Neuro Exam 1_Cholinergics MedChem
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
1. alpha
2. beta
what are the subtypes of cholinergic receptors
asthma
M3 antagonists can be used to treat ____
ligand-gated ion channels
nicotinic ACh receptors are ___(ligand gated ion/G protein coupled)
5 transmembrane domains.
TM2 is the component of the domains that is responsible for opening and closing the channel upon binding/unbinding of ACh
describe the structure of nicotinic ACh receptors
cholinergic
neurons that release acetylcholine
cholinergic receptors
receptors that respond to acetylcholine
nicotinic
acetylcholine receptors that are particularly responsive to nicotine
muscarinic
acetylcholine receptors that are particularly responsive to muscarine
a single monomeric protein that spans the cell membrane seven times
explain the structure of muscarinic receptors
Aspartic acid (Asp)
amino acid
component of nicotinic and muscarinic receptors necessary for binding of a ligand
carboxy of aspartic acid forms ionic interactions with quaternary amine of ACh
carboxy
functionality if aspartic acid that forms ionic bonds with muscarinic and nicotinic receptors
required for binding to receptors
parasympathomimetics
Drugs that mimic the parasympathetic nervous system
also referred to as cholinergic agonist drugs.
yes
are muscarinic agonists parasympathomimetics
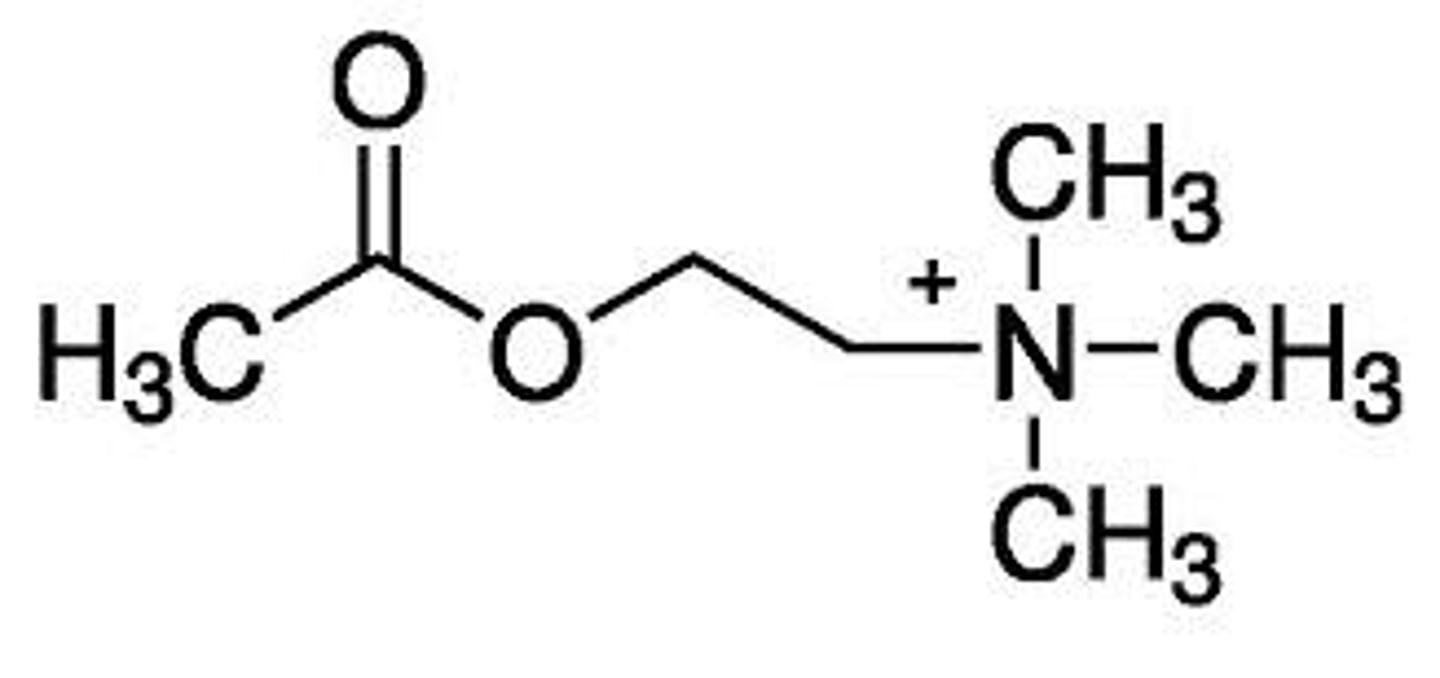
acetylcholine
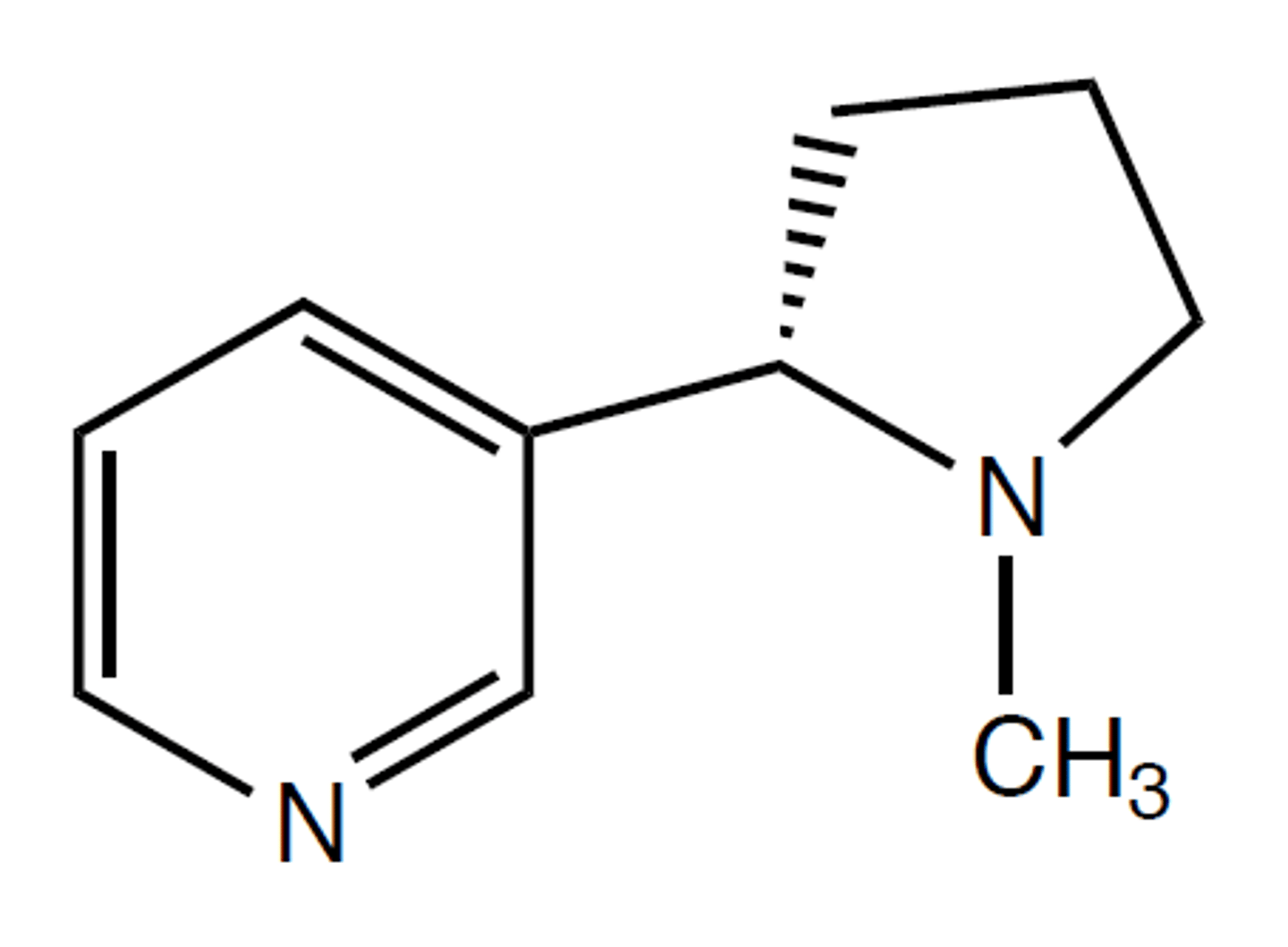
S-nicotine
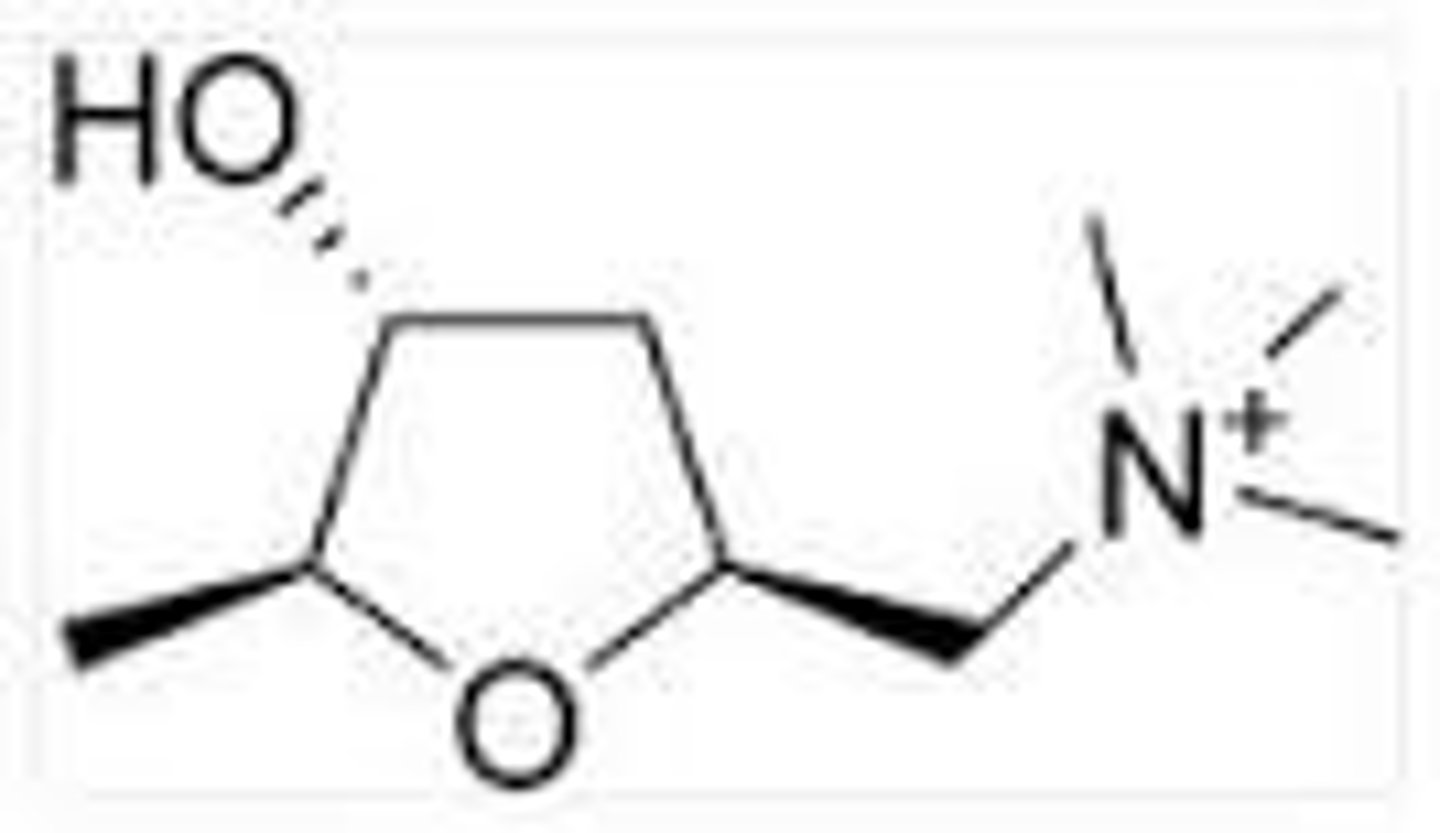
muscarine
1. methacholine (beta-methylcholine)
2. carbachol
3 bethanechol
4. acetylcholine
what are acetylcholine-like structures that can activate nicotinic and muscarinic receptors
pilocarpine
what are non-acetylcholine like structures that can activate nicotinic and muscarinic receptors
AChE (acetylecholine enzyme)
enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine to acetate and choline
inactivates ACh
controls the action of acetylcholine
AChE
what controls the action of acetylcholine
increased acetylcholine concentrations and prolonged action on the nuerons
what would AChE inhibition result in
3*10^8 molecules/second
speed at which AChE can hydrolyze ACh
summary cleaves the ester bond to form acetate and choline
1. AChE anionic site binds to the positively charged quaternary ammonium of acetylcholine
2.esteratic site that contains a serine residue performs hydrolysis of the ester bond. A tetrahedral intermediate is formed on the ester carbonyl group of acetylcholine
3. choline is released
4. acetylated serine is hydrolyzed and acetate is released
describe the activity of AChE, include info about the active site of AChE

1. it is not selective for muscarinic vs nicotinic
2. poorly absorbed through cell membranes/GI tract bc of the quaternary ammonium salt. (summary poor bioavailability)
3. metabolized rapidly (ester functional group is hydrolyzed in the gut, skin, blood and most tissues)
why can acetylcholine not be used as a drug
false
the stereochemistry of ACh determines activity.
