Human Biology - Renal Unit
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Kidney Function
Removes waste and excess water (to regulate blood volume)
2 quarts of urine (waste + water) per 200 quarts of blood daily
Produces:
Erythropoietin (EPO) - Increases RBC production rate under hypoxia
Renin - Regulates blood pressure
Active form of Vitamin D - Maintains calcium for bones and chemical balance in body
Kidney Location
Posterior to diaphragm, abdominal wall and at retroperitoneal position
T12-L3 (superior lumbar region)
Encased in perirenal fat
Anchored by fibrous renal fascia
Due to liver, right kidney (reaches 12th rib) is lower than left kidney (reaches 11th rib)
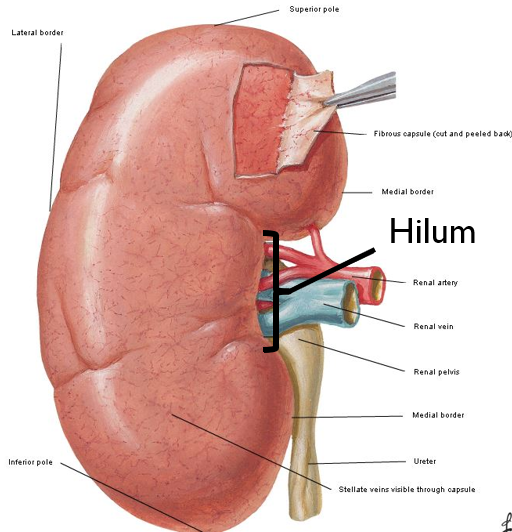
Kidney Shape and Structures
Pair of beans
Renal hilum
Concave
Entering and exiting of structures like:
Renal veins, arteries, ureter, lymph vessels, nerves
Pelvis (transitional epithelium) funnels kidney products to ureter
External Supporting Kidney Structures (internal to external)
Renal capsule - Thin fibrous connective tissue; Attached to kidney
Perirenal fat - Provides cushion around kidney
Renal fascia (of Gerota) - Dense fibrous tissue enclosing kidney and suprarenal gland
Pararenal fat - Adipose tissue holding to abdominal wall
Renal Ptosis
Floating kidney (sinks below normal)
Found in anorexic people
Decline of adipose tissue
Ureter distends
Urine builds up pressure (hydronephrosis) leading to necrosis
Internal Kidney Structures
Renal cortex (outer 1/3) - Granular
Lighter colored
Cortical tissue
Renal corpuscle and tubule of nephron
Has renal columns through medulla to sinus
Renal medulla (inner 2/3) - Striated
Dark and reddish/brown
Has 5-8 renal pyramids
Renal Lobe
Renal pyramid + surrounding cortical tissue
Renal Lobule
Tissue between renal pyramid and kidney surface
Has nephrons with single collecting duct
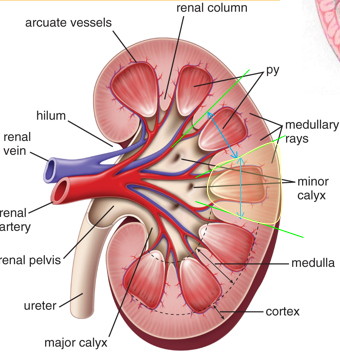
Renal Pyramid Structure
Cone-shapped and striated
Renal papilla
Has perforated end called area cribrosa
Connects to minor calyx
Kidney Drainage Anatomy
Apex of renal pyramid
Minor Calyx - Cup-shaped enclosing papilla
Major Calyx - 2 to 3 branches
Renal Pelvis
Ureter
Bladder
Peristalsis is movement of urine through calyces and pelvis using smooth muscle
Renal Arteries and Veins
Arteries come off aorta at right angles from L1-L2
Reach glomeruli where filtration starts
Right renal arteries longer than left
Aorta → Renal arteries → Segmental → Lobar → Interlobar → Arcuate → Interlobular → Afferent arteriole → Glomerulus → Efferent arteriole
Peritubular capillary network → Interlobular veins → … → Renal → IVC
Renal Nerves
Renal plexus
Autonomic
Alters arteriole size
Sympathetic innervation (preganglions at T10-L1) vasoconstrict arterioles → reduce blood flow to glomerulus
Parasympathetic innervation (CN X) vasodilate arterioles → increase blood flow to glomerulus
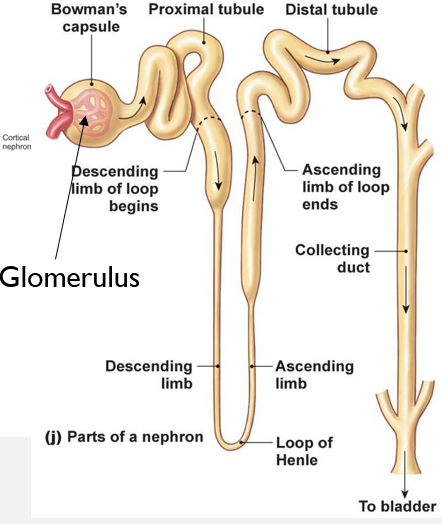
Nephron Structure and Parts
Functional unit of kidney
1-2 million per kidney
Renal corpuscle
Bowman’s capsule
Glomerulus sits in Bowman’s space
Renal tubule - Proximal tube, loop of Henle, distal tube
Urine from multiple tubules drain to collecting ducts
Two types of nephrons
Cortical nephrons
Majority (85%)
Almost entirely in cortex
Short loop of Henle that dips into medulla
Peritubular capillaries entwine around nephron
Juxtamedullary nephrons
Minor (15%)
Found in corticomedullary region
Longer loop of Henle that is deep into medulla
More concentrated urine made (can reabsorb more water)
Peritubular capillaries from hairpin vascular loops called vasa recta
