Unit 4: Equilibrium and chemical systems
1/3
Earn XP
Description and Tags
graphing, math, and mixture of unit 3 rates of reaction
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
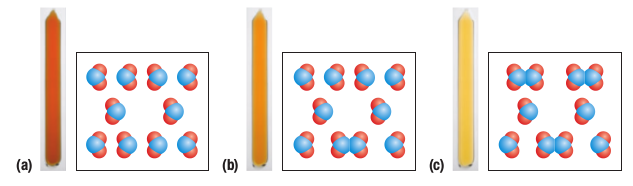
Conditions for an equilibrium system
a closed system (energy ONLY leaves or enters NOT MATTER)
reversible reaction (both forward and reverse direction)
reactants and products are present at the same time (rates of the forward and reverse reactions must be equal)
equations use this symbol “⇌”
Solubility Equilibrium—> balance b/tw solid and ions
Phase Equilibrium—> balance b/tw 2 states of a substance
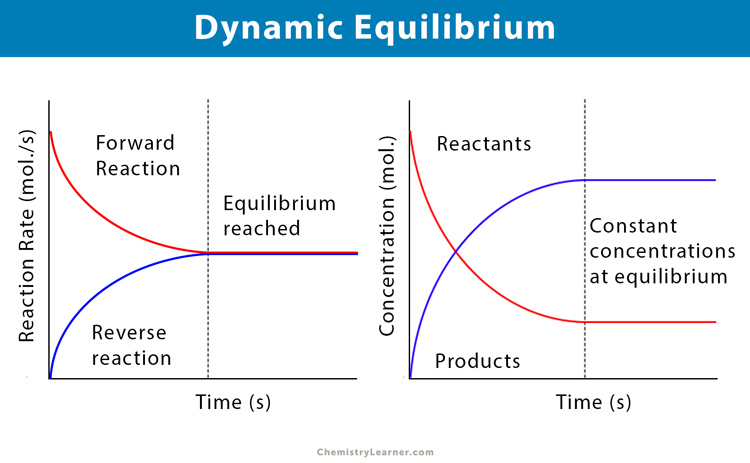
Analyzing graphs
on the graph, there is a constant period (reached Chemical Equilibrium)
