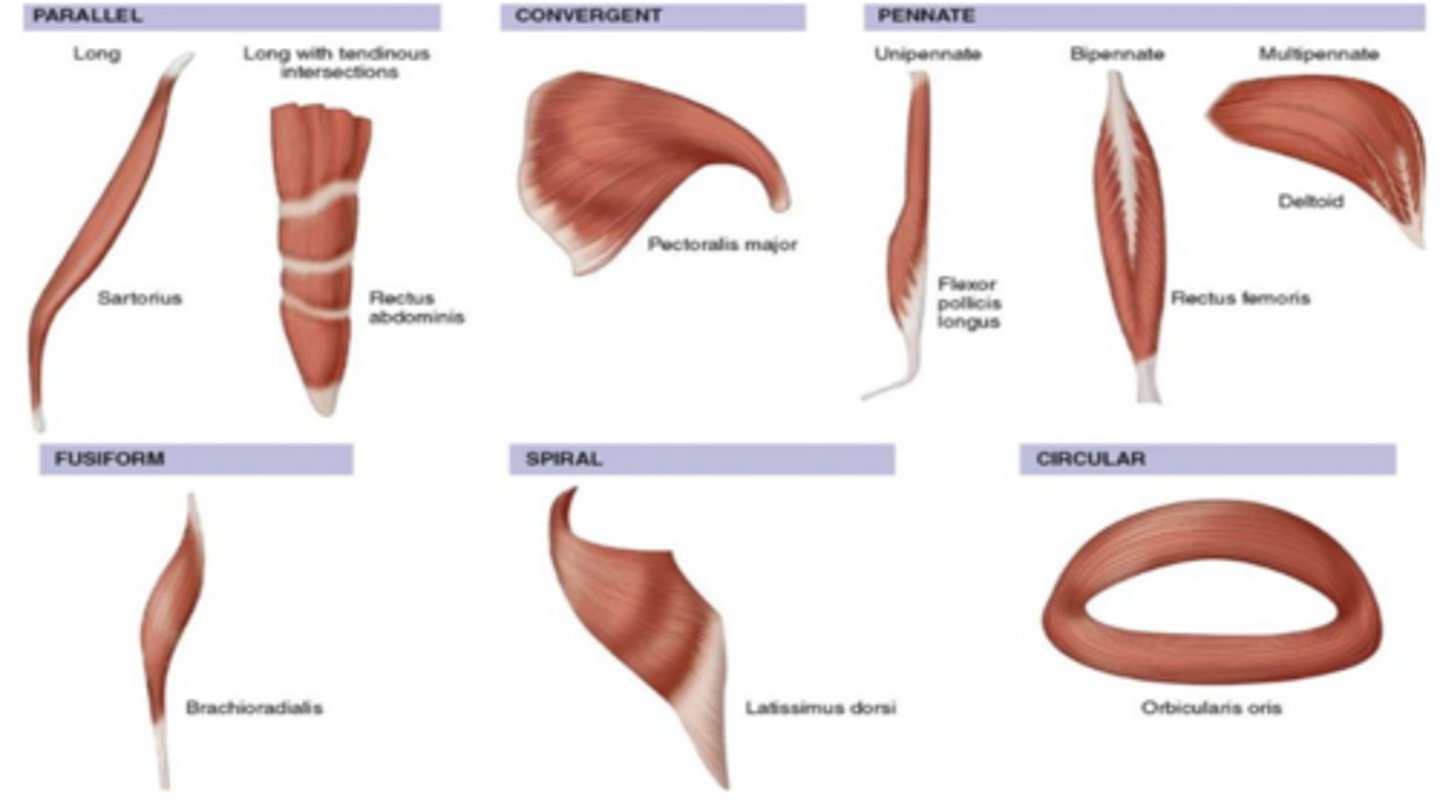
Muscle Fiber Orientations
1. Parallel
2. Convergent
3. Pennate
4. Fusiform
5. Spiral
6. Circular
Muscle Play Assessment
Perpendicular deformation
- Define borders
- DO NOT move over muscle, just pushing it
- To see how well it moves
Muscle Tone Assessment
Strumming
- Sliding OVER muscle
- Finding trigger points
- Feeling differences
Muscle Play Interventions
1. Parallel Strokes:
- Steam roller
- Bear Claw
- Splaying
- Forearm
2. Perpendicular Deformation
Bone expectation
Hard consistency, clearly defined border
Bone difficulty
Difficuly to locate bony contours when superficial tissue is TENSE
- Muscles tense up when patients are seated or unsupported
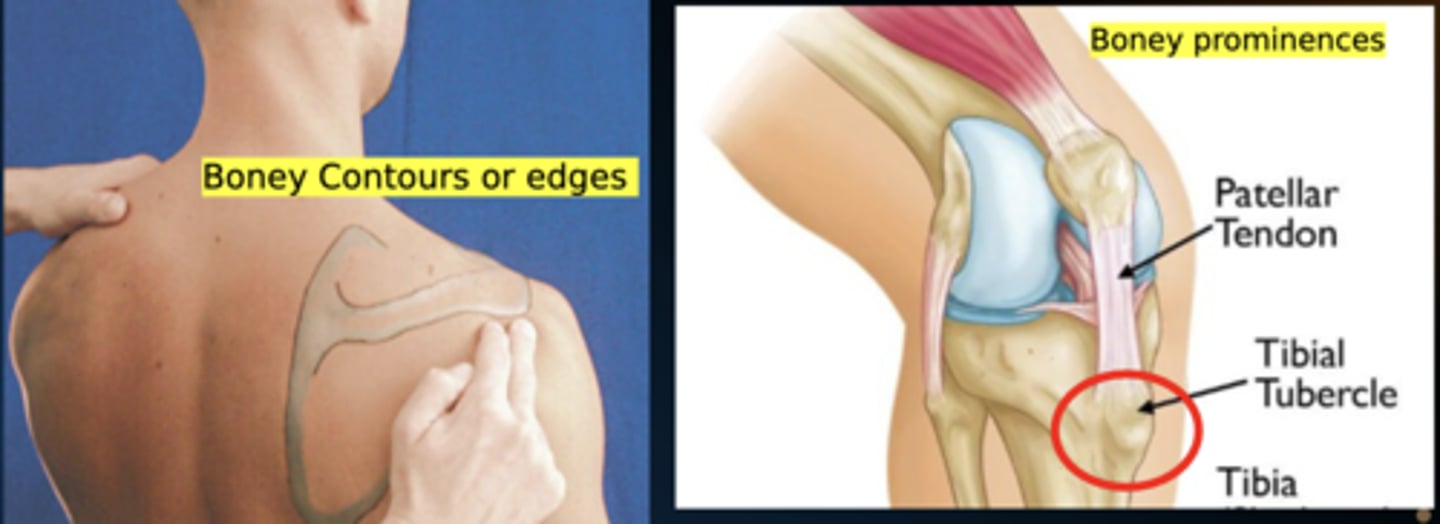
Bony Contour vs Prominence
Contour = Overall shape/outline of bone
- i.e. Borders of scapula
Prominence = Distinct, localized projection of bone
- i.e. Tibial tuberosity