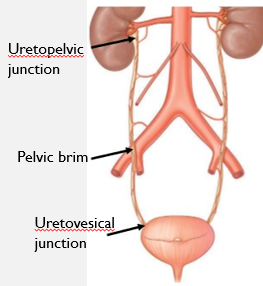
Ureters
Long slender tubes of smooth muscle
Pushes urine through peristaltic waves
Diameter is ~3mm
Starts from L2 of renal pelvis and descends to bladder
Passes anterior to iliac arteries
3 constriction areas (kidney stones here are dangerous)
Uretopelvic junction - Near hilus
Pelvic Brim - Crossing iliac vessel
Uretovesical junction - Near bladder
Kidney Stones
Renal calculi (calcium, magnesium, and uric acid crystals)
Larger than 5 mm can block ureter and cause hydronephrosis
Caused by bacterial infection or blood with high calcium and alkaline levels
Shock wave lithotripsy or open surgery used to treat
Drink lots of water (to dilute urine) or cranberry juice and orange juice (to acidify urine)
Bladder
Carries up to 2 cups of urine
Trigone - Thick smooth muscle where urine enters
Detrusor - Smooth muscle of bladder wall
Urethra - Outlet of bladder
Internal urethral sphincter - Smooth muscle at bladder neck
External urethral sphincter - Skeletal muscle at pelvic floor
Bladder innervation
Parasympathetics - Pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2-4)
Motor to detrusor muscle for contraction
Relaxes internal urethral sphincter for micturition (peeing)
Sympathetics
Exact opposite mechanism of parasympathetics
Somatic nervous system
Controls external urethral sphincter
“Toilet training” muscle
Sensory stretch receptors
Signal afferent fibers from stretched bladder when full
Provides urge to urinate
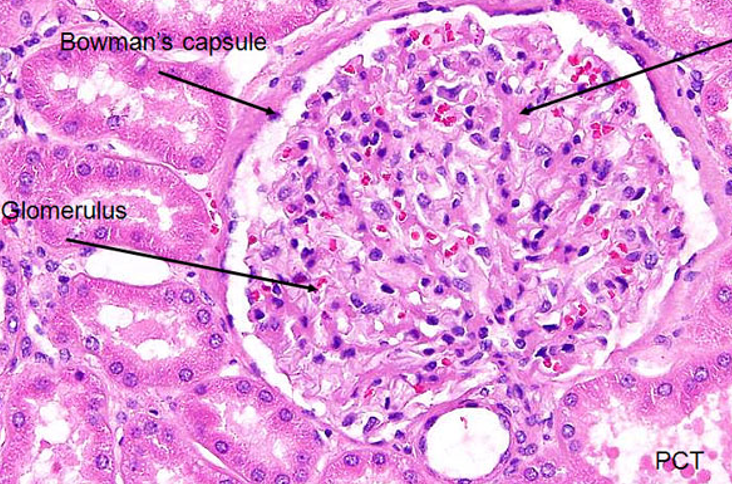
Renal Corpuscle Histology
Bowman’s capsule (from urinary pole)
Parietal layer - bowman’s capsule proper (flattened epithelial cells)
Visceral layer - podocytes
Bowman’s space
Glomerulus (from vascular pole)
Afferent arterioles
Efferent arterioles
Be able to identify all 3 layers of bowman’s capsule histologically
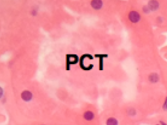
Proximal Convoluted Tubule Histology
Has long convoluted part (pars convoluta) and straight part (pars recta)
Does 75% of water and ion reabsorption
Long columnar epithelial cells with brush border
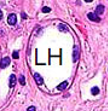
Loop of Henle Histology
Thin descending limb - simple squamous epithelium
Thick ascending limb - low cuboidal epithelium
Uses countercurrent system to generate high osmotic pressure in renal medulla
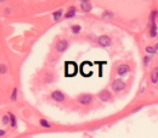
Distal Convoluted Tubule Histology
Actively reabsorbs sodium ions via aldosterone
Secretes hydrogen/potassium ions
Lumen is clearer (lacking brush border) and fewer in number than PCT
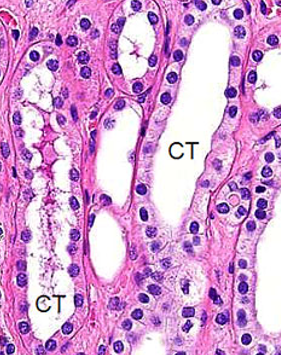
Collecting Tubule and Collecting Duct Histology
End of nephron
Urine is concentrated from passive water reabsorption in medulla
CT is simple cuboidal epithelium
CD is simple columnar epithelium
Duct of Bellini Histology
Formed when CDs merge
Drain urine from papilla to calyx
Renal Vasculature Components
Artery
Renal Artery (from aorta)
Segmental Artery
Lobar Artery
Interlobar artery (between pyramids and reaches corticomedullary junction)
Arcuate artery (at junction perpendicular to interlobar arteries)
Interlobular (cortical radial) arteries
Afferent glomerular arterioles
Efferent glomerular arterioles supply cortical labyrinth in cortex and form arteriolae recta in medulla
Veins
Venae recta in medulla; interlobular veins in cortex
Follows artery system from Arcuate vein to Renal vein and then IVC
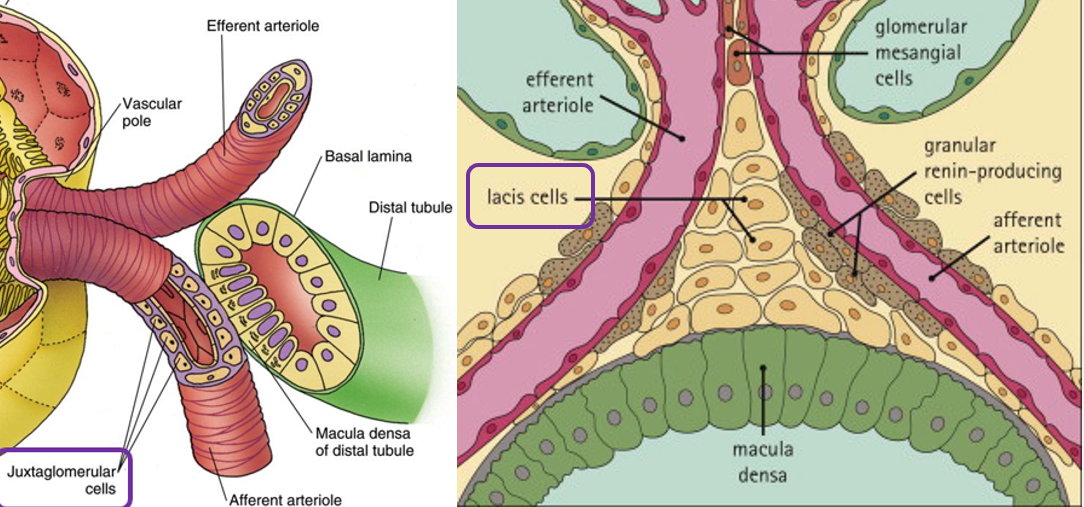
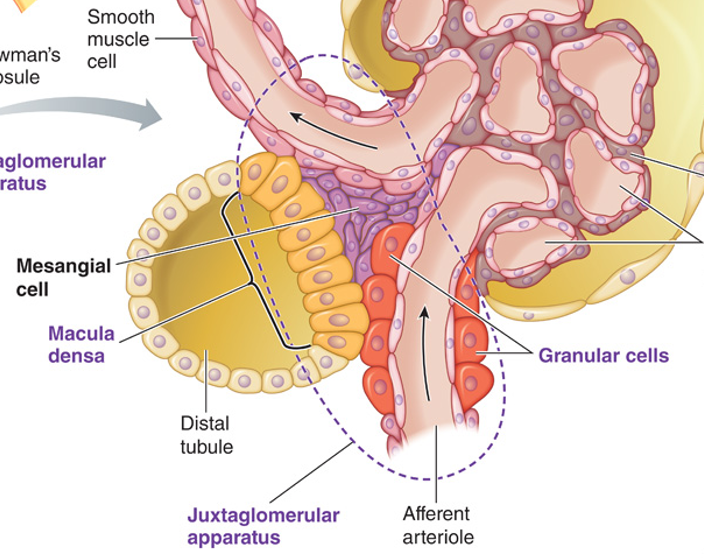
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Histology
