LECOM MMS Immunology 4B Cell Mediated Immunity I and II
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What is Cell Mediated Immunity a part of?
Adaptive Immune Response
What does Cell Mediated Immunity activate?
Humoral and Innate immune response
Where are T cells made?
Where do T cells mature?
- Bone Marrow
- Thymus
Are T cell Receptors always membrane bound?
Yes
What do T cell Receptors recognize?
Antigens presented on MHC and peptides
What is the most common type of TCR and requires MHC presentation?
α:β TCR
TCR cannot signal alone. What proteins are required for signal transduction leading to T cell activation and differentiation?
CD3 and ζζ (Zeta)
Explain the steps involved in TCR signaling.
1. CD4/8 tightly binds to MHC
2. Lck phosphorylates ITAM (immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs)
3. ZAP-70 is then activated via phosphorylation
4. This leads to the activation of transcription factors
5. Activation of T cells
What is TCR Gene Rearrangement similar to?
BCR gene arrangement
- The β chain is like the HC of the BCR
* VDJ segments
-The α chain is like the LC of the BCR
* VJ segments
What does a Double negative T cell (Pro T cell) lack?
CD4/8
What does a Pre-T cell do?
Test a β chain with a pre-Tα (Pre-TCR). THIS IS THE FIRST CHECKPOINT
* similar to pre-BCR
What does a Double positive immature T cell contain?
It has CD4 and CD8; this is the only time a T cell will have both
What happens after T Cell Development?
Thymic Education
In the Bone Marrow, do T cells lack CD4 & CD8?
Yes
What is Thymic Education: Positive Selection?
TCR's must recognize antigens on MHC displayed by cortical thymic epithelial cells
Where does Thymic Education: Positive Selection occur?
In the cortex
What happens in Thymic Education: Positive Selection?
T cell becomes single positive T cells
Thymocytes recognize antigen on class I MHC. What does it become?
CD8
Thymocytes recognize antigen on class II MHC. What does it become?
CD4
What is Thymic Education: Negative Selection?
T cells with TCR's that bind with high affinity to self MHC: self antigen complex are eliminated through apoptosis
What do medullary thymic epithelial cells express?
Class I and II MHC with self peptides
If a TCR binds tightly to the MHC+ self antigen, what happens?
It is negatively selected and is signaled to go through apoptosis
Where is Autoimmune Regulator Gene (AIRE) expressed?
In medullary thymic epithelial cells
What does Autoimmune Regulator Gene (AIRE) allow cells to express?
Hundreds of tissue restricted organs
What does Autoimmune Regulator Gene (AIRE) check for?
Self-reactive T cells for self antigens
What happens if there is a mutation in Autoimmune Regulator Gene (AIRE)?
It leads to Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy (APECED)
What is the symptomatology of Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy (APECED)?
- Multiple autoimmune diseases
- Chronic candidiasis
With age what happens to the thymus?
It atrophies
What does Thymic Involution lead to?
A decrease in T cells being matured
What is DiGeorge Syndrome?
Lack of a thymus and reduced or lack of T cells; there is also decreased Cell-Mediated Immunity and Humoral-Mediated Immunity
During the development of αβ T cells in the thymus, the T cell must pass the first checkpoint. Which of the following is true of checkpoint one?
A. Tests for the α-chain associated with the β-chain
B. Tests for the β-chain associated with the pTα
C. Tests for the presence of both CD4 and CD8
D. Tests for negative selection
E. Tests for the heavy chain associated with VpreB
B. Tests for the β-chain associated with the pTα
A geneticist mutates several genes in a line of T cells. He notices after the mutations the T cells no longer become activated when antigens are presented. Analysis reveals one of the genes mutated is required for T cell signaling once the TCR interacts with an MHC + antigen. Which of the following molecules has the same function as the mutated molecule but found on B cells?
A. CD3
B. CD19
C. Igα
D. IgM
E. ζ chain
C. Igα
A patient is told that he is suffering from Bare Lymphocyte Syndrome Class I. The physician explains this mutation has led to the total absence of class I MHC on all cells. Based on this information which of the following cells would the patient be lacking?
A. B cells
B. CD4 T cells
C. CD8 T cells
D. Macrophages
E. Red blood cells
C. CD8 T cells
What is Igα similar to?
It is the B-cell signaling equivalent of CD3/ζ in T cells.
T cell-precursors travel from the bone marrow to develop in the ______
thymus
Mature T cells leave the thymus and travel to _________ ________ _______
secondary lymphoid tissues
What will APC's do to antigens?
APC's will process them
Where will APC's travel?
To draining lymph node
What will APC's present? Which location of a lymph node will this occur?