T/F all confirmations of ACh are equivalent in activity
rotation occurs on the bond between the alpha and beta carbon
note: other bonds in the molecule can rotate but that alpha-beta carbon bond is the most significant
what bond of acetylcholine is responsible for the conformation changes
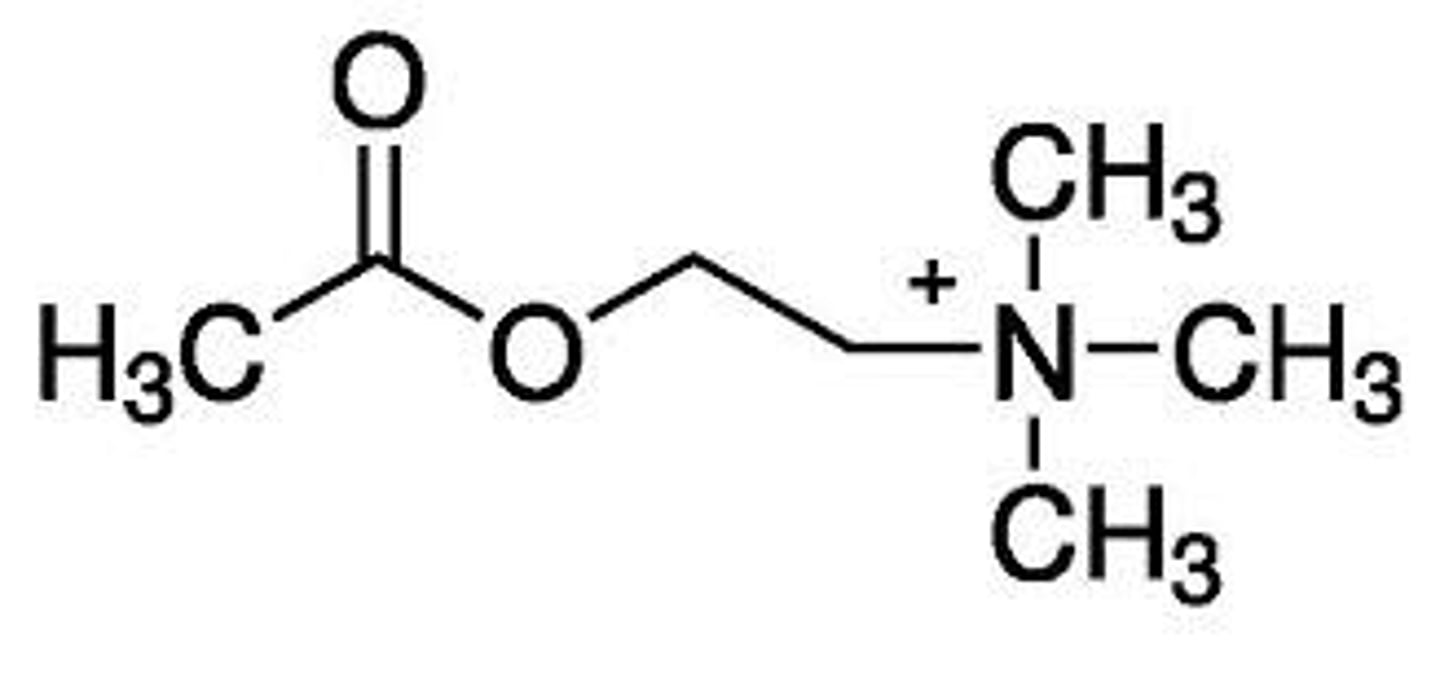
synclinal/gauche/trans
it is the most stable with the lowest energetic state.
what is the most common/preferred confirmation of ACh
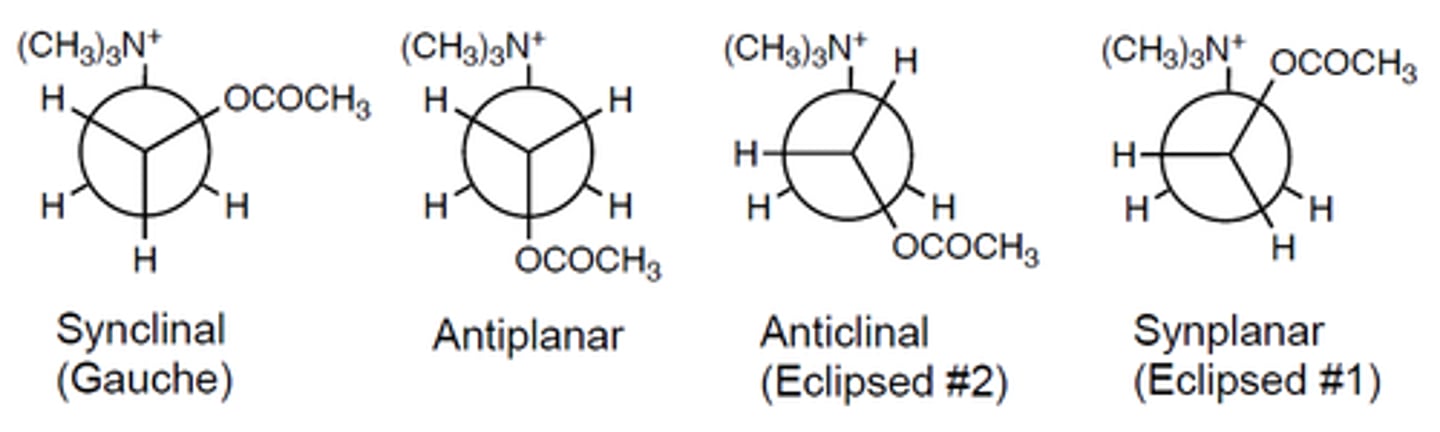
trans-ACTM
note: it is more predominant bc it is more stable. cis-ACTM has higher energy
is the cis-ACTM or trans-ACTM more potent at muscarinic receptors?
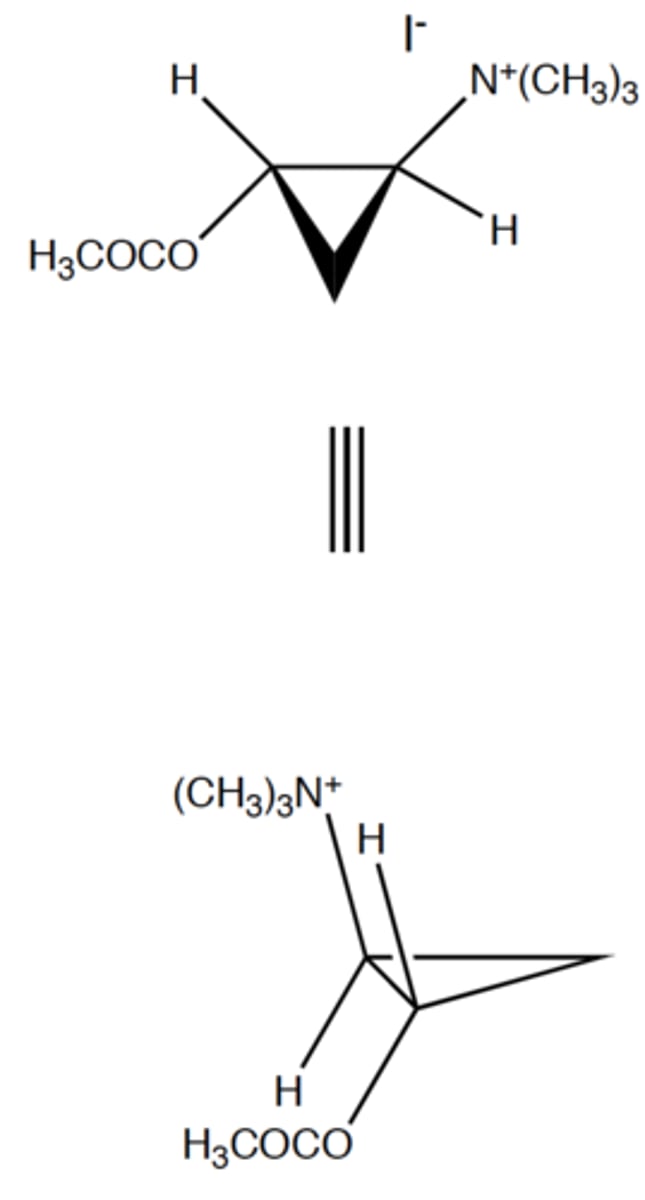
true
T/F while designing cholinergic ligands, chirality and stereochemistry is important
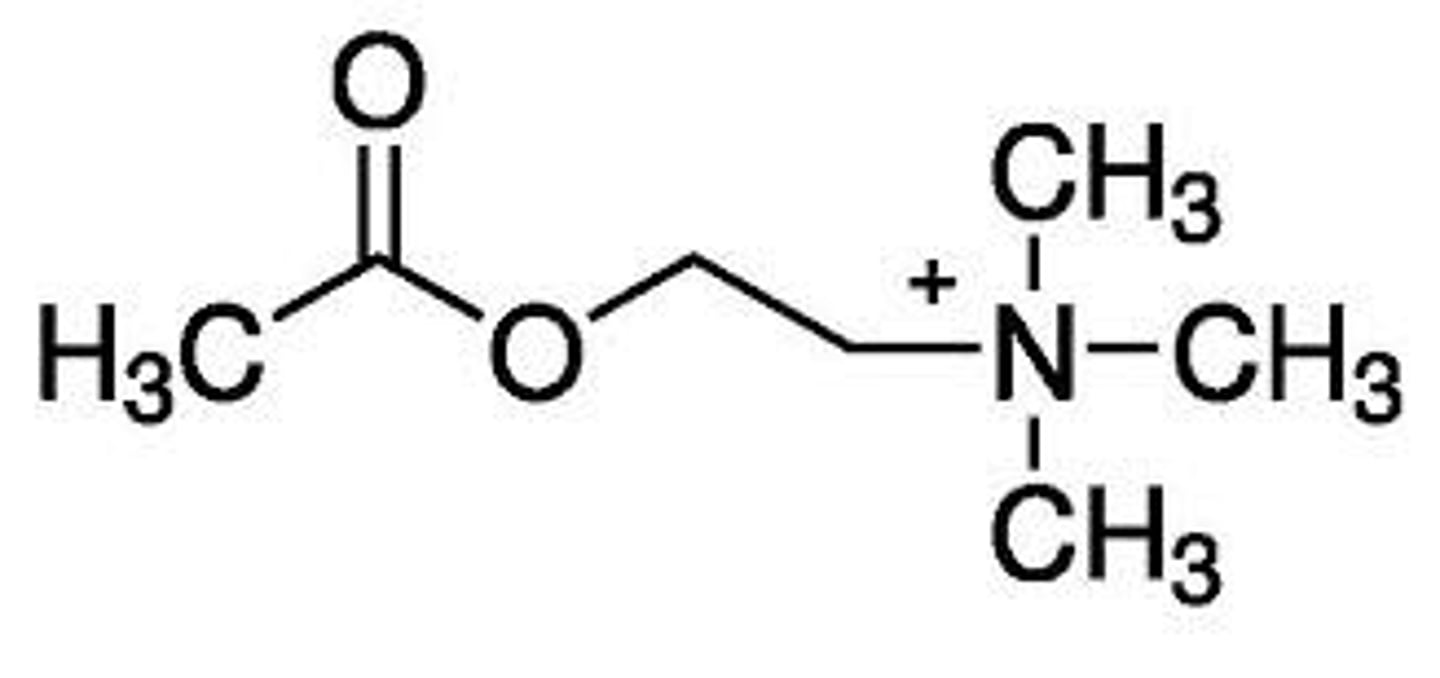
1. quarternary ammonium group: responsible for ionic binding to Asp of receptors
2. oxygens and nitrogens: take part in hydrogen bonding, which is needed for receptor interactions
3. Ing's rule: there should not be more than 5 atoms between the N and terminal H atom for maximal muscarinic potency
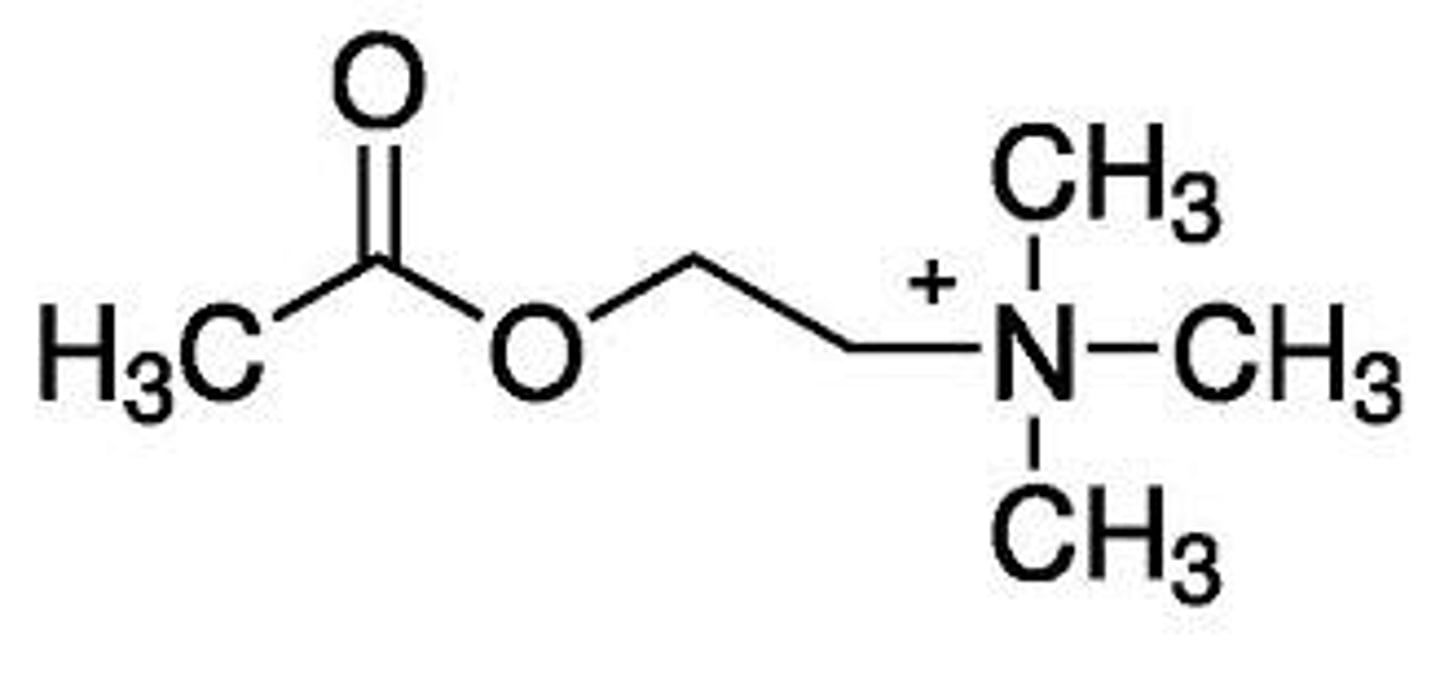
explain the important structural characteristics of acetylcholine that play a role in its activity
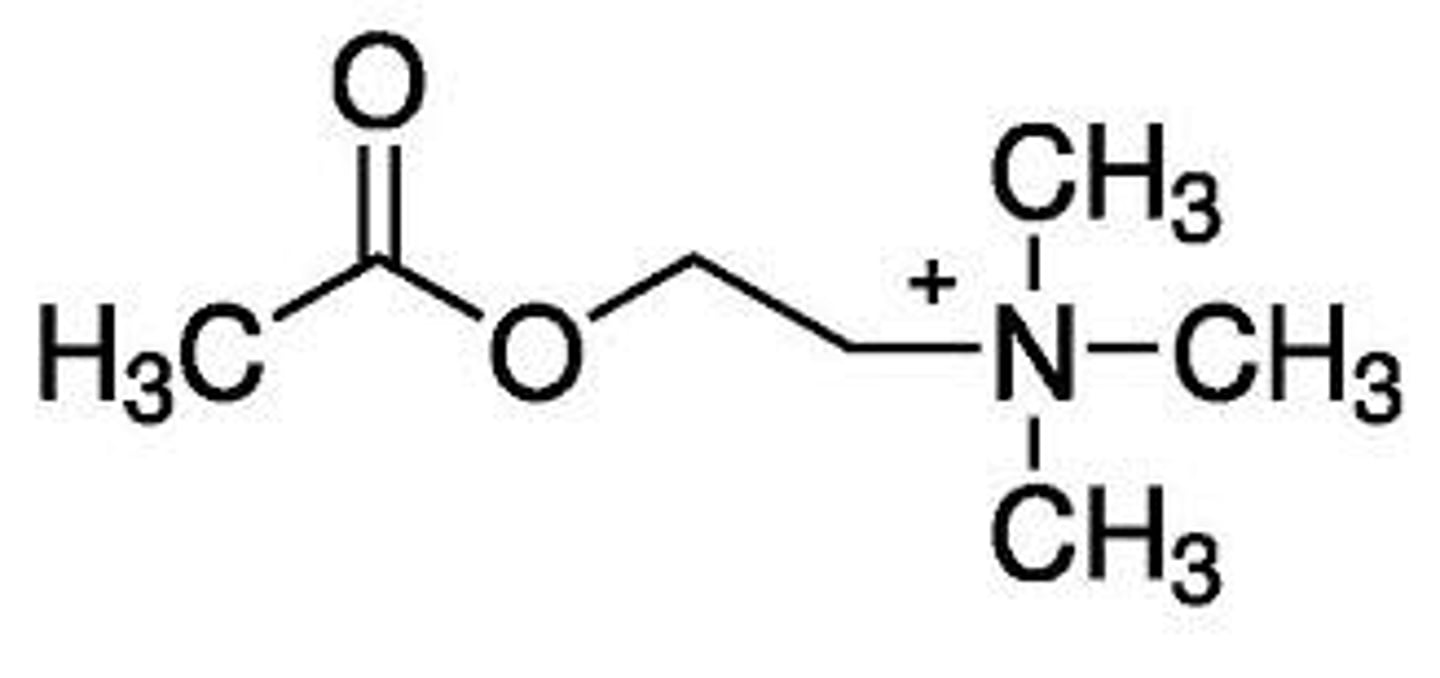
removal of methyls: decrease of activity
addition of bulkier groups: loss of activity
specific replacement with ethyl groups: becomes antaognist