Regulates systemic blood pressure via RAAS system
Macula Densa
Specialized cells of DCT
Sensitive to sodium ion concentration
Use osmoreceptors for renin secretion
Juxtaglomerular cells
Specialized smooth muscles cells of afferent arterioles
Contain renin granules
Use renal baroreceptors for renin secretion
Extraglomerular mesangial cells
Conical mass of cells between afferent and efferent arterioles
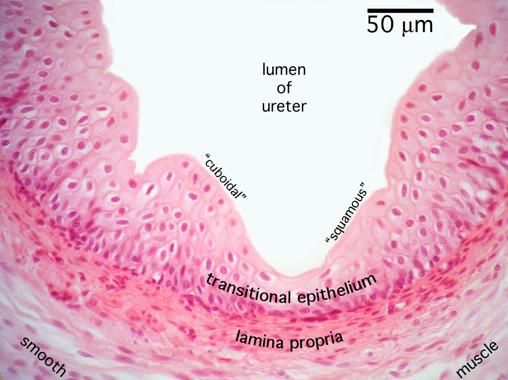
Ureter Histology
Convoluted lumen
Transitional epithelium
Lamina propria
Smooth muscle - longitudinal
Smooth muscle - circular
Urinary Bladder Histology
Transitional epithelium
Lamina propria
Smooth muscle - longitudinal
Smooth muscle - circular
Smooth muscle - longitudinal
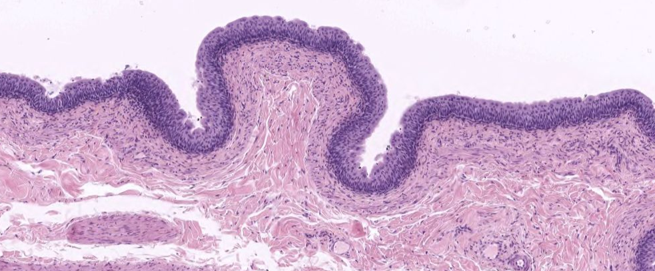
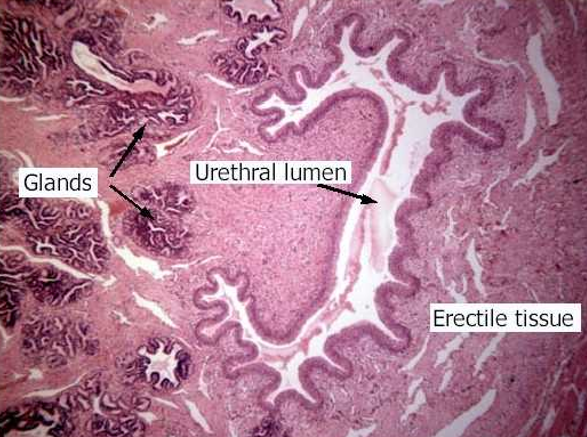
Urethra Histology
Kidney Functions
Maintain H2O balance (vasopressin)
Maintain osmolarity
Maintain plasma volume (aldosterone)
Regulate ECF ions
Use RAAS system to modulate blood pressure
Eliminate waste products
Maintain acid-base balance in body
Convert vitamin D to D3 (active form)
Produce erythropoietin
Vascular Parts of Nephron
Afferent Arteriole - Carries unfiltered blood to glomerulus
Glomerulus - Tuft of capillaries filtering protein-free plasma
Efferent Arteriole - Carries filtered blood from glomerulus
Peritubular capillaries - Supply renal tissue and exchange fluid in tubular lumen
Tubular Parts of Nephron
Bowman’s capsule - Collects glomerular filtrate
Proximal tubule - Uncontrolled reabsorption and secretion of some substances
Loop of Henle (of juxtamedullary nephrons) establishes osmotic gradient in medulla to produce urine of varying concentration
Distal Tubule and Collecting Duct - Variable reabsorption of K+ and H+; urine leaves
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
Combines vascular and tubular components
Macula Densa
Distal Tubule
Responds to sodium changes (decrease causes renin release)
Granular (Juxtaglomerular) cells
Smooth muscles of afferent arteriole
Produces renin when innervated by sympathetic fibers
Detect decrease in blood pressure or NaCl
Extraglomerular mesangial/lacis cells
Innervated by sympathetic fibers
Have actin filaments
Modulate GFR
Kidney Fun Facts
180 L of plasma filtered and 1.5 L is eliminated
Kidney filters plasma about 65 times a day
If no reabsorption happens, the entire plasma volume will be urinated in <30 minutes
1 in 7 adults have kidney disease (90% do not know about it)
Up to 75% kidney tissue can be destroyed before loss of kidney function is detected
Glomerular Filtration
Plasma is passively forced through glomerular membrane
Damage (from high BP, diabetes, family history, infection, autoimmune disease, toxic agents, obstruction, or loss of blood supply) causes protein and RBC leakage
Fluid passes through three layers
Glomerular capillary wall (single endothelial cell layer; 100x more permeable to water and other solutes)
Basement membrane (collagen and negatively charged glycoproteins)
Inner layer of bowman’s capsule (podocytes encircling glomerulus tuft)
Correlation of Charge and Size of Proteins
Freely at below 7000D
From 7000-70000D, it becomes difficult with increased size
Three forces
Glomerular capillary blood pressure - Depends on heart contraction and blood flow resistance by arterioles (55 mm Hg)
Plasma-colloid osmotic pressure (oppose filtration) - Osmotic pressure on plasma proteins across membrane (30 mm Hg)
Bowman’s capsule hydrostatic pressure (oppose filtration) - Pressure exerted by initial part of tubule (15 mm Hg)
