Embryo 9 - Vasculature
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
What are the two processes of vascular development?
Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis
What is vasculogenesis?
Angioblasts coalesce to form major vessels
What is angiogenesis?
Sprouting of new vessels from existing vessels
What regulates angiogenesis?
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)
Where do extraembryonic vessels initially form?
From the yolk sac during the 3rd week
What cells form blood islands?
Hemangioblasts
Where do hemangioblasts form blood vessels?
Within the yolk sac and lateral plate mesoderm
When do blood islands appear?
Week 3
Where do blood islands appear?
Mesoderm surrounding the yolk sac
How do the dorsal aortae form?
From blood islands bilaterally
What major structures are associated with the dorsal aortae?
Primitive heart tube and foregut
The dorsal aortae form by which process?
Vasculogenesis
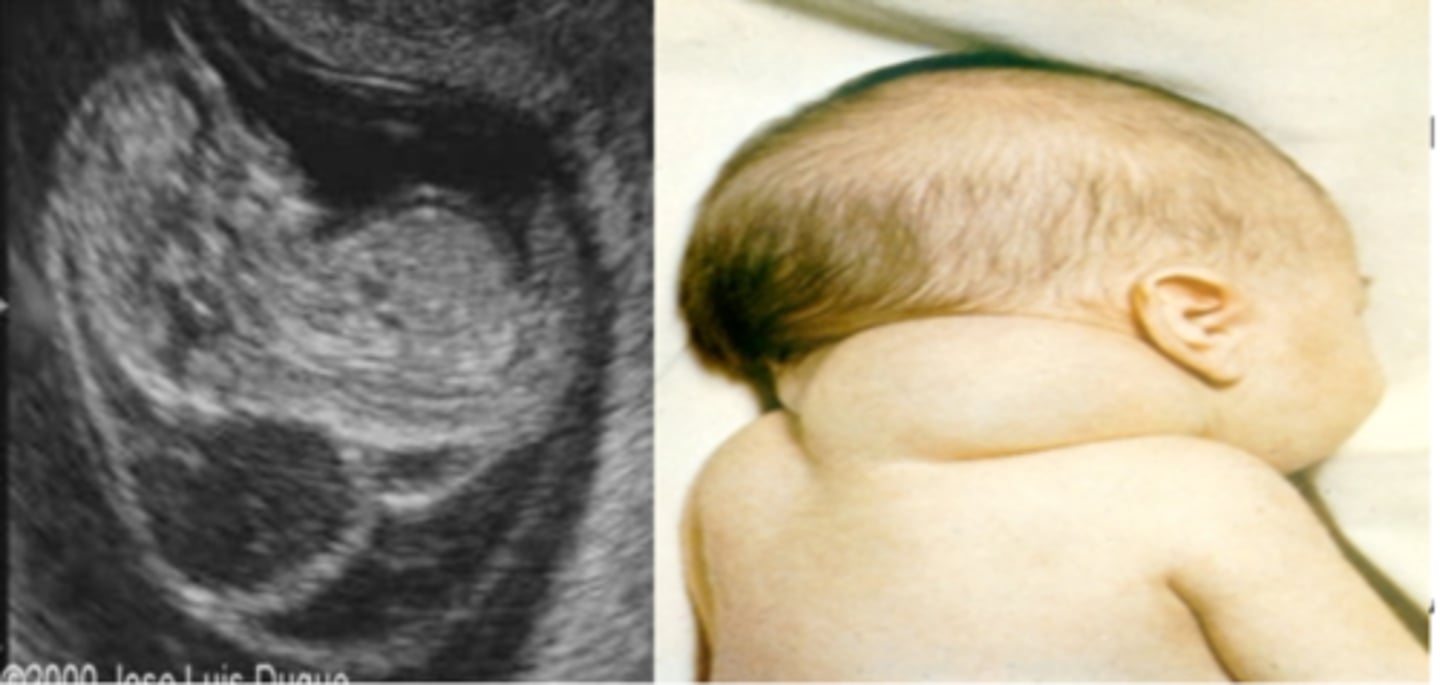
What is the most likely diagnosis for a 14-month-old with a scalp mass?
Hemangioma
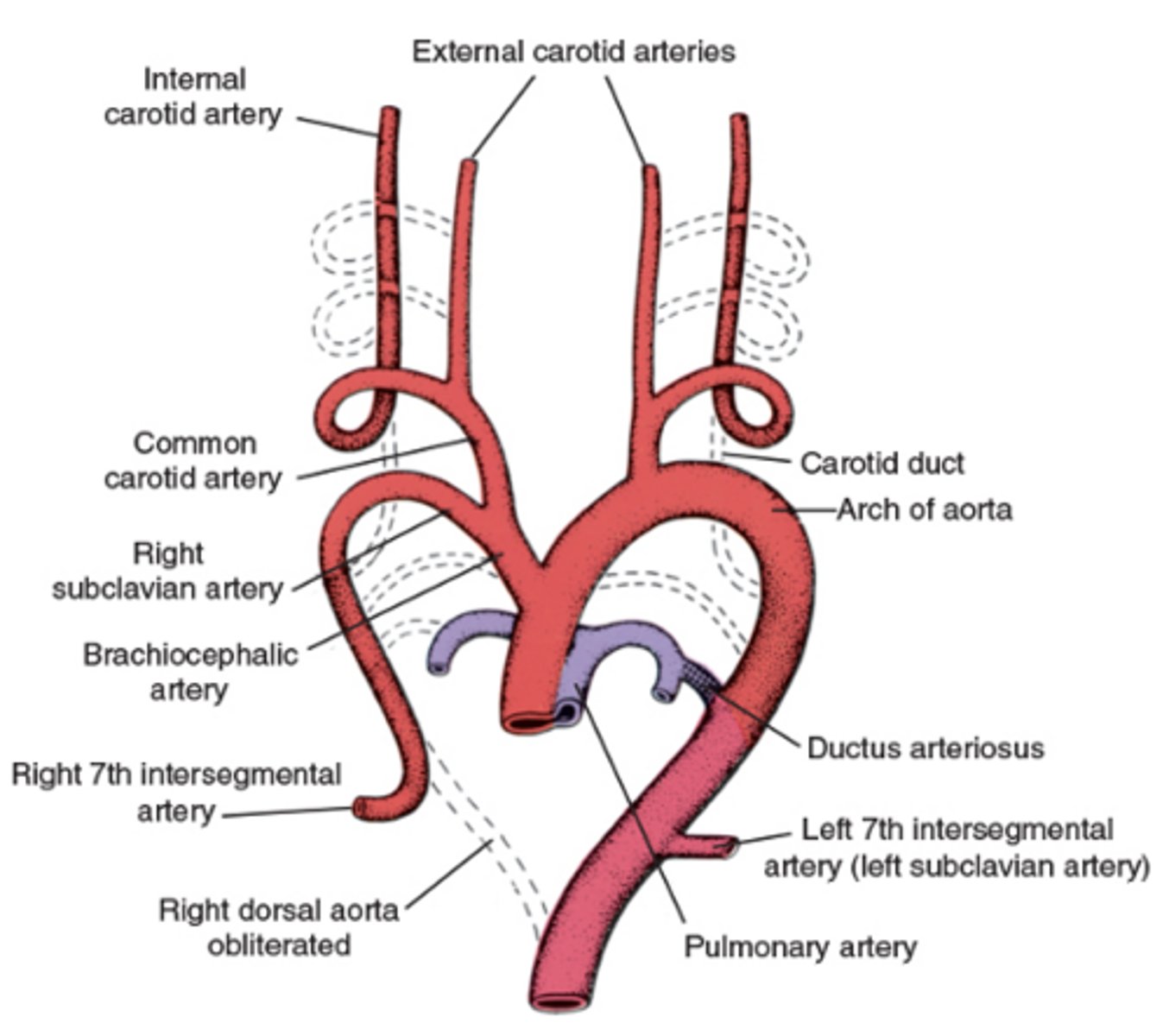
How many paired aortic arches initially form?
Six paired aortic arches
Where do the aortic arches arise from?
Aortic sac
Where do the aortic arches terminate?
Dorsal aortae
What happens to the 1st and 2nd arches by the end of week 4?
Large portions regress
What does Arch 1 form?
Maxillary artery (think 1st is max)
What does Arch 2 form?
Hyoid and stapedial arteries (think second for stapedial)
What does Arch 3 form?
Common carotid and internal carotid arteries (Think the 3rd letter in the alphabet is C for carotid)
Where do cranial portions of carotids come from?
Dorsal aortae
What are the external carotids?
Branches of the common carotid arteries
What does Arch 4 form on the right?
Right subclavian artery
What does Arch 4 form on the left?
Segment of the aortic arch
What happens to Arch 5?
Regresses / fizzles
Why does the right recurrent laryngeal nerve loop higher?