what would happen to the activity of acetylcholine if the methyl groups attached to the nitrogen were subsequently removed or replaced with a bulkier group
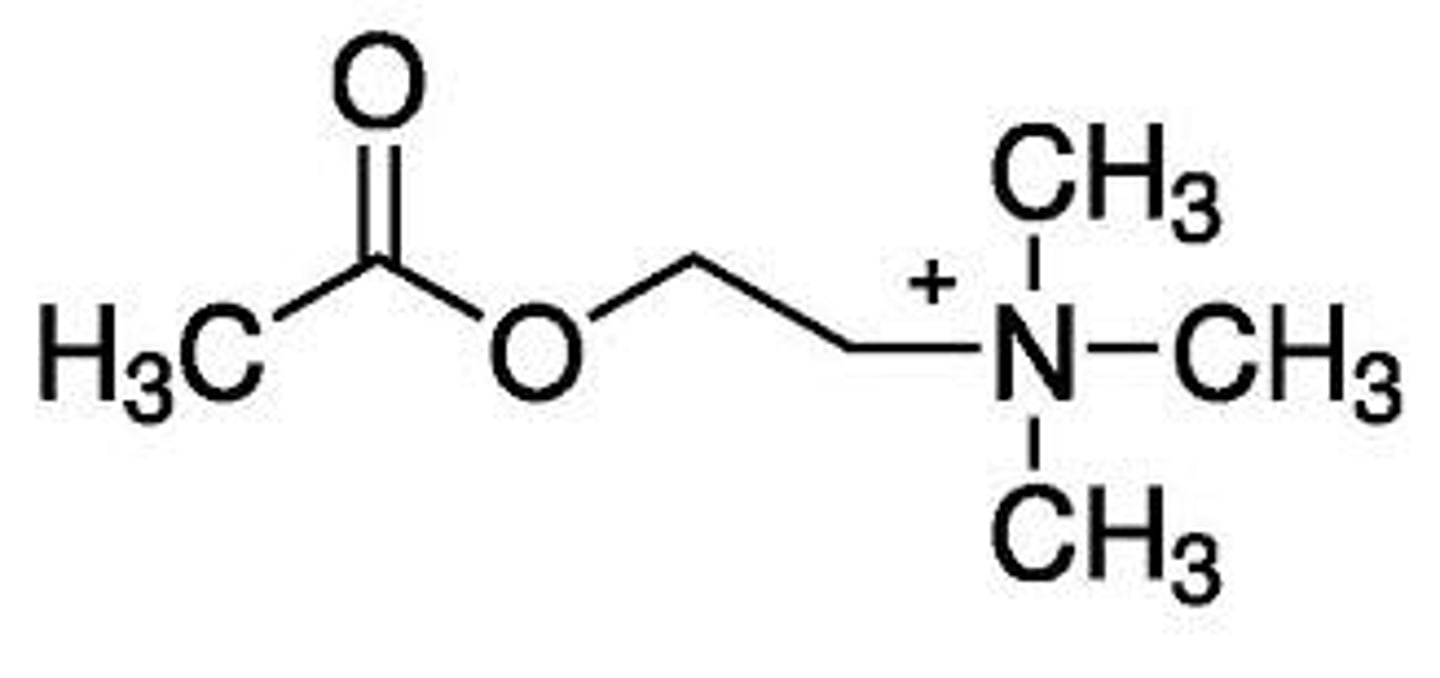
decreased activity
what would happen to the activity of acetylcholine if the nitrogen was replaced (with S, As, P, or Se)
Ing's rule
no more than 5 atoms between the nitrogen and the terminal hydrogen atom
what is required for ACh and similar molecules to have the maximum muscarinic potency
muscarinic selectivity: addition of methyl group on the beta carbon to nitrogen
nicotinic selectivity: addition of methyl group on alpha carbon to nitrogen
how to make acetylcholine more selective for muscarinic or nicotinic receptors
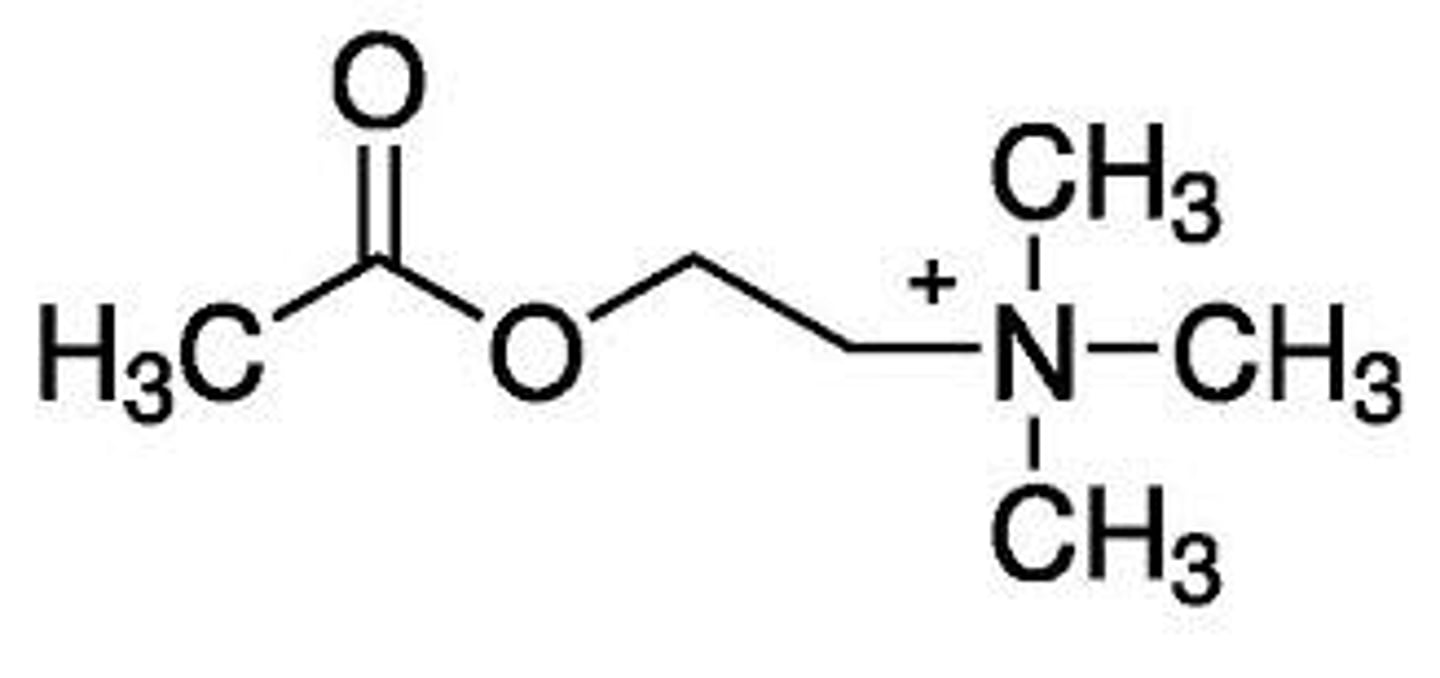
changes in oral stability and activity
what can modification of the acyloxy group of ACh result in
acyloxy
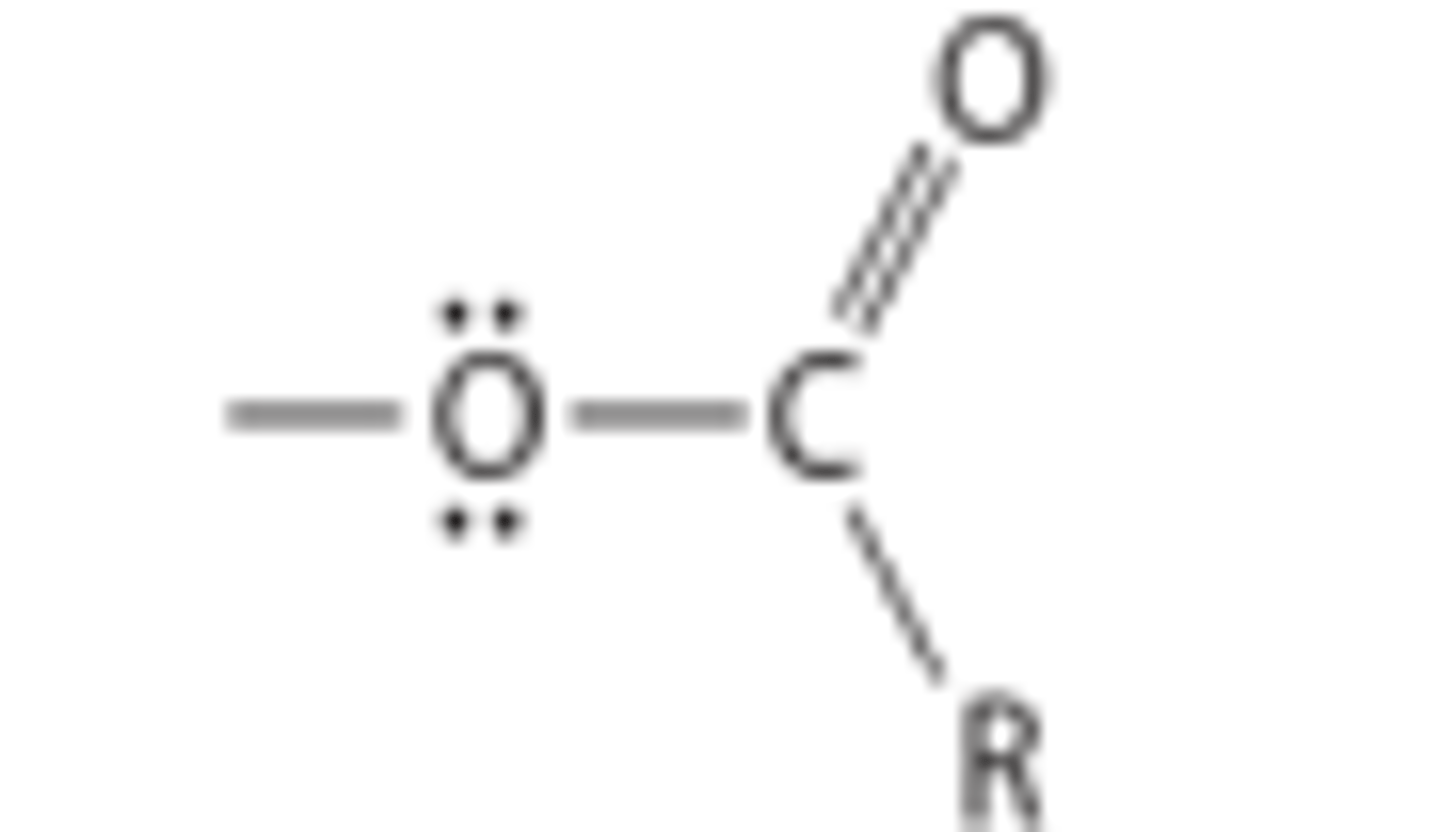
cholinergic antagonist
choline esters of aromatic acids or higher molecular weight acids possess ___ activity
decreased activity
what does replacement of the acetyl group of ACh with higher homologues (propionyl, butyryl) result in
carbamic acid ester
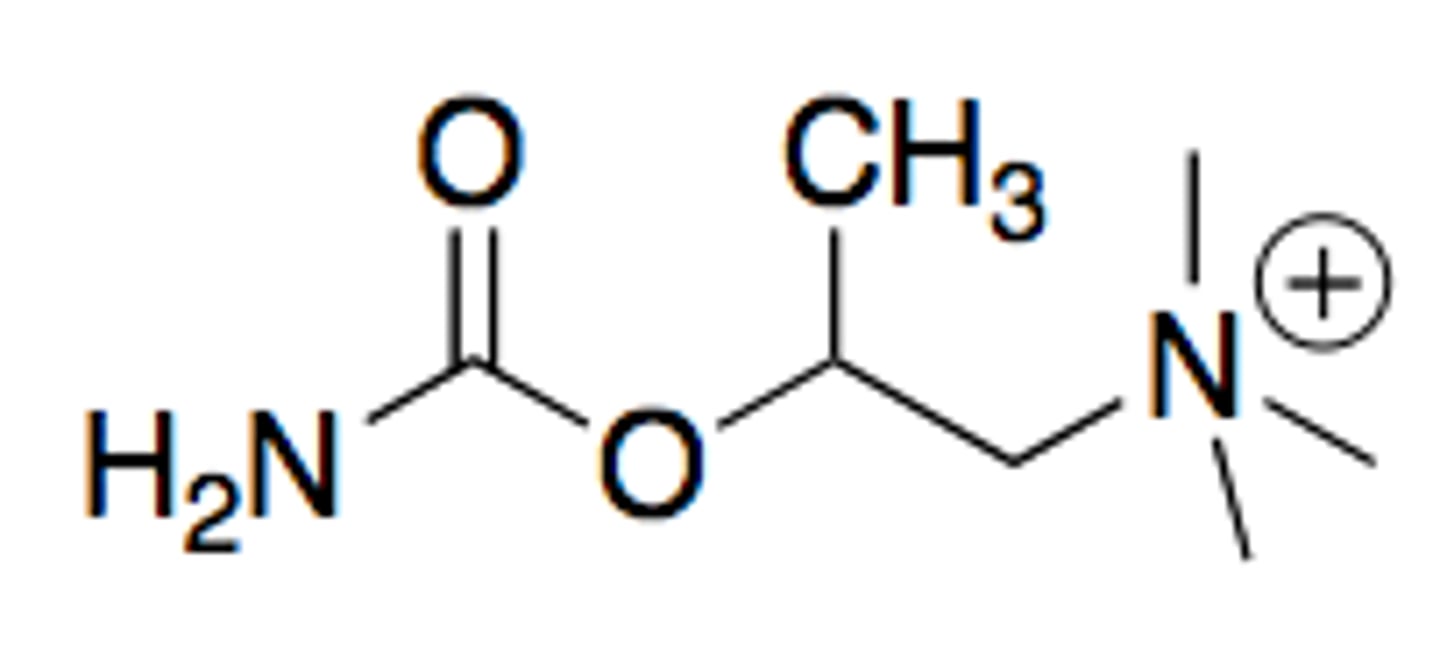
replacement of carbon 5 with a nitrogen. creates carbachol
modification of the acyloxy group of ACh that results in a more stable molecule with better oral availability
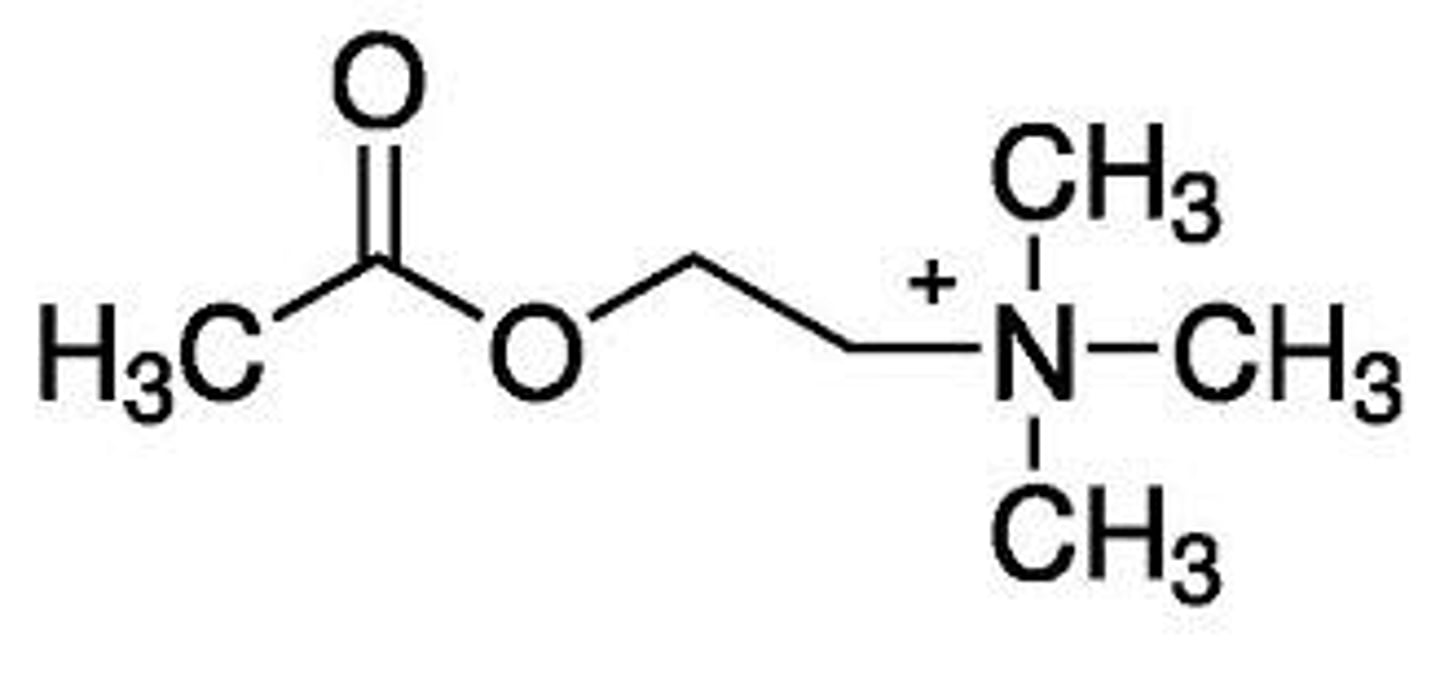