GFR = Kf * Net Filtration Pressure
Kf depends on surface area and permeability
Unregulated and Controlled Influences on GFR
Unregulated Influences
Liver disease causes loss of plasma proteins (inc GFR)
Dehydrating Diarrhea is loss of fluid (dec GFR)
Obstructions such as kidney stones (dec GFR)
Controlled Adjustments
Autoregulation - Preventing spontaneous GFR changes by keeping MAP at 80-180 mmHg, prevents dangerous salt/water balance changes, protects glomerular capillaries from hypertensive damage
Myogenic Mechanism - Responds to high GFR from high blood pressure by constricting afferent arteriole when high oxygen or sympathetic activity occurs to reduce GFR
Tubuloglomerular Feedback - Macula densa in distal tubule will respond to NaCl levels in filtrate: high GFR → high NaCl → ATP production → vasoconstriction decreasing GFR; low GFR → low NaCl → Nitric Oxide production → vasodilation increasing GFR
Extrinsic Sympathetic Control - Long-term regulation of arterial blood pressure overriding autoregulation via sympathetic nervous system to afferent arterioles
Low arterial blood pressure → Detection by baroreceptors → increase sympathetic activity → arteriolar vasoconstriction → dec GFR → conservation of fluid and salt → increase arterial blood pressure
Tubular Reabsorption
Transfer of substances from tubular lumen to peritubular capillaries
Substance must cross luminal cell membrane, then cytosol, then basolateral cell membrane, then interstitial fluid, and then the capillary wall
Can be passive (ex: water or urea) or active (ex: glucose, amino acid, Na+, PO43-)
Na+ Reabsorption
Active (using Na+/K+ ATPase)
Early and Unregulated
Occurs in proximal tubule, ascending limb of loop of Henle (causing varying urine concentrations), and distal/collecting tubules (hormonal; renin release results in aldosterone [places more Na+ leak channels and Na+/K+ pumps])
Reabsorption of nutrients in proximal tubule mechanism
Primary active transport: Epithelial cell removes all sodium using Na/K pump
Secondary active transport: Sodium and glucose enter epithelial cell via symport carrier (SGLT)
Facilitated diffusion: High concentration of glucose uses GLUT to move glucose out of cell to blood
Water follows reabsorbed sodium by osmosis, affecting blood volume and pressure
Inhibited by ACE inhibitors (prevents Angiotensin II formation), ARB (Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker), and Aldosterone Receptor Blocker
ANP (in atria) and BNP (in ventricle) are released when cardiac muscle is stretched (indicating high volume) to promote natriuresis and diuresis
Inhibits RAAS system, dilates afferent arterioles to increase GFR, and inhibits sympathetic activity
Only substance that does not have tubular maximum
Unique Drugs inhibiting Sodium Reabsorption
Loop diuretics - Inhibit Na/K/Cl cotransporter in thick ascending limb
Thiazide diuretics - Inhibit Na/Cl transporter in distal tubule (less efficacious and most commonly used)
Potassium sparing diuretics - Prevents aldosterone-based sodium reabsorption in distal tubule (does not cause hypokalemia)
PO43- Reabsorption
Subject to control
Most filtered phosphate is reabsorbed in proximal tubule via sodium symporter
Tubular maximum is very similar to normal plasma concentration unless an excessive amount is present
Urea Reabsorption
Made from protein degradation
Water reabsorption causes urea concentration in tubular fluid to increase → 50% of urea passively diffuses and gets reabsorbed in proximal tubule
Improper urea elimination causes high BUN and prevents hemostasis (increases bleeding)