Right distal 6th arch regresses; nerve recurs around right subclavian artery
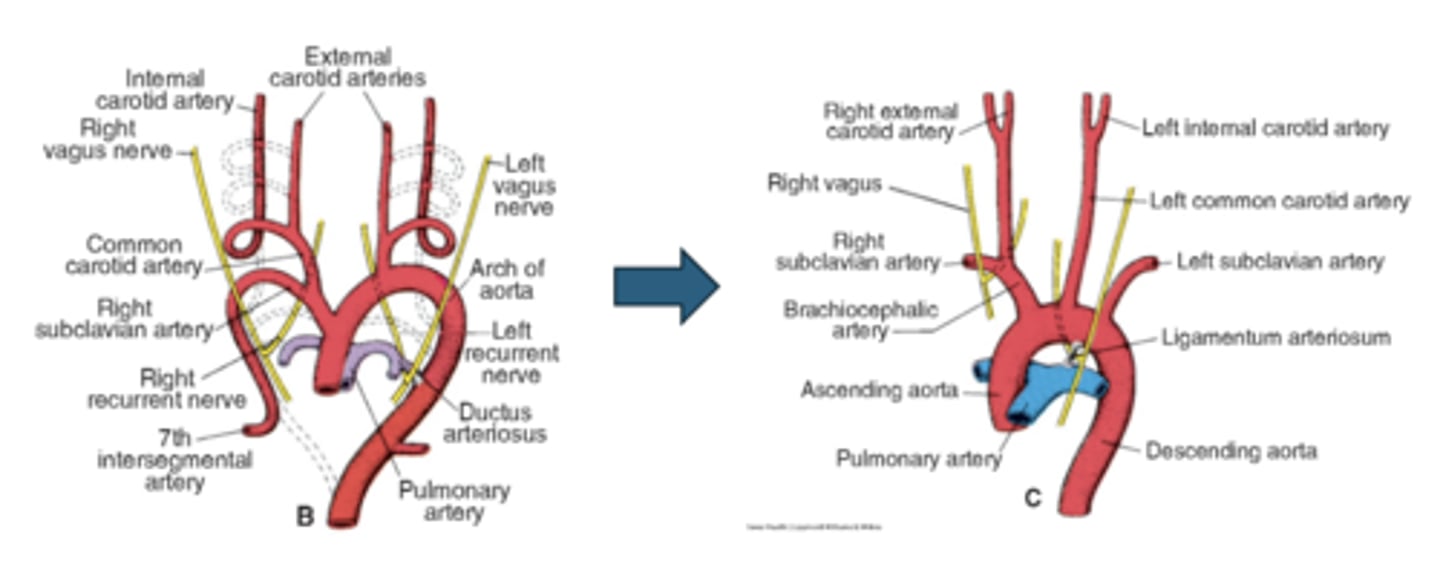
Where does the left recurrent laryngeal nerve loop?
Around the aortic arch
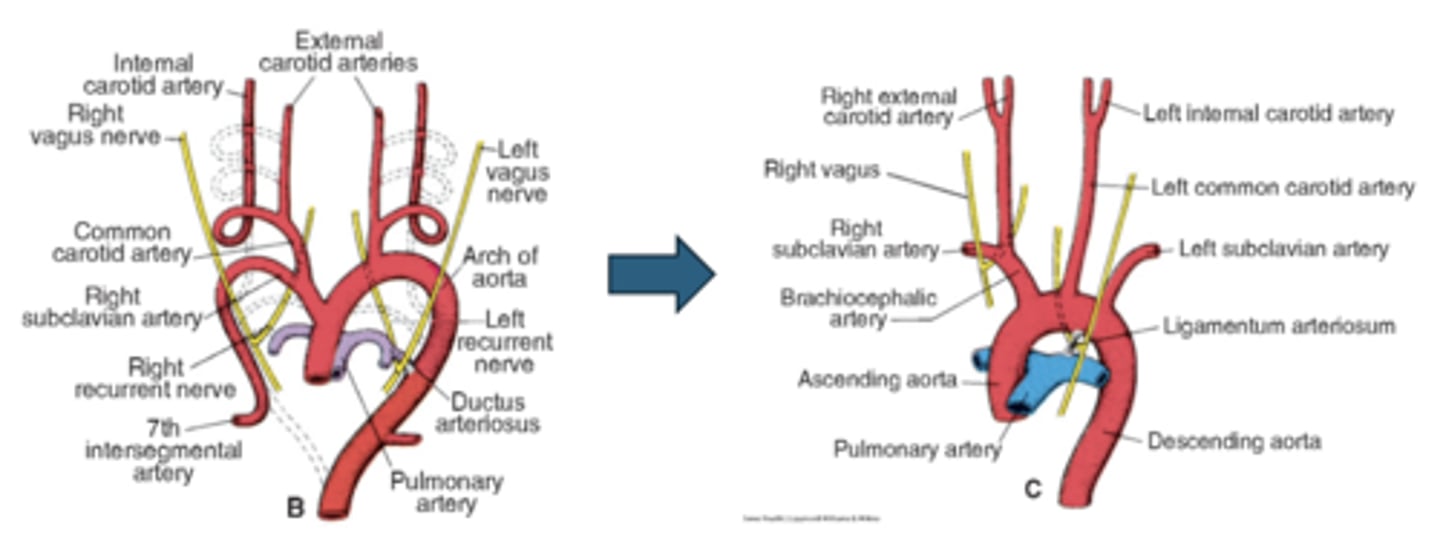
What is the 6th aortic arch called?
Pulmonary arch
Right proximal portion of Arch 6 forms what?
Right pulmonary artery (think RP RP)
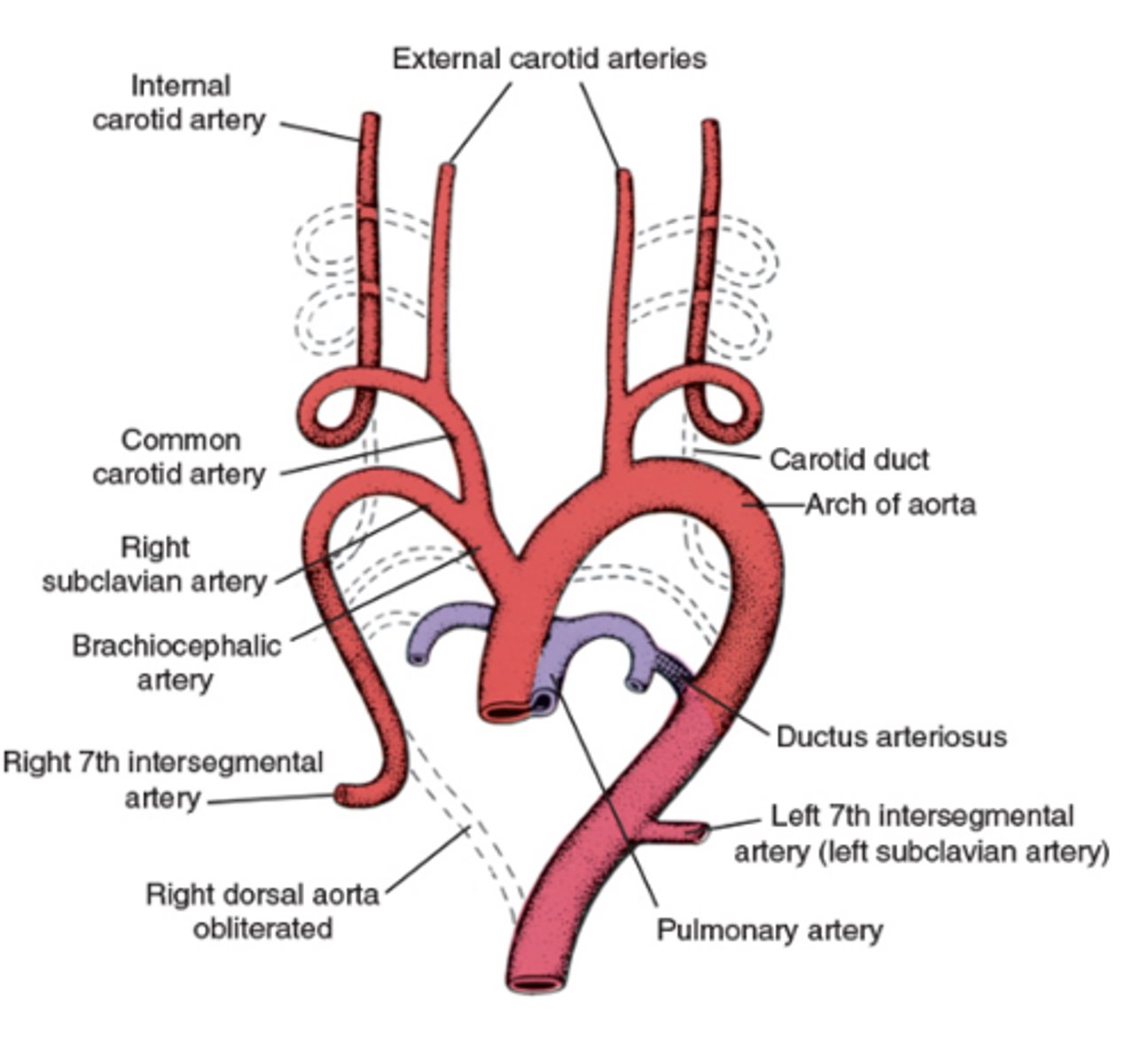
Right distal portion of Arch 6 does what?
Regresses
Left proximal portion of Arch 6 forms what?
Left pulmonary artery (think LP LP)
Left distal portion of Arch 6 persists as what?