carbachol
modified ACh. Nitrogen replaced carbon 5
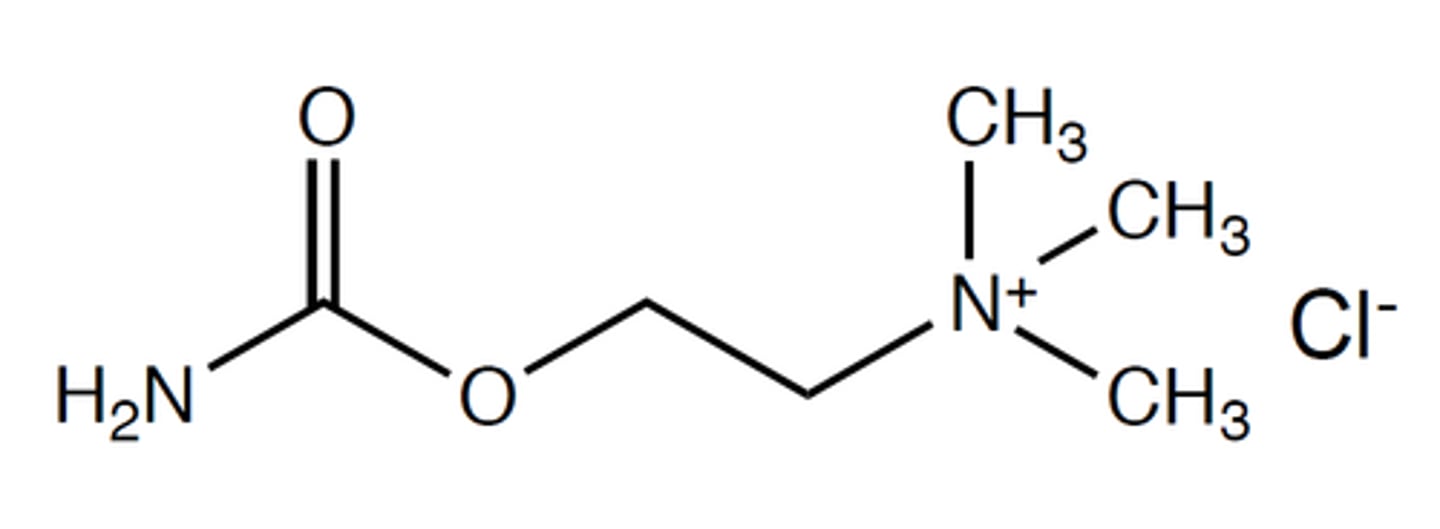
bethanechol
modified carbachol
methyl group on beta carbon to the quaternary nitrogen
has better stability and oral bioavailability due to nitrogen in place of carbon 5. AND the methyl group on the beta carbon provides muscarinic selectivity and provides steric hinderance to make molecule more resistant to hydrolysis
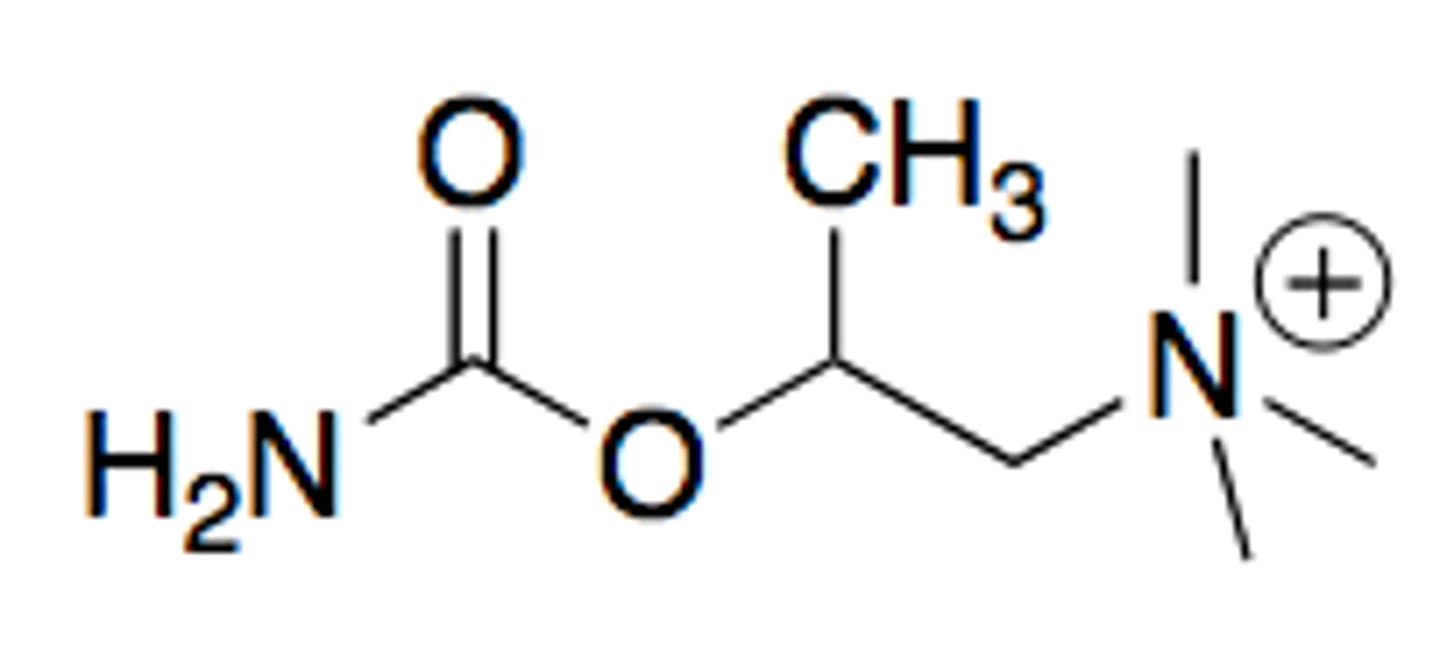
bethanechol
an orally available potent muscarine agonist with almost no nicotinic acitivity
yes
S (counterclockwise rotation) enantiomer has greater binding affinity for muscarine receptors than R (clockwise rotation) enantiomer
note: beta carbon to nitrogen is the chiral center
do the enantiomers of bethanechol have varying activity
muscarine
substance obtained from the red mushroom
has cholinergic agonist activity
has three chiral centers
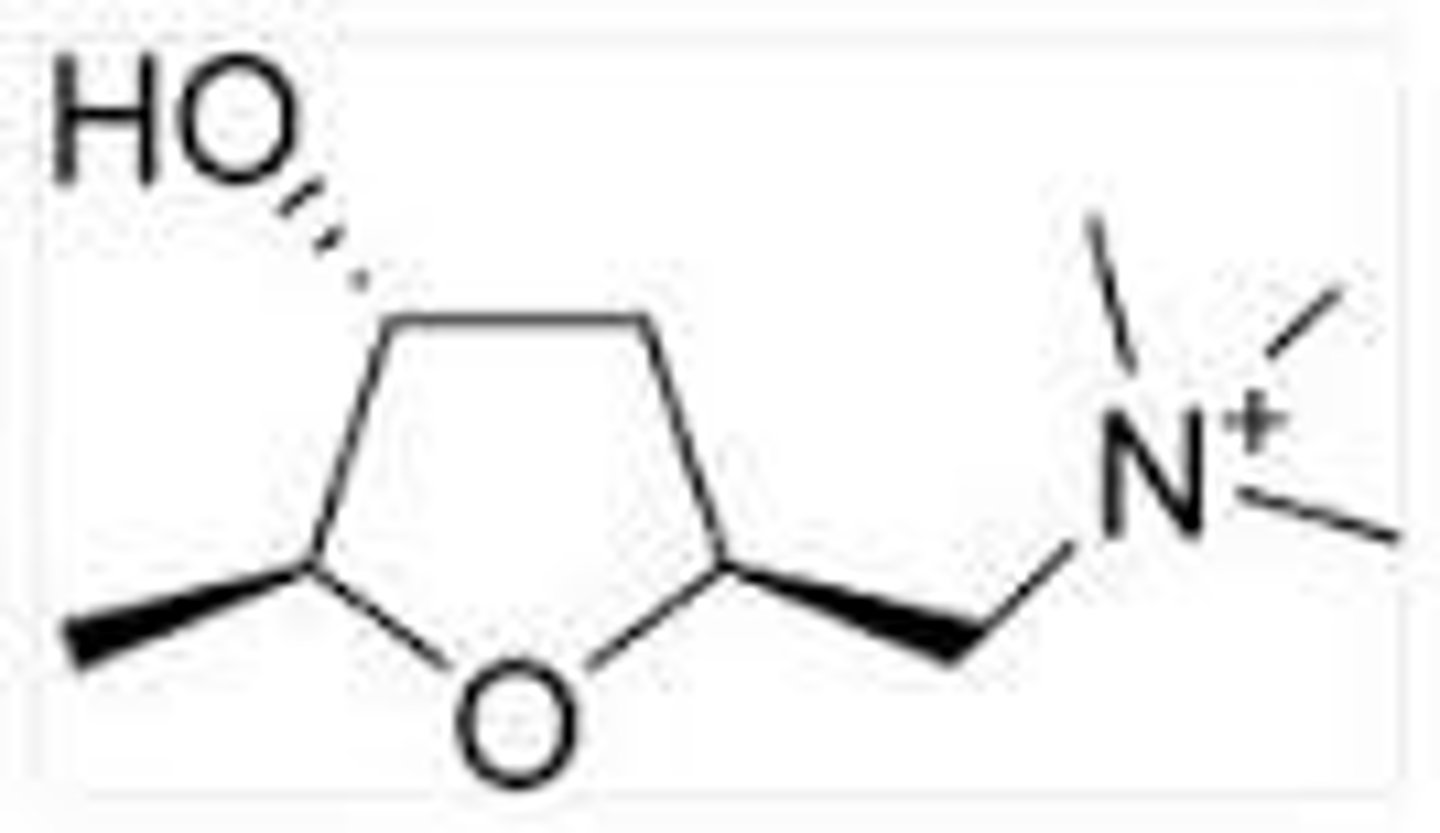
3
note: the alpha carbons and beta carbon to the oxygen
how many chiral centers does muscarine have
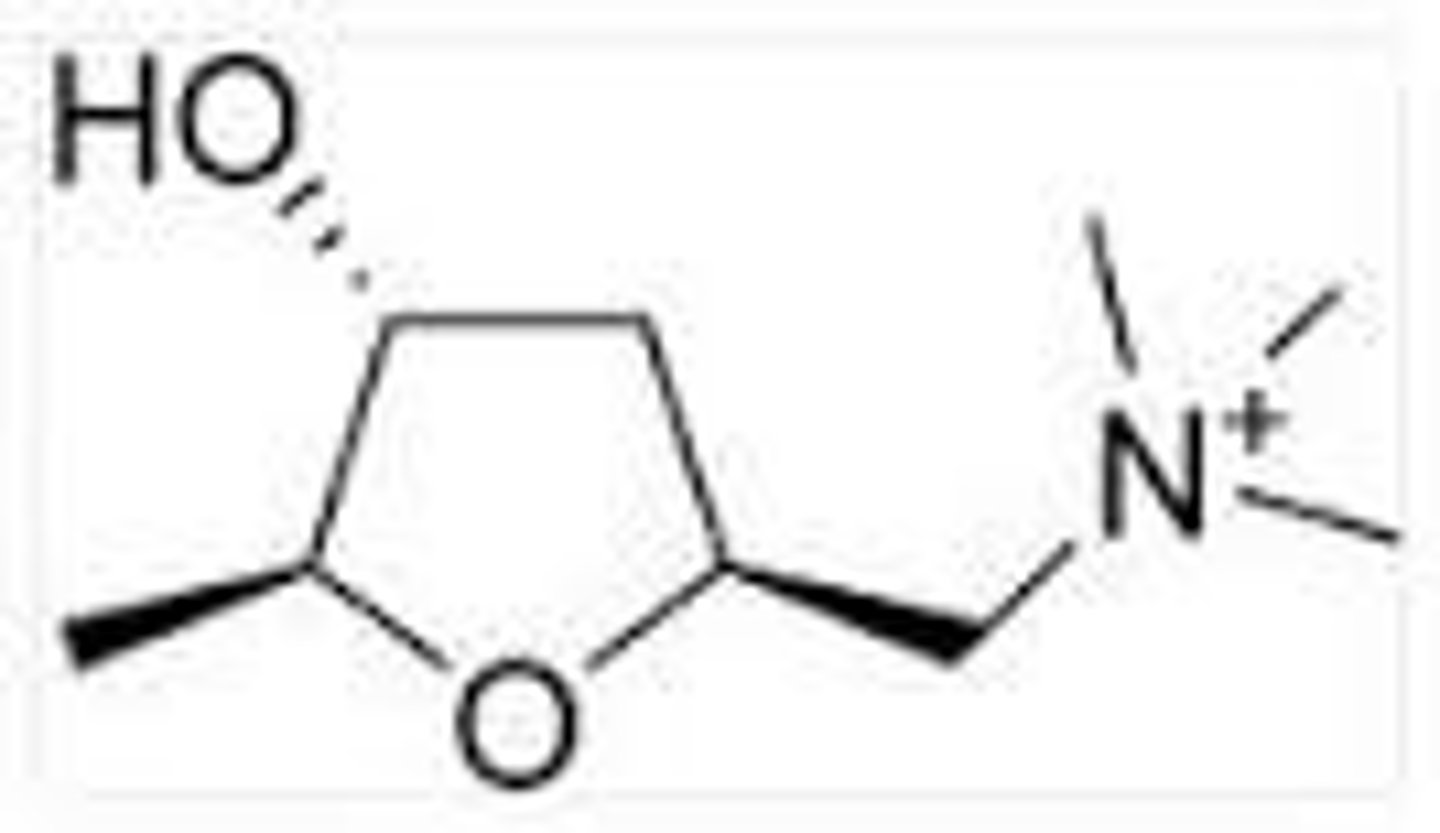
1. posses a quaternary nitrogen atom with a positive charge
2. size of alkyl groups substituted on the nitrogen must not exceed the size of a methyl group
3. contain an oxygen atom, preferably in the form of an ester, to participate in hydrogen bonding
4. there is a two carbon unit linker between the oxygen and nitrogen