Tubular Secretion
Transfer of substances from peritubular capillaries to tubular lumen
Can add substances to hasten elimination
K+ Secretion
Actively secreted in distal tubule by Na/K ATPase with help of aldosterone
Depending on stimulus, aldosterone performs either sodium reabsorption or potassium secretion
H+ Secretion
Regulates acid-base balance and secreted in proximal and distal tubules
Organic ion secretion
Usually are foreign compounds in body like food additives, pollutants or drugs
Removed in proximal tubule
Can not adjust to increased dosages
Stages of CKD
Stage 1 - Kidney damage with normal function (GFR > 90 mL/min)
Stage 2 - Kidney damage with mild function loss (60-89)
Stage 3a - Mild to moderate kidney function loss (45-59)
Stage 3b - Moderate to severe kidney function loss (30-44)
Stage 4 - Severe kidney function loss (15-29)
Stage 5 - Kidney failure (GFR < 15)
Types of Renal Failure
Acute - Sudden onset, rapidly reduced urine formation, reversible
Chronic - Slow, progressive, insidious loss of renal function
End-Stage - 90% of kidney function is lost and every organ system is affected
Kidney Failure Symptoms and Treatment
Symptoms
Nausea, vomiting, fatigue, abnormal swelling of feet, puffiness around eyes, anemia
Treatment
Hemodialysis - Blood cleaned through special filter in dialysis machine via artificial kidney
Peritoneal Dialysis - Blood uses peritoneal lining as natural filter (self-administered)
Kidney Transplant - Long wait list, compatibility and medical tests needed, better quality of life and less restricted diet, needs immunosuppressant medications
Dental Management of End Stage Kidney Disease
Patients with stage 4-5 kidney disease require special considerations
Patients on dialysis have higher risk of bleeding from anti-coagulants and dental procedures should be avoided on dialysis days
Patients with kidney transplant have high risk of infection due to immunosuppression medications and need dental examination pre and post-transplant
Patients with oral lesions have low GFR values
Oral lesions are very common in CKD patients
Kidney Disease Warning Signs
Hypertension
Hematuria or Proteinuria
Creatinine and BUN levels outside normal range (indicating metabolic waste buildup)
BUN accumulates for other reasons too like dehydration or high protein meal so BUN/creatinine test is recommended
GFR < 60 mL/min
More frequent and painful urination
Puffiness around eyes, swelling of hands and feet
Plasma Clearance
Volume of plasma cleared of substance per minute
C = Ucon*Uvol/Pcon
Inulin (produced from Jerusalem artichokes) is not reabsorbed or secreted. Used to calculate GFR because Cinulin = GFR
Glucose is filtered and completely reabsorbed (C = 0)
Urea is filtered and partially reabsorbed, but not secreted (C < GFR)
Creatinine, H+ and PAH are filtered and secreted but not reabsorbed (C > GFR)
PAH is almost completely removed in one pass
Filtered Fraction = GFR/RPF (renal plasma flow = total urine excretion) = Cinulin/CPAH
Kangaroo Rats
Survive with very little water from seeds
Do not pant or sweat
Have long loops of Henle from juxtamedullary nephrons to retain water
Excrete urine pellets
Countercurrent Multiplication
Osmotic gradient formed by hairpin loop deep in medulla only
Countercurrent flow allows for multiplication in concentrating effect
Ascending limb actively transports only NaCl allowing descending limb to diffuse only water
Entering fluid is isotonic, exiting fluid is hypotonic, bottom of loop is hypertonic