Ductus arteriosus
Know the development of the aortic arches figure
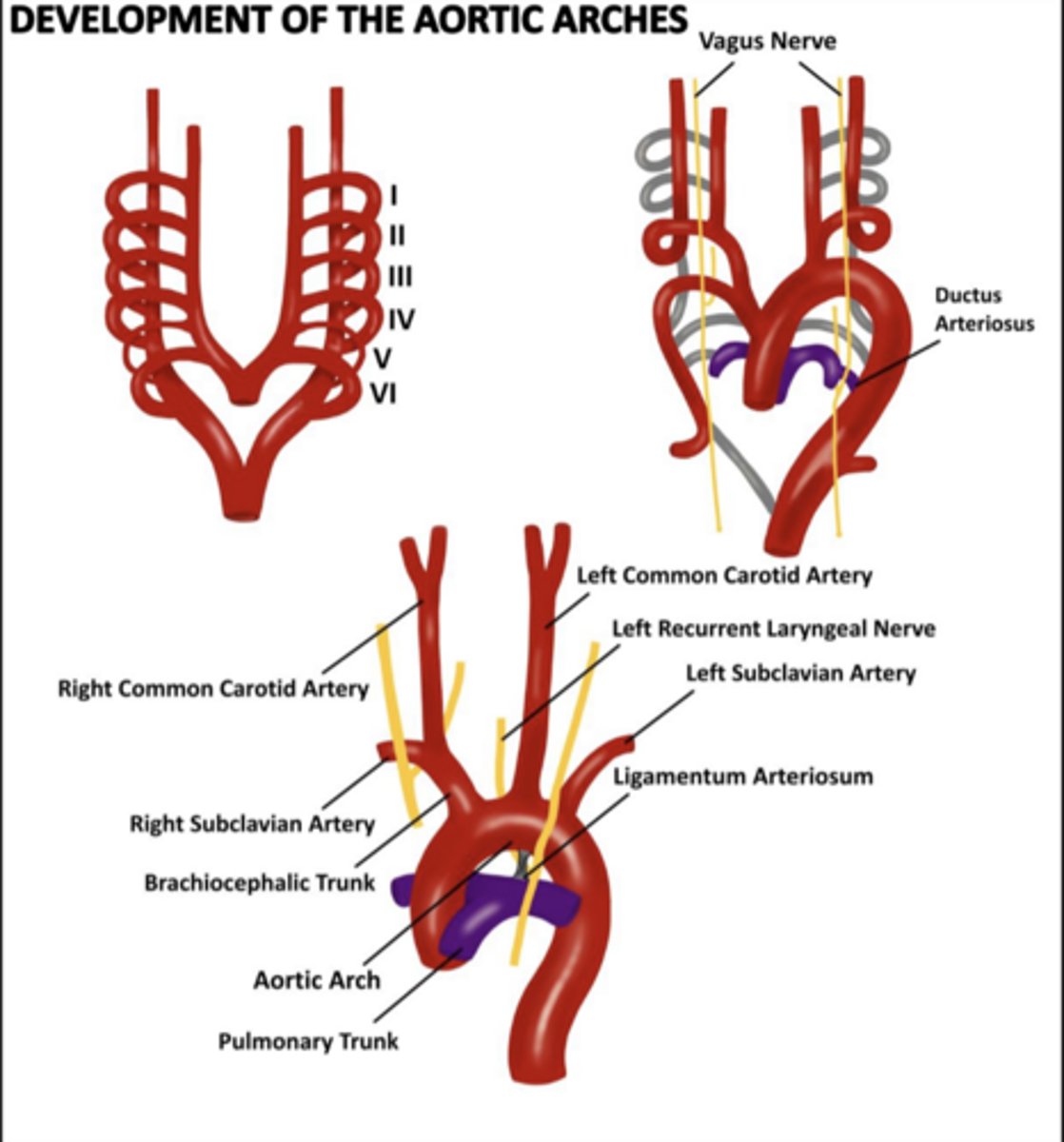
What is the ductus arteriosus?
A structure in embryo connecting the pulmonary trunk to the aorta.
Acts as a shunt - prevents blood from going back to lungs and instead dumps it back into aorta.
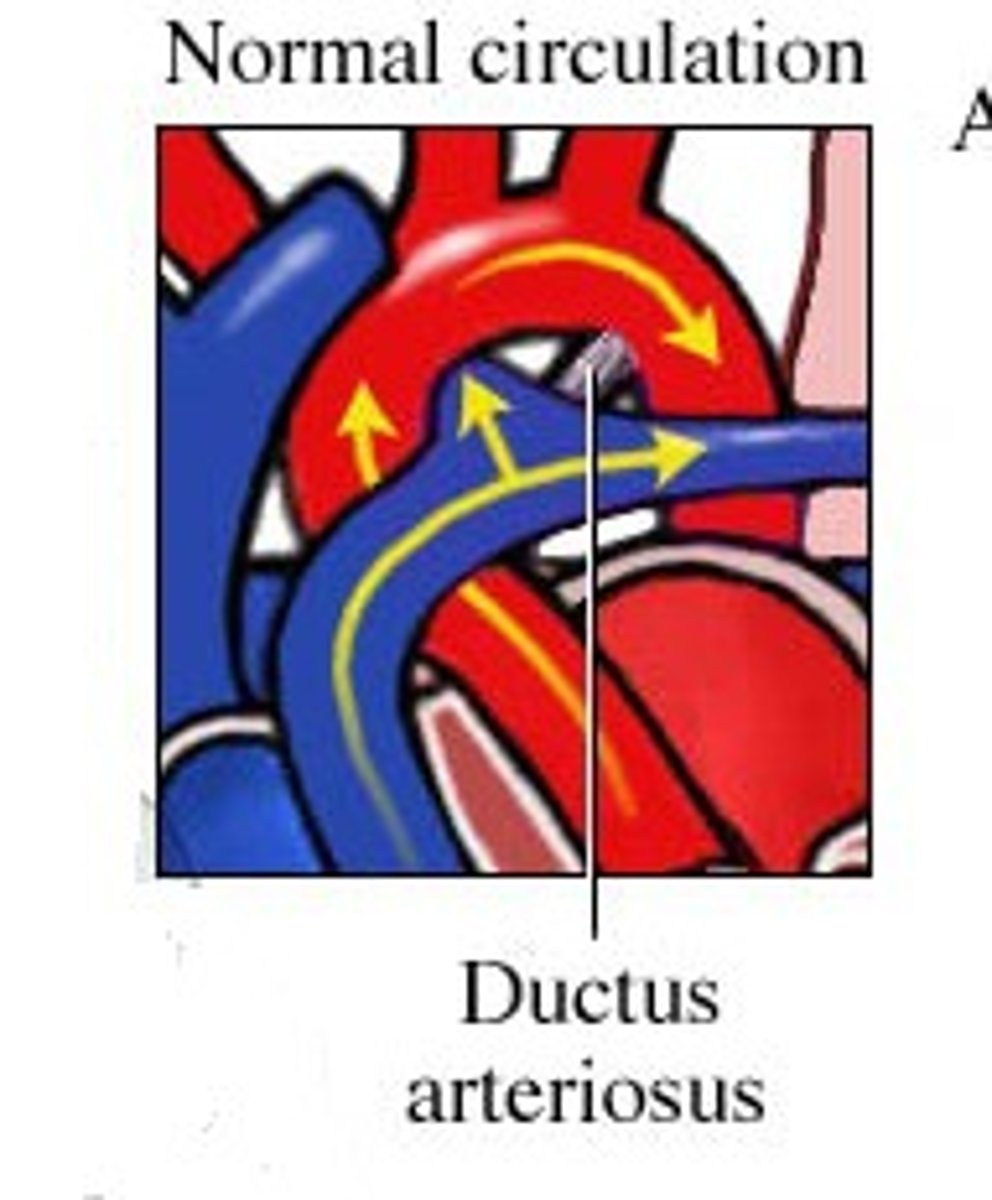
What does a machine-like murmur at the left 2nd intercostal space suggest?
Patent ductus arteriosus
Dysphagia with aberrant vessel—most likely cause?
Aberrant right subclavian artery
Where do the vitelline arteries arise from?
arise from abdominal aorta and supply derivatives of the yolk sac
Vitelline arteries give rise to which vessels?
Celiac and superior mesenteric arteries
What do umbilical arteries form via secondary connections?
Common iliac arteries, internal iliac (proximal), superior vesical arteries (proximal)
Basically vessels in the pelvis
What do regressed umbilical arteries become?
Medial umbilical ligaments
By week 5, what three paired veins exist?
Umbilical, vitelline, cardinal veins
Where will vitelline veins carry blood from?
yolk sac (GI tract) to the sinus venosus
Where will umbilical veins carry blood?
carry oxygenated blood from the placenta to the embryo (through umbilical cord)
Where will cardinal veins drain blood from?
Cardinal veins: principle veins of the embryo, drains body wall, trunk, limbs, head and neck
drain blood from the embryo and deliver it to the R. side of the heart
What does the left horn eventually develop?
coronary sinus
What does the right common cardinal vein become?
superior vena cava (SVC)
What does the right vitelline vein form?
Inferior vena cava (IVC)
What happens to the umbilical veins?
Right regresses; left carries blood from placenta to liver
What does the left vitelline vein form?
Portal vein
What is the sinus venosus?
bottom of the embryonic heart, collects all the venous blood from the embryo (send it to right atrium)
What is the function of the ductus venosus?
A shunt at the end of the umbilical cord which allows blood coming from the placenta to bypass the liver and empty directly into the IVC
allows nutrient rich blood to reach the brain and face
How is the portal vein formed?
Vitelline vein network around the duodenum coalesces into a single portal vein
Superior mesenteric vein derives from which embryologic vessel?
Right vitelline vein
Which structures arise from vitelline veins?
i. small region of the IVC (see below)
ii. portal vein
iii. ductus venosus
iv. hepatic
v. superior mesenteric
vi. inferior mesenteric
vii. splenic
Think Stressed People Don’t Have Sex In School
What do cardinal veins do?
Main venous drainage of embryo
What do anterior cardinal veins drain?
Cephalic portion
What do posterior cardinal veins drain?
Rest of embryo
Anterior cardinal veins form which adult vessels?
Internal jugular veins (drain the head)
Which veins form between weeks 5-7?
Subcardinal, sacrocardinal, supracardinal veins
What do subcardinal veins drain?
Kidneys
What do sacrocardinal veins drain?
Lower extremities
What do supracardinal veins drain?