rules for designing a muscarinic (and nicotinic) agonist
1. presence of methyl group on alpha or beta carbon to the nitrogen to create stability
2. replacement of carbon 5 with a nitrogen
note: these modifications slow hydrolysis
modifications to ACh that can slow down its metabolism by AChE
R
enantiomer of bethanicol that is weaker in activity but is hydrolyzed slower
pilocarpine
muscarinic agonist
imidazole alkaloid from the plant pilocarpus jaborandi
has stability problems due to stability
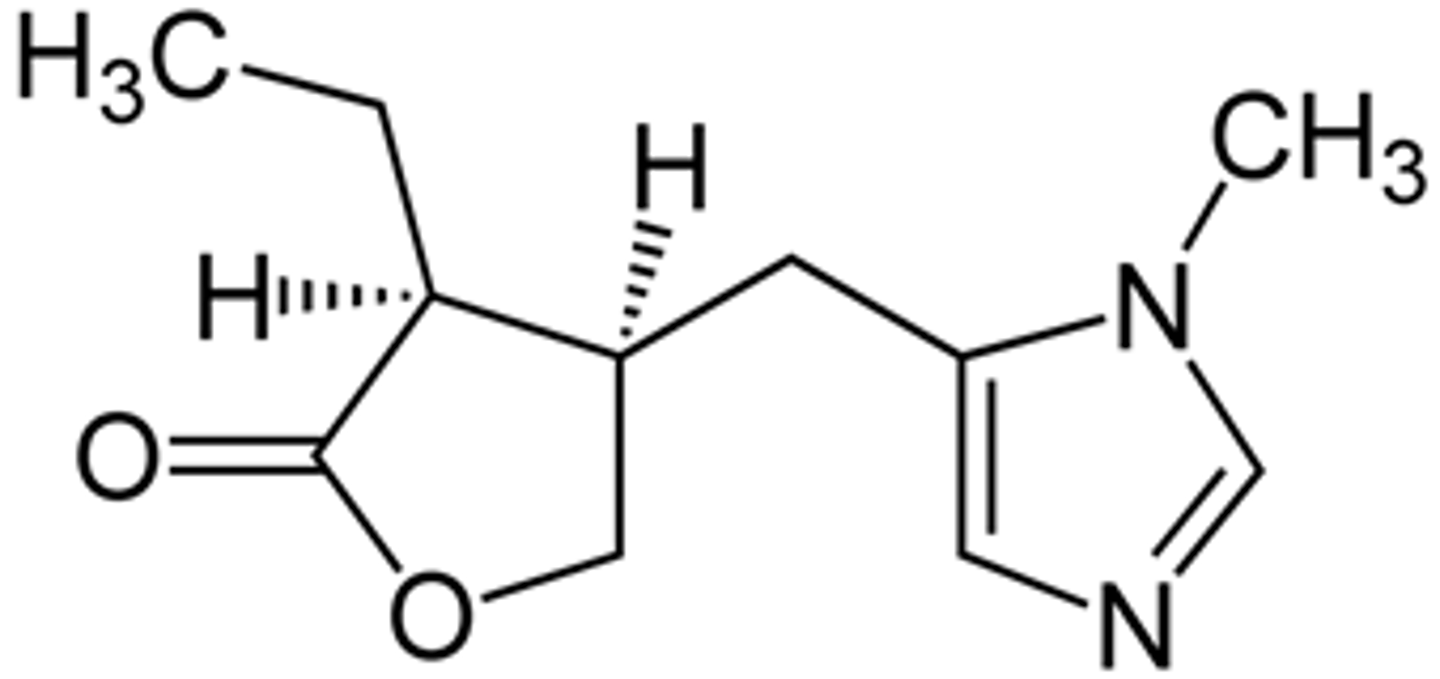
1. hydrolysis of lactone
2. epimerization
note. this occurs rapidly so pilocarpine has stability issues and a short shelf life
how is pilocarpine metabolized/inactivated
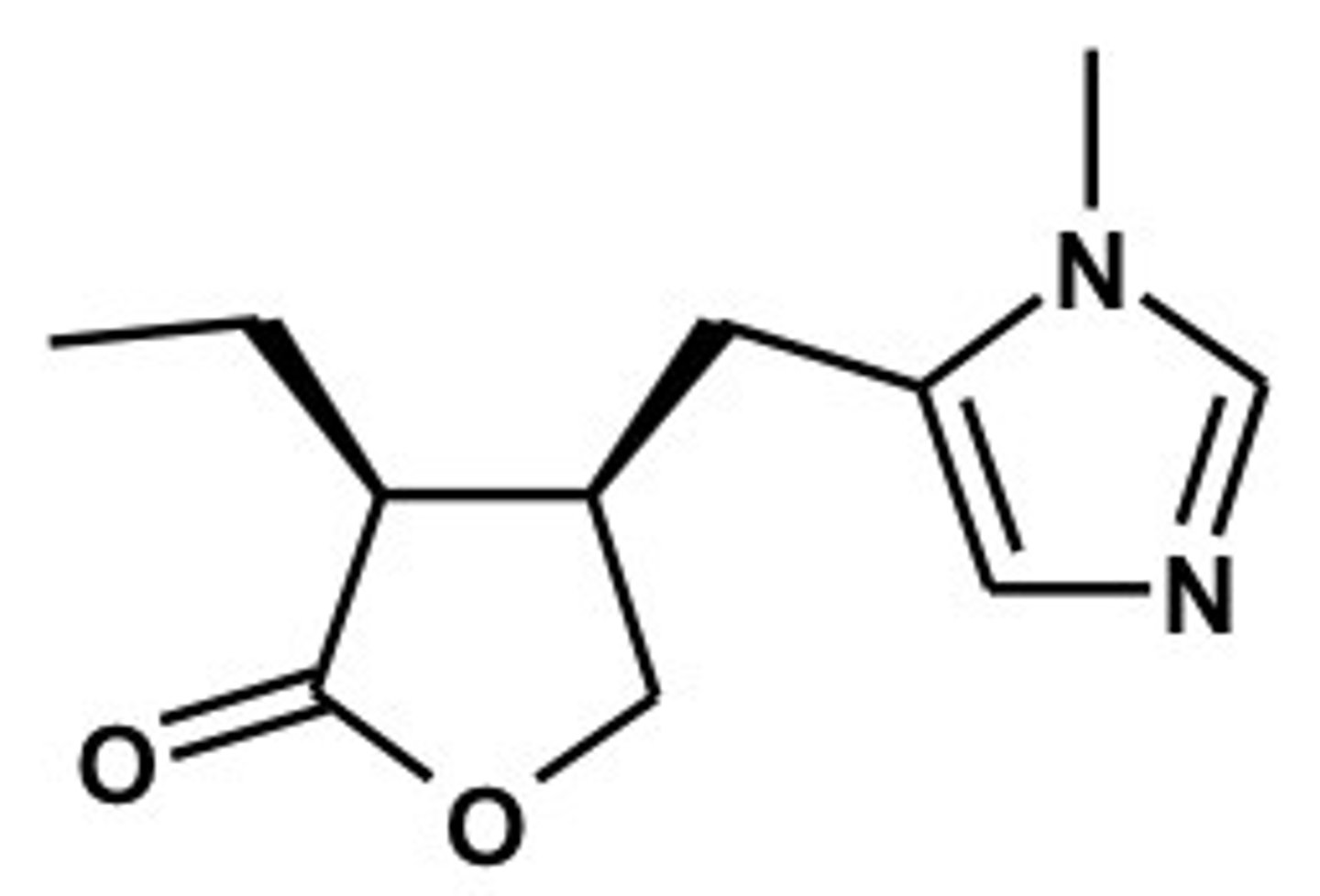
AChE inhibitors
substances that interfere with the mechanism by which the action of ACh is terminated
cause increased concentrations of ACh at the synapse
physostigmine
AChE inhibitor
a natural alkaloid with a carbamate moiety which remembers the ester linkage of acetylcholine
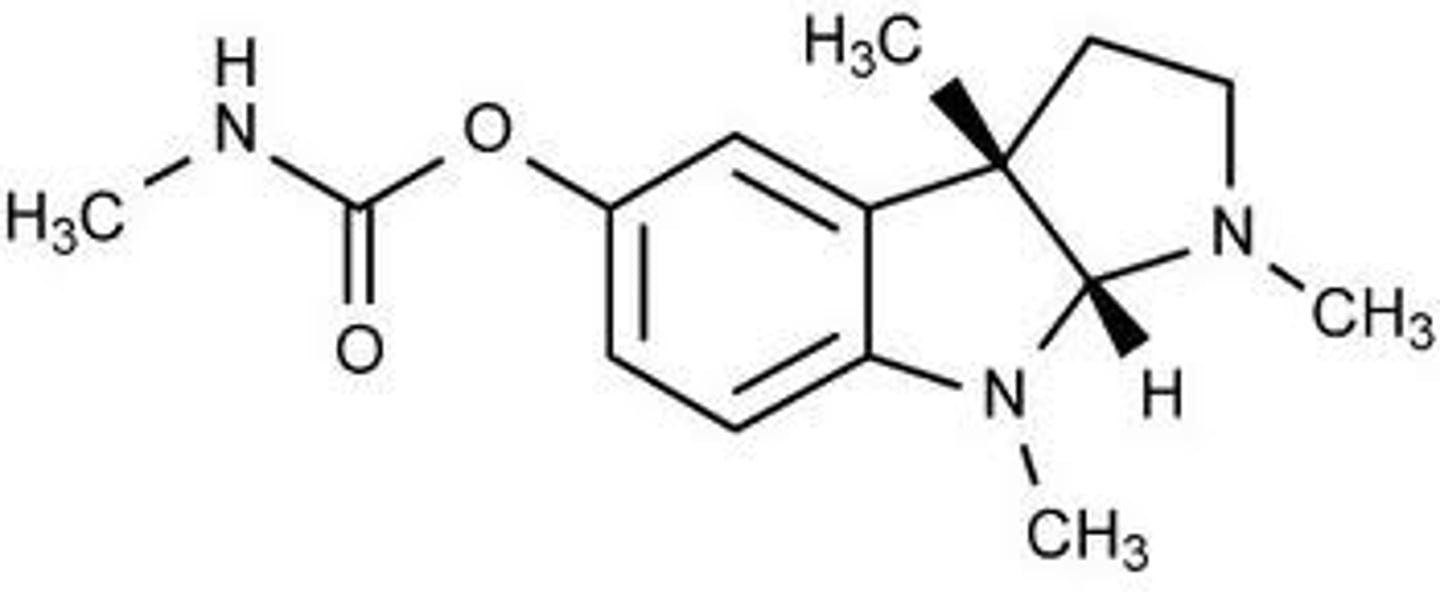
1. ester forms a tetrahedral intermediate with the serine of AChE (carbamoylated enzyme)
2. slow hydrolysis of the intermediate results in physostigmine's antagonistic effects
this is considered slowly reversible inhibition (aka pseudo-irreversible inhibition) due to the covalent bond formation of the tetrahedral intermediate and its slow cleavage
describe the mechanism of AChE inhibition by phsostigmine