Interstitial fluid has concentration gradient from 300-1200 mOsm/L
Vasa Recta maintains this same gradient to allow for proper reabsorption
Benefit is that urine exiting distal tubule is dilute and interstitial fluid can make more concentrated urine
Vasopressin
Independent of solute reabsorption
Produced in hypothalamus and stored in posterior pituitary
Signals distal tubule and collecting duct to reabsorb water (using AQP-2 channels)
AQP-3 and 4 used for outside tubule osmosis to blood
Alcohol inhibits vasopressin
Micturition
High urine levels in bladder → stretch receptors activate parasympathetics → smooth muscle of bladder wall contracts to urinate
Internal (involuntary) and external (voluntary) urethral sphincters
Micturition is stopped by voluntarily tightening external sphincter and pelvic diaphragm
Urinary Incontinence - Inability to prevent urine discharge (impaired external sphincter decreases incontinence)
Water Inputs, Outputs, and Breakdown in Body
Inputs -
Drinking liquids and eating solid foods
Metabolically produced water
Output -
Lungs (insensible)
Non-sweating skin (insensible)
Sweating
Feces and urine
Body Composition -
60% water (fairly constant within individuals; variation between different tissue types like adipose tissue vs muscle)
ICF - 2/3 of H2O
ECF - 1/3 of H2O (20% plasma, 80% interstitial fluids like cerebrospinal, synovial and digestive fluid)
Differences between ECF and ICF
Proteins in ICF do not permeate the cell membrane to leave cells
Na+ and K+ levels differ in each because of ATPase pump
Mechanisms to regulate blood pressure using ECF Volume
Short-term
Baroreceptor reflex alters cardiac output and total peripheral resistance
Bulk flow between plasma and interstitial fluid
Modify sodium levels
Low blood pressure → sympathetic stimulation (→ decreased GFR → decreased Na+ filtered) or RAAS (→ increased aldosterone → increased Na+ reabsorbed) → decreased Na+ and Cl- excretion → conserve NaCl and fluid → increases blood pressure
Afferent arterioles in nephrons have more alpha-1 adrenergic receptors than efferent arterioles causing decreased GFR in sympathetic stimulation
Long-term
Kidneys and thirst mechanism control urinary output and fluid intake
Congestive Heart Failure
BP and CO decrease
Patients have increased ECF volume
Granular cells respond as if ECF has decreased, triggering RAAS system and NaCl/water retention
ECF increases but not in vascular system causing pulmonary and generalized edema
Tonicity
Deficit of free water in ECF causes hypertonicity causing cells to shrink
Caused by insufficient water intake, excessive water loss (sweating/vomiting/diarrhea) or ADH deficiency by either alcohol consumption or diabetes insipidus
Results in brain neuron shrinkage, circulatory disturbances, and dry skin, sunken eyeballs, dry tongue
Excess free water in ECF causes hypotonicity causing cells to swell
Caused by patients with renal failure who drink lots of water, healthy people who rapidly ingest water, or improper use of vasopressin
Results in brain failure, weakness (muscle cell swelling), hypertension and edema, water intoxication
ADH Trigger Mechanisms
Hypothalamic osmoreceptors and thirst centers of hypothalamus secret ADH when osmolarity increases
Left atrial volume receptor monitors blood pressure. When artery pressure reduces, vasopressin is released and stimulates thirst (large scale changes only)
Angiotensin II stimulates ADH and thirst (also does arteriolar vasoconstriction) when RAAS is activated to conserve Na+
Factors that do not link vasopressin and thirst