Body wall
What veins drain the embryonic kidney and what will they become?
the posterior cardinal veins play a major role in draining the embryonic kidney
as the embryonic kidney regresses so does the blood supply; the vast majority of the posterior cardinal veins disappear
as a result the supracardinal veins take on the role of draining the body wall and become the azygos system of veins
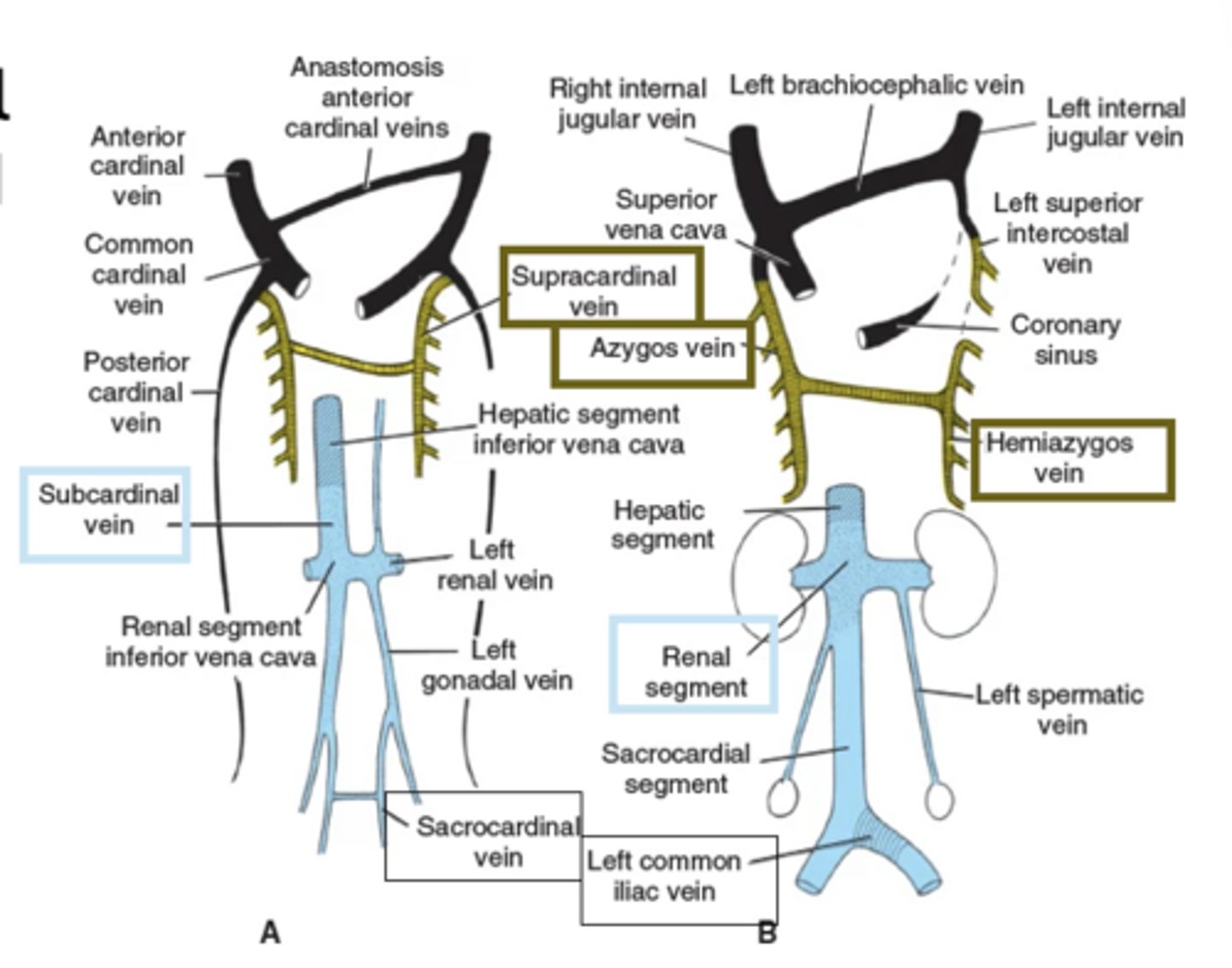
What segments make up the IVC?
Hepatic, renal, sacrocardinal
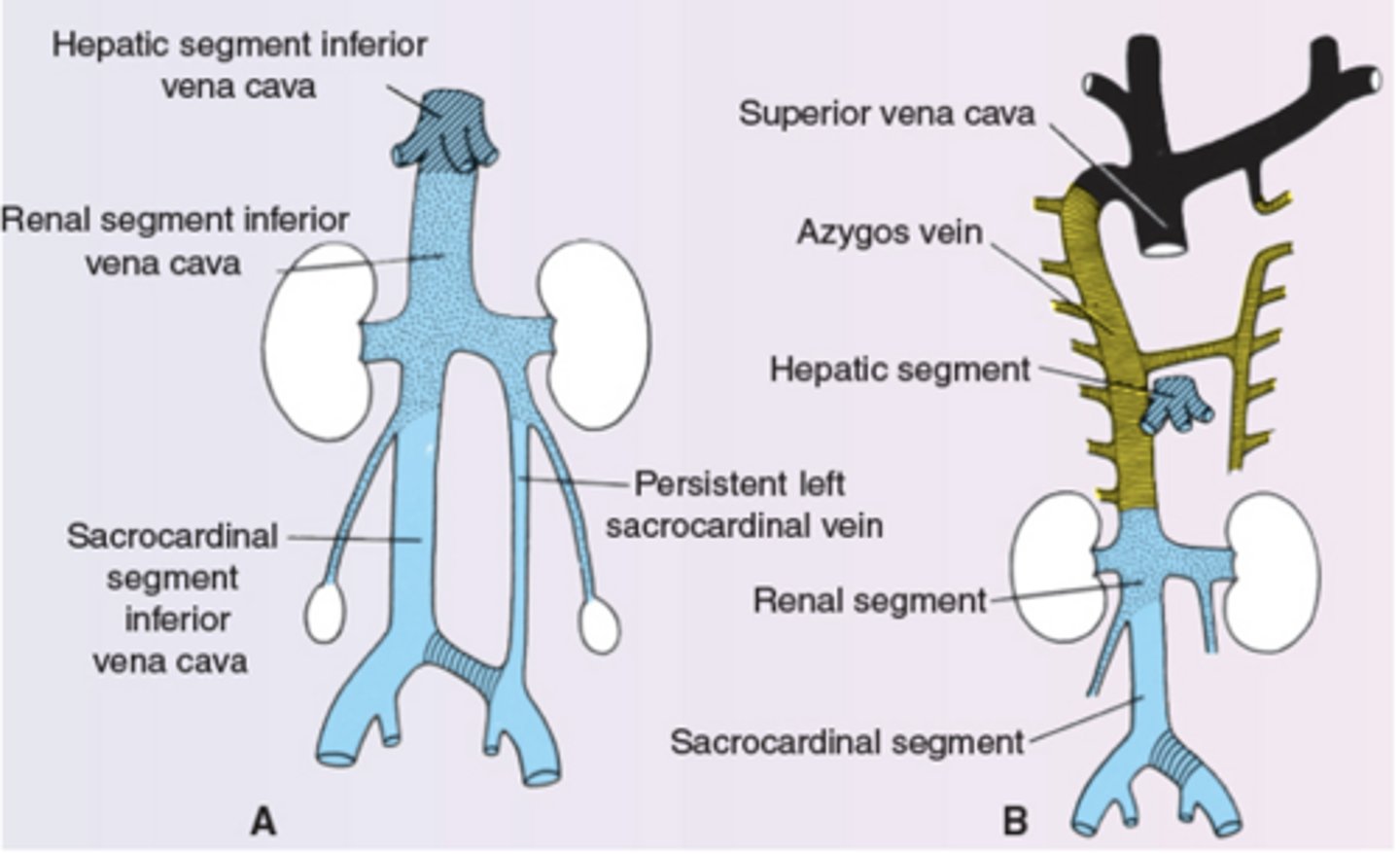
How is the left common iliac vein formed?
anastamosis between sacrocardinal veins
What are the five components of fetal circulation?