- Antigen to T cells
- Paracortex
How Do T Cells Reenter the Lymph Node from the Blood?
Through the HEV
What do Stromal cells and DC's in the lymph node secrete?
CCL19 and CCL21 which recruit T cells to the lymph node
What do CCL19 and CCL21 bind to?
CCR7 on naïve T cells and DC's which enhances integrin-dependent adhesion and migration and activates LFA-1
Explain the steps in Integrin-dependent adhesion and migration.
1. L-selectin binds to GlyCAM (selectin-ligand)
- ROLLING
2. Activated LFA-1 binds to ICAM
- STOP or ARREST
3. Diapedesis
- Drop
T cell Activation requires 3 signals. What are they?
1. TCR interacting with peptide on MHC
* Activates T cells leading to IL-2 production
2. Costimulation of CD28 with CD80/86 (B7.1/B7.2)
* Survival signal for T cell
3. Cytokine stimulation
* Differentiation
What happens if there is no co-stimulatory of CD28 on T cell with CD80/86 on dendritic/macrophage?
The cell with go through apoptosis/ become anergic (tolerant) T cells
Explain what Superantigens do (S. aureus and S. pyogenes)?
Superantigen binds to the TCR with the MHC II providing signal 1 and 2. This activates many different T cells. Results in the release of a ton of cytokines = cytokine storm
Superantigens can cause Toxic Shock Syndrome. What are common symptoms of toxic shock syndrome?
- Rash
- Hypotension
- Fever
- Multiorgan system involvement
What do Activated T cells become?
Effector T cells
What is an Effector T cell?
An effector T cell is one that has been activated by its antigen and now has effector function
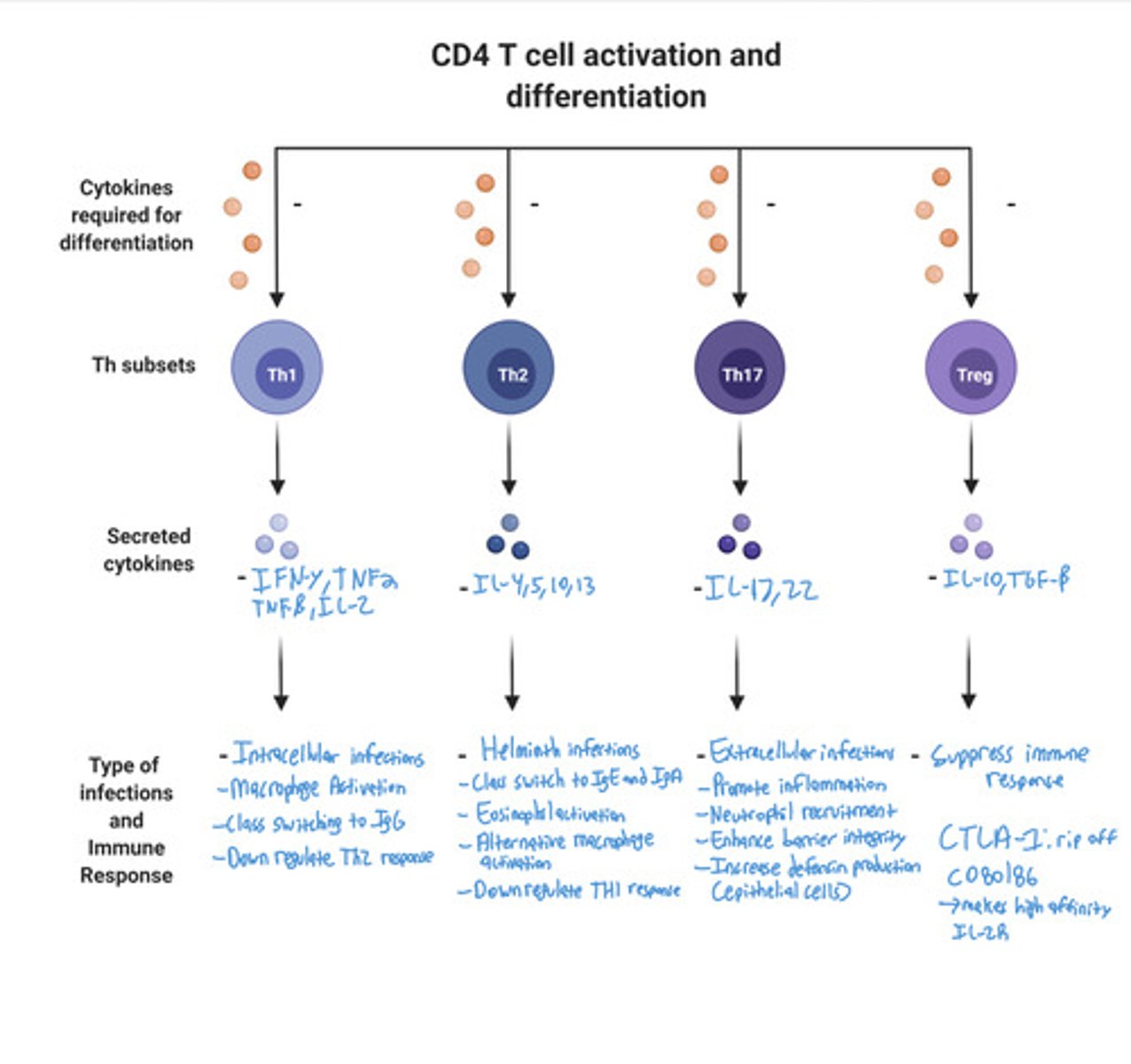
What do TH1 CD4 T Cells respond against?