Dry Mouth triggers thirst
Alcohol and Caffeine inhibit ADH; Pain and infection trigger ADH
Exercise Physiology
Heat exhaustion causes hypotension, sweating and disorientation
Heat stroke causes failure of temperature control center in hypothalamus causing extreme confusion/unconsciousness
Exercising muscles and cooling mechanisms compete for plasma volume and exercising muscles win tug of war
Adaptations include increased sweating at lower temperatures and more dilute
Urinalysis
Detects kidney disorders in three ways:
Appearance
Pale yellow or clear indicates hydration
Red or red-brown indicates blood or drug
Cloudy indicates excess salts, protein, or pus
Dipstick
pH range from 6-7.4 normally
High pH may indicate kidney stones or urinary infection
Low pH indicates acidosis
1.002 to 1.03 specific gravity normally
Increases with dehydration, proteinuria, or excess ADH secretion
Decreases with diabetes insipidus or nephritis (inability to concentrate urine)
Microscopic
Tamm Horsfall protein appears in small amounts
Albumin is abnormal and represents leak
Proteinuria is represented from 0 to 1+ to 4+ for creatinine or albumin
Athletes undergo athletic pseudonephritis where many have proteinuria after strenuous exercise from decreased glomerular flow rate caused by RAAS (renin)
Positive cases in Urinalysis
Positive test for glucose (tastes sweet) - diabetes mellitus
Lack of anything (tastes bland) - diabetes insipidus
Positive test for ketones - diabetic ketoacidosis (body breaks down fat in absence of insulin causing ketone buildup)
Positive test for nitrite - urinary tract infection
Positive test for leucocyte esterase - white blood cell presence
Positive test for bilirubin - liver or gall bladder dysfunction
Positive test for RBC - urinary tract damage or kidney stones
Positive test for WBC - Urinary tract infection
Ultrasound, CT Scan, Kidney Biopsy
Ultrasounds - abnormalities in size or position of kidneys and obstructions like stones or tumors using sound waves
CT Scan - structural abnormalities and presence of obstruction using X-rays
Kidney Biopsy - Identify disease process and extent of damage of kidney. It’s also why kidney transplant may not be doing well
Fluoride
Fluoride is associated with hard tissue such as bone and teeth because of affinity to calcium
99% of fluoride is in bones and teeth
Fluoride reduces incidence of dental caries and reverses progression of lesions
US Public Health Services optimal range of 0.7 ppm fluoride with upper limit of 2.0 ppm (recommended) and 4.0 ppm (enforceable)
Major route of fluoride removal from body is by kidneys
Amount of H2O, beverages, toothpaste, plasma concentration, GFR and urine flow, and partial reabsorption of F- affect renal clearance of F-
Because HF can diffuse back to blood and not F-, diets that promote acidic urine help F- remain deposited on bones
Person with advanced kidney disease and high fluoride consumption risks fluorosis
Potassium
Needed for action potentials and maintaining resting membrane potential (Potassium Nitrate used in sensitivity relief toothpastes due to depolarization)
Intake remains constant despite dietary fluctuations (K+ excretion only occurs during high intake)
ATPase maintains high potassium levels in cell
Adrenal gland tumor increases aldosterone causing increased plasma Na+ levels and decreased K+ levels; Addison’s Disease causes opposite effect
Diuretics cause potassium depletion (only potassium sparing diuretics do not cause hypokalemia)
End-stage renal disease causes hyperkalemia