Umbilical vein, ductus venosus, oval foramen, ductus arteriosus, umbilical arteries
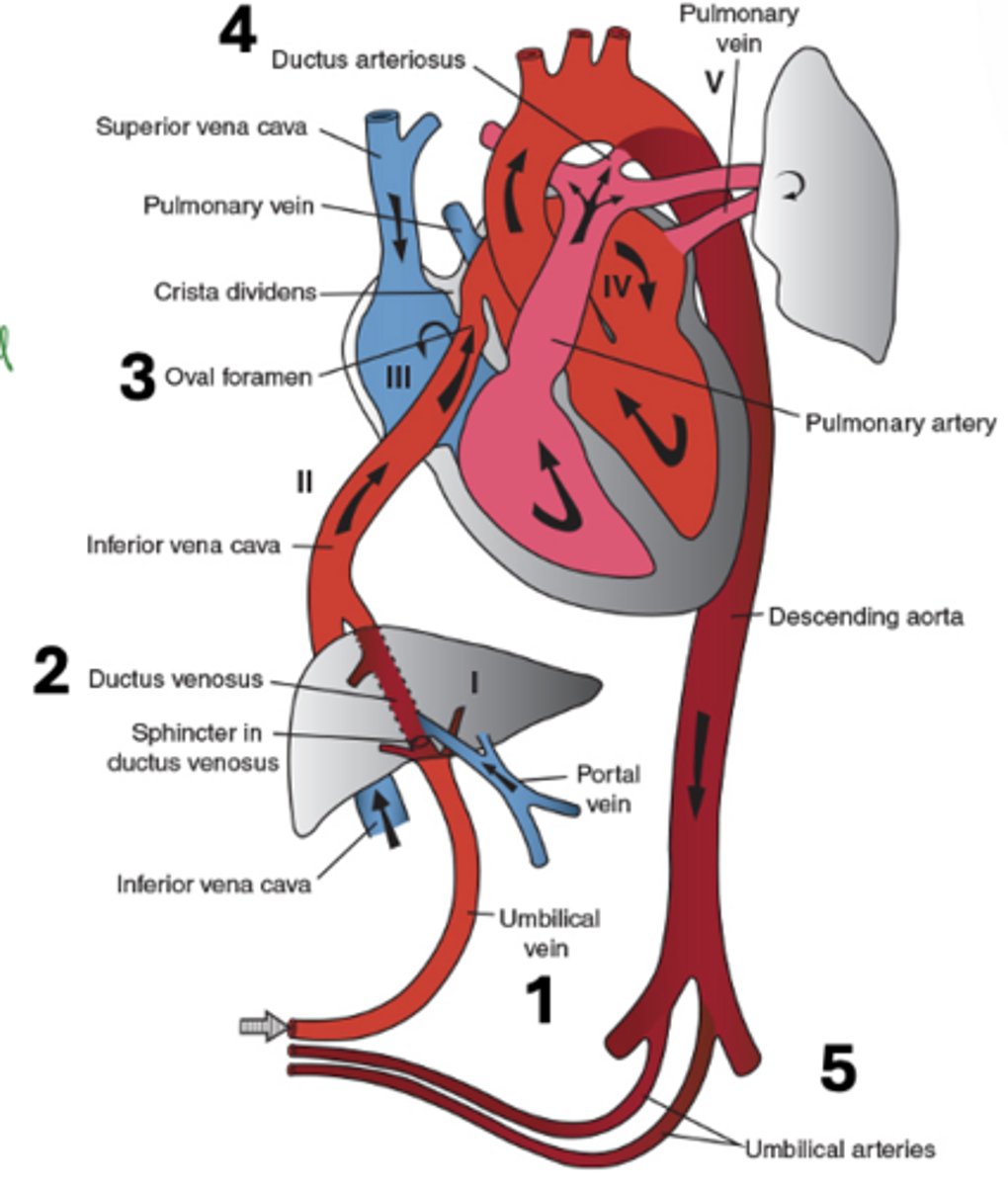
What does closure of umbilical arteries form?
Medial umbilical ligaments
Closure of umbilical vein forms what?
Ligamentum teres hepatis
Closure of ductus venosus forms what?
Ligamentum venosum
Closure of ductus arteriosus forms what?
Ligamentum arteriosum
Closure of oval foramen forms what?
Fossa ovale
When does the lymphatic system begin forming?
Around week 6
Lymphatics are derived from what germ layer?
Mesoderm
How many lymphatic sacs form?
Six sacs
What are the six lymphatic sacs?
2 jugular, 2 iliac, 1 retroperitoneal, 1 cisterna chyli
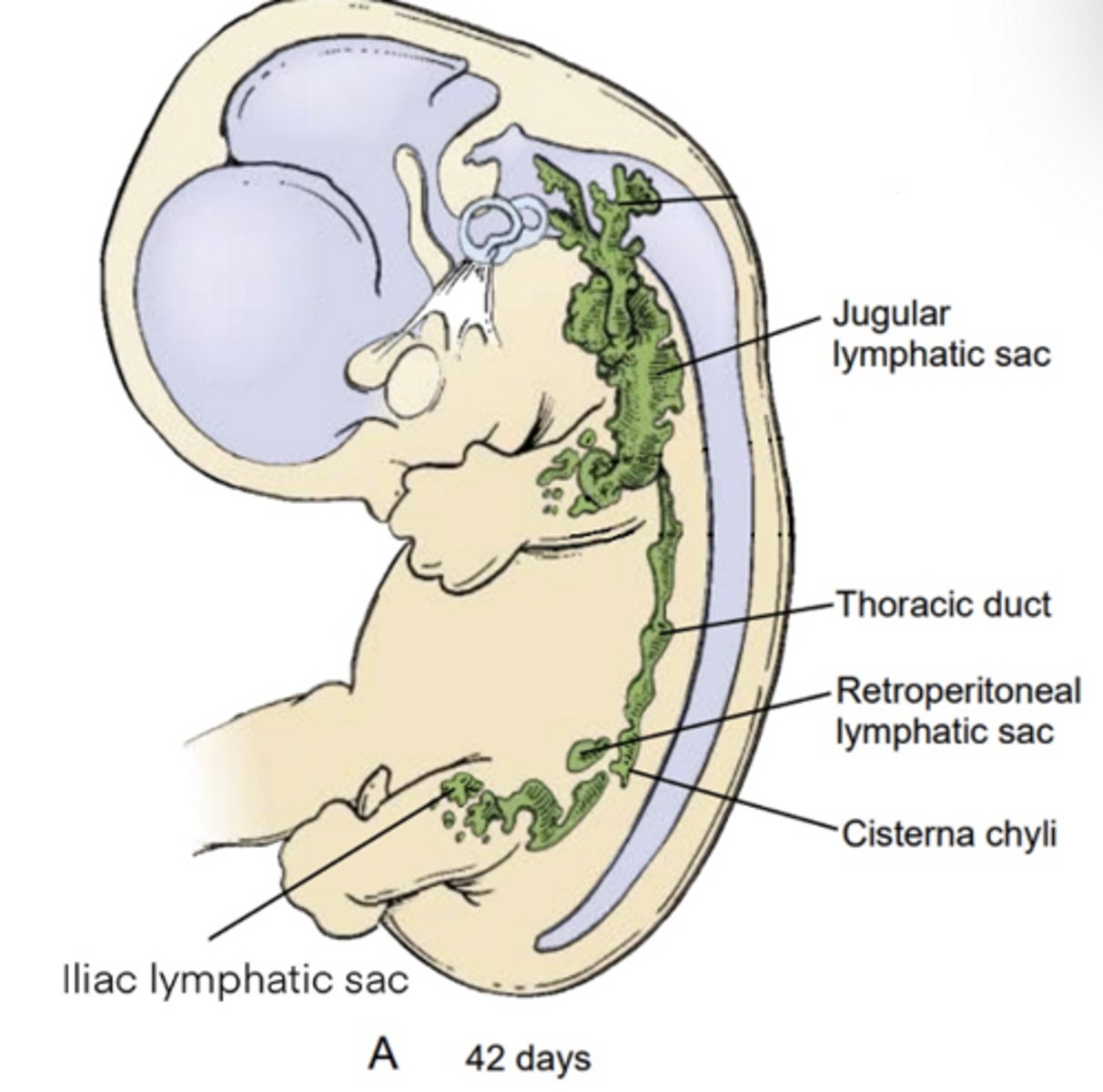
Where does lymph ultimately drain?
Thoracic duct -> left jugulovenous angle
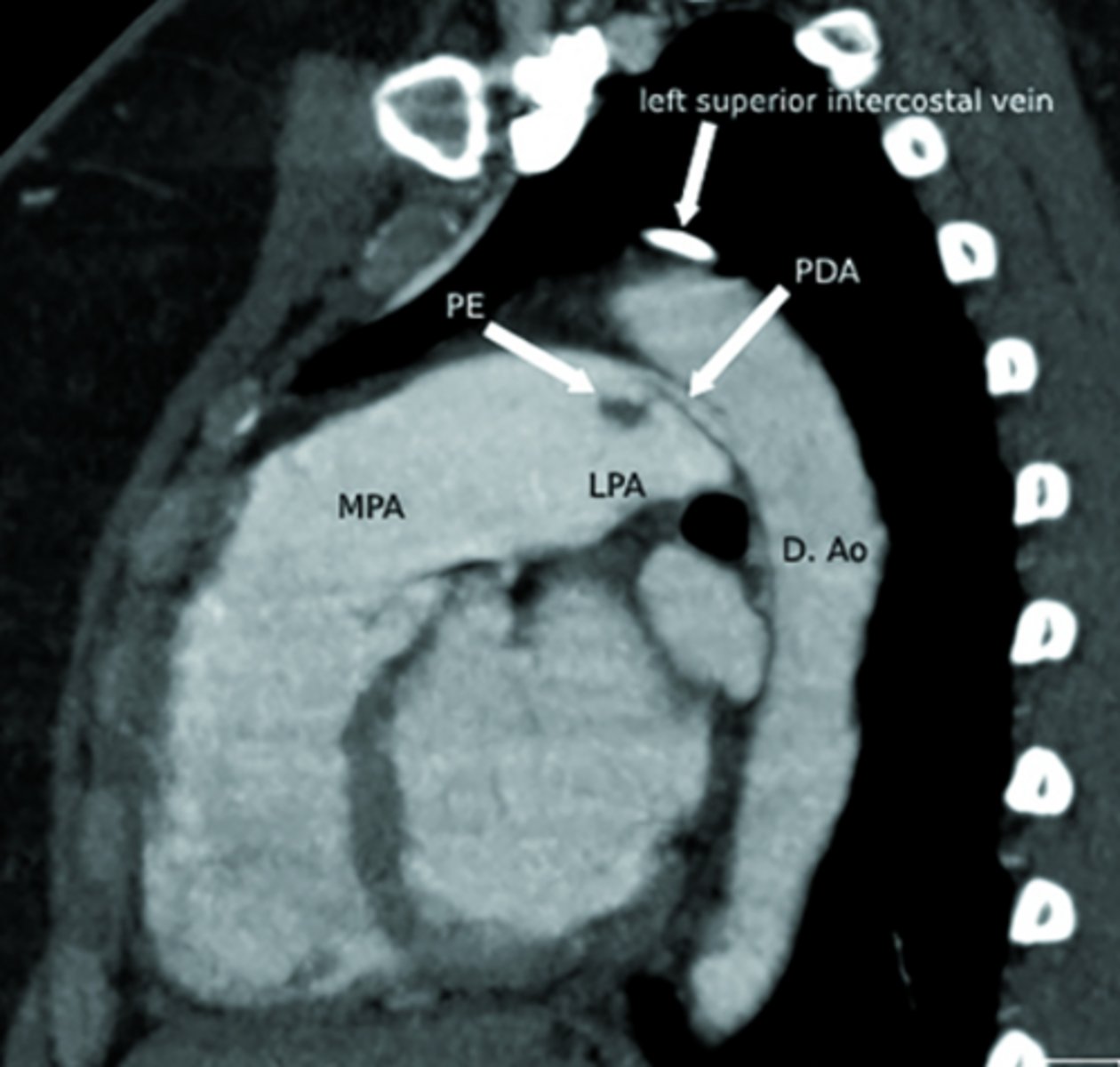
What is patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)?