the constant period is shown by the straight line/Plateau (concentration of react. and prod. will NOT CHANGE)
reactants never COMPLETELY “disappear”
Position of Equilibrium—> on the graph, it is the point where the formation of react. or prod. is favored (concentration is higher than the other)
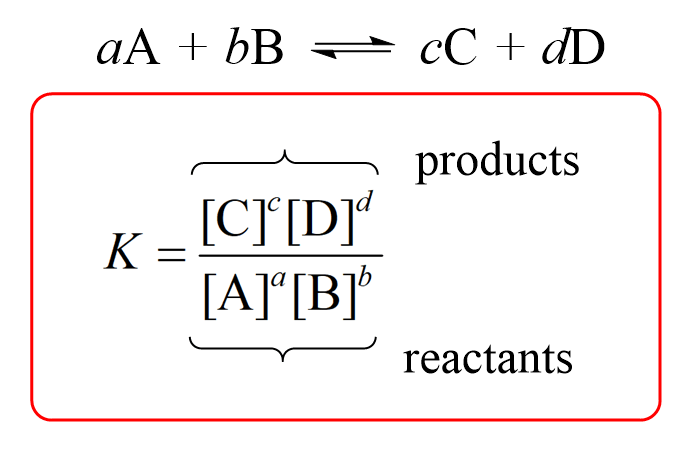
Equilibrium Law and constant
uses stoichiometric coefficients= exponents
“K”—> defines the equilibrium law (CONSTANT and NO UNITS)
K is constant UNLESS temp. change
Heterogenous Equilibrium—> react. and prod. are present in 2 differ states (NOT INCLUDED in the EXPRESSION for the system)
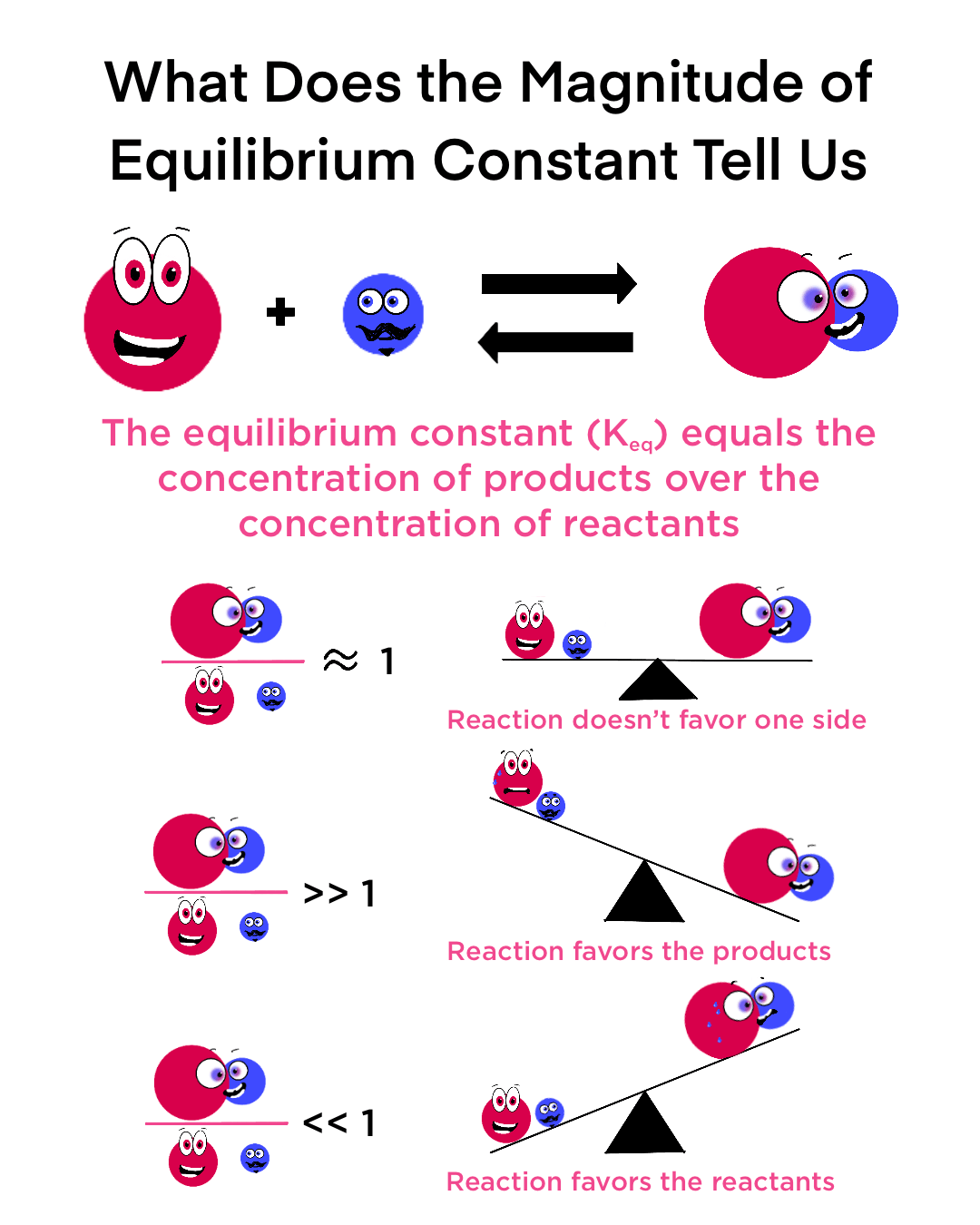
‘K” in more depth
K<1—> more react. are present
K=1—> 50/50
K>1—> more prod. are present
Kforward and Kreverse are INVERSLY related