MAB Ch 11
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
myeloma
cancer cell + b cell
model organisms
organisms that help scientists study human diseases
homologues
genes we have in common with other organisms based on DNA sequence
Ob gene
(in fat tissue)
codes for leptin hormone (tells hypothalamus in brain that it’s full )
if defunct → mouse becomes obese
pre-clinical trials
testing on model organisms
clinical trials
testing on humans
Biomarkers
indicators of disease
Ex: PSA (prostate-specific antigen) present when the prostate is inflamed
Ex: Circulating Tumor DNA (ctDNA)
when blood is drawn, you can get some cancerous DNA, if you see none, you know that the treatment is effective
Ex: Nanotech Tattoo for Glucose
tattoo that can measure blood sugar levels
Prognosis
likelihood of developing disease
Diagnosis
identifying gene/disease
Amniocentesis
from amniotic fluid surrounding the embryo
16 week fetus
amni. fluid removed w/ needle
Cells cultured/chromosomes stained
takes longer than CVS
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
from portion of the placenta
8-10 week fetus
Suction tube removes outer layer of chorion
more invasive
Noninvasive Prenatal Genetic Diagnosis (NIPD)
also known as prenatal cell free (cfDNA)
mother’s blood can be used to detect DNA of the baby
The Cancer Genome Atlas Project (TCGA)
identify how genetic changes are linked to cancer
Cells of interest: brain / mammary glands / ovaries / pancreas / liver / lungs
Karyotype
→ all chromosomes
Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH)
fluorescent probes bind to the ssDNA (chromosome), when binding it fluoresces, stuck to a slide
identifies translocations (crossing over, genes from certain chrms. swap with each other )
chromosome painting
ASO
can detect single nucleotide changes in a gene, even if restriction site is the same
can measure SNPs
is labeled with fluorescent tag
used for preimplantation genetic diagnosis/testing (PGD/PGT)
Allele Specific Oligonucleotide (ASO) analysis
If A=Has Dominant Trait
If B=Has Recessive Trait
then what is the genotype for 5?
Hh
DNA microarray
Gene chip, screens for diseases
single stranded cDNA attached in each well (probe)
nothing binds → black
Healthy tissue binds → green
yellow (red + green) → both binds
diseased tissue → red
Protein microarray
antibodies attached to chip
run patient proteins over chip
binds = fluorescence
How would you describe a gene’s presence in cell if it binds to cDNA in a microarray and the well turns red?
the gene is mostly present in diseased cells
Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)
Anorexia, Alzheimer’s, Autism, detecting foodborne pathogens
Whole Exome Sequencing (WES)
Identify cancers (melanoma, breast, colorectal, ovarian)
Undiagnosed Disease Network
NIH initiative- diagnose rare diseases
Genome Wide Association Studies (GWAS)
Genomes of several 100 (or 1000) individuals analyzed to compare to individuals without a particular disease
Oncogenes
cause cancer (Ex: BRCA1/2)
small molecule inhibitors
target cancer w/o hurting other cells
Magic bullet” drugs (look for proteins only on cancer cells)
Herceptin
inhibits HER-2 (aggressive, metastatic prone breast cancer)
Gleevec
targets BCR-ABL protein, treats chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
CML (chronic myelogenous leukemia)
Translocation between 9 and 22 chromosome
Identified in 1960
90% survival rate after 10 years
Microspheres (1-100 nm)
used as a mist to treat lung cancer and administer insulin
Usually made of lipids
nanoparticles
can be made of lipids, silica, gold, graphite
potential future → removing cholesterol
Provenge
→ therapeutic cancer vaccine, treat prostate cancer
harvest immune cells
induce them into dendritic cells
Expose to prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP) → causes immune cells to fight prostate cancer
Monoclonal Antibodies (mab) → for specific diseases
inject mouse w antigen
remove mouse spleen (rich in B cells)
Mix b cells w cancer cells (in culture)
fusion = hybridomas → secret antibodies in liquid culture
delivering radioactive materials to treat cancer
treating substance addiction
pregnancy test
strep throat
monoclonal ab treatment
Immunotherapy
using immune system to attack cells
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (car-t)
extracellular antigens (leukemias/lymphomas)
Kymriah for ALL
Recombinant T cell receptors (TCRs)
can target intracellular antigens and solid tumors
Oncolytic Viruses
engineered to bind to and infect cancer cells,without causing illness
Vectors
Adenovirus (common cold)
Adeno Associated Virus (AAV; the flu)
Retrovirus
Integration → permanently becomes a part of the genome
Viral DNA → provirus
Lentivirus
Liposomes → lipids packaged w/ genes
Antisense RNA
complementary strand to mRNA, blocks translation
RNAi
dicer (enzyme) chops delivered dsRNA → siRNA
siRNA joins w/RISC (RNA induced silencing complex) → siRNA is single stranded, looks for target mRNA
Triggers miRNA (micro), inhibits gene expression
Hematopoietic Stem Cell (HSC)
in bone marrow, becomes blood cells
Isolated from patient, modified (in vitro), given back to patient
Severe Combined immunodeficiency (SCID)
Lacking immune system bc of faulty ADA (adenosine deaminase) production
ADA breaks down dATP (deoxyadenosine triphosphate)
Buildup of dATP is toxic to T cells
Leber’s congenital amaurosis (LCA)
Degenerative retinal disease, misshapen rods & cones
RPE65 gene breaks down retinol (allows rods/cones to detect light)
Hemophilia
Faulty FIX gene → Factor IX → blood clotting
Modified AAD delivered into liver cells
Lipoprotein lipase deficiency (LPLD)
high levels of triglycerides in blood → pancreatic inflammation → pancreatitis
Glycera → modified AAV → delivers LPL gene
Regen. Medicine
growing cells/tissue to replace damaged tissue/organ
Fetal Tissue Transplantation
used since 80’s
from accident victims/abortions
possibly for parkinson’s/alzheimer’s
new cells can’t produce growth hormone
Organ Transplant
first → liver transplant, 1963
must take anti-rejection drugs (immunosuppresive)
autografting → transplant of tissue from one part of body from another
must be typed
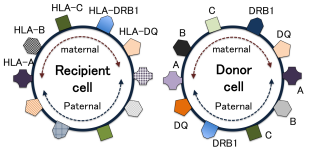
Major Histocompatibility complex (MHC)
tissue typing proteins from 70+ genes
donor & recipient must be a match
Xenotransplantation
→ donation from another species
1984 → human gets a baboon heart, died 3 weeks later
possibility of using pigs?
Knockout Pig
→ get rid of GGTA1
doesn’t produce sugars on tissue cells
lower chance of rejection
Anti-Zoonotic
CRISPR pigs, released by eGenesis
Eliminated 62 copies of porcine (pig) endogenous retrovirus (PERV)
Biocapsules
used to deliver therapeutic proteins/nutrients
Tissue Engineering
create a scaffolding
put the cells on it → seeding
bathe in nutrients
Embryonic → ESC
Cell lines- cultured stem cells that continually grow (hela)
Development
1 cell → zygote
16 cells → morula
32 cells → blastocyst
directed differentiation
Transcription factors → turn off Nanog gene → stem cells is no longer pluripotent
Nuclear Reprogramming
→ using genes to turn somatic cells pluripotent
retroviruses used to deliver 4 transgenes, from fibroblasts to stem cell
OCT3/4, SOX2, c-MYC, KLF4
Cloning
reproductive → create a fetus
Somatic cell nuclear transfer → enucleated egg + somatic cell nucleus, grow on plate, implant in surrogate
therapeutic, enucleated egg + somatic cell nucleus, embryo used for stem cells