physostigmine
does physostigmine or acetylcholine have a higher affinity for AChE
false
physostigmine is a tertiary amine so it does not have a positive charge
T/F it is the positive charge of physostigmine that allows it to bind to AChE
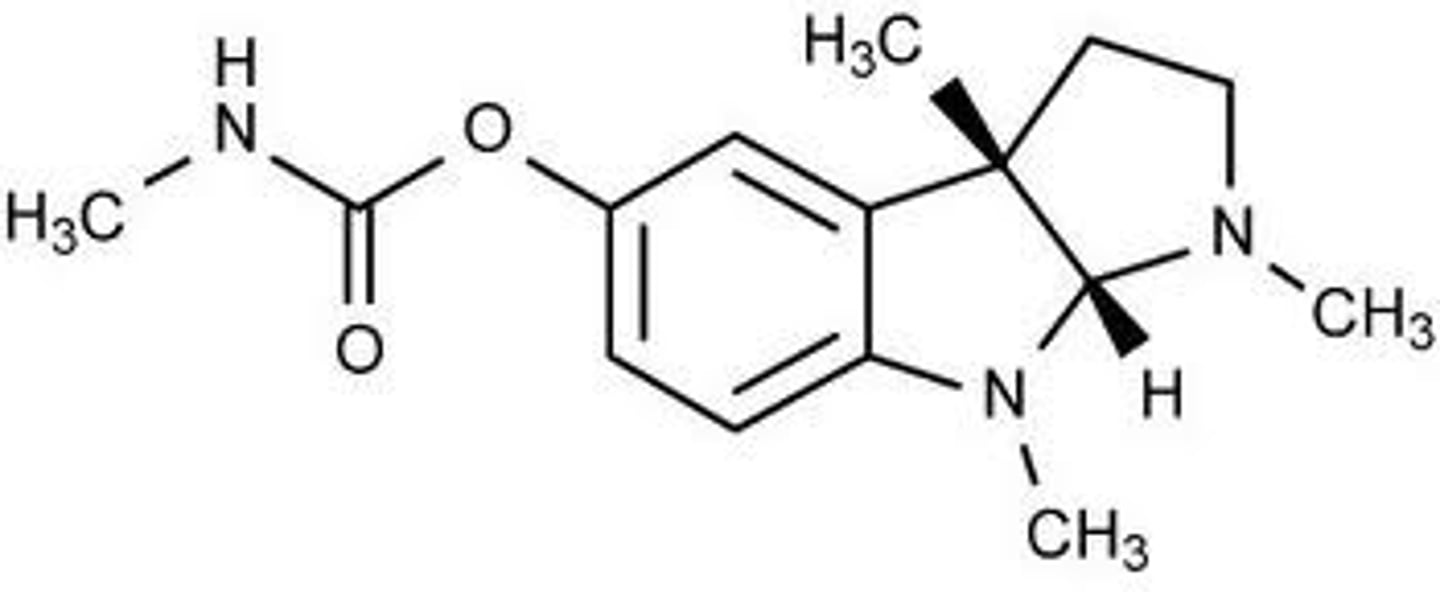
it is more lipophilic and can cross the BBB
what is the advantage of physostigmine being a tertiary amine without a positive charge instead of a quaternary ammonium salt
1. esterases hydrolyze the carbamate ester to eseroline (which is an inactive metabolite bc it lose the carbamate)
2. eseroline is oxidized to rubreserine (no carbamate so inactive)
how is physostigmine metabolized
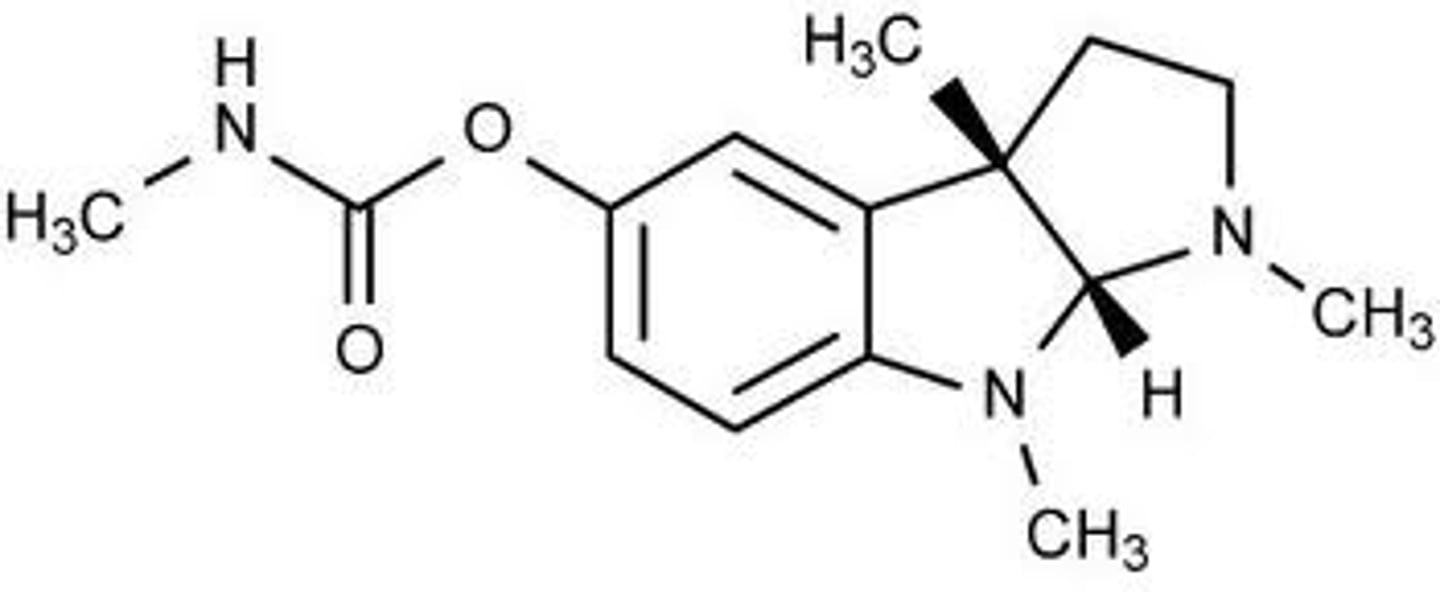
noestigmine
AChE inhibitor that has a substituted carbamate group, benzene ring, and quaternary ammonium
formulated as a salt
has low CNS/BBB penetration bc it is hydrophilic due to the quaternary ammonium
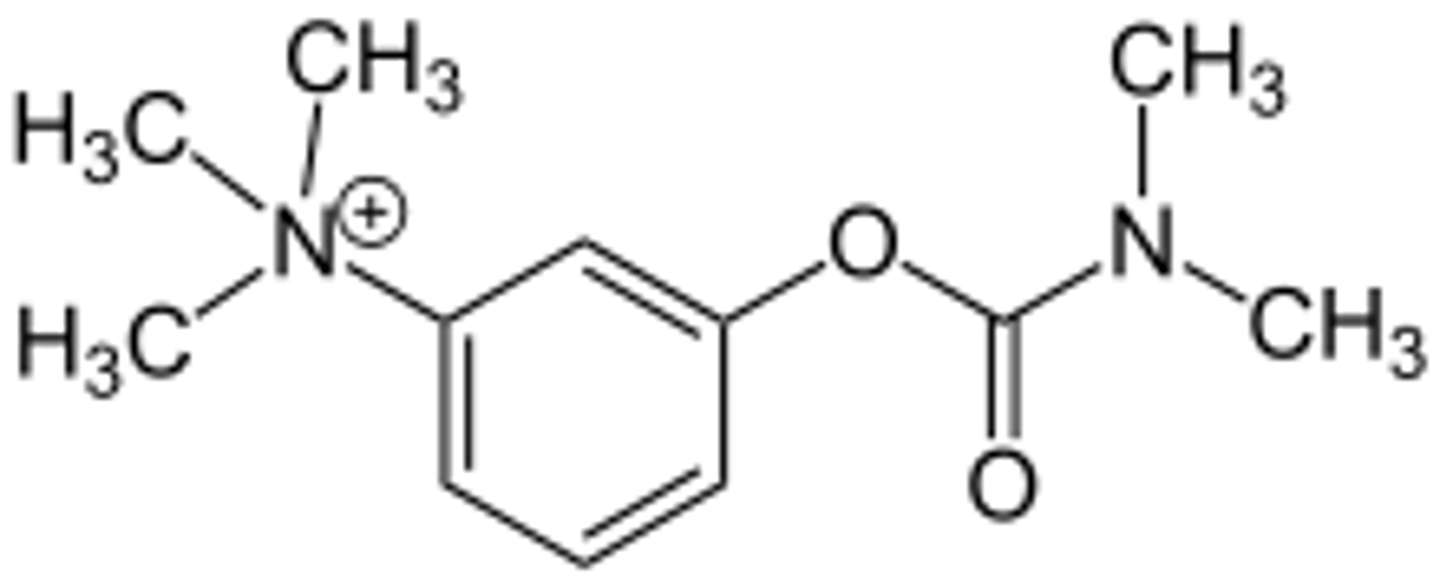
cholineesterases in the liver and skeletal muscle
how is neostigmine metabolized
no
it be polar
can this molecule (pyridostigmine) cross the BBB
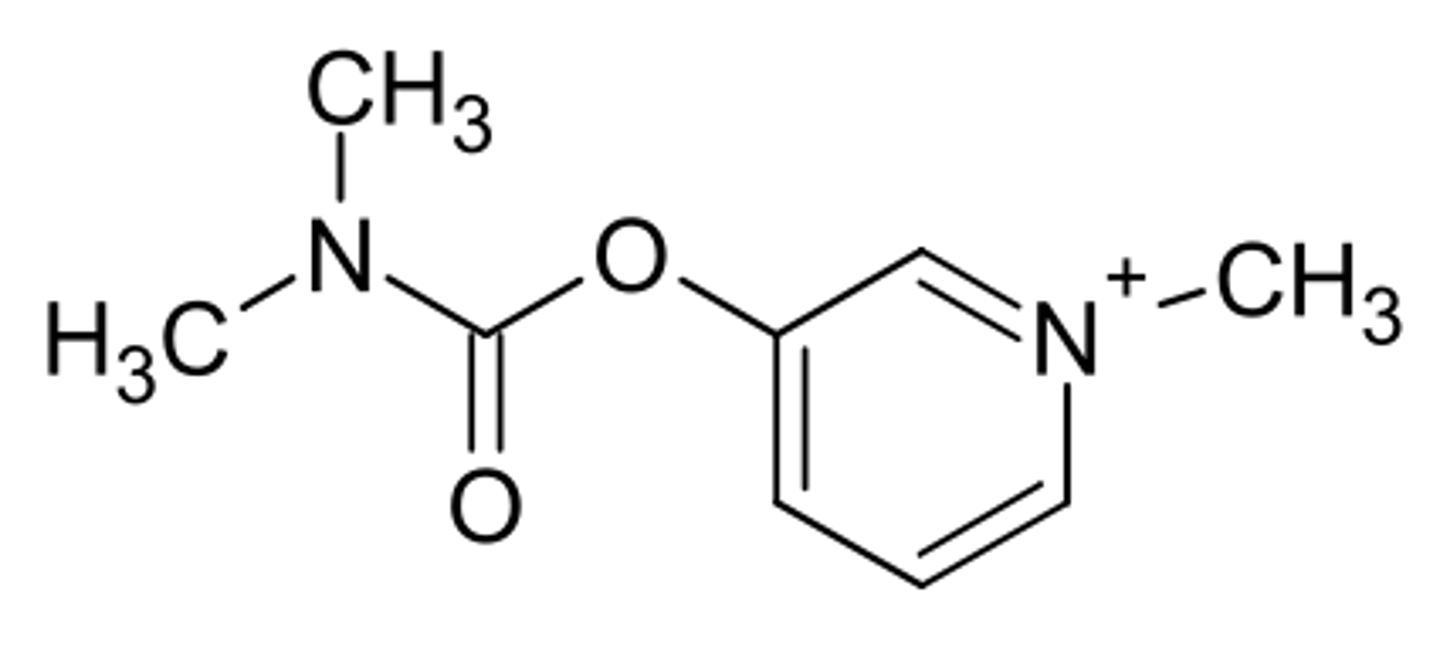
pyridostigmine
AChE inhibitor
closely related to neostigmine
incorporated a charged nitrogen into the pyridine ring
is orally effective and has longer half life than neostigmine
carbamate ester is cleaved by esterases
how is pyridostigmine metabolized