Intracellular pathogens (bacterial, fungal, or protozoal)
What is required for TH1 differentiation?
IL-12 and IFN-γ
What do TH1 CD4 T Cells function?
Macrophage activation and Class switching to IgG
What do macrophages increase?
CTL and NK cell activity
What cytokines are produced in TH1 CD4 T Cells?
IFN- γ , IL-2, TNF-α, TNF-β, IL-3, & GM-CSF
What do TH1 CD4 T Cells do with IFN- γ?
Down regulates Th2 response
What is IFN- γ released by to do what?
TH1 to activate macrophages
What are the functions of Macrophages via TH1 / IFN-γ?
1. Increases killing ability
2. Increases secretion of inflammatory cytokines
3. Increase expression of MHC and co-stimulatory molecules
What do TH2 CD4 T Cells respond to?
Parasite and Helminth infections
What is required for TH2 differentiation?
IL-4
What are the functions of TH2 CD4 T Cells?
- Class switch to IgE (IL-4, IL-13)
- Class switch to IgA (IL-5)
- Eosinophil activation ( IL-5)
- Alternative macrophage activation (IL-4, IL-13)
- Mucus secretion and peristalsis (IL-4, IL-13)
How do TH2 CD4 T Cells downregulate Th1 response?
With IL-10
What does TH17 CD4 T Cells respond to?
Extracellular infections
What is required for TH17 CD4 T Cells differentiation?
IL-1, IL-6, IL-23, and TGF-β
What do TH17 CD4 T Cells release?
IL-17 and IL-22
What are the Functions of TH17 CD4 T Cells?
- Promote inflammation
- Neutrophil recruitment
- Enhance barrier integrity
- Increase defensin production from epithelial cells
What are TREGS CD4 T Cells responsible for?
Suppressing immune response
What is required for TREGS CD4 T Cells differentiation?
TGF-β and IL-10
* Occurs in the thymus
What do TREGS CD4 T Cells produce?
TGF-β and IL-10
What do TREGS have?
Many high affinity IL2R and CTLA-4
What is the function of CTLA-4?
Blocks and removes B7 from APC
What are Effector CD8 Cells (CTL)?
The Serial Killer of the immune system
For Effector CD8 Cells (CTL), which MHC must an antigen be presented on? Is this endogenous or exogenous?
- MHC I
- Endogenous
What do Effector CD8 Cells (CTL) require help from?
Th1 CD4 T cells
Do naïve T cells require costimulators?
Yes
Once naïve T cells are activated to Effector CD8 cells, do they still require costimulation?
No
What enzymes do Effector CD8 Cells (CTL) secrete?
- Perforin
* Forms pores on the cell membrane
- Granzyme
* Induces apoptosis
What do Effector CD8 Cells (CTL) secrete?
IFN-γ and TNF-β leading to apoptosis
CD4 T cell Activation and Differentiation Image
A 2-year-old patient has already had several viral and bacterial infections as well as a fungal infection. Believing the patient has an immunodeficiency, blood is collected and sent to the lab. Testing reveals the patient suffers from Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) due to a defect in γ chain of the patient's IL-2 receptor. Which of the following cells would be affected by this defect?
A. CD3 cells
B. CD16 cells
C. CD19 cells
D. CD20 cells
E. C40 cells
A. CD3 cells
During T cell development in the thymus, a double- positive cell binds with low affinity to self-peptide: self- MHC class II. Which of the following would occur?
A. Negative selection followed by apoptosis
B. T cell activation
C. Positive selection for CD4 T cell
D. Positive selection for CD8 T cell
E. Rearrangement of the β-chain
C. Positive selection for CD4 T cell