Persistent connection between the pulmonary artery and aorta after birth.
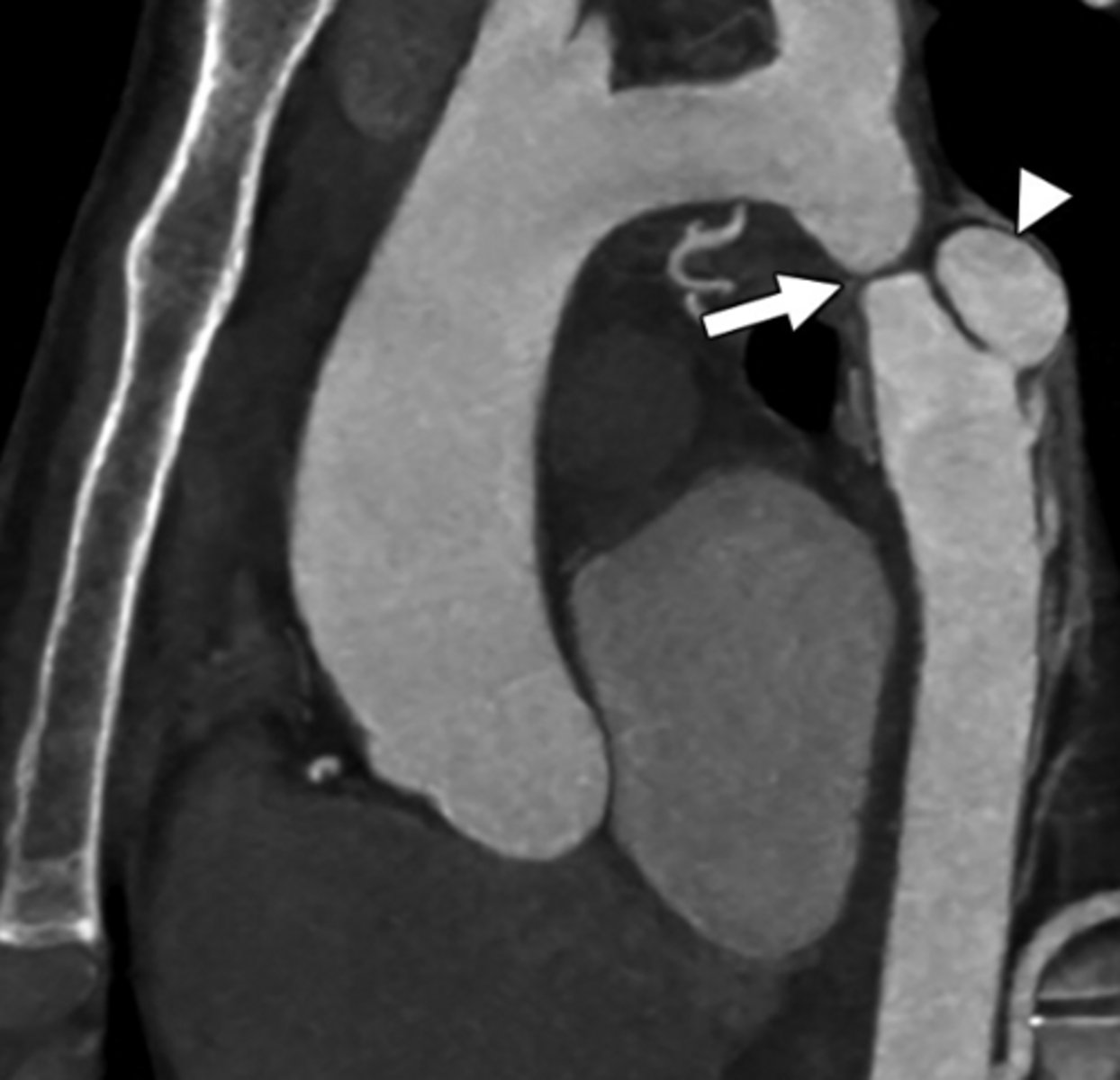
What is coarctation of the aorta?
Congenital narrowing of the aorta.
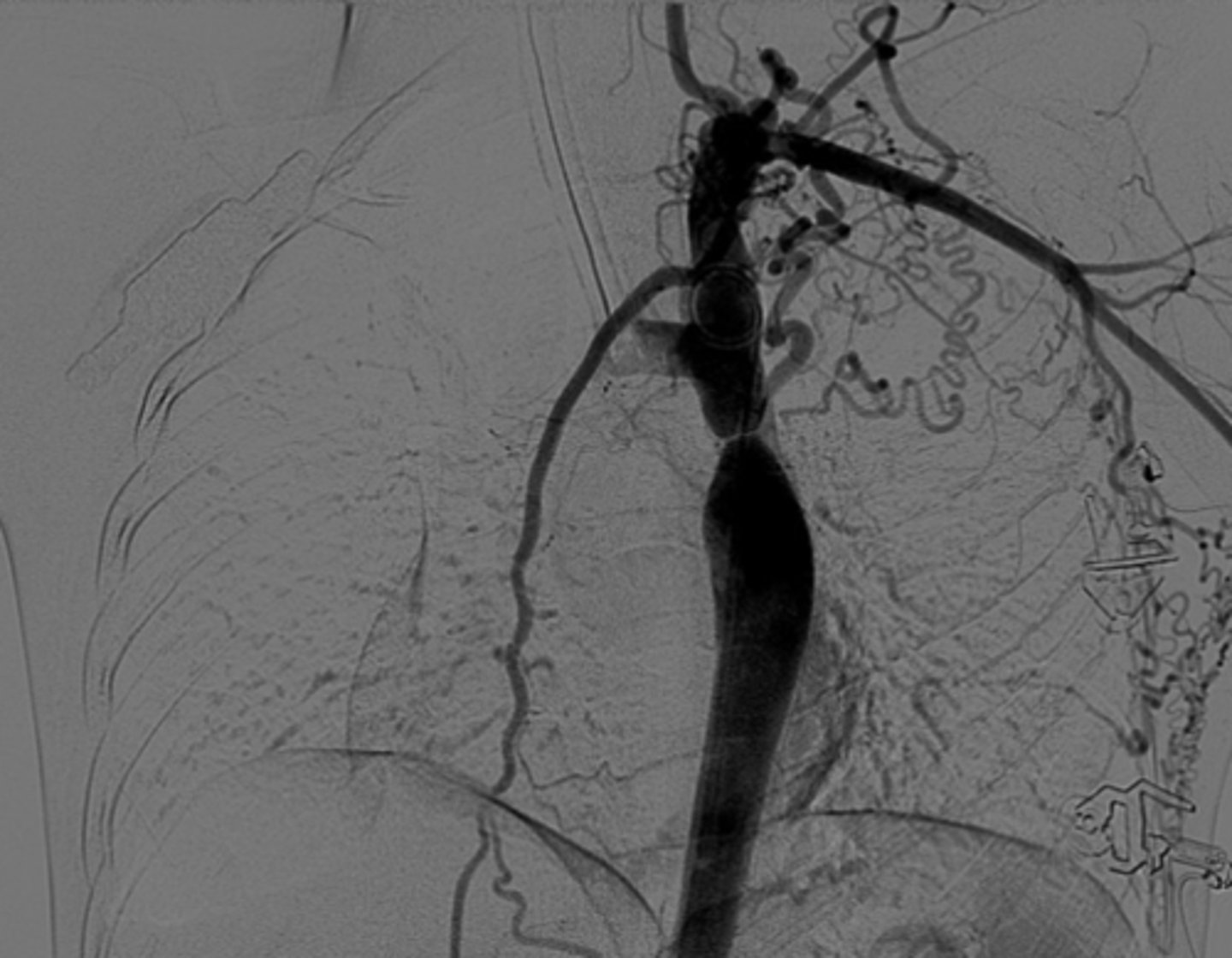
What are the key features of infantile coarctation of the aorta?
Symptomatic in early childhood, tubular hypoplasia of the aortic arch, occurs proximal to a PDA.