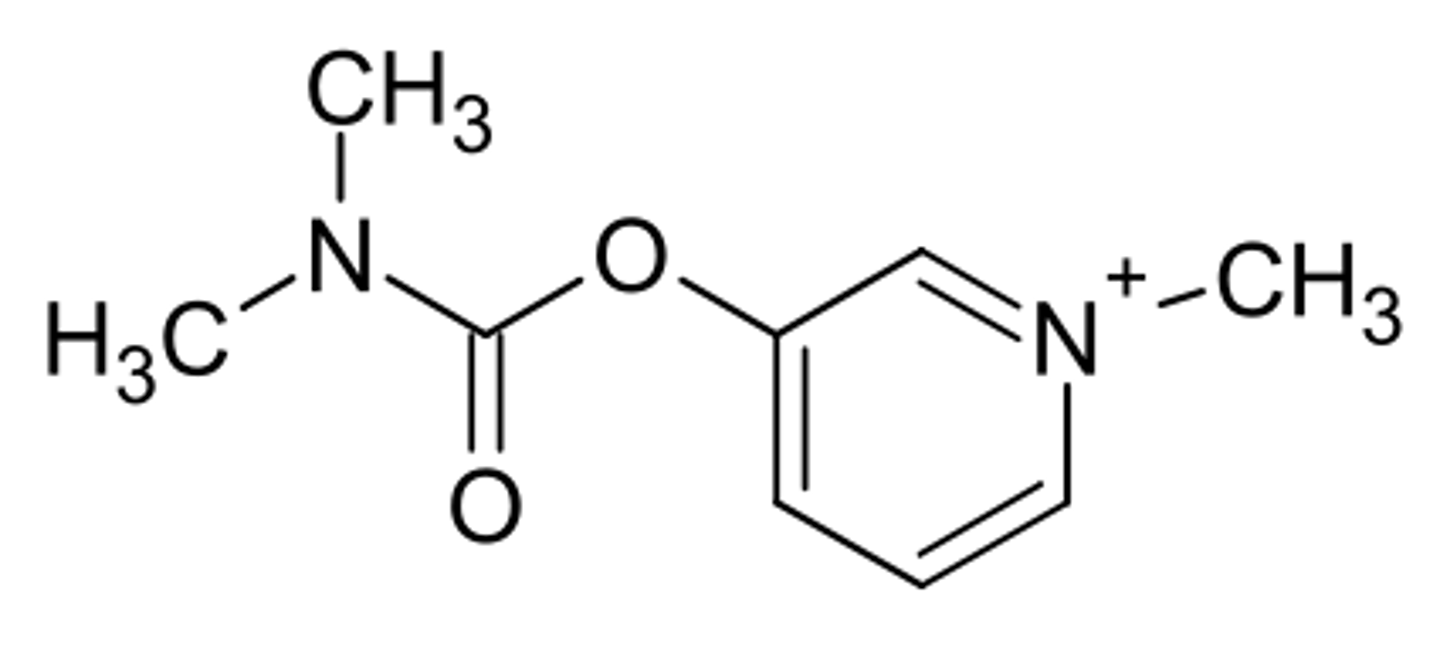
edrophonium chloride
a reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor
competitively inhibits AChE at the neuromuscular junction
used to treat myasthenia gravis to prolong ACh presence in the synaptic cleft
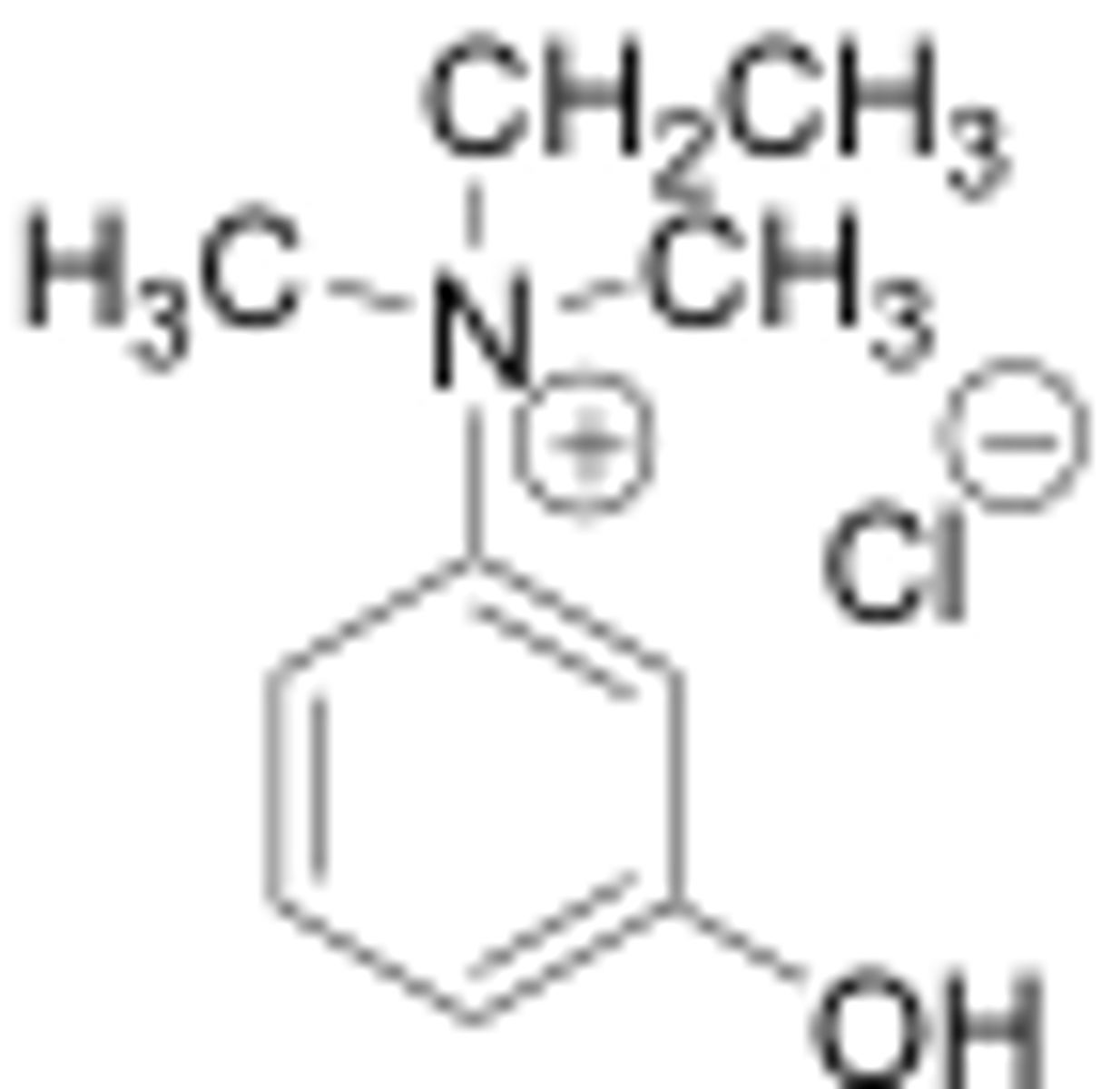
myasthenia gravis
condition in which the body produces autoantibodies which block, inhibit or destroy nicotinic ACh receptors in the neuromuscular junction
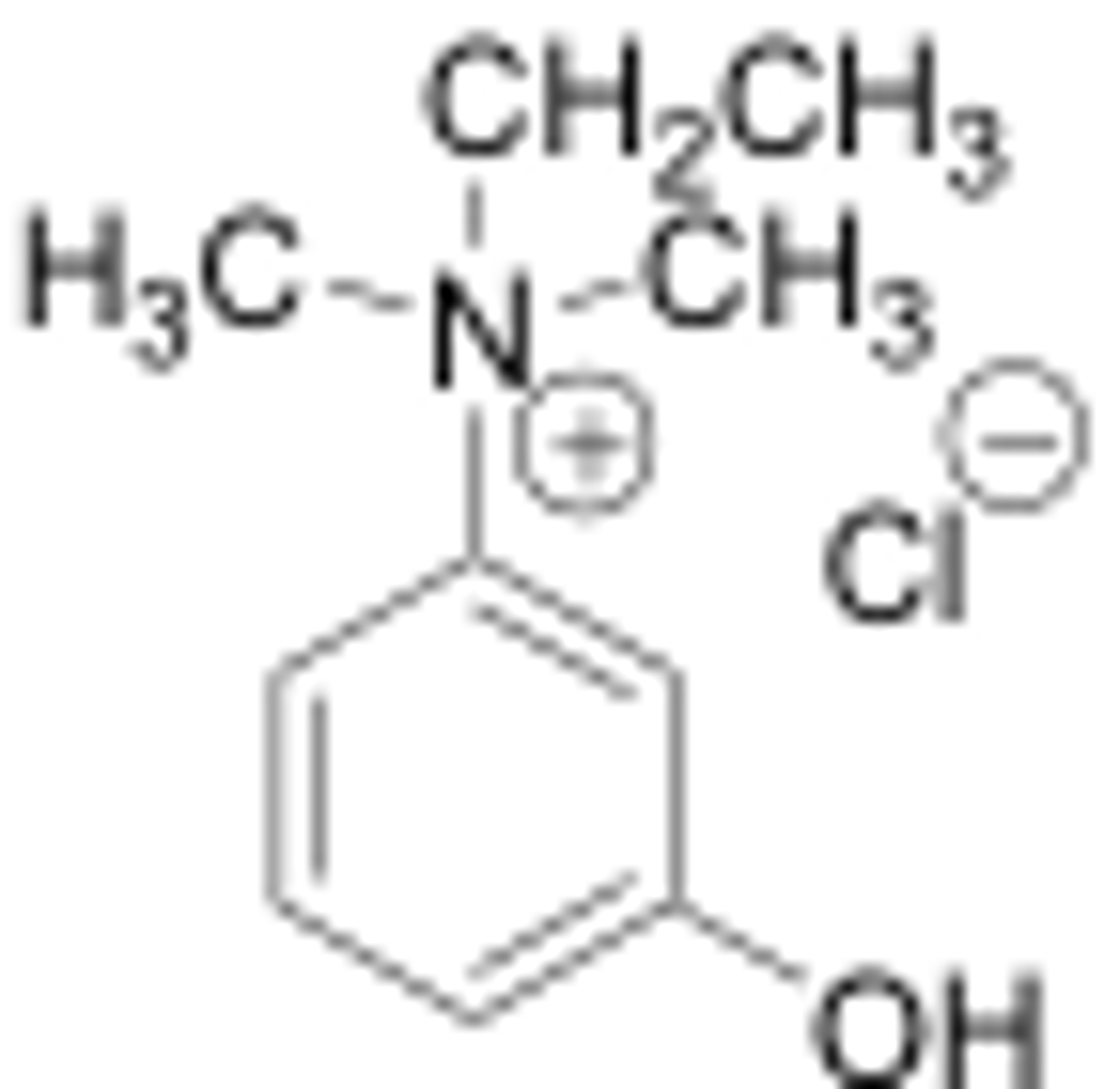
false
it is not a carbamate ester so it does not carbamoylate AChE
T/F edrophonium carbamoylates AChE
insecticidies
what are irreversible inhibitors of AChE used as
prefer reversible inhibition bc irreversible is toxic
irreversible AChE inhibitors cannot be used as medications
are reversible or irreversible AChE inhibitors preferred for medication development
muscarinic antagonists/anticholinergic
substances that bind mAChRs and cause conformational changes that result in no response being produced
parasympatholytics
Drugs that reduce the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system
also called anticholinergics.
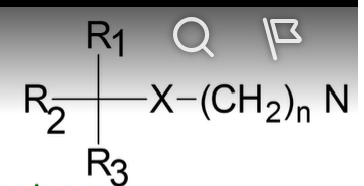
amine group separated by a distance to ester functional group
atropine is usually used
base of muscarinic antagonists
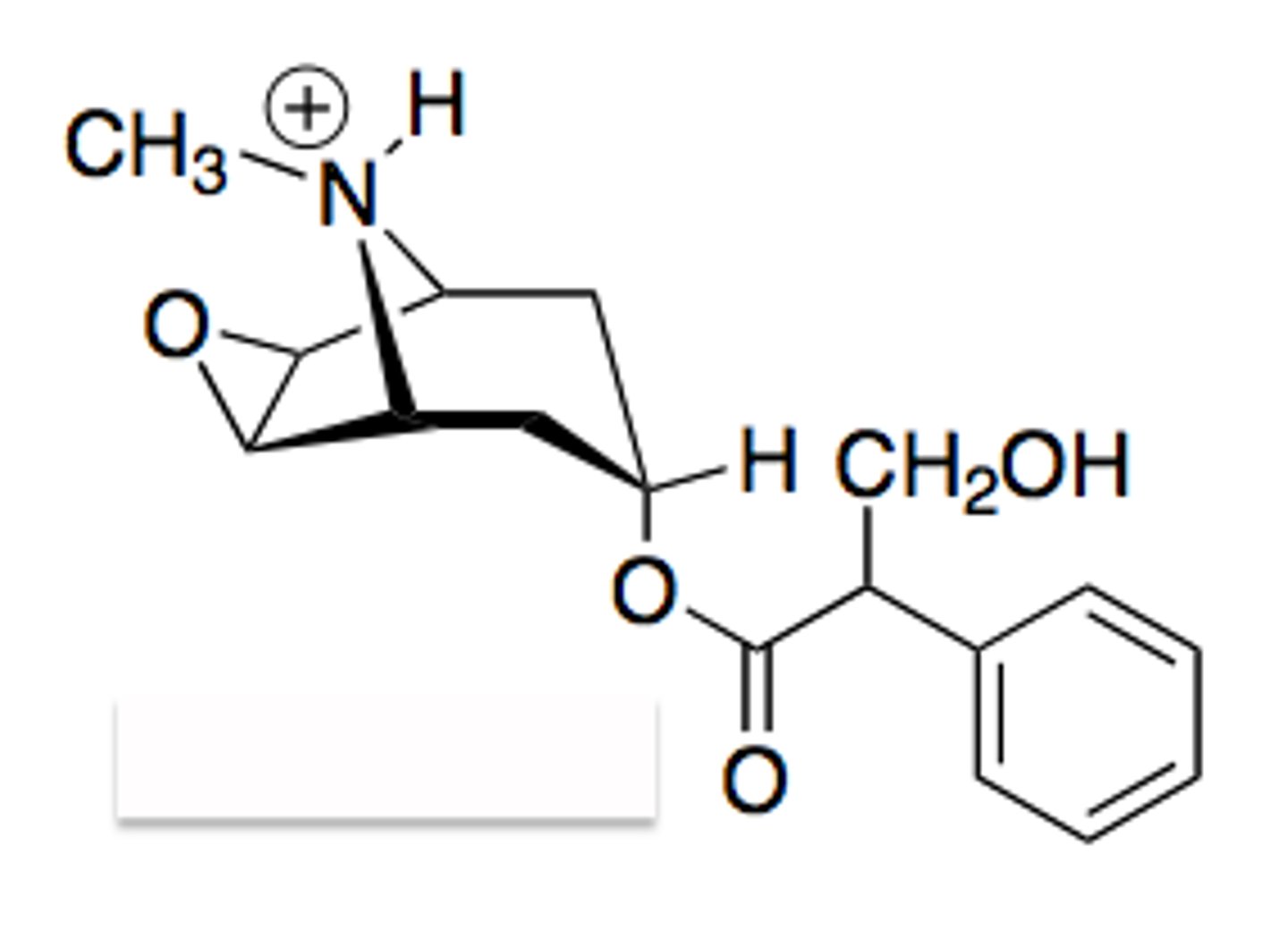
increase potency as mAChRs antagonists
substitution of lipophilic rings on the carbonyl carbon of the ester moiety...