Insulin (diabetics have hyperkalemia), epinephrine (beta2 stimulation; prevents hyperkalemia during exercise; beta blockers cause hyperkalemia), and aldosterone promote K+ uptake into cells
High K+ levels, ADH, and aldosterone cause K+ excretion
Aldosterone paradox allows K+ secretion or Na+ reabsorption based on stimulus
H+ and pH of Blood
Normal H+ concentration is 4×10^-8 M (pH of 7.4)
Beyond 7.35-7.45 is considered acidosis/alkalosis
Beyond 6.8-8.0 is not compatible with life
Acidosis causes CNS depression; alkalosis causes over excitability
H+ levels affect shape of function of proteins
H+ levels affect K+ levels in body
Carbonic acid formed from combining CO2 and H2O and releases H+ and HCO3-
Inorganic acids produced during breakdown of nutrients
Organic acids result from intermediary metabolism
Chemical Buffer Mechanism
First line of defense against pH changes
H2CO3:HCO3- buffer system against non-carbonic acids in ECF
(H2CO3 ←> H+ + HCO3-)
Shifts to H2CO3 production when exercising muscles
Shifts to H+ production during vomiting and loss of digestive juices
pH = pK + log[HCO3-]/[CO2]
[HCO3-]/[CO2] = kidney function/lung function = 20/1
When pH is near pK, the buffering power is very strong
Protein buffer system works intracellularly and contains both acidic and basic groups that can accept or give H+ ions
Hemoglobin buffer system buffers H+ generated from CO2 between tissues and lungs
Phosphate buffer system undergoes intracellular buffering and is only buffer system in kidneys (most HCO3- and CO2 is reabsorbed)
Respiratory Buffering Mechanism
Second line of defense against pH changes (can partially return pH to normal)
Acts in minutes
Ventilation eliminates acid from body
Kidney Buffering System
Third line of defense against pH changes acting in hours to days
Either secretes excess H+ or adds new HCO3- to plasma during acidosis; does opposite for alkalosis
Renal H+ secretion in proximal tubule uses ATPase pumps and Na+-H+ antiporters
Renal H+ secretion in distal and collecting tubules uses Type A and B intercalated cells interspersed among principal cells
CO2 (from blood vessel) and H2O combine to make HCO3- and H+
Under acidosis, Type A Intercalated disks have ATPase in luminal membrane, causing hydrogen ion secretion along with potassium and bicarbonate reabsorption
Under alkalosis, Type B Intercalated disks have ATPase in basolateral membrane, causing hydrogen ion reabsorption along with potassium and bicarbonate secretion
In acidosis, secreted H+ ions are buffered by either NH3 or phosphate before being excreted
Renal Handling of Potassium and Acid-Base Balance
Na+ reabsorption is matched by either K+ or H+ secretion by Aldosterone
Acute Metabolic Acidosis causes H+ secretion and K+ retention/hyperkalemia
Hypokalemia causes K+ retention and H+ secretion
Hyperkalemia causes K+ secretion and H+ retention
Metabolic and Respiratory Alkalosis and Acidosis
Respiratory Acidosis
CO2 retention from hypoventilation caused by lung disease, reduced respiratory activity from nerve/muscle disorders or holding breath
Respiratory Alkalosis
CO2 loss from hyperventilation caused by fever, anxiety and high altitudes
Metabolic Alkalosis
Caused by vomiting or ingesting alkaline drugs
Relieved by buffers liberating H+, reducing ventilation to retain CO2, or kidneys conserving H+ and excreting HCO3-
Metabolic Acidosis
Caused by severe diarrhea, diabetes mellitus, strenuous exercise, or uremic acidosis
Relieved by buffers taking up more H+, or lungs blowing off H+ by removing CO2, or kidneys excreting more H+ and conserving HCO3-