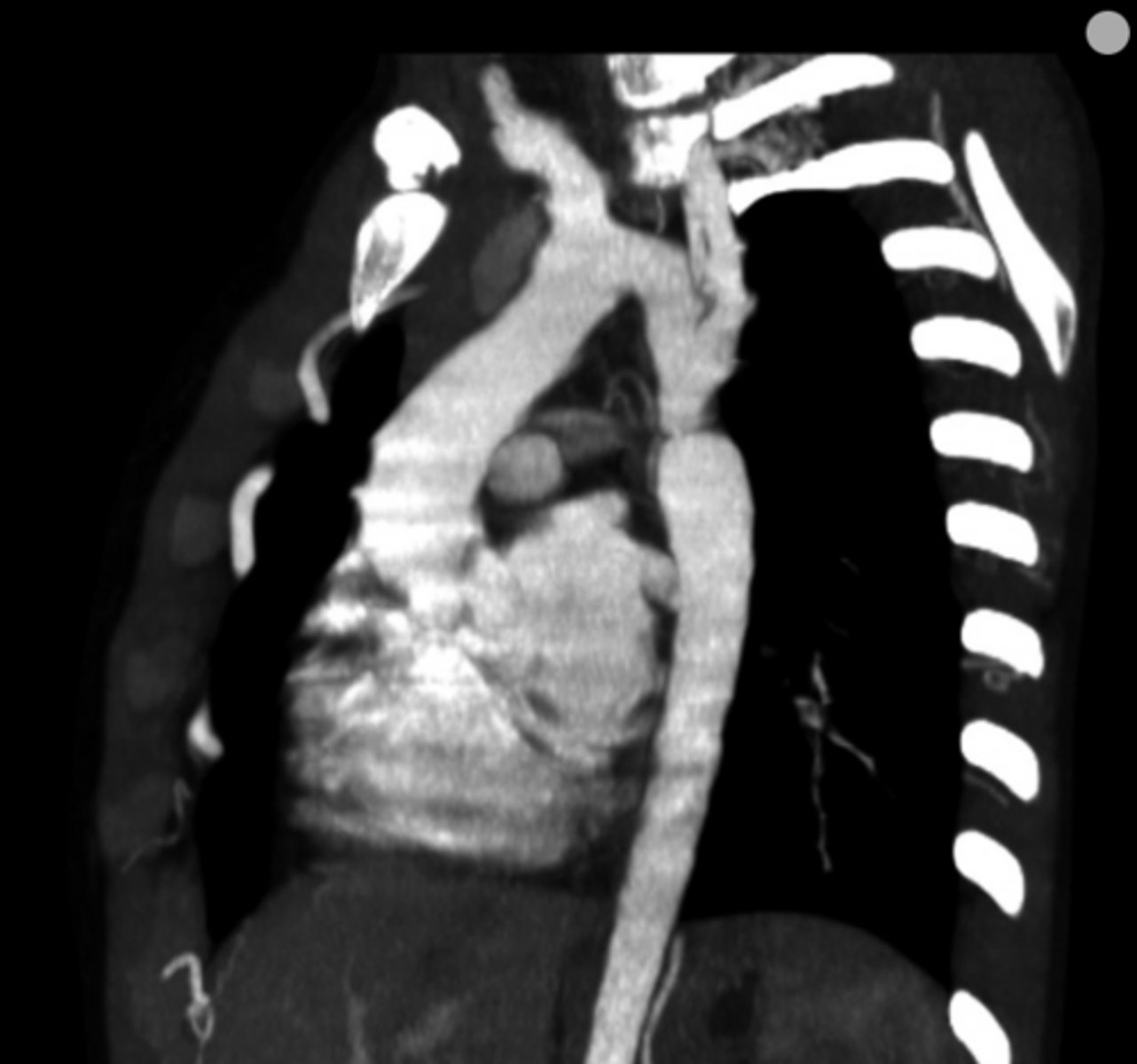
What are the key features of adult coarctation of the aorta?
Narrowing opposite a closed ductus arteriosus, distal to the great vessels from the aortic arch.
What is the chest radiograph finding in coarctation of the aorta?
Figure 3 sign.
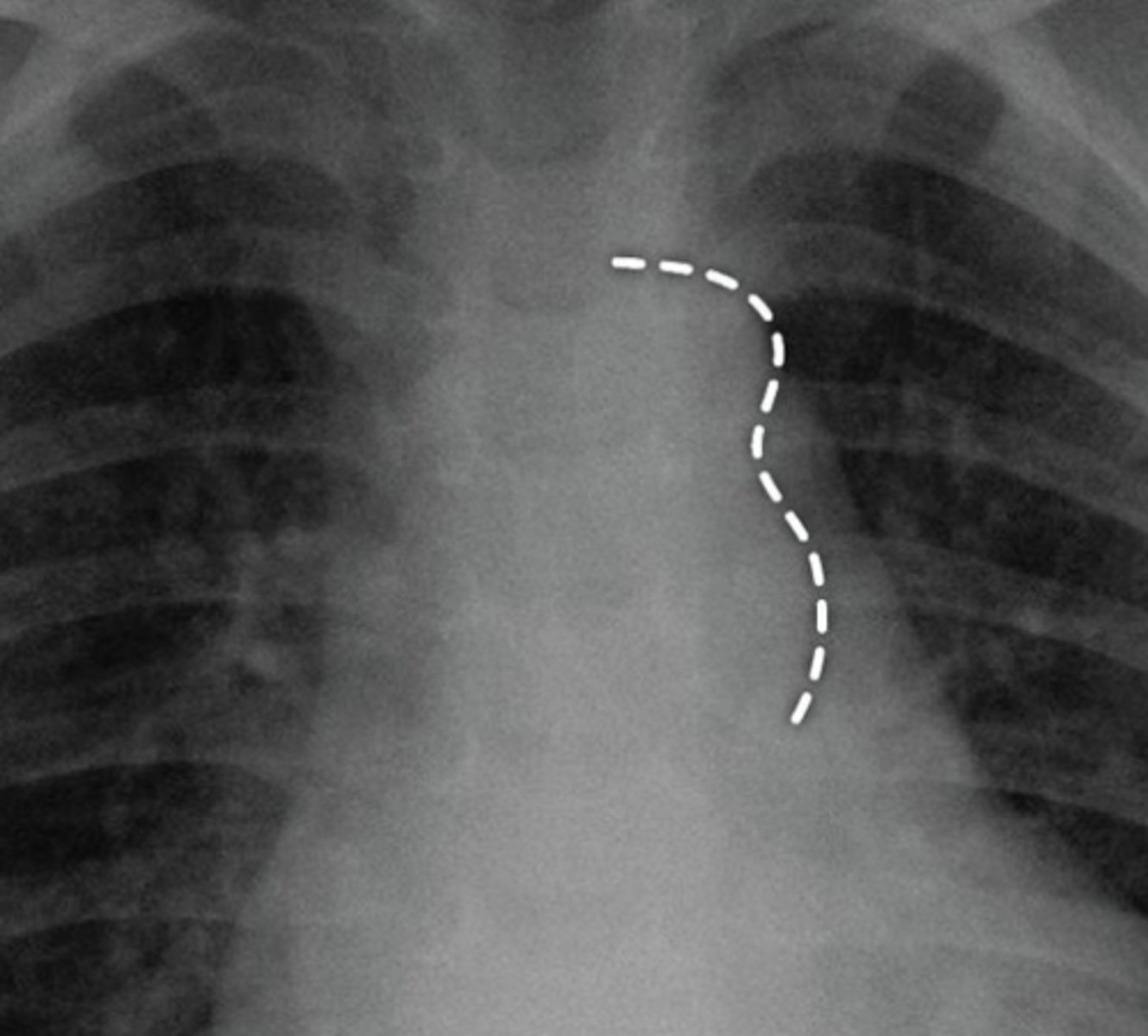
What causes dysphagia lusoria?