yes
does atropine follow Ing's rule of 5 (which is necessary for cholinergic binding)
substituents at R1 and R2 should be carboxcylic or heterocyclic for max activity
**napthalene type rings will decrease activity
R3 substitution can be H, OH, CH2OH, or CONH2
** substitution must be able to participate in hydrogen bonding
X substitution is best if it is an ester, but presence of an ester is not necessary for activity
N substituent can be a quaternary ammonium salt but it’s not necessary
distance between N and substituted C is usually 2-3 Cs
using the base of mAChR antagonists that is pictured, explain the basic structure and relationship
competitive antagonists
means they must compete with agonists for binding
what type of antagonists are muscarinic antagonists
oxybutinin
muscarinic antagonist
used to relieve urinary and bladder difficulties, including frequent urination and inability to control urination, by reducing muscle spasms
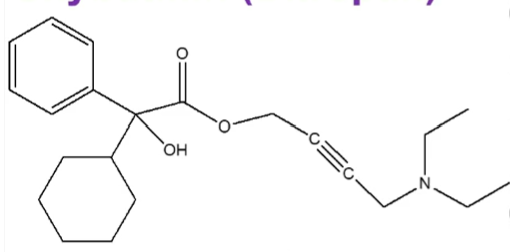
M1-M3
what subtypes of muscarinic receptors does oxybutinin antagnoize
M3
antimuscarinic drugs that maintain bronchiole tone
used in combination with B2 agonists to treat asthma
nicotinic antagonists
nueromuscular blocking agents
chemical compounds that bind to AChR but have no efficacy
1. skeletal neuromuscular blocking agents
2. ganglionic blocking agents
types of nAChR antagonists
tubocurarine
nAChR antagonist
toxic alkaloid derived from the bark of the chondrodendron tometosum plant; known for its use as an arrow poison
a depolarizing neuromuscular blocing agent
decamethonium
first synthesized neuromuscular blocking agent
10-12 unsubstituted Ch2 are optimum for activity
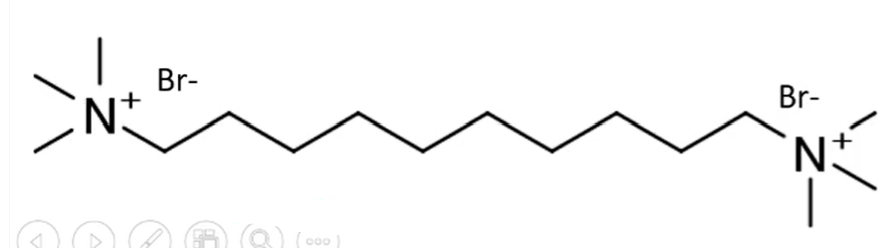
10-12
ideal number of carbons between the nitrogens of decamethonium for optimal activity
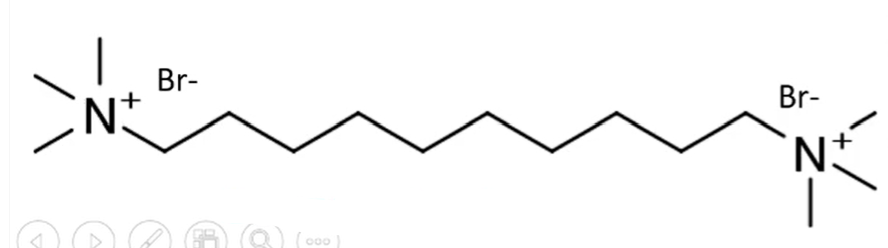
succinylcholine chloride
anticholinergic
dimer of acetylcholine bonded through an alpha carbon of each ACh
is rapidly hydrolyzed and is used for rapid induction of neuromuscular blockage
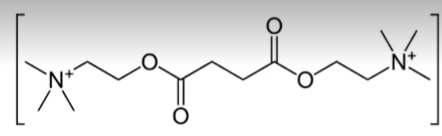
non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents
anticholinergics
agents that have one or two quaternary ammonium groups
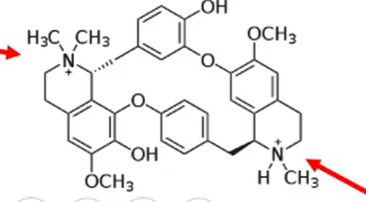
the protonated tertiary amine is converted to a quaternary ammonium group in vivo
what happens to non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents that only have one quaternary ammonium group and a protonated tertiary amine like the one pictured
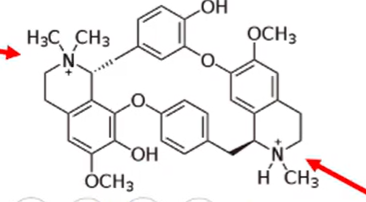
activity differences:
d-tubocurarine: formulations contain bisulfites and can create allergic reactions in patients with bisulfite allergy
metocurine: has two quaternary amines instead of one. formulated as an iodide salt so allergy issue is gone. significantly more potent than d-tubocurarine with a longer duration of action
structure differences:
d-tubocurarine: one quaternary amin and one tertiary amine
metocurine: two quaternary amines. the hydroxyl groups are changed to methyl esthers
difference between d-tubocurarine and metocurine

atracurium besylate
a tetrahydroisoquinoline based neuromuscular blocking agent
nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocker
consists of 2 quaternary ammonium groups located on two substituted tetrahydroisoquinolines with an aliphatic diester connection
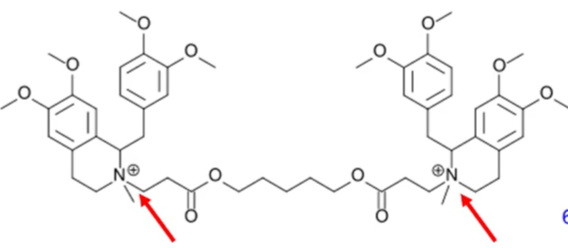
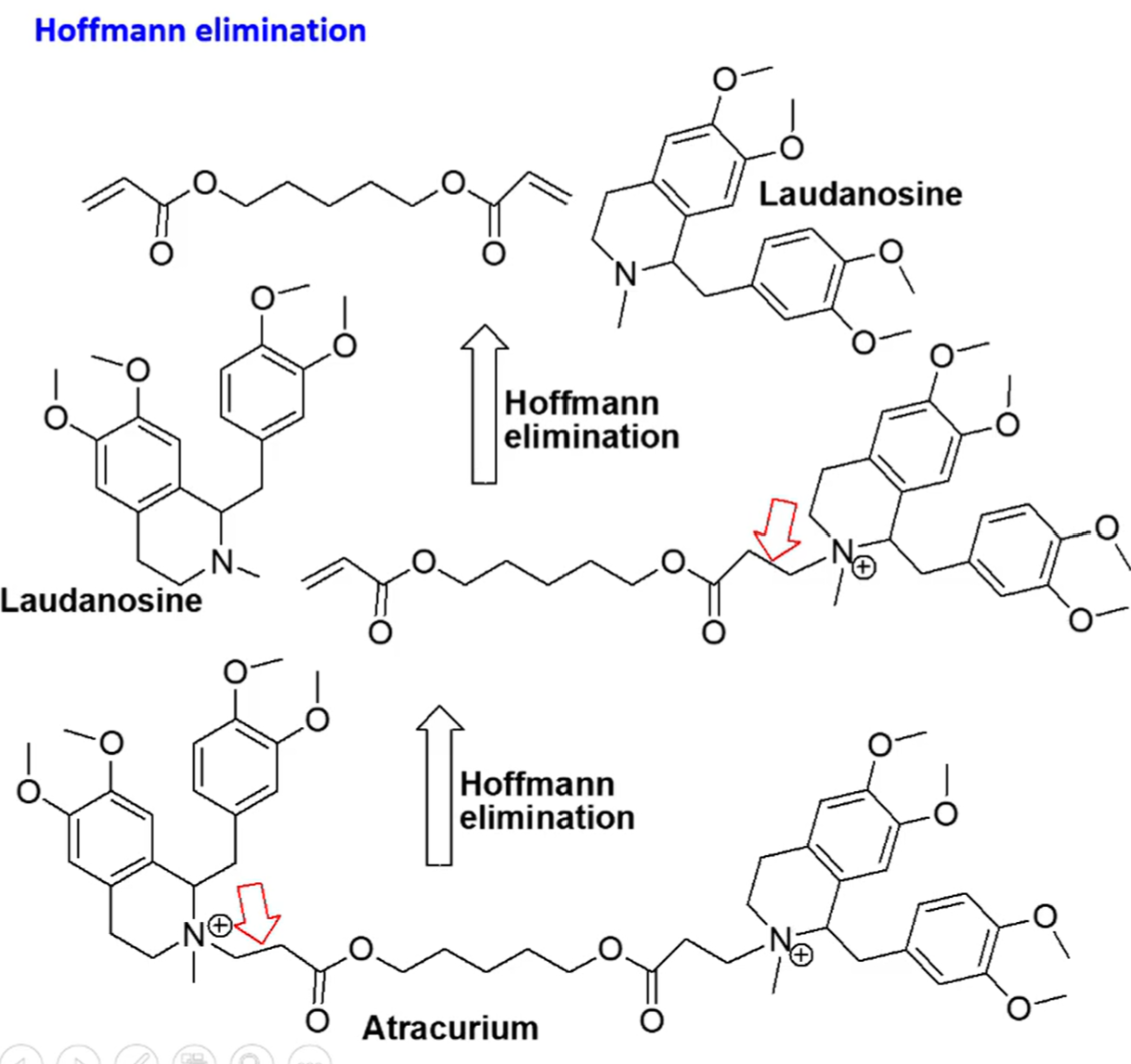
hydrolysis of the ester groups
MAIN PATHWAY non-enzymatic base-ctalyzed reactions (Hoffmann elimination)
metabolism results in formation of laudanosine (an inactive compound)
explain the metabolism of atracurium besylate
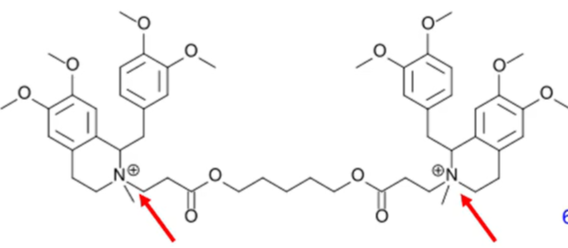
false
it is not metabolized in the liver. Its esters are hydrolyzed and it undergoes Hofmann eliminiation
T/F atracurium besylate is metabolized in the liver
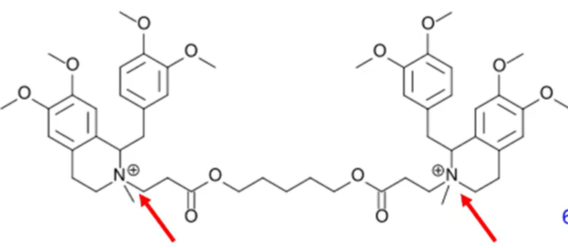
hoffman elimination
aka exhaustive methylation
process where a quaternary amine is reacted to create a tertiary amine and an akene by treatment with excess methyl iodide followed by treatment with silver oxide, water, and heat
temperature and pH
note: increased body pH increases elimination where as decreased temperature decreases elimination
what is hofmann elimination dependent upon
false
hofmann elimination is dependent upon temperature and pH. it is NOT dependent on plasma esterase activity, obesity, age, or status of renal/hepatic function
T/F Hoffman ELIMINATION of atracurium is affected by the level of plasma esterase activity, obesity, age, and the status of renal/hepatic function
true
T/F EXCRETION of atracurium and its metabolite laudanosine is dependent on hepatic and renal functions
mivacurium chloride and doxacurium chloride
anticholinergic
a short duration non depolarizing neuromuscular blocking drug
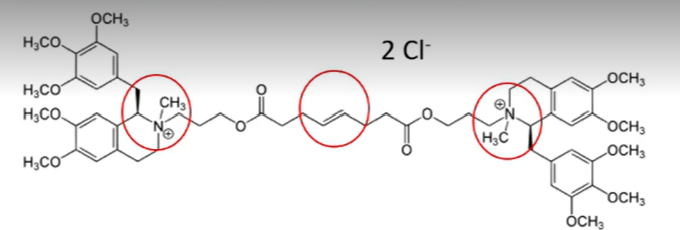
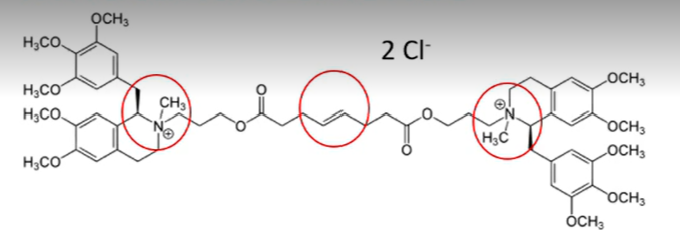
cis-cis
note: trans-trans and cis-trans
which conformation of the diesters of mivacurium chloride has the lowest potency
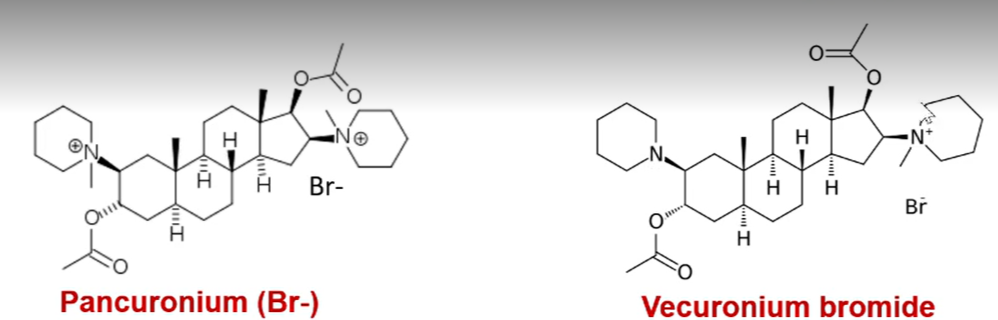
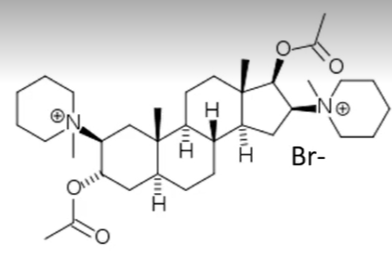
pancuronium
steroid based neuromuscular blocking agent
has a mix of active and inactive metabolites
increases blood pressure and heart ratev
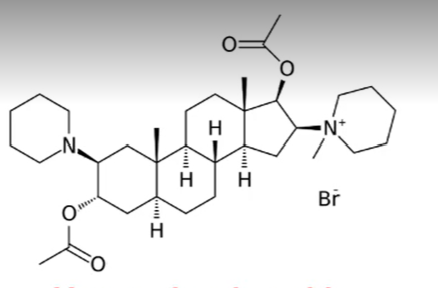
vecuronium bromide
steroid based neuromuscular blocking agent
all of its metabolites are active so it has prolonged neuromuscular action
does not induce histamine so it has no CV side effects
pipecuronium bromide
steroid based neuromuscular blocking agents
excreted unchanged and has minimal cardiovascular side effects
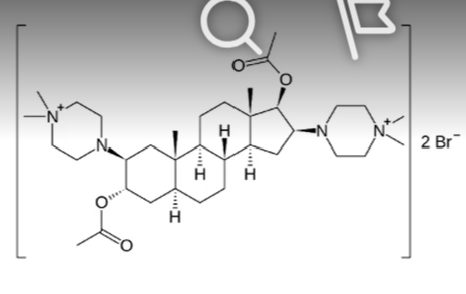
rocuronium bromide
steroid based neuromuscular blocking agent
intermediate acting neuromuscular agent that does not induce release of histamine
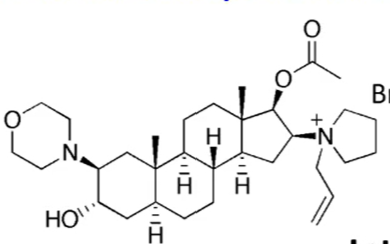
pancruonium: has two quaternary ammoniums and induces histamine to cause side effects of increased blood pressure and heart rate
vecuronium bromide: only has one quaternary ammonium. the tertiary nitrogen is converted to a quaternary ammonium in vivo. it does not induce histamine so it has no CV side effects
pancuronium vs vercuronium bromide. what is the difference