Abnormal origin of the right subclavian artery results in compression of the esophagus -impairment of swallowing
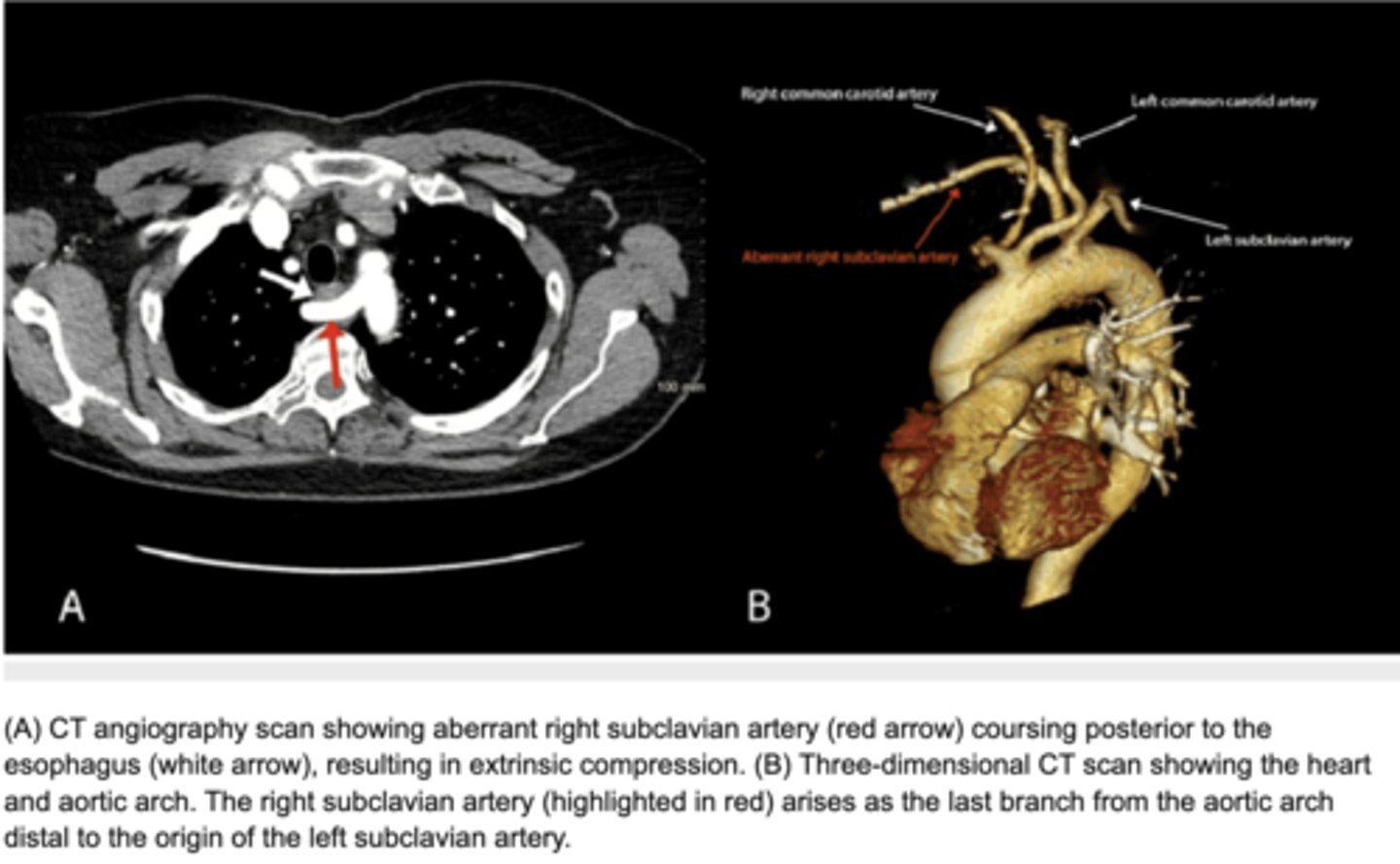
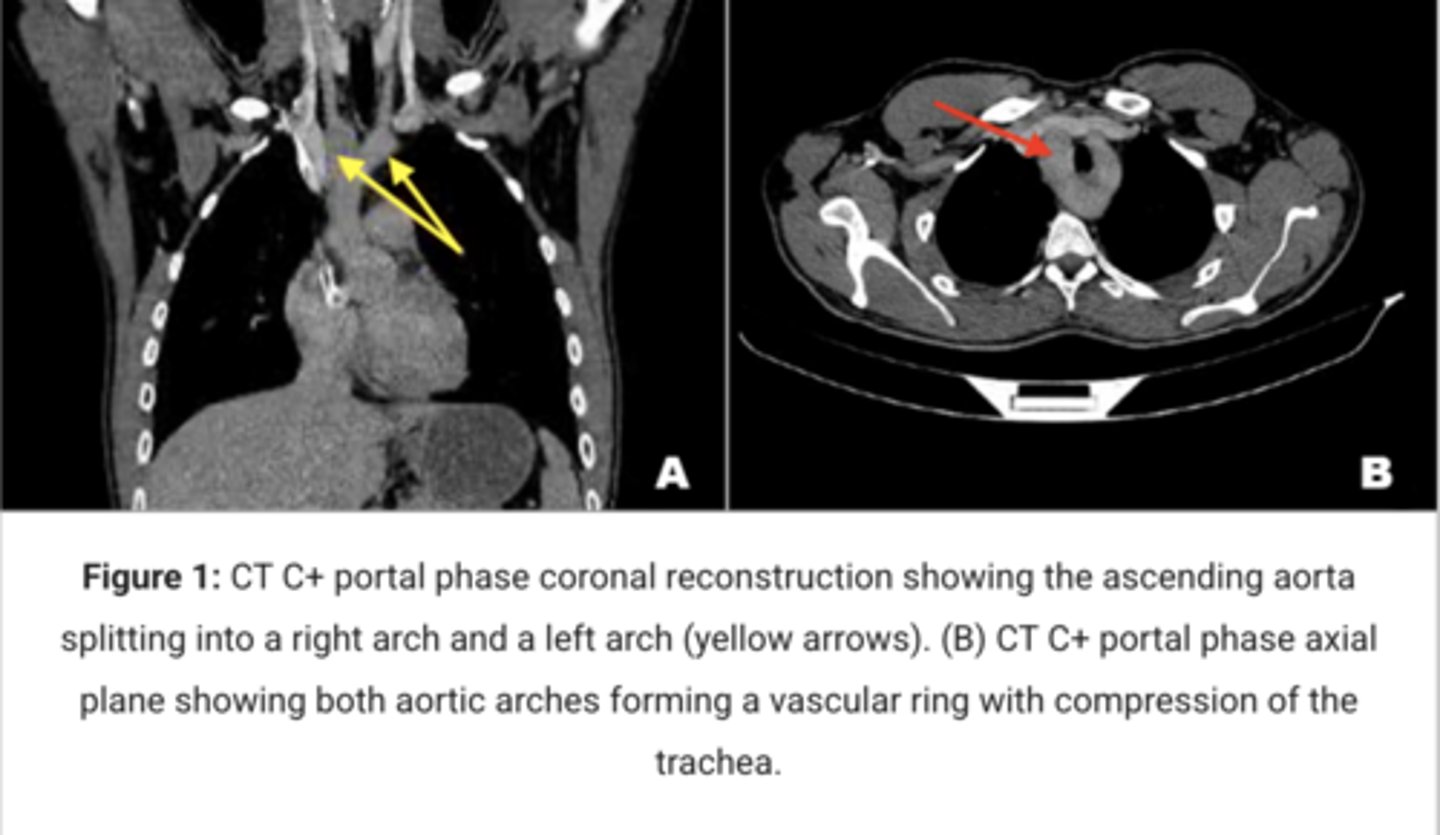
What is a double aortic arch?
Persistence of both right and left aortic arches forming a vascular ring.
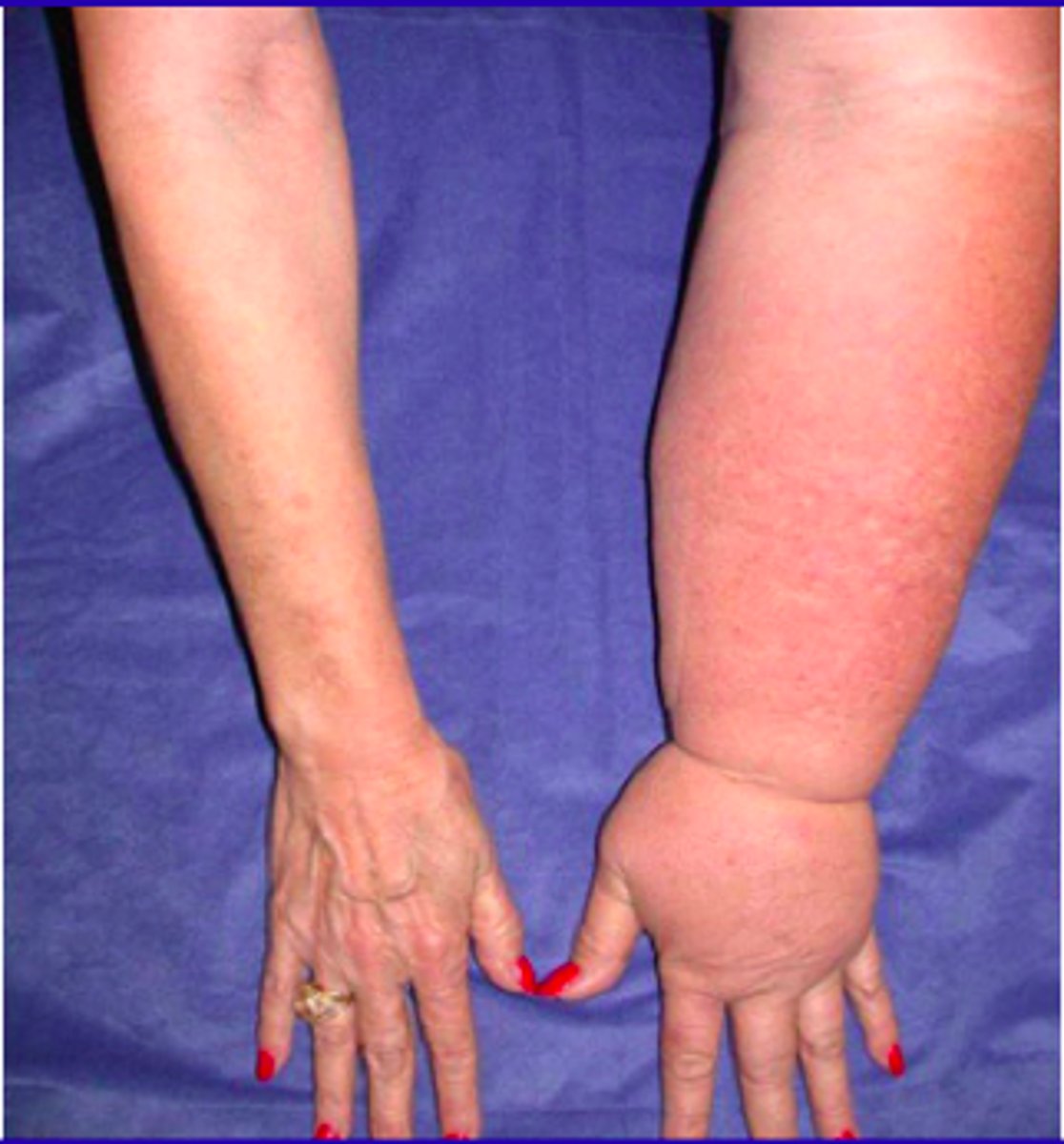
What is congenital lymphedema?
Dilation or congenital hypoplasia of lymphatic channels.
What is a cystic hygroma?
Large fluid-filled swellings involving jugular lymph sacs that fail to connect to lymphatic vessels.